Микробиотический фактор, здоровье и стресс-индуцированные психические расстройства
Автор: Михайлова Анна Павловна, Ченченко Дарья Валерьевна, Штрахова Анна Владимировна
Журнал: Психология. Психофизиология @jpps-susu
Рубрика: Библиографические обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.11, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Описаны исследования многомерных связей между фактором микробиоты человека, воздействием стрессоров и связанными с этим нарушениями психического здоровья, включая стресс-индуцированные психические расстройства. Представлен анализ теоретических и эмпирических исследований современного состояния проблемы кишечной и оральной микробиоты в контексте ее влияния на психическую деятельность в норме и при стрессовых воздействиях, включая процедуры экспериментально-индуцированного стресса. Особое внимание уделяется во-первых, анализу многоуровневых соотношений в самой микробиоте желудочно-кишечного тракта человека и, в частности, микробиоте ротовой полости как репрезентативному корреляту общих характеристик кишечной микробиоты. Во-вторых, исследовались теоретические и описанные в научной литературе эмпирически подтвержденные взаимосвязи изменений микробиотического фактора при хроническом стрессе и остром экспериментальном стрессе. В третьих, представлены данные о соотнесенности микробиоты, с одной стороны, и патогенеза и симптоматики аффективных (тревожных, депрессивных и тревожно-депрессивных) расстройств. В-четвертых, отражены ранее выполненные зарубежные исследования микробиоты при классических психических (на примере расстройств аутистического спектра) и нейродегенеративных заболеваниях (на примере болезней Альцгеймера и Паркинсона).
Микробиота человека, стресс-индуцированные расстройства
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147233028
IDR: 147233028 | УДК: 159.944.4 | DOI: 10.14529/psy180107
Текст обзорной статьи Микробиотический фактор, здоровье и стресс-индуцированные психические расстройства
Современное состояние проблемы влияния микробиотического фактора человека (микробиоты, микробиома) на стресс-индуцированные психические расстройства характеризуется неуклонным ростом публикаций. По запросу с тегом «microbiota» в научной базе Pubmed [ресурс ] отмечается рост числа публикаций с 51 статьи в 1997 г. до 385 – в 2007 г. и до 5851 публикации – в 2017 г. Обобщенно микробиота рассматривается в качестве симбиотического партнера в поддержании здоровья человека, в том числе психического здоровья. Доступны данные о влиянии присутствующего в организме человека микробиома на структуры и функции головного мозга. При этом предполагается, что кишечные бактерии могут являться причиной ряда психических и психосоматических отклонений и заболеваний. Накопленные данные показывают, что такое влияние осуществляется взаимодействием кишечной микро- биоты с центральной нервной системой – через ряд нервных, эндокринных и иммунных путей (Lyte, Cryan, 2014; Thakur et al., 2014; Sherwin, 2016а, Sherwin et al., 2016б).
Перспективы изучения микробиоты предполагают принципиально новые взгляды на стратегии профилактики и лечения психических и психосоматических расстройств с учетом фактора микробиоты, что требует более детальных и системных, междисциплинарных исследований. За рубежом существует ряд такого рода масштабных проектов, например, American Gut Project, Human Microbiome Project, American Gut – Human Food Project, British Gut Project и другие.
В то же время большинство публикаций в базе Pubmed отражают результаты исследований, проведенных на доклиническом уровне, что требует решения задачи корректной экстраполяции такого рода данных на человека методами трансляционной медицины. В области трансляционных исследований основная проблема адекватной экстраполяции полученных на модельных организмах результатов на уровень человека связана с тем, что физиология высшей нервной деятельности и системное строение психики человека являются более сложными и развернутыми, чем у любого животного. По данным, имеющимся на сегодняшний день, психика животного более существенно ограничена, поэтому прямая экстраполяция экспериментальных результатов на лабораторных животных не представляется возможной.
Кроме того, одной из принципиально важных клинико-психологических задач является поиск и идентификация новых объективных биомаркеров в целях помощи в определении диагноза стресс-индуцированных заболеваний, их прогноза или клинической реакции организма человека на их лечение. В свете этого выбор исследования микробиоты как одного из нетрадиционных объектов исследования позволяет установить и конкретизировать ее роль при стресс-индуци-рованных психических расстройствах. Такого рода исследования новых кластеров биомаркеров считаются в настоящее время наиболее полезными в психиатрии и психологии, наряду с методами нейровизуализации и пато-нейропсихологическими методами фенотипической диагностики болезней мозга и функциональных расстройств психики (Lozupone, Seripa, Stella et al., 2017).
Микробиотический фактор в контексте проблемы здоровья и болезни
Влияние микробиоты как одного из ведущих системных факторов, определяющих состояние здоровья и болезни происходит не только за счет собственно микробиологического воздействия, но и за счет включения ее во взаимосвязанные биопсихосоциальные механизмы сано- и патогенеза (Rajilic-Stojanovic, 2013). Считается, что микробиота пищеварительной системы является одной из наиболее важных микробиотических систем. Патопла-стическая и патопротекторная роль микробиоты очевидна для ряда соматических (например, гастроэнтерологических), психических (в частности, тревожно-депрессивных) и социально-детерминированных заболеваний, в частности, ожирение, сахарный диабет и метаболический синдром (Rosenbaum, Knight, Rudolph, 2015; Fond, Boukouaci, Chevalier et al., 2015). Другим аспектом влияния микробиоты на состояние здоровья является ее роль в развитии пограничных нарушений, вызванных, в частности, воздействием факторов хронического стресса и дистресса, и определяемых в современных медико-биологических классификаторах как дезадаптивные состояния (Kelly, Borre, O' Brien, 2016). Одним из основных патогенетических факторов развития таких состояний являются нарушения многоуровневых системных механизмов гомеостаза (сохранения постоянства внутренней среды, рассматриваемой с позиции биопсихо-социальной системной модели человека).
