Метаболические факторы риска и формирование мочевых камней. Исследование VII: литогенные свойства урикозурии у мужчин и женщин
Автор: Голованов С.А., Просянников М.Ю., Сивков А.В., Анохин Н.В., Войтко Д.А., Дрожжева В.В.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Мочекаменная болезнь
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.16, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Гиперурикозурия обычно рассматривается в качестве основного метаболического фактора образования камней из мочевой кислоты, однако этот вопрос остается неясным. Гендерные различия распространенности мочекаменной болезни (МКБ) указывают на необходимость более подробного изучения литогенных свойств урикозурии и ее роли в развитии МКБ того или иного метаболического типа. В настоящей работе исследовали влияние различной степени урикозурии у мужчин и женщин с МКБ на метаболические показатели и частоту выявления мочевых камней различного химического состава.
Гиперурикозурия, мочекаменная болезнь, метаболические типы мочекаменной болезни, риск формирования мочевых камней у мужчин и женщин
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142240013
IDR: 142240013 | DOI: 10.29188/2222-8543-2023-16-3-154-164
Текст научной статьи Метаболические факторы риска и формирование мочевых камней. Исследование VII: литогенные свойства урикозурии у мужчин и женщин
Распространенность мочекислого уролитиаза в значительной степени зависит от географического региона и этнического состава населения. Среди жителей индустриально развитых стран на долю мочекислого уролитиаза приходится около 10-15% всех мочевых камней,хотя распространенность этой формы уролитиаза может значительно повышаться при наличии метаболического синдрома [1, 2], ожирения [3-6] и диабета 2 типа [5, 7, 8]. Полагают, что это связано с ги-перурикозурией и низкими значениями рН мочи [9] Кроме того, гиперурикозурия может быть результатом избыточного питания и усиленной эндогенной продукции вследствие недостаточности некоторых ферментов. Нередко повышенная экскреция мочевой кислоты наблюдается при миелопролиферативных нарушениях приеме химиотерапевтических препаратов, подагре и других патологических состояниях [10].
Хотя гиперурикозурия обычно рассматривается в качестве основного механизма образования камней из мочевой кислоты при первичной подагре,некоторые исследования не обнаруживают повышенной экскреции мочевой кислоты у пациентов с подагрой [11, 12] Напротив,у таких пациентов имеются более низкие значения рН мочи и фракционной экскреции уратов, чем у здоровых людей, что считают характерными признаками первичной подагры [13].
Тем не менее, роль гиперурикозурии в развитии мочекислого литогенеза остается неясной и требует более детального изучения. На протяжении последних десятилетий наибольшая распространенность мочекаменной болезни (МКБ) наблюдается у мужчин по сравнению с женщинами. Соотношение мужчины/ женщины (гендерный коэффициент) в различных странах мира составляет 1,5-2,5, что позволяет предполагать существование неких гендерных факторов, в том числе, возможно, и метаболических, от которых зависит процесс камнеобразования [2, 14-16].
Изучение гендерных особенностей литогенного влияния урикозурии на формирование камней различного химического состава представляет определенный клинический интерес для разработки персонифицированного подхода к метафилактике МКБ. Наличие характерных различий в экскреции мочевой кислоты у пациентов мужчин и женщин при развитии ожирения было выявлено в предыдущей нашей работе [6].
Учитывая сказанное, целью настоящего исследования являлось изучение зависимости литогенной активности урикозурии от половой принадлежности пациентов с МКБ.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Материалом для исследования служили результаты биохимического исследования сыворотки крови, суточной мочи и данные анализа минерального состава мочевых конкрементов 982 пациентов с мочекаменной болезнью (439 мужчин и 543 женщин в возрасте от 18 до 79 лет), проходивших обследование и лечение в НИИ урологии и интервенционной радиологии Минздрава России и городской клинической урологической больнице № 47 г. Москва. Биохимические исследования мочи и крови пациентов,индекс массы тела (ИМТ), определение минерального состава мочевых камней,классификацию камней по химическому составу и оценку литогенной активности урико-зурии с помощью метода ранжирования показателей экскреции на 10 диапазонов проводили, как описано нами ранее [17]. В каждом из диапазонов определяли процентное распределение типов мочевых камней и биохимические показатели мочи и крови. Статистический анализ результатов проводили с помощью программ Statistica v12 и MedCalc v13. Для сглаживания колебаний кривых при построении диаграмм и некоторых графиков применяли метод скользящих средних [18].
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
В исследуемой выборке данных, состоящих из 982 наблюдений, мужчин с МКБ насчитывалось 439 пациентов (44,7% от общего числа больных), а женщин с МКБ – 543 (55,3% от общего числа больных).
Отмечено, что, по мере развития урикозурии от минимальных ее значений 0,27-1,8 мМ/сут (первый 10%-й перцентиль) до максимальных ее значений 5,24-10,40 мМ/сут (десятый 10%-й перцентиль) доля пациентов мужчин, страдающих МКБ, прогрессивно возрастала в 2,53 раза по сравнению с пациентами женщинами (рис. 1, Хи-квадрат (χ2) тест для тренда, p < 0,0001). Однако существенных различий между уровнями урикозурии в исследуемых 10%-х перцентильных интервалах между мужчинами и женщинами обнаружено не было, за исключением незначительного снижения уровня экскреции мочевой кислоты у женщин на 1,78% по сравнению с мужчинами ( p =0,012) в интервале урикозурии 3,5-3,9 мМ/сут.
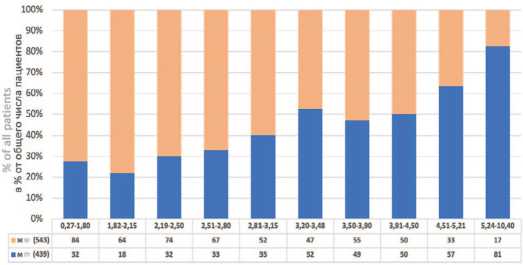
Рис. 1. Соотношение пациентов мужчин (м) и женщин (ж) при нарастании ури-козурии (мМ/сут) в % от общего числа пациентов
Fig. 1. Increasing of uric acid excretion (mM/day) and men(m) to women(w) stone formers ratio (in %)
Доля камней из оксалата кальция среди мужчин-пациентов увеличивалась более значительно по мере роста урикозурии и была в 1,4-2,5 раза выше, чем у женщин (рис. 2, χ2 тест для тренда p =0,0001). Особенно выраженные различия (в 2-2,5 раза) наблюдались в диапазоне урикозурии 2,5 – 3,15 мМ/сут (рис. 2, р <0,05, χ2 тест).
