Mechanical stimulation of distraction regenerate. Mini-review of current concepts
Автор: Cherkashin A.
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Обзор литературы
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.29, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction One of the key limitations of distraction osteogenesis (DO) is the absence or delayed formation of a callus in the distraction gap, which can ultimately prolong the duration of treatment.Purpose Multiple modalities of distraction regenerate (DR) stimulation are reviewed, with a focus on modulation of the mechanical environment required for DR formation and maturation.Methods Preparing the review, the scientific platforms such as PubMed, Scopus, ResearchGate, RSCI were used for information searching. Search words or word combinations were mechanical bone union stimulation; axial dynamization, distraction regenerate.Results Recent advances in mechanobiology prove the effectiveness of axial loading and mechanical stimulation during fracture healing. Further investigation is still required to develop the proper protocols and applications for invasive and non-invasive stimulation of the DR. Understanding the role of dynamization as a mechanical stimulation method is impossible without a consensus on the use of the terms and protocols involved.Discussion We propose to define Axial Dynamization as the ability to provide axial load at the bone regeneration site with minimal translation and bending strain. Axial Dynamization works and is most likely achieved through multiple mechanisms: direct stimulation of the tissues by axial cyclic strain and elimination of translation forces at the DR site by reducing the effects of the cantilever bending of the pins.Conclusion Axial Dynamization, along with other non-invasive methods of mechanical DR stimulation, should become a default component of limb-lengthening protocols.
Bone regeneration, mechanical stimulation, axial dynamization
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142240037
IDR: 142240037 | УДК: 616.71-003.93:615.81(048.8) | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2023-29-6-656-661
Текст обзорной статьи Mechanical stimulation of distraction regenerate. Mini-review of current concepts
Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children, Dallas, Texas, United States of America, ,
Introduced by G.A. Ilizarov, the principles of distraction osteogenesis (DO) are now used to lengthen and reconstruct limbs to help treat multiple orthopedic conditions, both congenital and acquired [1-3]. However, several challenges remain duringitsclinical application, includinglong treatment duration. Extended time in an external fixator exponentially increases the risk of complications [3-8]. Due to long treatment time spent in a frame, “patients may have non-surgical problems, such as social, domestic, educational, and psychological problems, as well as problems that may be cared for by the nursing and physiotherapy staff” [9]. Treatment is often long because the distraction regenerate
(DR) must mature enough to withstand weight-bearing. The process is often further prolonged due to delayed consolidation and/or the development of pathologic distraction regenerate [10, 11].
In an effort to decrease fixation time, multiple research efforts are currently focused on stimulating DR maturation utilizing different methods. Proposed solutions include biological stimulation of the regenerate, pharmacological stimulation, physical stimulation, and any combination of the above (Table 1). All these solutions can be performed using invasive (through various surgical interventions) and non-invasive approaches.
Table 1
Various modalities to stimulate distraction regenerate
|
Distraction Regenerate Stimulation |
||
|
Physical |
Biological |
Pharmacological |
|
Mechanical (see below) |
Grafts [12-14] |
Vitamins [15-17] |
|
Ultrasound [18-21] |
Bone marrow and PRP [22, 23] |
Biometals [24, 25] |
|
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy [26, 27] |
BMPs [28, 29] |
Supplements [30, 31] |
|
Electromagnetic 21, 32, 33] |
Growth factors [34, 35] |
Bisphosphonates [36-38] |
|
Laser therapy [39, 40] |
Cell therapy [41-43] |
|
Mechanical stimulation is the foundation of the entire DO process. During the distraction phase of limb lengthening, tension stress affects all tissues inside and surrounding the distraction gap [44]. The mechanobiological phenomena of DR formation during the DO process essentially prolong the body’s evolutionary-developed mechanism of fracture healing, where tension stress stimulates connective tissue proliferation, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis. Both angiogenesis and a proper mechanical environment are necessary for successful bone regeneration during DO [45, 46]. As the distraction forces are seized, bone resorption and remodeling take place to convert DR into a mature bone structure that is capable of bearing a physical load [47]. Known as the consolidation stage, this is the longest phase in the DO process, where different mechanical DR stimulation techniques are typically applied.
All known mechanical stimuli can be divided into invasive (surgical) and non-invasive techniques (Fig. 1).