В исследовательском плане представляет особый интерес микробиота полости рта как важная и в то же время доступная изучению составляющая микробиоты пищеварительной системы.
Во-первых, важной особенностью микробиоты пищеварительной системы и полости рта, в частности, является наличие в ней двух составляющих: резидентной, облигатной (относительно постоянной на всем протяжении жизни человека) и факультативной или транзитной, дополнительной (нестабильно существующей в полости рта на протяжении определенного периода жизни). При этом представляется очевидным, что как облигатная, так и факультативная составляющая микробиоты вносят свои доли вклада в состояние здоровья и развитие заболеваний и дезадап-тивных состояний, в частности. Также представляется очевидным, что влияние на факультативную составляющую микробиоты является фактором управления состоянием здоровья и дезадаптивных состояний за счет воздействия на механизмы гомеостаза (Rosenbaum, Knight, Rudolph, 2015).
Во-вторых, одним из индикаторов подверженности стресс-факторам являются изменения психовегетативного (психофизиологического) статуса (в понимании Н. Selye) и психоэмоционального (в понимании R. Lazarus), определяющие развитие дезадаптивных состояний, высоковероятностно разворачивающихся, в частности, в виде психосоматических реакций, состояний и заболеваний (по нисходящей «соматической» оси биопсихосо-циалъной модели) и в виде психических и поведенческих (в том числе и так называемых психосоциальных) расстройств (по восходящей «психосоциальной» оси) (Fond, Boukouaci et al, 2015; Wang, 2016; Parashar, Udayabanu, 2016). Регуляторную роль, определяющую степень вероятности развития рас- стройств либо сохранения здоровья, выполняют многоуровневая система гомеостаза, функционирующая, в частности, на психосоматическом и психосоциальном уровнях. Центральную роль в механизме поддержания соматопсихосоциального гомеостаза занимает аффективное реагирование на стресс (дистресс). Адаптивный ресурс личности определяет характер и особенности совладающего поведения в ситуации дистресса (по H. Selye). В условиях дефицита личностного ресурса возможен патологический вариант стресс-реакции с последующим формированием аффективных расстройств, что усугубляется дисбалансом на уровне микробиоты. При этом аффективные расстройства формируются вследствие двух механизмов формирования – психовегетативного (за счет патологической активации гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковой оси) и психоэмоционального (за счет нарушений эмоциональной регуляции психической деятельности и поведения). Таким образом, исследование аффективной составляющей психического статуса как маркера одновременного проявления психовегетативных и психсоциальных феноменов.
В-третьих, имеются данные о влиянии микробиоты желудочно-кишечного тракта на деятельность головного мозга в целом (Foster et al., 2016) и формирование психической патологии и аффективных расстройств в частности (De Palma et al., 2014).
В-четвертых, имеются данные о влиянии такой микробиоты на процессы стресс-реагирования, включая развитие постстрессовых расстройств (Kieran Reaa, et al., 2016).
Таким образом, представляется вполне обоснованным и актуальным междисциплинарное исследование роли микробиоты в устойчивости человека к психоэмоциональному стрессу, выполняемое на стыке нескольких предметных областей: медицины (микробиологии, гастроэнтерологии, психиатрии), психологии (психофизиологии, психодиагностики, клинической психологии, психологии стресса и посттравматических расстройств).
При этом представляется важным, что более 97 % популяции населяющих желудочно-кишечный тракт (ЖКТ) микроорганизмов составляют лишь четыре их семейства (Rosenbaum, Knight, Leibel, 2015): Bacteroidetes (20–25 %), Firmicutes (60–65 %), Proteobacteria (5–10 %), и Actinobacteria (3 %). Считается, что набор и соотношение компо- нентов в составе микробиоты каждого человека является строго индивидуальным, а основным фактором различий ее родо-видового состава являются, скорее всего, различия в диете (Rajilic-Stojanovic, 2013). Вместе с тем установлено, что состав микробиоты пожилых людей более индивидуально изменчив и подтверждено наличие взаимосвязи между диетой, микробиотой и состоянием здоровья, а также имеются указания на роль обусловленных диетой изменений микробиоты и ее особенности при изменении темпов снижения здоровья и при старении (Claesson et al., 2012). Причем изучение микробиоты ЖКТ происходит на примере оральной и кишечной микробиоты. Чаще и больше исследована вторая из них (Mu, Yang, Zhu, 2016; Collins, Surette, Bercik, 2012; Kumar, 2013). В то же время имеются исследования, которые доказывают, что по изменению состава микробиоты ротовой полости можно судить об общем состоянии иммунной системы и тревоге у человека (Lamb et al., 2017).
В более ранней публикации по этой проблеме (Микробиотический фактор…, 2017) упоминалось, что одним из наиболее убедительных доказательств роли кишечных микробов в психике является широко распространенная концепция оси «кишечник – мозг», которая в настоящее время расширена до оси «микробиота – кишечник – мозг», что позволяет рассматривать эту ось как «энтеральную нервную систему», в которой кишечник считается «вторым мозгом» (Gershon, 1998) или, более строго (учитывая величину его анатомо-функциональных параметров) – «наибольшим сенсорным органом в теле человека», оказывающим мощнейшее влияние на психику и поведение человека (Эндерс, 2015). В настоящее время предложены классификация ЭНС и описана ее организация (Hansen M.B., 2003).
При этом сама микробиота является важным связующим, даже опосредующим звеном, а роль самого микробиома представляется недостаточно оцененной. Так, совокупность генов в пределах микробиоты человеческого кишечника очень велика: общий геном кишечной микробиоты (метагеном) содержит, по меньшей мере, в 100 раз больше генов, чем геном всего человеческого организма. При этом многие человеческие гены являются гомологами бактериальных генов, в основном полученных по происхождению, но некото-
Библиографический обзор рые – путем переноса генов от бактерий (Dinan, Stilling, 2015).