В противоположность этому, нарастание урико-зурии у женщин, в отличие от мужчин, сопровождалось значительным повышением доли карбонатапатит-ных камней в 1,6-3,3 раза (рис. 2, χ2 тест для тренда p <0,0001) с максимальным повышением в 3,2-3,3 раза при невысокой экскреции мочевой кислоты от 2,2 до 2,8 мМ/сут.
Это свидетельствует о различной активности литогенеза фосфатных и оксалатных камней у мужчин и женщин с МКБ при нарастании урикозурии.
Хотя процентное распределение мочекислых камней между мужчинами и женщинами не имело различий при нарастании урикозурии, у мужчин наблюдалась отчетливое увеличение относительной доли мочекислых камней при росте экскреции мочевой кислоты (рис. 2, χ2 тест для тренда p =0,002). У пациентов женщин такая связь отсутствовала.
Распределение типов мочевых камней при мочекаменной болезни у мужчин и женщин в условиях нарастающей урикозурии зависело от изменения уровней некоторых метаболических показателей крови и мочи
0,27-1,80 1,82-2,15 2,19-2,50 2,51-2,80 2,81-3,15 3,20-3,48 3,50-3,90 3,91-4,50 4,51-5,21 5,24-10,40
мочевая кислота мм/сут uric acid мМ/dav
■ оксалатные мочекислые ■ карбонатапатитные струвитные ■ из аммония урата oxalate uric acid carbonatapatite struvite ammonium urate
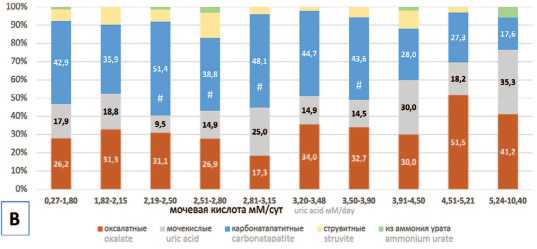
Рис. 2. Распределение типов мочевых камней при мочекаменной болезни (в % от общего количества камней) у мужчин (А) и женщин (В) при развитии урикозурии. Показатели достоверности различия в распределении типов мочевых камней между мужчинами (А) и женщинами (В): * р <0,05, (χ 2 тест) при сравнении распределения оксалатных камней; # р <0,005, (χ 2 тест) при сравнении распределения камней из карбонатапатита.
Fig. 2. Increasing of uric acid excretion (mM/d) and urinary stones composition (% of total stones) in men (A) and women (B). Comparison of oxalate stones: men (A) vs women (B) * р <0.05, (χ 2 test); comparison of carbonatapatite stones: men (A) vs women (B) # р <0.005, (χ 2 test)
Отмечено, что прогрессирующая экскреция мочевой кислоты сопровождалась изменениями показателей рН утренней мочи как у мужчин, так и у женщин. Превышение экскреции мочевой кислоты более 3,48 мМ/сут приводило к постепенному снижению значений рН мочи, более выраженному у женщин (с 5,96±1,05 до 5,18±1,82 мМ/сут, р =0,0015), чем у мужчин (с 5,86±0,81 до 5,61±1,14 мМ/сут, р =0,080) (рис. 3).
Интересно, что это не сопровождалось, как можно было полагать, активацией уратного литогенеза, что наблюдается при повышении кислотности мочи.Частота выявления мочекислых камней в этих условиях не изменялась ни у мужчин, ни у женщин с МКБ (рис. 3А) Однако увеличение экскреции мочевой кислоты приводило к изменению процентного содержания доли уратов в мочевых камнях, что свидетельствовало об
Pser(w)
Caser(w)
Mgser(m)
Uaser(m
Pser(m)
Caserim
CaUr m
MgUr(m)
мочевая к-та (мМ/сут)
uric acid (mM/day)
Purim
BMI m
Dh-St m
Str-St(m
Dh-St(w)
Str-St(w)
мочевая к-та (мМ/сут)
uric acid (mM/day
Ox-St(m)
UA-St m
Ox-St w
UA-St w
CaUr w
MgUrlw мочевая к-та (мМ/сут)
uric acid (mM/day)
Mgser(w
Uaser(w)
мочевая к-та (мМ/сут)
uric acid (mM/day)
мочевая к-та (мМ/сут)
uric acid (mM/day)
мочевая к-та (мМ/сут)
uric acid (mM/day
Pur(w
BMI w
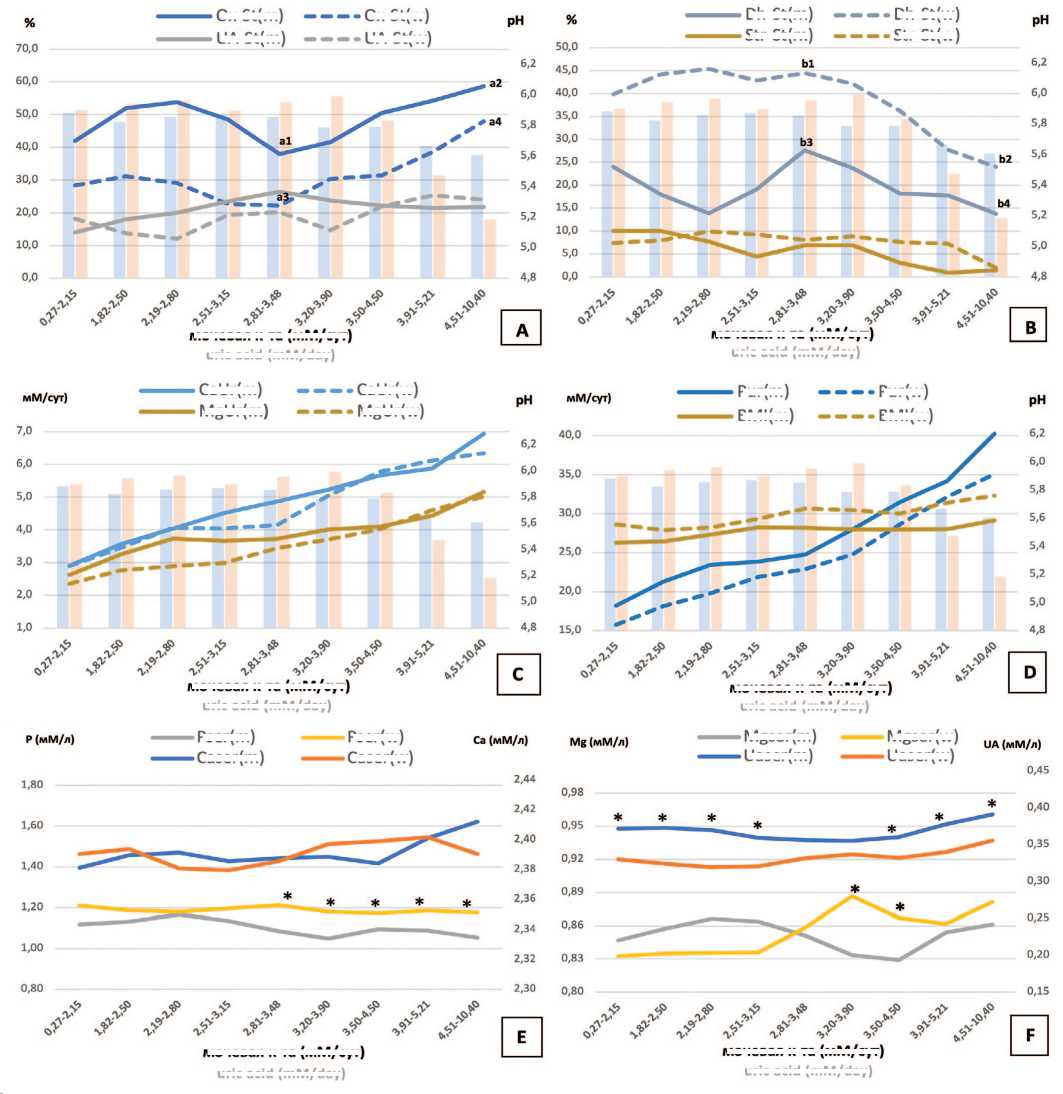