Historically, mechanical stimulation techniques were applied following an abnormal formation of DR in an effort to fight the so-called delayed consolidation. However, there has recently been a shift towards a prophylactic application of mechanical stimulation to accelerate the consolidation and avoid delayed consolidation all together.
The goal of this work is to review the current methods of reducing treatment time during limb-lengthening procedures, with a particular interest on the use of mechanical stimulation to promote maturation of the distraction regenerate.
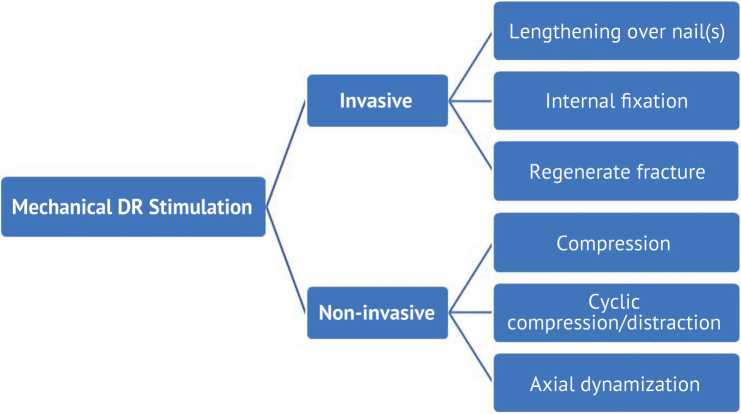
Fig. 1 Various techniques of mechanical stimulation of the distraction regenerate
MATERIAL AND METHODS
We summarize recently (no more than 30 years) published studies about definition, classification, indications and clinical application of methods for mechanical stimulation of bone healing in lengthening procedures. To prepare the review, we searched for information sources at the scientific platforms such as Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, ResearchGate, RSCI, as well as other published products (Elsevier, Springer) using search words or word constructions: bone lengthening, Ilizarov method, mechanical stimulation of bone healing, dynamization, external frame, clinical translation.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Invasive (surgical) mechanical stimulation
Most surgical methods that involve a change to the mechanical environment are performed at the end of the consolidation stage as a response to delayed consolidation problems. These techniques include plating or intramedullary fixation after lengthening [4]. In most cases, these techniques are considered desperate measures to avoid a regenerate fracture after frame removal. Another desperate technique involving surgical stimulation of the pathologic distraction regenerate relies on performing a fracture through the DR site. The fracture helps re-stimulate fracture healing mechanisms, initiate additional angiogenesis, and re-introduce growth and biological stimuli supplied to the pathologic regenerate. A new development, introduced by Popkov et al. [48], uses a prophylactic placement of intramedullary devices during the initial surgery. This provides extra stability during distraction, as well as creates an environment to recruit additional biological factors for DR maturation. They also illustrated that the use of HA-coated implants increases the effect of DR stimulation [49].
Non-invasive mechanical modulation
Non-invasive mechanical stimulation can be performed in various ways: weight-bearing [46, 50], cyclic compression/distraction (accordion technique) [51-53], destabilization of the frame by releasing nuts on threaded rods, destabilization of the frame by removing fixation elements (wires and pins), and replacing threaded rods with dynamization devices.
Weight-bearing
Since the very first application of the Ilizarov circular fixator, lower limb lengthening has required at least partial weight-bearing as part of the process. Ilizarov listed weight-bearing as a categorically required part of leg lengthening [2]. There are multiple papers emphasizing the positive effect of lower extremity loading during DO treatment for DR maturation and remodeling. It is also the least costly method to mechanically stimulate the regenerate. The only consideration must be patient education and compliance, as a majority of non-invasive DR stimulation techniques rely on patient weight-bearing to be effective [50, 54].
Compression
Compression of the DR is often another desperate measure to solve poor regeneration. It is usually performed during the lengthening stage, when the distraction interzone does not progressively display signs of mineralization on X-rays, or at the consolidation stage, when there are no signs of improvement at the lengthening site [55, 56]. There are two important points to consider. First, patient preparation and education are necessary as the planned amount of lengthening may not be achieved. Second, the shape of the pathologic regenerate must be considered when a fully mineralized cortex on one side of the bone is present [57, 58]. This is commonly known as a regenerate cyst. The cyst prevents any ability to compress the DR and can ultimately cause the development of a deformity, either during compression orlater following frame removal. Similar problems can arise from the premature mineralization of the fibula in cases of tibial lengthening. This occurs when the tibial regenerate lags behind, resulting in the fibula acting as a strut that shields the tibia from necessary axial loading. In these cases, early surgical intervention may salvage the lengthening by breaking through the thin mineralized band of regenerate or the prematurely consolidating fibula along with the use of various grafting techniques. An acute compression performed at the end of distraction phase with compression tension of 5.6 N/cm2 is considered as optimal for bone healing stimulation [59].