Микробиотический фактор, центральная нервная система и психика
Предполагается, что кишечные бактерии через ряд путей могут влиять на функции головного мозга и поведение человека.
Ось мозг – кишечник представляет собой двунаправленную систему связи между центральной нервной системой и желудочнокишечным трактом (O’Mahonya et al., 2015) и целостно влияет на разные органные системы организма (рис. 1).
Включение в состав этой биполярной двунаправленной оси, помимо центральной нервной системы (ЦНС), еще и нейроэндокринной и нейроиммунной системы, симпатической и парасимпатической ветви вегетативной нервной системы, энтеральной нервной системы и кишечного микробиома предполагает необходимость определить особенности взаимодействие последних с интегративными структурами ЦНС (например, с гипоталамусом такое взаимодействие происходит посредством сложной сети афферентных и эф- ферентных волокон, Dinan, Stilling, 2015).
Например, нейроны энтеральной нервной системы являются первой точкой контакта для кишечной микробиоты в просвет. Эти сообщения из кишечника передаются в мозг через блуждающий нерв – vagus (Parashar, Udayabanu, 2016). Последний имеет эфферентные и афферентные подразделения и играет фундаментальную роль в обеспечении сигналов от мозга к кишечнику и наоборот. При этом такой «второй мозг» находится в системной связи с головным мозгом: более 90 % проходящих по nervus vagus импульсов исходит от нейронов ЭНС (так называемая «восходящая афферентация») и только 10 % приходится на нисходящее звено – от головного мозга к внутренним органам через это звено парасимпатической нервной системы. Кроме того, косвенное воздействие микробиоты кишечника на врожденную иммунную систему может привести к изменениям в циркулирующих уровнях про- и противовоспалительных цитокинов, которые непосредственно влияют на функцию мозга, особенно в таких областях, как гипоталамус. Так, кортиколибе-рин является доминирующим пептидным ре-
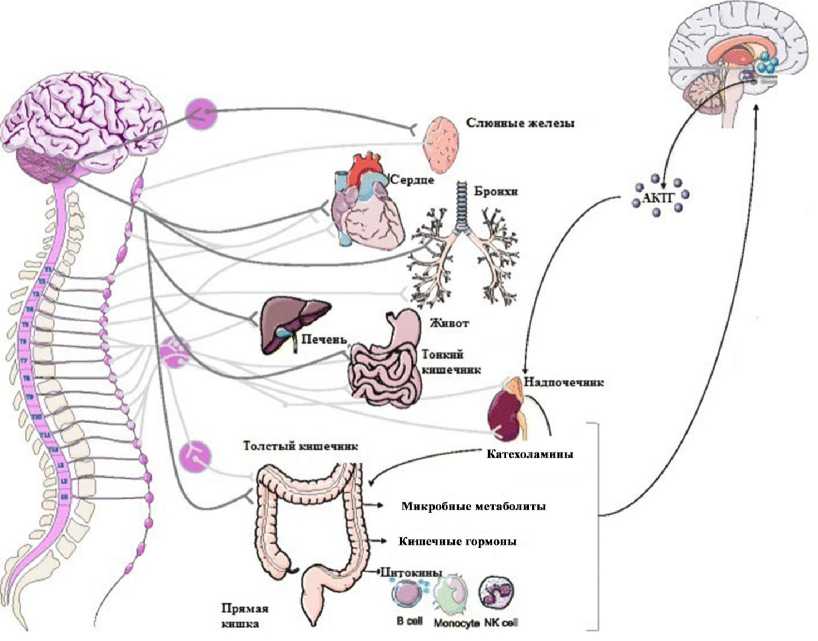
Рис. 1. Ось «микробиота – кишечник – мозг» в функционально-структурном единстве организма
гулятором гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпо-чечниковой оси, которая сама по себе обеспечивает другой двунаправленный маршрут связи. Триптофан является незаменимой аминокислотой и является предшественником многих биологически активных веществ, в том числе нейромедиатора серотонина. Существует ряд доказательств, указывающих на то, что пробиотическая бактерия Bifidobacterium infantis может существенно влиять на синтез серотонина (Dinan, Stilling, 2015), более 95 % объема которого приходится на расположенные в кишечнике нейроны (Gershon, 2013). Кроме того, кишечные микроорганизмы могут самостоятельно синтезировать ряд ключевых нейротрансмиттеров (см. таблицу).
Из всех этих синтезируемых кишечной микробиотой нейротрансмиттеров наиболее изучена роль серотонина в функционировании оси «микробиота –кишечник – мозг». Так, микробное воздействие на метаболизм триптофана и серотонинергическую систему является необходимым звеном во взаимодействии мозга с кишечником. Серотонин играет важную роль в психическом функционировании человека. В частности, он участвует в модуляции тревоги, реакций страха и стрессовых реакций, социального поведения. Мета-анализ посмертных исследований обнаружил повышение префронтальных рецепторов 5-HT1A и снижение префронтальных рецепторов 5-HT2A при шизофрении (Kelly et al., 2017). Экспериментально установлена связь между поведением, формирующимся под влиянием микробиоты кишечника, и теми типами поведенческих паттернов, которые опираются на интактную серотонинергическую нейротрансмиссию. Механизмы, лежащие в основе этого, могут быть связаны со способностью микробиоты кишечника контролировать метаболизм триптофана вдоль пути кинуре-ненина, тем самым одновременно уменьшая долю, доступную для синтеза серотонина, и увеличивая производство нейроактивных ме- таболитов. Ферменты этого пути являются иммунными и чувствительными к стрессу. Кроме того, в желудочно-кишечном тракте существуют нейронные процессы, на которые могут влиять местные изменения концентрации серотонина. Микробиота кишечника как терапевтическая мишень может быть обоснованной стратегией для лечения связанных с серотонином расстройств этой оси (O’Mahonya et al., 2015).