Рис. 3. Биохимические показатели мочи и крови при урикозурии различной степени у мужчин и женщин. На оси абсцисс указаны значения экскреции мочевой кислоты (в мМ/сут) в 10%-х перцентилях распределения с использованием, скользящих средних; значения рН утр мочи у мужчин (голубые столбцы), у женщин (оранжевые столбцы) A – частота встречаемости оксалатных и мочекислых камней у мужчин [Ox-St(m), Ua-St(m)], и женщин [Ox-St(w), Ua-St(w)] (% от всех камней); B – частота встречаемости камней из карбонатапатита и струвита у мужчин [Dh-St(m), Str-St(m)], и женщин [Dh-St(w), Str-St(w)], (% от всех камней); С – показатели кальциурии и магнийурии у мужчин и женщин); D – показатели ИМТ (кг/м 2 ) и фосфатурии у мужчин и женщин); E – показатели кальцемии и фосфатемии у мужчин и женщин; F – показатели урикемии и магниемии у мужчин и женщин * – р <0,05 при сравнении различий показателей между мужчинами и женщинами
Fig. 3. Biochemical parameters of urine and blood in uricosuria of varying degrees in men and women. The values of uric acid excretion (in mM/day) in 10% percentiles of distribution using moving averages are indicated on the abscissa axis; Urine pH values in men (blue columns), in women (orange columns)
A – oxalate and uric acid stones frequency in men [Ox-St(m), Ua-St(m)], and women [Ox-St(w), Ua-St(w)] (% of all stones); B – carbonatapatite and struvite stones frequency in men [Dh-St(m), Str-St(m)], and women [Dh-St(w), Str-St(w)], (% of all stones); C – calciuria and magnesiuria in men and women; D – BMI (kg/m 2 ) and phosphaturia in men and women); E – calcemia and phosphatemia in men and women; F – uricemia and magnesiemia in men and women * – p <0.05 comparison differences between men and women
особенностях уратного литогенеза у мужчин и женщин под влиянием урикозуриии различной степени (рис. 4B)
У женщин общая доля в камнях уратного компонента [мочевая кислота безводная (UA) + мочевой кислоты дигидрат (UAD)] при урикозурии выше 3,48 мМ/сут возрастала с 73,93±34,0% до 99,17±2,89% (рис. 4B p =0,0179,), а у пациентов мужчин не изменялась. Однако у мужчин в отличие от женщин при возрастании урикозурии до 3,48 мМ/сут наблюдалось постепенное накопление в камнях безводной мочевой кислоты 31,0±13,7% до 64,4±34,3% (рис. 4B, p =0,0056).
Такие изменения объясняются разной направленностью процессов уратного литогенеза у мужчин и женщин. У женщин при урикозурии выше 3,48 мМ/сут наблюдался рост доли мочевой кислоты (UA) в камнях в 1,47 раза с 56,92±31,21% до 83,64±24,6% ( p =0,0164), в отличие от мужчин, у которых доля мочевой кислоты (UA) в камнях, наоборот, снижалась в 1,36 раза с 64,4±34,29% до 47,42±29,21% (рис. 4В, p =0,0504).
Отмечено, что рост урикозурии в диапазоне 2,8 – 3,48 мМ/сут сопровождался снижением частоты выявления оксалатных камней у мужчин в 1,42 раза до 37,9% (рис. 3, p =0,0509, χ2 тест). Это сопровождалось снижением доли оксалатного компонента в камнях в 1,32 раза (рис. 4А, p =0,0018).
Однако при дальнейшем нарастании урикозурии наблюдалась активация оксалатного литогенеза. Рост урикозурии от 3,48 мМ/сут и до максимальных значений (4,51-10,4 мМ/сут) приводил к увеличению числа случаев выявления оксалатного уролитиаза у мужчин в 1,55 раза (рис. 3A, a1-a2, р =0,0025, χ2 тест), а у женщин в 2,16 раза (рис. 3A, a3-a4, р =0,0013, χ2 тест). Тем не менее активность оксалатного литогенеза при этих условиях у мужчин все же преобладала и была выше, чем у женщин (рис. 3А, χ2 тест для тренда p <0,0001). Повышение экскреции мочевой кислоты свыше 3,48 мМ/сут сопровождалось увеличением доли оксалатного компонента в камнях пациентов мужчин с 59,64±31,62% до 76,70±29,02% ( р =0,0008), а у женщин с 48,17±36,18% до 67,35±36,43% (рис.4A, p =0,0183), в основном за счет роста доли вевеллита (на 19,4% у мужчин, p =0,063 и 38,1% у женщин, p =0,019 соответственно).