Cyclic compression/distraction
Ilizarov was the first to suggest the use of alternating cycles of distraction and compression to improve the quality of bone formation in the distraction gap [2]. Under the optimal frame stability, patient’s weight-bearing creates alternating distraction/compression (ADC) forces at the lengthening site as part of the DO process. Therefore, it is logical that the ADC forces created on a fixation device might further improve regeneration. This practice was later named as an accordion maneuver [53] and widely reported as a treatment for poor regenerate [51, 60-63]. Liu et al. [52] performed impressive animal studies to uncover the underlying mechanisms of ADC. The studies showed an improvement of bone formation during DO, suggesting that better outcomes may be achieved by moderately increasing the amplitude and slowing down the rate of the ADC technique [52].
Axial Dynamization
For many years, rigid fixation with internal or external devices was the paradigm of fracture treatment. However, recent advances in our understanding of bone healing and mechanotransduction suggest that systematically altering the construct’s stiffness throughout different phases of healing improves regeneration [64-66]. Dynamization has recently become a buzz word in multiple DO publications; however, there are some problems regarding terminology and definitions. Multiple terms that describe DR dynamization are ill-defined and ambiguous at the present. Starting with dynamization itself – multiple publications currently describe different techniques of bone healing stimulation under the same term.
The term dynamization is described as “the transfer of a progressive load to the fracture site at a given point in the healing cycle” [67]. Nowadays, dynamization encompasses many different methods of altering the fixation of fractures as the bone heals [68], such as decreasing the external fixator’s stiffness during the healing process by removing stabilizing elements [69]. A new concept of “reverse dynamization” was also recently introduced by Glatt et al., where frame destabilization is performed during the early stages of fracture healing (during the first week after the initial fixation) to produce a larger volume of newly formed callus. The frame instability is reversed to a more rigid fixation after 3-4 weeks to, in theory, encourage blood vessel growth within the callus. Reverse dynamization somewhat contradicts the original Ilizarov idea that frame stability plays an important role in bone healing [1, 2]. In contrast to the intramembranous ossification described by Ilizarov, reverse dynamization generates a large volume of bone callus, possibly through endochondral and trans-chondral types of ossification.
Many other vague terms are often used in conjunction with dynamization to describe the mechanical stimulation of the distraction regenerate, including but not limited to stable fixation, rigid fixation, and micromotion. First, the term micromotion should be avoided in scientific literature. The physiologic load of an external fixator typical configuration can lead to an axial displacement of bone fragments away beyond 3 mm [70]. This amount of fragment displacement cannot be described as micro [71]. Secondly, we propose that rigid fixation be reserved to describe stabilization without any meaningful load on the bone healing site, essentially inhibiting the mechanobiological processes necessary for optimal bone regeneration as fixation is too rigid. In contrast, stable fixation of bone fragments minimizes the amount of shear and bending strains at the fracture or lengthening site, while still allowing for some axial loading to promote bone regeneration.
Dynamization should only describe and be used interchangeably with Axial Dynamization. We propose to define Axial Dynamization as the ability to provide axial load at the bone regeneration site with minimal translation and bending strain. Shear and bending strains are both undesirable forces, whereas axial loading and unloading promote regeneration [2]. However, it remains doubtful that most modern external fixator assemblies will be able to entirely eliminate all instances of bending strain [70]. The original fixator developed by Ilizarov incorporates built-in Axial Dynamization with the use of thin wires only, which act as a fixed beam bending when under a load. As a result, the frame provides some axial displacement of bone fragments during weight-bearing [72]. Extended use of half-pins in modern external fixators has increased frame rigidity and replaced fixed beam bending with cantilever bending, which ultimately creates undesirable bending and translation forces.
There are many other methods of altering fixation stability that should not be considered dynamization, including removing stabilizing elements of the fixation device, destabilizing connecting elements of the fixator, or removing some of the external fixation pins and wires. These methods would be better named as partial fixation removal or fixator destabilization.