Представляется очевидным, что описанные выше процессы иллюстрируют лишь часть данных о влиянии микробиоты на функционирование мозга и протекание психических процессов.
Микробиота и стресс. Объем фактических данных, подтверждающих мнение о том, что комменсальные организмы кишечника играют определенную роль в генезе стресса, неуклонно растет. Однако по описанным выше основаниям они отражают в своем абсолютном большинстве результаты лабораторных исследований на экспериментальных животных. Общая схема связи микробиоты и стресса в оси «микробиота – кишечник – мозг» проиллюстрирована в рис. 2.
Предполагается, что микробиота влияет на формирование и развитие стрессового реагирования, начиная с раннего постнатального периода развития, в частности, на раннее программирование и более позднее реагирование системы стресса. Основная доля исследований в этой области сосредоточена на изучении связи оральной и кишечной микробиоты с осью «гипоталамус – гипофиз – кора надпочечников», которая является центральным компонентом нейроэндокринной реакции мозга на стресс. Еще в 2004 году N. Sudo и его коллеги в фундаментальной публикации в области микробиоты и стресса определили, что кишечная микробиота непрерывно взаимодействует с этой осью уже на ранних возрастных этапах, влияя на постнатальное развитие стресс-реакции у мышей.
Нейротрансмиттеры, синтезируемые кишечной микробиотой
|
Вид микроорганизмов |
Синтезируемый нейротрансмиттер |
|
Candida, Streptococcus, Enterococcus |
Серотонин (5НТ) |
|
Lactobacillus (специфические штаммы), Bifidobacteria (специфические штаммы), L. rhamnosus (JB-1) |
Гамма-аминомасляная кислота (ГАМК) |
|
Escherichia, Bacillus, Saccharomyces SPP |
Норэпинефрин |
|
Bacillus |
Допамин |
|
Lactobacillus |
Ацетилхолин |
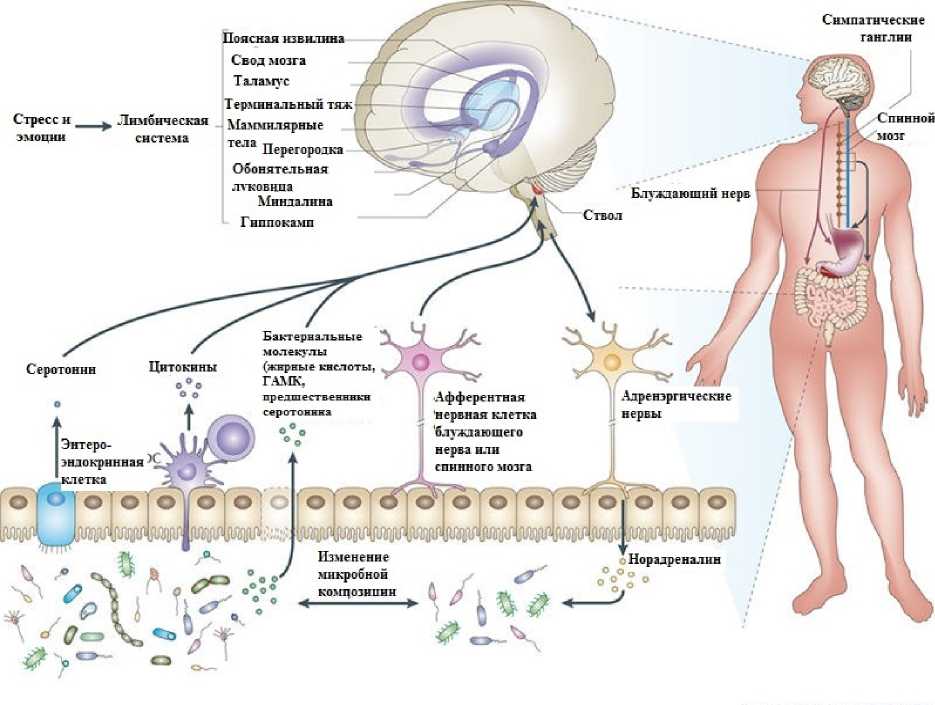
Рис. 2. Микробиота и стресс
В исследовании M. Crumeyrolle-Arias с коллегами (2014) подтвердилась гипотеза о том, что стерильные крысы, выращенные в свободной от микробов среде, демонстрируют преувеличенные реакции оси «гипоталамус-гипофиз-кора надпочечников» на стресс.
В обзоре исследований регулирующих стресс механизмов микробиоты T.G. Dinan и J.F. Cryan (2017) утверждают, что стресс вызывает повышенную проницаемость кишечника, позволяя бактериям и бактериальным антигенам пересекать эпителиальный барьер и активировать иммунный ответ слизистой оболочки, что вторично изменяет состав микробиоты и ведет к усиленному ответу оси «гипоталамус – гипофиз – кора надпочечников».
Такого рода иммунные дисфункци, вызванные повышенной проницаемостью кишечного барьера, подтверждаются рядом исследований, в которых животные были подвергнуты различного рода социальным стрессорам (Golubeva, 2015, Yang, 2017, Galley, 2017, Liang et al., 2015).
Так, воздействие стрессора вызывало существенные изменения в сообществе микро- биоты, что было выявлено с помощью пиросеквенирования в исследовании M.T. Bailey (2011): в частности, произошло снижение относительного содержания бактерий рода Bacteroides при увеличении относительной численности рода Clostridium.
В работе Galley (2017) была оценена структура микробиоты у мышей, подвергнутых социальному стрессору (воздействие мыши-агрессора). Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о воздействии стресса на микробиоту толстой кишки во время заражения с микроорганизмами рода C. Rodentium и подтверждена стойкость этого эффекта, который не снижается даже при терапии пробиотиком.