Обращает на себя внимание тот факт, что повышение экскреции мочевой кислоты свыше 3,48 мМ/сут является неким критическим уровнем, влияющим также и на фосфатный литогенез. При росте урикозу-рии до 3,48 мМ/сут частота выявления камней из кар-бонатапатита у женщин в 1,61-3,28 раз была выше, чем у пациентов мужчин (рис. 3B, р <0,05, χ2 тест). Дальнейшее возрастание экскреции мочевой кислоты более 3,48 мМ/сут приводило к снижению частоты выявления карбонатапатитных камней у мужчин в 1,85 раза (рис. 3B, b3-b4, р =0,0104, χ2 тест), а у женщин в 2,0 раза (рис. 3B, b1-b2, р =0,0153, χ2 тест). Доля минерального компонента из карбонатапатита имела тенден-
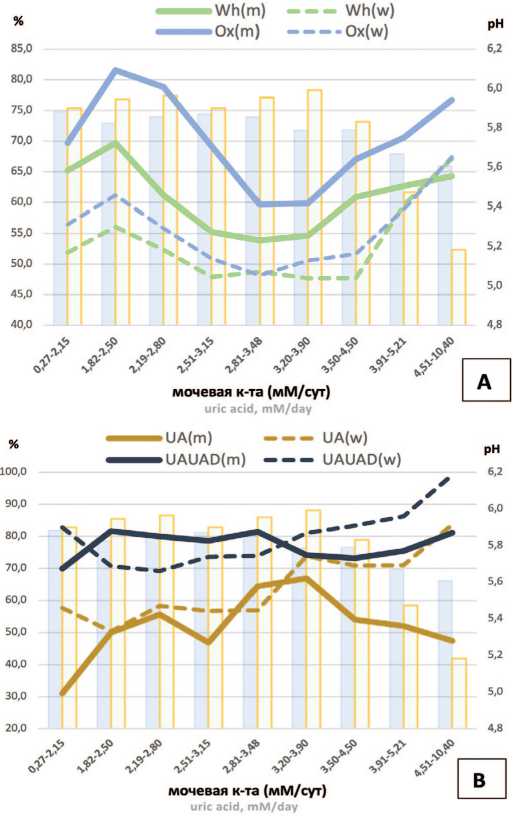
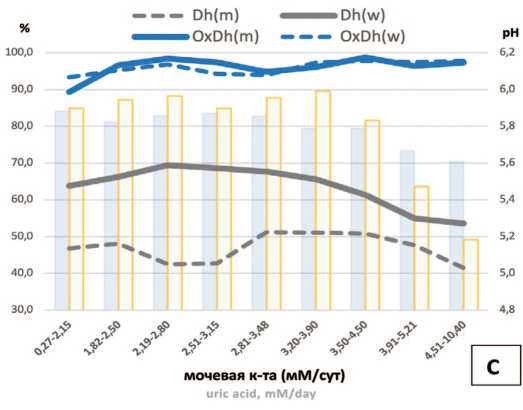
Рис. 4. Влияние урикозурии на содержание минеральных компонентов в мочевых камнях и рН утренней мочи у мужчин и женщин. А – оксалатный компонент (Wh+Wd), Wh; B – уратный компонент (UA+UAD), UA; C – оксалатно-фосфатный компонент (Wh+Wd+Dh), Dh. Значения рН утренней мочи у мужчин (голубые столбцы), у женщин (зеленые столбцы)
Сокращения: Wh – Whewellite (вевеллит), Wd – Weddellite (ведделлит), UA – Uric acid (мочевая кислота), UAD – Uric acid dihydrate (мочевой кислоты дигидрат), Dh – Dahllite (карбонатапатит; Carbonate apatite phosphate)
Fig. 4. The influence of uricosuria on mineral components in urinary stones and morning urine pH in men and women. A – oxalate component (Wh+Wd), Wh; B – urate component (UA+UAD), UA; C – oxalate-phosphate component (Wh+Wd+Dh), Dh. Urine pH values in men (blue columns), in women (green columns)
Abbreviations: Wh – Whewellite, Wd – Weddellite, UA – uric acid, UAD – uric acid dihydrate, Dh – Dallite (carbonate apatite phosphate)
цию к снижению при урикозурии более 3,48 мМ/сут у женщин с 67,71±2 7,59% до 53,61±33,93% (рис. 4C, р=0,056), а мужчин с 51,20±29,84% до 41,53±2 6,96% (рис. 4C, р =0,085). Процент оксалатно-фосфатного компонента не изменялся при урикозурии различной степени (рис. 4С).
Активность формирования струвитных мочевых камней при нарастании урикозурии прогрессивно падала у мужчин (рис. 3B, р =0,0062, χ2 тест), у женщин изменения были статистически недостоверны
При нарастании урикозурии от минимальных до максимальных значений и у мужчин, и у женщин наблюдалось повышение уровней экскреции кальция, фосфатов и магния (рис. 3C, D, р <0,0001). Эта зависимость была практически линейной и не изменялась при возрастании урикозурии более 3,48 мМ/сут. Как было отмечено ранее,превышение экскреции мочевой кислоты выше этого уровня сопровождается снижением значений рН мочи, что, как полагают, может оказывать влияние на уратный литогенез.При прогрессивном нарастании урикозурии ИМТ повышался незначительно: на 10,7% у мужчин ( р =0,0001) и на 12,8% у женщин ( р =0,0018).
В отличие от экскреторных показателей, сывороточные метаболические показатели у пациентов с МКБ проявляли стабильность при нарастающей урикозу-рии (рис. 3E, F). За исключением магния, уровень которого у женщин повышался незначительно – на 5,7% (рис. 3F, р =0,035).
Уровень фосфатов крови у женщин в среднем превышал этот уровень у мужчин на 7-11,6%, при увеличении экскреции мочевой кислоты выше 3,9 мМ/сут (рис. 3E, р <0,05). Уровень урикемии у мужчин был выше, чем у женщин, на 8,5%-16,0% практически при всех значениях урикозурии, тогда как содержание магния в крови женщин превышало его уровень у мужчин на 4,6-6,5% только при экскреции мочевой кислоты в диапазоне 3,2-4,5 мМ/сут (рис. 3F, р <0,05). Уровни кальцемии у мужчин и женщин не имели статистически значимых различий при всех значениях урикозу-рии.
Для определения уровня урикозурии,при котором статистически достоверно повышается риск оксалатного литогенеза образования камней,в исследуемых диапазонах урикозурии рассчитывали показатель относительного риска (ОР)по отношению к уровню урикозурии 2,81-3,48 мМ/сут, выше которого наблюдается активация оксалатного литогенеза. Результаты представлены в таблице 1.
Результаты показывают, что экскреция мочевой кислоты на уровне 3,91-5,21 мМ/сут достоверно увеличивает риск формирования оксалатных камней у мужчин ( p =0,0289) и женщин ( p =0,0183). В то же время возрастание степени экскреции мочевой кислоты от минимальных до максимальных значений не оказывало существенного влияния на риск формирования мочекислых камней ни у пациентов мужчин, ни у пациентов женщин.
Как отмечалось,между больными МКБ мужчинами и женщинами не было обнаружено существенных различий по уровню экскреции мочевой кислоты в исследованных диапазонах урикозурии. Однако различия в экскреции мочевой кислоты у мужчин и женщин наблюдались почти во всех возрастных группах (рис. 5B).