When applying dynamization, simply untightening the nuts of the fixator connecting rods, will not provide the proper conditions to eliminate shear and bending strains. Instead, the best way to dynamize is with springloaded devices or elastic washers to provide axial loading with a dampening effect. An example of such dynamization would involve mounting the original De Bastiani dynamization washer [67] or a spring-loaded device between the external fixator rings [70]. Use of such spring-loaded dynamization devices not only stimulates bone healing but also improves patient comfort, allowing better weightbearing and indirectly improving the healing process [70].
Axial Dynamization works [73, 74] and is most likely achieved through multiple mechanisms: direct stimulation of tissues by axial cyclic strain and elimination of translation forces at the DR site by reducing the effects of the cantilever bending of the pins. However, it remains unclear when dynamization should be applied during limb lengthening. Frames are traditionally dynamized at the end of the consolidation period before the external fixator is removed. Nonetheless, we have started dynamizing frames earlier, at around 3-4 weeks after lengthening is complete. There is also an argument to initiate dynamization during the distraction period to mimic the effects of all-wire frames, which include properties of built-in dynamization as previously stated. Introducing dynamization during the early distraction period would likely result in a mechanical environment similar to the traditional all-wire fixator developed by Ilizarov and ultimately help develop better DR. However, it must be noted that dynamization also depends upon the patient putting weight on the treated extremity, which could be a challenge during the early stages of limb lengthening. Whereas late dynamization performed during the consolidation period would actually improve patient comfort by reducing the cantilever bending of the fixator pins and providing a dampening effect. This would allow for more weight-bearing and physiologic walking that will help stimulate DR maturation.
Advancements in automated distraction will possibly allow for a more frequent rhythm of distraction, plus the ability to use passive Axial Dynamization techniques alongside frequent patient-independent cycles of compression/distraction.
CONCLUSION
Mechanical stimulation is the most accessible and usually most affordable way to speed-up the mineralization of the distraction regenerate. Multiple publications prove the effectiveness of mechanical modulation techniques involved in DO for improving the conditions of bone healing. Non-invasive techniques of DR mechanical stimulation should become a default component of the limb-lengthening procedure, rather than reserved to rescue pathologic regeneration and delayed consolidation. Axial
Dynamization using spring-loaded or elastic devices proves effective in achieving cyclic axial loading, while minimizing shear and bending forces on the regenerate. There is a need for a consensus on the definitions and protocols that surround Axial Dynamization. Therefore, additional research is needed to develop the protocols and process of Axial Dynamization, which will most likely involve incorporating a combination of early and late dynamization techniques into the treatment of limb lengthening.
Список литературы Mechanical stimulation of distraction regenerate. Mini-review of current concepts
- Ilizarov GA. The principles of the Ilizarov method. Bull Hosp Jt Dis Orthop Inst. 1988;48(1):1-11.
- Ilizarov GA. Clinical application of the tension-stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(250):8-26.
- Birch JG, Samchukov ML. Use of the Ilizarov method to correct lower limb deformities in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004;12(3):144-154. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200405000-00002
- Sheridan GA, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Integrated Limb Lengthening Is Superior to Classical Limb Lengthening: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Literature. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2020;4(6):e20.00054. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-20-00054
- Cherkashin AM, Samchukov ML, Birch JG, Da Cunha AL. Evaluation of complications of treatment of severe Blount's disease by circular external fixation using a novel classification scheme. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2015;24(2):123-130. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000138
- Black SR, Kwon MS, Cherkashin AM, et al.. Lengthening in Congenital Femoral Deficiency: A Comparison of Circular External Fixation and a Motorized Intramedullary Nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(17):1432-1440. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.N.00932
- Blum AL, BongioVanni JC, Morgan SJ, et al. Complications associated with distraction osteogenesis for infected nonunion of the femoral shaft in the presence of a bone defect: a retrospective series. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(4):565-570. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.92B4.23475
- Biz C, Crimi A, Fantoni I, et al. Functional outcome and complications after treatment of comminuted tibial fractures or deformities using Ilizarov bone transport: a single-center study at 15- to 30-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141(11):1825-1833. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03562-9
- Saleh M., Scott BW. The Complications of Leg Lengthening. In: De Bastiani, G., Apley, A.G., Goldberg, A. (eds) Orthofix External Fixation in Trauma and Orthopaedics. Springer, London; 2000:496-510. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-0691-3_47