Подобный результат также был получен в исследовании K. Yoshikawa (2017) с изучением влияния психологического стресса на энтеропатию, вызываемую нестероидными противовоспалительными препаратами. Было подтверждено существенное влияние стресса на слизистый барьер при наличии желудочнокишечных расстройств, что указывает на полезность изучения микробиоты кишечника для выяснения патофизиологии энтеропатии при лечении нестероидными противовоспалительными препаратами.
В исследовании с использованием перорального введения микроорганизмов рода Citrobacter rodentium и Campylobacter jejuni в качестве пищевых патогенов доказано, что проживающие в желудочно-кишечном тракте бактерии могут активировать стресс-реакции посредством активации блуждающего нерва (Parashar, Udayabanu, 2016).
Таким образом, описанные исследования подтверждают гипотезу о том, что стресс-реакции организма могут опосредованно влиять на состав микробиоты и различные аберрации в составе микробного сообщества могут являться фактором, ослабляющим адаптивные процессы в организме. В целом такие исследования являются показателями наличия двусторонней связи между микробиотой желудочно-кишечного тракта и структурами головного мозга, регулирующими гомеостаз на разных уровнях.
Микробиота и стресс-индуцированные аффективные расстройства, психические и нейродегенеративные заболевания
Аффективные, прежде всего, тревожнодепрессивные расстройства занимают значительную долю в структуре всех психических нарушений, что обосновывает высокий исследовательский интерес к этой группе расстройств. Недостаточная эффективность существующих стратегий лечения заставляет искать новые биологические и инструментально верифицируемые маркеры этой группы расстройств.
Одним из перспективных направлений исследований в этой области является изучение связи тревоги и депрессии с определенными компонентами микробиоты желудочнокишечного тракта. Так, J.R. Kelly с коллегами (2016), проводя исследование на мышиных моделях депрессии, получили значимые различия в составе микробиоты кишечника у депрессивных мышей по сравнению со здоровыми животными. Но наиболее показательна такая связь в работах, посвященных изучению реактивной депрессии и тревожных реакций, вызванных стрессовым воздействием (Yang, 2017, Liang et al., 2015).
Актуальным является вопрос о возможности повышения эффективности стратегии терапии депрессии путем коррекции композиции микробов в просвете желудочнокишечного тракта. Доминирование симптоматического подхода в лечении пациентов с депрессией не всегда оказывается эффективным, что требует поиска новых связей, лежащих в основе этиопатогенеза этого психического расстройства.
Установлено (Dinan, Cryan, 2013), что при большом депрессивном расстройстве у пациентов возникают изменения гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковой системы (повышение уровеня кортизола в плазме, повышенный уровень высвобождающего фактора кортикотропина в спинномозговой жидкости в сочетании с неспособностью подавлять кортизол в ответ на вызов дексаметазоном). Поскольку, как описано выше, микробиота имеет очевидные связи с осью «гипоталамус – гипофиз – кора надпочечников» (что особо подчеркивается в многочисленных и процитированных исследованиях микробиоты и стресса), можно предположить, что такое направление исследований также могут открыть новые подходы в комплексной терапии тревоги, депрессии и аффективных расстройств в целом посредством целенаправленного изменения характеристик микробиоты на фоне приема специализированной фармакотерапии.
Другой важной областью изучения связи микробиоты с психическими расстройствами является исследование эндогенных психических расстройств. Установлена связь между кишечной микробиотой и поведенческими проявлениями при шизофрении и расстройствах аутистического спектра (РАС). Эти расстройства представляют особый интерес, поскольку в настоящее время до конца неизвестны механизмы, лежащие в основе их этиологии и патогенеза. Важным аргументом в пользу связи шизофрении и РАС с микробиотой является то, что они часто сочетаются у пациентов с заболеваниями ЖКТ, при этом причинно-следственная детерминация этой взаимной связи не установлена. Однако наличие доказанной дисфункции в работе кишечника позволяет предполагать наличие задей-ствованности кишечных микроорганизмов (Li, 2016).
Кроме того, известно, что РАС сильно ассоциируется с атипичными схемами питания. Перенос микробиоты от здоровых людей к пациентам с этими расстройствами также оказывает позитивный эффект на проявление симптомов РАС. Подтверждением этого является клиническое исследование трансплантации фекальной микробиоты от здоровых детей, проведенное на выборке в 18 детей с РАС, показавшее наличие единовременного улучшения как симптомов нарушений работы ЖКТ, так и поведенческих симптомов, наблюдаемое на фоне увеличения титров Bifidobacterium, Prevotella и Desulfovibrio в композиции микробиоты (Kelly, Minuto, Cryan et al., 2017).
Приведенная выше информация подтверждает факт связи микробиоты с аффективными нарушениями, а также с эндогенными расстройствами, проявляющимися в нарушении социального взаимодействия.
Ряд исследований демонстрируют существенное влияние кишечных бактерий на когнитивную сферу, подтверждаемое как у нормативно развивающихся испытуемых, так и у лиц с нейродегенеративными расстройствами (прежде всего – страдающими болезнью Альцгеймера и болезнью Паркинсона). Однако собственно когнитивное функционирование в связи с состоянием микробиоты также изучены на относительно здоровых моделях.
Например, E.E. Fröhlich с коллегами (2016) провели исследование, в результате которого выявили, что распознавание объектов (но не пространственное) было нарушено у обработанных антибиотиками мышей. Такого рода когнитивный дефицит был связан с рядом специфичных изменений в головном мозге и дисрегуляцией мозговых сигнальных молекул, происходящих из-за дисбактериоза кишечника, вызванного антибиотиком. C. O'Hagan с соавторами (2017) испытывали память и поведенческую гибкость у пожилых крыс и выявили, что хроническая диетическая добавка с многовидовыми живыми микроорганизмами вида Lactobacillus и Bifidobacteria может изменять метаболиты мозга у пожилых крыс и оказывать благотворное влияние на пространственную навигацию, кратковременную и долговременную память. В исследовании M. Gareau с коллегами (2014) с оценкой поведения животных после инфицирования неинвазивным кишечным патогеном (Citrobacter rodentium) после острого дистресса установлено наличие дисфункции памяти, проявлявшейся после заражения и стресса, но предотвращавшейся ежедневным лечением инфицированных мышей пробиотиками.