Распределение пациентов мужчин и женщин в возрастных группах имело особенности. В группах 4049 лет и 50-59 лет наблюдалось нарастание числа пациентов мужчин с последующим снижением. У женщин отмечалось увеличение числа пациентов почти во всех возрастных группах, вплоть до группы 60-69 лет (рис 6А, χ2 тест для тренда р =0,0109) с наибольшим числом пациентов с МКБ в группах 50-59 лет и 60-69 лет.
Прямого соответствия между распределением числа пациентов мужчин и женщин в возрастных группах и экскрецией в этих группах мочевой кислоты отмечено не было (рис. 5A, B).
Начиная с возрастной группы 30-39 лет, более высокое и стабильное повышение экскреции мочевой кислоты наблюдалось у мужчин по сравнению с жен-щинами,которое сохранялось вплоть до возрастной группы 60-79 лет (рис. 5B, p <0,01).
Таблица 1. Показатели относительного риска (ОР) формирования оксалатных камней у мужчин (ОР муж) и женщин (ОР жен) при урикозурии более 3,48 мМ/сут
Table 1. Indicators of the relative risk (RR) of oxalate stones formation in men (RR men) and women (RR women) with uricosuria more than 3.48 mM/day
|
Относительный риск |
Экскреция мочевой кислоты (мМ/сут) Uric acid excretion (mM/d) |
||||
|
Relative risk |
2,81-3,48 |
3,20-3,90 |
3,50-4,50 |
3,91-5,21 |
4,51-10,4 |
|
ОР (муж) / RR (men) |
1,096 |
1,332 |
1,429 |
1,547 |
|
|
р |
0,6112 |
0,0911 |
0,0289 |
0,0047 |
|
|
ОР (жен) / RR (women) |
1,368 |
1,414 |
1,735 |
2,16 |
|
|
р |
0,1928 |
0,1928 |
0,0183 |
0,0013 |
|

экспериментальная и клиническая урология № 3 2023

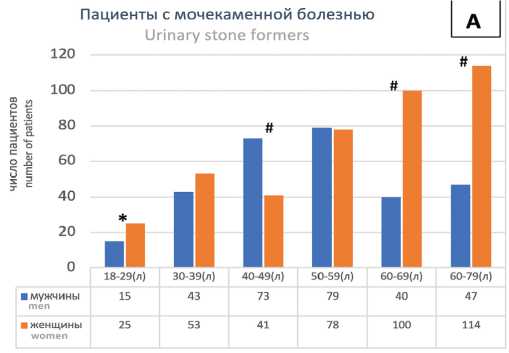
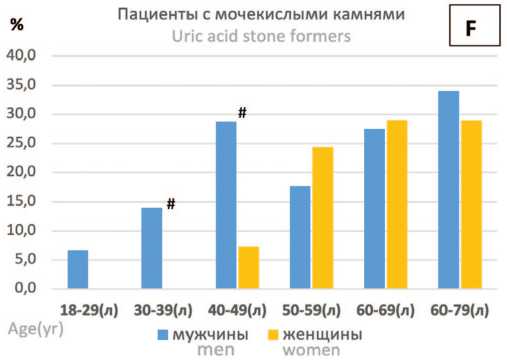
Рис. 5. Распределение в возрастных группах мужчин и женщин с МКБ [A], показателей экскреции мочевой кислоты (мМ/сут) [B], пациентов с мочекислыми [C, число пациентов; F, %] и оксалатными камнями [D,%]
* р <0,05,# p <0,01, о р <0,10 при сравнении различий показателей между мужчинами и женщинами. Группа 60-79 лет на [A-F] представлена дополнительно из-за малочисленности группы 70-79 лет
Fig. 5. Distribution in age groups of stone former men and women [A], uric acid excretion values (mM/day) [B], uric acid stone formers [C,number of patients; F,%] oxalate stone formers [D,%]. Comparison men vs women:
* p <0,05,# p <0,01 о p <0,10. The group 60-79 (y) on [A-F] is additionally represented due to the smallness of the group 70-79 (y)
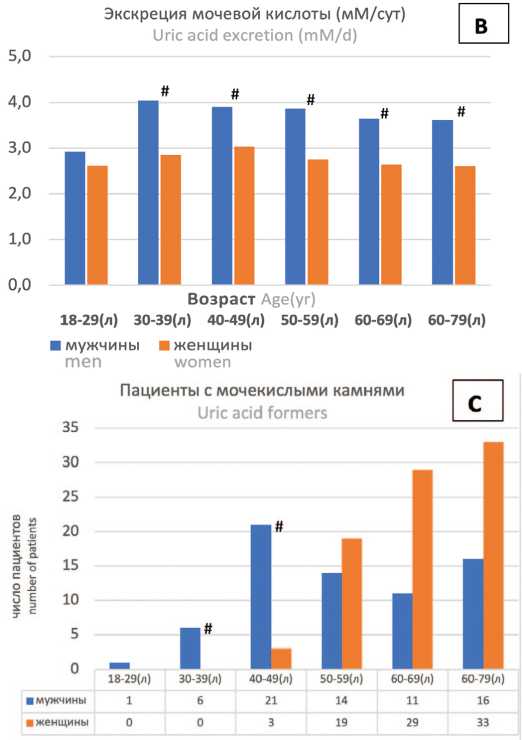
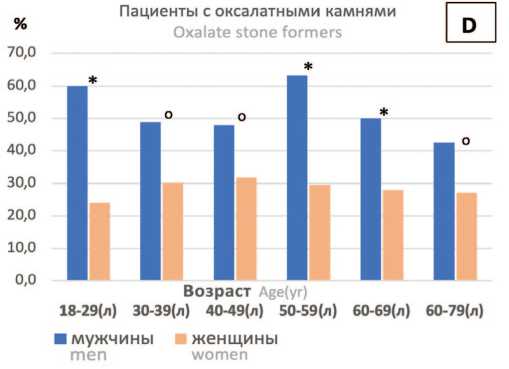
Высокая урикозурия у мужчин по сравнению с женщинами наблюдается в группах 30-39 лет (в 1,42 раза), 40-49 лет (в 1,29 раза), 50-59 лет (в 1,40 раза) и 60-69 лет (в 1,38 раза, рис. 4B, p <0,01). Это соответствовало более высокой частоте встречаемости оксалатных камней у мужчин, значительно превышающей этот показатель у женщин во всех возрастных группах в 2,5-1,8 раз (рис. 5D, p <0,05).
Что касается пациентов с мочекислыми камнями, то у мужчин возрастных групп старше 18-29 лет наблюдался постепенный рост частоты выявления таких камней по сравнению с женщинами с максимальным увеличением в 3,95 раза в возрастной группе 40-49 лет (рис. 5F, р =0,007) и сохранением высокого уровня в группах старше 60 лет. У женщин возрастание частоты выявления мочекислых камней отмечался только с возрастной группы 40-49 лет (рис. 5F).