- Li R, Saleh M, Yang L, Coulton L. Radiographic classification of osteogenesis during bone distraction. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(3):339-347. doi: 10.1002/jor.20026
- Sabharwal S. Enhancement of bone formation during distraction osteogenesis: pediatric applications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(2):101-111. doi: 10.5435/00124635-201102000-00005
- Sangkaew C. Distraction osteogenesis for the treatment of post traumatic complications using a conventional external fixator. A novel technique. Injury. 2005;36(1):185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2004.04.012
- Borzunov DY, Kolchin SN, Malkova TA. Role of the Ilizarov non-free bone plasty in the management of long bone defects and nonunion: Problems solved and unsolved. World J Orthop. 2020;11(6):304-318. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v11.i6.304
- Hvid I, Horn I, Huhnstock S, Steen H. The biology of bone lengthening. J Child Orthop. 2016;10(6):487-492. doi: 10.1007/s11832-016-0780-2
- Akijay H, Kuru K, Tatar B, §im§ek F. Vitamin E Promotes Bone Formation in a Distraction Osteogenesis Model. J Craniofac Surg. 2019;30(8):2315-2318. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005685
- Kurklu M, Yildiz C, Kose O, et al. Effect of alpha-tocopherol on bone formation during distraction osteogenesis: a rabbit model. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(3):153-8. doi: 10.1007/s10195-011-0145-z
- Sax OC, Nequesha M, Rivera JC, et al. Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adult Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction Patients. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr. 2021;7(2):110-113. doi: 10.4103/jllr.jllr_4_21
- Gebauer D, Correll J. Pulsed low-intensity ultrasound: a new salvage procedure for delayed unions and nonunions after leg lengthening in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25(6):750-754. doi: 10.1097/01.bpo.0000173245.12184.7e
- Song MH, Kim TJ, Kang SH, Song HR. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound enhances callus consolidation in distraction osteogenesis of the tibia by the technique of lengthening over the nail procedure. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2490-7
- Harrison A, Alt V. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for stimulation of bone healing - A narrative review. Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2:S91-S96. doi: 10.1016-1.injury.2021.05.002
- Jauregui JJ, Ventimiglia AV, Grieco PW, et al. Regenerate bone stimulation following limb lengthening: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1259-5
- Lee DH, Ryu KJ, Kim JW, et al. Bone marrow aspirate concentrate and platelet-rich plasma enhanced bone healing in distraction osteogenesis of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(12):3789-9377. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3548-3
- Karakayali M, Alpay Y, Sarisözen B. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on bone regenerate consolidation in distraction osteogenesis: An experimental study in rabbits. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2022;56(1):8-13. doi: 10.5152/j.aott.2022.20443
- Li Y, Pan Q, Xu J, et al. Overview of methods for enhancing bone regeneration in distraction osteogenesis: Potential roles of biometals. J Orthop Translat. 2021;27:110-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2020.11.008
- Glenske K, Donkiewicz P, Köwitsch A, et al. Applications of Metals for Bone Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):826. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030826
- Eralp L, Ozkan K, Kocaoglu M, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on distraction osteogenesis. Adv Ther. 2007;24(2):326-32. doi: 10.1007/ BF02849901
- Wang IC, Wen-Neng Ueng S, Yuan LJ, et al. Early administration of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in distraction osteogenesis--a quantitative study in New Zealand rabbits. J Trauma. 2005;58(6):1230-1235. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000169872.38849.b0
- Sailhan F, Gleyzolle B, Parot R, et al. Rh-BMP-2 in distraction osteogenesis: dose effect and premature consolidation. Injury. 2010;41(7):680-6. doi: 10.10161.injury.2009.10.010
- Mizumoto Y, Moseley T, Drews M, et al. Acceleration of regenerate ossification during distraction osteogenesis with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-7. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 3:124-30. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200300003-00019
- Wei H, Zili L, Yuanlu C, et al. Effect of icariin on bone formation during distraction osteogenesis in the rabbit mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40(4):413-8. doi: 10.10161.ijom.2010.10.015
- Bereket C, Özan F, §ener 1, et al. Propolis accelerates the consolidation phase in distraction osteogenesis. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(5):1912-1916. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000946
- Taylor KF, Inoue N, Rafiee B, et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on maturation of regenerate bone in a rabbit limb lengthening model. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(1):2-10. doi: 10.1002/jor.20014
- Yong Y, Ming ZD, Feng L, et al. Electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis of rat mesenchymal stem cells through the PKA and ERK1/2 pathways. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10):E537-E545. doi: 10.1002/term.1864
- Makhdom AM, Hamdy RC. The role of growth factors on acceleration of bone regeneration during distraction osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19(5):442-53. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2012.0717