В 2017 году было опубликовано первое исследование по связи когнитивных функций и микробиоты, проведенное на детях младенческого возраста (Carlson, Xia et al., 2017), в котором получены результаты, мало совпадающие с доклиническим исследовательским опытом их коллег. Изучение соответствия микробной композиции у 89 детей в возрасте 1 года их когнитивным результатам в возрасте 1 и 2 лет (зарегистрированных с использованием Малленских шкал раннего обучения и с использованием структурной магниторезонансной томографии) и составу фекальной микробиоты показало, что в двухлетнем возрасте у этих детей более высокое альфа-разнообразие микробиоты сопровождалось более низкими оценками по трем показателям когнитивного функционирования: суммарному комбинированному баллу, шкале визуального восприятия и шкале экспрессивной речи. Анализ данных магнитно-резонансной томографии свидетельствует о том, что микробиота кишечника оказывает минимальное влияние на объем мозга и регионального кровотока в возрасте 1 и 2 лет.
Наиболее клинически значимыми в этой области являются исследования нейродегене-ративных расстройств. Так, например, известно, что воспалительный процесс, вызванный локальными отложениями пептида Aβ42 в головном мозге, является ключом к патогенезу и прогрессированию болезни Альцгеймера. Так, в исследовании болезни Альцгеймера (Bonfili et al., 2017) показано, что обработка пробиотическим препаратом SLAB51 влияет на состав кишечной микробиоты и ее метаболитов, что оказывает эффект на плазменную концентрацию воспалительных цитокинов и ключевых метаболических гормонов, считающихся терапевтическими мишенями при нейродегенерации. Это в целом повлияло на восстановление двух нарушенных протеолитических путей нейронов. Как следствие, модуляция микробиоты вызывает положительные эффекты на нейрональные проводящие пути, которые способны замедлить прогрессирование болезни Альцгеймера.
Болезнь Паркинсона как пример нейроде-генеративного расстройства, характеризующегося нарушением работы дофаминэргиче-ской системы проявляется с невропатологическими изменениями в обонятельных и желудочно-кишечных тканях. Более раннее доклиническое исследование предполагало, что из- менения в микробиоме человека представляют собой фактор риска для этого заболевания (Sampson et al., 2016). В связи с этим существует гипотеза о том, что внешний микробный агент может инициировать патологический процесс в отдаленных от центральной нервной системы органах, а затем распространиться на головной и спинной мозг (Pereira, 2017). Однако анализ оральной и назальной микробиоты пациентов с болезнью Паркинсона не выявил значительных различий и специфических агентов в их составе.
В плане оценки эффективности терапии такого рода расстройств представляется важным, что по данным современных экспериментальных исследований на лабораторных животных, восстановление и обогащение кишечной микробиоты влияет на снижение депрессивных симптомов и тревоги (Macedo et al., 2017; Burokas A. et al., 2017), улучшает когнитивные функции (Carlson, Xia et al., 2017) и иммунитет в целом (Belkaid, Timothy, 2014).
Микробиотический фактор и стресс-индуцированные психосоматические расстройства
В психосоматической медицине (Психосоматическая медицина…, 1999) признано, что эндокринные и иммунные функции во всем организме представлены интегральными системами с разнообразными прямыми и непрямыми связями, особенно с центральной и вегетативной нервной системой, и через них – с окружающим миром. Именно благодаря этим связям осуществляются процессы регуляции ритма сна и бодрствования, температуры тела и восприимчивости к боли, регуляции голода и жажды, сексуальные и эмоциональные реакции, а также реакции на действия стрессоров. Вместе с тем между психическими процессами и биологическим субстратом существуют определенные «медиаторы», поиск которых является важнейшей задачей для развития психосоматики в будущем. В плане исследований с психосоматических позиций следует учитывать, что при любом акте психической деятельности структурнофункциональные изменения происходят также на физиологическом и морфологическом уровнях. Описанные выше положениями концепции микробиоты дают основания рассматривать ось «микробиота – кишечник – мозг» как один из таких «медиаторов», опосредующих интегрированность структурно-функ- ционального (соматического) и собственно психического в рамках психосоматического подхода.
Заключение
Представленные выше данные убедительно показывают, что микробиотический фактор влияет на организм и психику непрерывно в течение жизни. Изучение микробиоты в различных моделях психических расстройств демонстрирует значимую связь кишечных бактерий с психикой. При этом очевидно, что микробиота может влиять на процесс возникновения и протекания психических феноменов различного типа и уровня выраженности как в норме, так и при различного рода патологиях. Но важно также отметить, что микробиотический фактор непосредственно оказывает влияние на фармакокинетику и фармакодинамику препаратов, направленных на лечение соматических, психических и психосоматических заболеваний. Вероятно, причины случаев, когда фармакотерапия оказывается недостаточно эффективной, находятся внутри нашего микробного сообщества. И более пристальное внимание к этому фактору раскроет новую коррекционную мишень для терапии различного рода расстройств.
При этом стратегии изучения микробиоты условно разделяются на два типа:
-
а) поиск ключевых агентов в составе микробиоты, которые достаточно изолированно влияют на развитие психических и психосоматических расстройств;
-
б) подтверждение/опровержение гипотезы о том, что действие микробиоты на ЦНС связано не со специфической бактерией или их группой, а с их метаболической активностью, при том, что на этот метаболический профиль оказывают влияние факторы окружающей среды, в частности диета, стресс или воспаление.
Предположительно, метабономический подход с большей вероятностью может дать ответы на вопросы, чем идентификация отдельных бактерий (Bersik, Collins, Verdu, 2012).