Было отмечено,что формирование мочекислых камней наблюдается у мужчин раньше, чем у женщин, а именно с возраста 18-29 лет, в то время как у женщин камни такого типа появляются только начиная с возрастной группы 40-49 лет и старше (рис. 5С, F).
Соотношение мужчин и женщин,страдающих МКБ, изменялось с возрастом. Доля пациентов мужчин в диапазоне возрастных групп от 18-29 лет до 4049 лет возрастала в 1,7 раза, а доля пациентов женщин в той же степени относительно снижалась (Рис. 5А, р =0,0036, χ2 тест).
В группах от 40-49 до 60-79 лет динамика менялась на противоположную: доля пациентов мужчин по отношению к пациентам женщинам падала в 2,2 раза, а процент пациентов женщин в соответствующей степени возрастал (рис. 5А, р =0,00012, χ2 тест).
При этом в диапазоне возрастных групп от 18-29 лет до 40-49 лет частота случаев мочекислого уролитиаза у мужчин возрастала в 4,3 раза (рис. 5C, F, t-test one-sided p =0,040). В дальнейшем, начиная с возрастной группы 50-59 лет до группы 60-79 лет, частота случаев выявления мочекислых камней у мужчин продолжала возрастать в 1,92 раза (рис. 5C, F, χ2 тест р =0,0383).
Интересно отметить:случаи мочекислого уролитиаза у женщин наблюдались только с возрастного диапазона 40-49 лет, и частота этих случаев была невысокой (7,3%), но затем прогрессивно возрастала почти в 4 раза,достигая максимального значения в 28,9% в группе 60-79 лет. (рис. 5C, F, χ2 тест, р =0,0051)
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Повышенную экскрецию с мочой мочевой кислоты обычно традиционно рассматривают в качестве основного фактора формирования мочекислых камней. Нередко это приводит к трудностям дифференциальной диагностики таких состояний как гиперурикоз-урический кальций-оксалатный уролитиаз и мочекислый (подагрический) диатез, часто называемый идиопатическим мочекислым уролитиазом [13, 19-21] Поэтому важным является вопрос о роли урикозурии в литогенезе как отдельного метаболического фактора риска МКБ.
Еще S. Millm an и соавт., наблюдая пациентов с кальциевыми камнями (в основном оксалатными) и пациентов с мочекислыми камнями, обратили внимание на то,что уровень гиперурикозурии у больных этих групп статистически не различался и составлял в среднем 4-4,2 мМ/сут, что, таким образом, не может являться характерной отличительной чертой и биохимическим критерием для пациентов с оксалатным и мочекислым уролитиазом.В то время как большее значение имеют такие показатели, как рН мочи и уровень кальцийурии [22]. Позднее C.Y. Pak и соавт., обследуя пациентов с гиперурикозурическим кальцийоксалатным уролитиазом, обнаружили заметно более высокую экскрецию мочевой кислоты, которая в среднем составляла 4,76 мМ/сут, и была в 1,6 раз выше, чем при идиопатическом мочекислом уролитиазе [23].
Кроме того, больные с идиопатическим мочекислым уролитиазом имели более низкую экскрецию мочевой кислоты (в среднем 3,24 мМ/сут), чем лица с абсорбтивной гиперкальциурией (4,26 мМ/сут) [13] Во всех упомянутых работах отмечается важная роль повышенной экскреции кальция и более щелочных значений рН в генезе оксалатных камней, в отличие от мочекислых конкрементов.
Одной из задач клинической практики является оценка степени риска развития той или иной соответствующей метаболической формы МКБ на основании данных лабораторных показателей. Важно установить диапазоны лабораторных показателей с соответствующими предельными значениями, которые можно рассматривать в качестве метаболических критериев литогенности и которые смогли бы более точно указывать на степень риска камнеобразования, учитывая различную степень влияния метаболического фактора По-видимому, некоторые из этих показателей могут отличаться от значений известных показателей нарушенной экскреции, указывающих на повышенную ли-тогенность [9]. Поскольку оценка показателей экскреции по средним значениям, получаемая при обследовании пациентов групп наблюдения,дает лишь приблизительное представление о степени риска развития различных типов уролитиаза, в частности оксалатного или мочекислого [13, 22, 23].
Однако использование в настоящем исследовании разделения вариационного ряда экскреции мочевой кислоты у пациентов с МКБ на децильные интервалы дает возможность более детально охарактеризовать и оценить литогенные свойства урикозурии при различной степени ее проявления. Такой подход был использован нами ранее для характеристики литогенных свойств кальцийурии [17].
Полученные нами результаты позволяют сделать вывод, что уровень урикозурии 3,48 мМ/сут можно считать критическим, выше которого происходит активация оксалатного литогенеза. При этом показатели относительного риска оксалатного литогенеза достигали у мужчин значений 1,43-1,55 ( p <0,03), а у женщин 1,74-2,16 ( p <0,03). Соответственно этому, у пациентов обоих полов относительно снижалась активность образования камней из карбонатапатита (табл. 1, рис. 3A, B).
Как полагают,активация образования оксалатных камней при гиперурикозурии обусловлена такими факторами, как ускорение преципитации оксалата кальция на поверхности кристаллов урата натрия в результате гетерогенной нуклеации [24, 25]; связывание и инактивация ингибиторов кальций-оксалатного кристаллообразования коллоидными частицами уратов [26]; снижение растворимости ионов кальция и оксалата при высокой концентрации уратов, что способствует преципитации оксалата кальция, благодаря механизму высаливания [27].
Следует отметить, что частота выявления случаев мочекислого уролитиаза у мужчин и женщин была практически стабильной, колеблясь в пределах 18-24% и не проявляя зависимости от степени выраженности урикозурии (рис. 3А). Отсутствие повышения частоты случаев мочекислого уролитиаза при гиперурикозурии отмечалось также в работах других авторов [11, 12].
В то же время известно,что повышение ИМТ и развитие ожирения сопровождается активным формированием мочекислых камней [5, 6, 28]. В настоящем исследовании при прогрессивном нарастании урико-зурии повышение ИМТ было незначительным: на 10,7% у мужчин (р=0,0001) и на 12 ,8% – у женщин (р=0,0018). Это повышение ИМТ не достигало высоких значений,характерных для морбидного ожирения, при котором у больных наблюдается преобладающий рост доли мочекислых камней по отношению к конкрементам других типов [28].
Интересно отметить, что нарастающая урикозу-рия хотя и не оказывала существенного влияния на частоту формирования мочекислых камней, в отличие от оксалатных конкрементов,однако вызывала изменения в соотношении компонентов минеральной основы мочевых камней.