- Raschke MJ, Bail H, Windhagen HJ, et al. Recombinant growth hormone accelerates bone regenerate consolidation in distraction osteogenesis. Bone. 1999;24(2):81-88. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(98)00158-6
- Kiely P, Ward K, Bellemore C M, et al. Bisphosphonate rescue in distraction osteogenesis: a case series. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27(4):467-71. doi: 10.1097/01.bpb.0000271326.41363.d1
- Saghieh S, Khoury NJ, Tawil A, et al. The impact of zoledronic acid on regenerate and native bone after consolidation and removal of the external fixator: an animal model study. Bone. 2010;46(2):363-8. doi: 10.1016-j.bone.2009.10.010
- Alp YE, Taskaldiran A, Onder ME, et al. Effects of Local Low-Dose Alendronate Injections Into the Distraction Gap on New Bone Formation and Distraction Rate on Distraction Osteogenesis. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(8):2174-2178. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002615
- Hübler R, Blando E, Gaiäo L, et al. Effects of low-level laser therapy on bone formed after distraction osteogenesis. Lasers Med Sci. 2010;25(2):213-9. doi: 10.1007/s10103-009-0691-2
- Gurler G, Gursoy B. Investigation of effects of low level laser therapy in distraction osteogenesis. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;119(6):469-476. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2018.05.006
- Xu J, Wang B, Sun Y, et al. Human fetal mesenchymal stem cell secretome enhances bone consolidation in distraction osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0392-2
- Yang Y, Pan Q, Zou K, et al. Administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in lengthening phase accelerates early bone consolidation in rat distraction osteogenesis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01635-5
- Kitoh H, Kawasumi M, Kaneko H, Ishiguro N. Differential effects of culture-expanded bone marrow cells on the regeneration of bone between the femoral and the tibial lengthenings. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009;29(6):643-649. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181b2afb2
- Liang W, Ding P, Qian J, et al. Polarized M2 macrophages induced by mechanical stretching modulate bone regeneration of the craniofacial suture for midfacial hypoplasia treatment. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;386(3):585-603. doi: 10.1007/s00441-021-03533-5
- Fang TD, Salim A, Xia W, et al. Angiogenesis is required for successful bone induction during distraction osteogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(7):1114-1124. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.050301
- Moore DC, Leblanc CW, Müller R, et al. Physiologic weight-bearing increases new vessel formation during distraction osteogenesis: a micro-tomographic imaging study. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(3):489-96. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00234-6
- Sinnesael M, Claessens F, Boonen S, Vanderschueren D. Novel insights in the regulation and mechanism of androgen action on bone. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013;20(3):240-244. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e32835f7d04
- Popkov A, Foster P, Gubin A, et al. The use of flexible intramedullary nails in limb lengthening. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2017;14(9):741-753. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2017.1367284
- Popkov A, Pietrzak S, Antonov A, et al. Limb Lengthening for Congenital Deficiencies Using External Fixation Combined With Flexible Intramedullary Nailing: A Multicenter Study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2021;41(6):e439-e447. doi: 10.1097/BP0.0000000000001816
- Radomisli TE, Moore DC, Barrach HJ, et al. Weight-bearing alters the expression of collagen types I and II, BMP 2/4 and osteocalcin in the early stages of distraction osteogenesis. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(6):1049-1456. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(01)00044-4
- Makhdom AM, Cartaleanu AS, Rendon JS, et al. The Accordion Maneuver: A Noninvasive Strategy for Absent or Delayed Callus Formation in Cases of Limb Lengthening. Adv Orthop. 2015;2015:912790. doi: 10.1155/2015/912790
- Liu Y, Cai F, Liu K, et al. Cyclic Distraction-Compression Dynamization Technique Enhances the Bone Formation During Distraction Osteogenesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;9:810723. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.810723
- Makhdom AM, Cartaleanu AS, Rendon JS, et al. The Accordion Maneuver: A Noninvasive Strategy for Absent or Delayed Callus Formation in Cases of Limb Lengthening. Adv Orthop. 2015;2015:912790. doi: 10.1155/2015/912790
- Waanders NA, Richards M, Steen H, et al. Evaluation of the mechanical environment during distraction osteogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(349):225-34. doi: 10.1097/00003086-199804000-00028
- Mori S, Akagi M, Kikuyama A, et al. Axial shortening during distraction osteogenesis leads to enhanced bone formation in a rabbit model through the HIF-lalpha/vascular endothelial growth factor system. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(4):653-63. doi: 10.1002/jor.20076
- Kim UK, Chung IK, Lee KH, et al. Bone regeneration in mandibular distraction osteogenesis combined with compression stimulation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64(10):1498-505. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2006.03.028
- Li R, Saleh M, Yang L, Coulton L. Radiographic classification of osteogenesis during bone distraction. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(3):339-347. doi: 10.1002/jor.20026
- Donnan LT, Saleh M, Rigby AS, McAndrew A. Radiographic assessment of bone formation in tibia during distraction osteogenesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22(5):645-651.