Статья выполнена за счет субсидии на финансовое обеспечение выполнения базовой части государственного задания (фундаментальное научное исследование) по договору № 19.8259.2017/БЧ.
Список литературы Микробиотический фактор, здоровье и стресс-индуцированные психические расстройства
- Штрахова А.В., Потороко И.Ю., Иванова Д.Г., Ченченко Д.В. Микробиотический фактор и психика: современные представления о транссистемных связях // Вестник ЮУрГУ. Серия «Психология». 2017. Т. 10, № 3. С. 72-80. DOI: 10.14529/psy170307
- Бройтигам, В., Кристиан П., Рад М. Психосоматическая медицина: краткий учебник; пер с нем. Г.А. Обухова, А.В. Бруенка; предисл. В.Г. Остроглазова. М.: ГЭОТАР МЕДИЦИНА, 1999. 376 с.
- Эндерс, Дж. Очаровательный кишечник. Как самый могущественный орган управляет нами. М.: Эксмо, 2015.
- Bailey M.T., Dowd S.E., Galley J.D., Hufnagle A.R., Allen R.G., Lyte M. Exposure to a social stressor alters the structure of the intestinal microbiota Implications for stressor-induced immunomodulation // Brain Behav Immun., 2011, vol. 25(3), pp. 397-407. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.10.023
- Belkaid Y., Timothy W. Hand Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and inflammation // Cell. 2014, vol. 157(1), pp. 121-141. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.011
- Bersik P., Collins S.M., Verdu E.F. Microbes and the gut-brain axis // Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012, vol. 24(5), pp. 405-413. 2012.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01906.x
- Bonfili L., Cecarini V., Berardi S., Scarpona S., Suchodolski J.S., Nasuti C., Fiorini D., Boarelli M.C., Rossi G., Eleuteri A.M. Microbiota modulation counteracts Alzheimer's disease progression influencing neuronal proteolysis and gut hormones plasma levels // Sci Rep., 2017, vol. 7(1), pp. 2426.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02587-2
- Burokas А., Arboleya S., Moloney R.D., Peterson V.L., Murphy K., Clarke G., Stanton C., Dinan T.G., Cryan J.F. Targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis: prebiotics have anxiolytic and antidepressantlike effects and reverse the impact of chronic stress in mice // Biol Psychiatry, 2017, vol. 82(7), pp. 472-487.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.12.031
- Carlson A.L., Xia K., Azcarate-Peril M.A., Goldman B.D., Ahn M., Styner M.A., Thompson A.L., Geng X., Gilmore J.H., Knickmeyer R.C. Infant gut microbiome associated with cognitive development // Biol Psychiatry, 2017, vol. 83(2), pp. 148-159.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.06.021
- Claesson M.J. et al., Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly // Nature, 2012, vol. 488(7410), pp. 178-84.
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11319
- Collins S.M., Surette M., Bercik P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain // Nat Rev Microbiol., 2012, vol. 10(11), pp. 735-42. Epub 2012 Sep 24.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2876
- Crumeyrolle-Arias M. et al., Absence of the gut microbiota enhances anxiety-like behavior and neuroendocrine response to acute stress in rats // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014, vol. 42, pp. 207-217.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.01.014
- Dinan, T.G., Cryan J.F. Melancholic microbes: a link between gut microbiota and depression // Neurogastroenterol Motil., 2013, vol. 25(9), pp. 713-719.
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12198
- Dinan T.G., Stilling R.M., Stanton C., Cryan J.F. Collective unconscious: how gut microbes shape human behavior // J. Psychiatr Res., 2015, vol. 63, pp. 1-9.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.02.021
- Dinan T.G., Cryan J.F. Gut Instincts: Microbiota as a Key Regulator of Brain Development, Ageing and Neurodegeneration // J Physiol., 2017, vol. 595(2), pp. 489-503.
- DOI: 10.1113/JP273106
- Dinan T.G., Cryan J.F. Regulation of the stress response by the gut microbiota implications for Psychoneuroendocrinology // Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2012, vol. 37(9), pp. 1369-1378.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.03.007
- De Palma G., Collins S.M., Bercik P., Verdu E.F. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in gastrointestinal disorders: stressed bugs, stressed brain or both? //J. Physiol., 2014, vol. 592(14), pp. 2989-2997.
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.273995
- Fröhlich E.E., Farzi A., Bercik P., Verdu E.F. Cognitive impairment by antibiotic-induced gut dysbiosis: analysis of gut microbiota-brain communication //Brain Behav Immun., 2016, vol. 56, pp. 140-155.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.02.020
- Fond G., Boukouaci W., Chevalier G., Regnault A., Eberl G., Hamdani N., Dickerson F., Macgregor A., Boyer L., Dargel A., Oliveira J., Tamouza R., Leboyer M. The "psychomicrobiotic": Targeting microbiota in major psychiatric disorders: A systematic review // Pathol Biol (Paris), 2015, vol. 63(1), pp. 35-42.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patbio.2014.10.003
- Galley J.D. Stressor exposure has prolonged effects on colonic microbial community structure in Citrobacter rodentium-challenged mice // Scientific Reports, 2017, vol. 7.
- DOI: 10.1038/srep45012
- Gareau M.G., Wine E., Rodrigues D.M., Cho J.H., Whary M.T., Philpott D.J. et al. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice // Gut, 2011, vol. 60(3), pp. 307-317.
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2009.202515
- Gershon M.D. The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and Intestine, 1998, 336 p.
- Golubeva A.V. Prenatal stress-induced alterations in major physiological systems correlate with gut microbiota composition in adulthood // Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2015, vol. 60, pp. 58-74.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.06.002
- Fond G., Boukouaci W., Chevalier G., Regnault A. et al. The «psychomicrobiotic»: Targeting microbiota in major psychiatric disorders: a systematic review // Pathol Biol (Paris), 2015, vol. 63(1), pp. 35-42.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patbio.2014.10.003
- Foster J.A., Lyte M., Meyer E., Cryan J.F. Gut Microbiota and Brain Function: An Evolving Field in Neuroscience // Int J Neuropsychopharmacol., 2016, vol. 19(5), pp. 35-42. Print 2016 May.