Возрастание экскреции мочевой кислоты до 3,48 мМ/сут, как было установлено в нашем исследовании приводило к росту доли безводной кислоты в мочевых камнях у мужчин более чем в 2 раза, что указывало на активацию мочекислого литогенеза.Однако эти процессы, затрагивающие структуру камней, по-види-мому, были недостаточно активны для накопления мочевой кислоты в преобладающих количествах, что проявлялось бы повышением числа случаев уратного уролитиаза.
Таким образом, более низкая экскреция мочевой кислоты у мужчин имела связь и с уменьшением доли безводной мочевой кислоты в мочевых камнях.По-добная связь между уровнем урикозурии и содержанием мочевой кислоты в камнях была отмечена в некоторых работах.
Было показано, что аллопуринол, снижая экскрецию мочевой кислоты [30], изменяет распределение состава камней у пациентов мужчин с подагрой так же, как и у мужчин с МКБ без подагры, снижая долю безводной мочевой кислоты в камнях [31]. Аналогичная связь между уровнем экскреции мочевой кислоты и ее долей в мочевых камнях была отмечена нами в настоящей работе.
У женщин такие процессы не наблюдались,что указывает на существование гендерных отличий в литогенезе мочекислого уролитиаза у мужчин и жен-щин.Эти гендерные отличия проявлялись также в различных возрастных группах.
У всех пациентов с МКБ, начиная с возрастной группы 30-39 лет вплоть до группы 60-79 лет, наблюдалось стабильное повышение экскреции мочевой кислоты. У мужчин урикозурия в 1,3-1,4 раза превышала уровень экскреции мочевой кислоты у женщин что проявлялось у мужчин и более высокой частотой встречаемости оксалатных камней во всех возрастных группах, в отличие от женщин.
Однако активность мочекислого литогенеза в большей степени зависела не от уровня урикозурии, а от возраста пациентов. По нашим данным, формирование мочекислых камней проявляется у женщин возрастной группы 40-49 л., в которой все пациентки были молодого возраста – 44 л.С увеличением возраста до 60-79 л. частота случаев мочекислого уролитиаза у женщин возрастала.Развитие мочекислого уролитиаза у мужчин начинается несколько раньше, в 20-29 л.
Полученные данные согласуются с результатами работы J.C. Lieske и соавт., которые анализировали распределение типов мочевых камней по полу и возрасту среди пациентов с МКБ. Наименьшее распространение мочекислых камней было зарегистрировано также у женщин молодого возраста 30-39 лет, и также отмечено постепенное увеличение частоты случаев мочекислого уролитиаза с возрастом до группы 80-89 лет и старше [32].
В работе Т. Knoll и соавт. было исследовано 224 085 мочевых камней, и определена активность образования камней из мочевой кислоты в зависимости от пола и возраста пациентов за период 1977-2006 гг [33] Активность литогенеза мочекислых камней выявлялась практически в одних и тех же в возрастных группах для мужчин и женщин,что было отмечено и в настоящем исследовании: минимальная активность образования мочекислых камней наблюдалась в молодом возрасте 20-29 лет, а максимальная – в пожилом возрасте 60-69 лет.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Литогенные свойства урикозурии различной степени выраженности зависят от половой принадлежности и возраста пациентов с МКБ.Процентное распределение мочекислых камней у мужчин и женщин не имело различий при нарастании степени ури-козурии. Разная направленность процессов уратного литогенеза у мужчин и женщин проявляется при ури-козурии выше 3,48 мМ/сут накоплением безводной мочевой кислоты в камнях у женщин и увеличением ее содержания в 1,47 раза, в отличие от мужчин, у которых доля мочевой кислоты в камнях, наоборот, снижалась в 1,36 раза. Однако урикозурия выше 3,48 мМ/сут сопровождается активацией не мочекислого,а оксалатного литогенеза: частота случаев выявления оксалатных камней у мужчин увеличивалась в 1,55 раза (р=0,0025), а у женщин в 2,16 раза (р=0,0013). При нарастании урикозурии от минимальных до максимальных значений и у мужчин, и у женщин наблюдается почти линейное повышение уровней экскреции каль- ция, фосфатов и магния (р<0,0001). Уровень фосфатов крови у женщин в среднем выше, чем у мужчин на 711,6%, а уровень урикемии у мужчин выше, чем у женщин, на 8,5-16,0% практически при всех значениях урикозурии. Уровни кальцемии у мужчин и женщин не имели статистически значимых различий при всех значениях урикозурии и не коррелировали с активностью литогенеза кальциевых камней.Экскреция мочевой кислоты выше 3,91мМ/сут достоверно увеличивает относительный риск формирования оксалатных камней у мужчин (p=0,0289) и женщин (p=0,0183).
Мужчины возрастных групп от 30-39 до 60-79 лет имеют более высокую экскрецию мочевой кислоты, чем женщины, что соответствует и более высокой частоте встречаемости оксалатных камней у мужчин превышающей этот показатель у женщин во всех возрастных группах в 2,5-1,8 раз (p<0,05). Формирование мочекислых камней наблюдается у мужчин в более раннем возрасте, чем у женщин, а именно с возраста 18-29 лет, в то время как у женщин формирование камней такого типа выявляется только с возрастной группы 40-49 лет и старше.
Таким образом, характерной особенностью ури-козурии различной степени является ее различная способность влиять на динамику метаболических показателей экскреции и литогенез кальциевых (оксалатных и фосфатных) камней у мужчин и женщин при отсутствии заметного эффекта на литогенез мочекислых камней,что необходимо учитывать при проведении персонифицированной метафилактики мочекаменной болезни.
ЛИТЕ РАТУPA/REFEREN CE S
ЛИТЕ РАТУРА/REFERENCE S
Список литературы Метаболические факторы риска и формирование мочевых камней. Исследование VII: литогенные свойства урикозурии у мужчин и женщин
- Stamatelou KK, Francis ME, Jones CA, et al. Time trends in reported prevalence of kidney stones in the United States:1976–1994. Kidney Int 2003;63(5):1817-23. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00917.x.
- Scales CD Jr, Smith AC, Hanley JM, Saigal CS. Prevalence of kidney stones in the United States. Eur Urol 2012;62(1):160-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.03.052.
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among us adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002;288(14):1723–7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.14.1723.
- Asplin JR. Obesity and urolithiasis. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2009;16(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2008.10.003.
- Daudon M, Lacour B, Jungers P. Influence of body size on urinary stone composition in men and women. Urol Res 2006;34(3):193-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0042-8.