- Shevtsov V, Popkov A, Popkov D, Prévot J. Réduction de la durée du traitement dans les allongements osseux progressifs. Technique et advantage [Reduction of the period of treatment for leg lengthening. Technique and advantages]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2001;87(3):248-256. (In French)
- Eldridge IC, Bell DF. Problems with substantial limb lengthening. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991;22(4):625-631.
- Simpson AH, Kenwright J. Fracture after distraction osteogenesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(5):659-665. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.82b5.9945
- Krishnan A, Pamecha C, Patwa JJ. Modified Ilizarov technique for infected nonunion of the femur: the principle of distraction-compression osteogenesis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006;14(3):265-272. doi: 10.1177/230949900601400307
- Mofid MM, Inoue N, Atabey A, et al. Callus stimulation in distraction osteogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(5):1621-1629. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200204150-00020
- Schmidt EC, Judkins LM, Manogharan G, et al. Current concepts in fracture healing: temporal dynamization and applications for additive manufacturing. OTA Int. 2022 M;5(1 Suppl):e164. doi: 10.1097/0I9.0000000000000164
- Cardozo CP. Mechanotransduction: Overview. In: Zaidi M, ed. Encyclopedia of Bone Biology. Academic Press; 2020:217.
- Isaksson H, Comas O, van Donkelaar CC, et al. Bone regeneration during distraction osteogenesis: mechano-regulation by shear strain and fluid velocity. J Biomech. 2007;40(9):2002-2011. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2006.09.028
- Pouliquen JC, Glorion C, Ceolin JL, et al. Allongement métaphysaire supérieur du tibia. 57 cas effectués par la méthode du callotasis chez l'enfant et l'adolescent [Upper metaphyseal lengthening of the tibia. Report of 57 cases in children and adolescents]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1994;80(6):532-541. (In French)
- Claes L. Dynamisierung der Osteosynthese: Zeitpunkt und Methoden [Dynamization of fracture fixation: Timing and methods]. Unfallchirurg. 2018;121(1):3-9. (In German) doi: 10.1007/s00113-017-0455-6
- Alzahrani MM, Anam E, AlQahtani SM, et al. Strategies of enhancing bone regenerate formation in distraction osteogenesis. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2017.1288725
- Honcharuk EM, Cherkashin AM, Pierce WA, et al. Effect of axial dynamization in circular external fixation on bone segment vertical and lateral displacements. J Limb Lengthening Reconstr. 2021;7(1):37-44.
- Fenton C, Henderson D, Samchukov M, et al. Comparative Stiffness Characteristics of Ilizarov- and Hexapod-type External Frame Constructs. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2021;16(3):138-143. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10080-1539
- Yang L, Nayagam S, Saleh M. Stiffness characteristics and inter-fragmentary displacements with different hybrid external fixators. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(2):166-172. doi: 10.1016/s0268-0033(02)00175-4
- Claes L, Meyers N, Schülke J, et al. The mode of interfragmentary movement affects bone formation and revascularization after callus distraction. PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0202702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202702
- Claes LE, Wilke HJ, Augat P, et al. Effect of dynamization on gap healing of diaphyseal fractures under external fixation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1995;10(5):227-234. doi: 10.1016/0268-0033(95)99799-8