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv114
- Hansen M.B. The enteric nervous system I: organisation and classification // Pharmacol Toxicol., 2003, vol. 92(3), pp. 105-113.
- Hagan C.O., Li J.V., Marchesi J.R., Plummer S., Garaiova I., Good M.A. Long-term multi-species Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium dietary supplement enhances memory and changes regional brain metabolites in middle-aged rats // Neurobiol Learn Mem., 2017, vol. 144, pp. 36-47.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.05.015
- Kelly J.R., Clarke G., Cryan J.F., Dinan T.G. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis: Challenges for Translation in Psychiatry // Ann Epidemiol., 2016, vol. 26(5), pp. 366-72. 10.1016/ j.annepidem.2016.02.008.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2016.02.008
- Kelly, J.R., Borre Y. et al. Transferring the blues Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat // J Psychiatr Res., 2016, vol. 82, pp. 109-118.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.07.019
- Kieran Reaa, Timothy G., Dinanab John, Cryanac F. The microbiome: A key regulator of stress and neuroinflammation // Neurobiology of Stress, vol. 4, 2016, pp. 23-33.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2016.03.001
- Kumar P. Oral microbiota and systemic disease // Anaerobe, 2013, vol. 24, pp. 90-3.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2013.09.010
- Lamb A., Hess D.E., Edenborn S., Ubinger E., Carrillo A.E., Appasamy P.M. Elevated salivary IgA, decreased anxiety, and an altered oral microbiota are associated with active participation on an undergraduate athletic team // Physiol Behav., 2017, vol. 169, pp. 169-177.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.12.004
- Li, Q., Zhow J.-M. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and its potential therapeutic role in autism spectrum disorder //Neuroscience, 2016, vol. 324, pp. 131-9.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.03.013
- Liang S., Wang T., Hu X., Luo J., Li W., Wu X., Duan Y., Jin F. Administration of lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress // Neuroscience, 2015, vol. 310, pp. 561-577.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.033
- Lozupone M., Seripa D., Stella E. Innovative Biomarkers in Psychiatric Disorders: a Major Clinical Challenge in Psychiatry // Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017, vol. 14(9), pp. 809-824.
- DOI: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1375857
- Lyte М., Cryan J.F. (Eds.) Microbial endocrinology: The microbiota-gut-brain axis in health and disease, 2014. 436 p.
- Macedo D., Filho A.J.M.C., Soares de Sousa C.N., Quevedo J., Barichello T., Júnior H.V.N., Freitas de Lucena D. Antidepressants, antimicrobials or both? Gut microbiota dysbiosis in depression and possible implications of the antimicrobial effects of antidepressant drugs for antidepressant effectiveness // J Affect Disord., 2017, vol. 208, pp. 22-32.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.09.012
- Mu С., Yang Y., Zhu W., Gut microbiota: the brain peacekeeper // Front Microbiol., 2016, vol. 7, 345 p.
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00345
- Patchev V.K., Patchev A.V. Experimental models of stress // Dialogues Clin Neurosci., 2006, vol. 8(4), pp. 417-432.
- O'Mahonya S.M., Clarke G., Borre Y.E., Dinan T.G., Cryan J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis // Behav Brain Res., 2015, vol. 277, pp. 32-48.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.07.027
- Parashar A., Udayabanu M. Gut microbiota regulates key modulators of social behavior // Eur Neuropsychopharmacol., 2016, vol. 26(1), pp. 78-91.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.11.002
- Pereira P., Aho V.T.E., Paulin L., Pekkonen E., Auvinen P., Scheperjans F. Oral and nasal microbiota in Parkinson's disease // Parkinsonism Relat Disord., 2017, vol. 38, pp. 61-67.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.02.026
- Rajilić-Stojanović M. Function of the microbiota // Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol., 2013, vol. 27(1), pp. 5-16.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.006
- Rosenbaum M., Knight R. Leibel R.L. The gut microbiota in human energy homeostasis and obesity // Trends Endocrinol Metab., 2015, vol. 26(9), pp. 493-501.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.07.002
- Sampson T.R., Debelius J.W., Thron T. et al., Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson's disease // Cell., 2016, vol. 167(6), pp. 1469-1480.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018
- Sherwin E. A gut (microbiome) feeling about the brain // Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 2016, vol. 32(2), pp. 96-102.
- DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000244
- Sherwin E., Sandhu K.V, Dinan T.G., Cryan J.F. May the Force Be with You: The Light and Dark Sides of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatry // CNS Drugs. 2016, vol. 30, pp. 1019-1041. 34.
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-016-0370-3
- Sudo N. Effects of Gut Microbiota on Stress Response and Behavioral Phenotype of the Host // Brain Nerve, 2016, vol. 68(6), pp. 595-605.
- DOI: 10.11477/mf.1416200447
- Thakur A.K., Shakya A., Husain G.M., Emerald M., Kumar V. Gut-microbiota and mental health: current and future perspectives // J Pharmacol Clin Toxicol, 2014, vol. 2(1), p. 10-16.
- Wang М., Monaco M.H., Donovan S.M. Impact of early gut microbiota on immune and metabolic development and function // Semin Fetal Neonatal Med., 2016, vol. 21(6), pp. 380-387.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.siny.2016.04.004
- Yang J., Guan L., Hou Y., Yang Y. The time course of psychological stress as revealed by event-related potentials // Neuroscience Letters, 2012, no. 530, pp. 1-6.
- Yoshikawa K. Psychological stress exacerbates NSAID-induced small bowel injury by inducing changes in intestinal microbiota and permeability via glucocorticoid receptor signaling // J Gastroenterol., 2017, vol. 52(1), pp. 61-71.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-016-1205-1