- Голованов С.А., Просянников М.Ю., Каприн А.Д., Сивков А.В., Анохин Н.В., Войтко Д.А., Дрожжева В.В. Метаболические факторы риска и формирование мочевых камней. Исследование V: избыточный вес и ожирение как метаболические факторы литогенеза. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2021;14(4):80-9. [Golovanov S.A., Prosyannikov M.Yu., Kaprin A.D., Sivkov A.V., Anokhin N.V., Voytko D.A., Drozhzheva V.V. Metabolic risk factors and urinary stone formation. Study v: overweight and obesity as metabolic factors of lithogenesis. Eksperimentalnaya i Klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2021;14(4):80-9. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2021-14-4-80-89.
- Daudon M, Lacour B, Jungers P. High prevalence of uric acid calculi in diabetic stone formers. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005;20(2):468-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfh594.
- Pak CYC, Sakhaee K, Moe O, Preminger GM, Poindexter JR, Peterson RD, et al. Biochemical profile of stone-forming patients with diabetes mellitus. Urology 2003;61(3):523-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(02)02421-4/.
- Skolarikos A, Jung H, Neisius A, Petnk A, Somani B, Tailly Т, et al. EAU Guidelines on Urolithiasis. European Association of Urology 2023. [Electronic resourse]. URL: https://d56bochluxqnz.cloudfront.net/documents/full-guideline/EAU-Guidelines-on-Urolithiasis-2023.pdf.
- Cameron MA, Sakhaee K. Uric acid nephrolithiasis. Urol Clin North Am 2007;34(3):335-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ucl.2007.05.001.
- Sakhaee K, Adams-Huet B, Moe OW, Pak CY. Pathophysiologic basis for normouricosuric uric acid nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 2002;62(3):971-9. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00508.x.
- Alvarez-Nemegyei J, Medina-Escobedo M, Villanueva-Jorge S, Vazquez-Mellado J. Prevalence and risk factors for urolithiasis in primary gout: is a reappraisal needed? J Rheumatol 2005;32(11):2189-91.
- Pak CY, Sakhaee K, Peterson RD, Poindexter JR, Frawley WH. Biochemical profile of idiopathic uric acid nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 2001;60(2):757-61. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.060002757.x.
- Chewcharat A, Curhan G. Trends in the prevalence of kidney stones in the United States from 2007 to 2016. Urolithiasis 2021;49(1):27-39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-020-01210-w.
- Walker V, Stansbridge EM, Grifn DG. Demography and biochemistry of 2800 patients from a renal stones clinic. Ann Clin Biochem 2013;50(Pt 2):127–39. https://doi.org/10.1258/acb.2012.012122.
- Zeng Q, He Y. Age-specifc prevalence of kidney stones in Chinese urban inhabitants. Urolithiasis 2013;41(1):91–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-012-0520-0.
- Голованов С.А., Просянников М.Ю., Сивков А.В., Анохин Н.В., Войтко Д.А., Дрожжева В.В. Метаболические факторы риска и формирование мочевых камней. Исследование VI: литогенная активность кальциурии у мужчин и женщин. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2023;16,(1):80-9. [Golovanov S.A., Prosyannikov M.Yu., Sivkov A.V., Anokhin N.V., Voytko D.A., Drozhzheva V.V. Metabolic risk factors and urinary stones formation. Study VI: Сalciuria lithogenic features in men and women. Eksperimentalnaya i Klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Uro- logy 2022;15(4):80-9. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2023-16-1-80-89.
- Грешилов А. А., Стакун В. А., Стакун А. А. Математические методы построения прогнозов. М.: Радио и связь, 1997. 112 с. [Greshilov A. A., Stakun V. A., Stakun A. A. Mathematical methods for constructing forecasts. Moscow: Radio and communication, 1997. 112 p. (In Russian)].
- Pak CY, Sakhaee K, Fuller C. Successful management of uric acid nephrolithiasis with potassium citrate. Kidney Int 1986;30(3):422-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1986.201.
- Levy FL, Adams-Huet B, Pak CY. Ambulatory evaluation of nephrolithiasis: an update of a 1980 protocol. Am J Med 1995;98(1):50-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9343(99)80080-1.
- Khatchadourian J, Preminger GM, Whitson PA, Adams-Huet B, Pak CY. Clinical and biochemical presentation of gouty diathesis: comparison of uric acid versus pure calcium stone formation. J Urol 1995;154(5):1665-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(01)66743-0.
- Millman S, Strauss AL, Parks JH, Coe FL. Pathogenesis and clinical course of mixed calcium oxalate and uric acid nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 1982;22(4):366-70. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1982.183.
- Pak CY, Sakhaee K, Peterson RD, Poindexter JR, Frawley WH. Biochemical profile of idiopathic uric acid nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 2001;60(2):757-61. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.060002757.x.
- Coe FL, Lawton RL, Goldstein RB, Tembe V. Sodium urate accelerates precipitation of calcium oxalate in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1975;149(4):926-9. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-149-38928.
- Pak CY, Arnold LH. Heterogeneous nucleation of calcium oxalate by seeds of monosodium urate. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1975;149(4):930-2. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-149-38929.
- Zerwekh JE, Holt K, Pak CY. Natural urinary macromolecular inhibitors: attenuation of inhibitory activity by urate salts. Kidney Int 1983;23(6):838-41. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1983.103.
- Grover PK, Marshall VR, Ryall RL. Dissolved urate salts out calcium oxalate in undiluted human urine in vitro: implications for calcium oxalate stone genesis. Chem Biol 2003;10(3):271-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-5521(03)00057-7.
- Ekeruo WO, Tan YH, Young MD, Dahm P, Maloney ME, Mathias BJ, et al. Metabolic risk factors and the impact of medical therapy on the management of nephrolithiasis in obese patients. J Urol 2004;172(1):159-63. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000128574.50588.97.
- Chu FY, Chang CC, Huang PH, Lin YN, Ku PW, Sun JT et al. The Association of uric acid calculi with obesity, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. Biomed Res Int 2017;2017:7523960. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7523960.
- Goldfarb DS, MacDonald PA, Gunawardhana L, Chefo S, McLean L. Randomized controlled trial of febuxostat versus allopurinol or placebo in individuals with higher urinary uric acid excretion and calcium stones. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2013;8(11):1960-7. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01760213.
- Marchini GS, Sarkissian C, Tian D, Gebreselassie S, Monga M. Gout, stone composition and urinary stone risk: a matched case comparative study. J Urol 2013;189(4):1334-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.09.102.
- Lieske JC, Rule AD, Krambeck AE, Williams JC, Bergstralh EJ, Mehta RA, et al. Stone composition as a function of age and sex. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2014;9(12):2141-6. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.05660614.
- Knoll T, Schubert AB, Fahlenkamp D, Leusmann DB, Wendt-Nordahl G, Schubert G. Urolithiasis through the ages: data on more than 200,000 urinary stone analyses. J Urol 2011;185(4):1304-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.11.073


