Многолетняя экспозиция населения гербицидами / диоксином как фактор риска здоровью
Автор: Трин Х.С., Ле В.К.
Журнал: Анализ риска здоровью @journal-fcrisk
Рубрика: Оценка риска в гигиене
Статья в выпуске: 2 (46), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Во время войны во Вьетнаме в 1961-1971 гг. американские военные распылили примерно 80 млн л гербицидов на территории Южного Вьетнама. Хранилища гербицидов были расположены в аэропортах Бьен Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат; также эти районы считаются опасными по критерию остаточного диоксина. В связи с этим изучены структура заболеваемости и риски для здоровья 1039 участников исследования, проживающих около аэропортов Бьен Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат (группа исследования), и 400 участников, проживающих в районе Сон Тра города Да Нанг на удалении от аэропорта Да Нанг (контрольная группа). Результаты анализа показывают, что распространенность некоторых заболеваний, связанных с гербицидами / диоксином, довольно высока в группе исследования: гипертония - 23,0-33,6 % (в среднем 29,6 %), диабет - 3,50-13,0 % (в среднем 9,62 %), а также некоторых других, например, заболеваний желудка - 23,6-37 % (в среднем 26,3 %), суставов - 34,6-40,3 % (в среднем 37,8 %), ЛОР-органов - 9,5-17,4 % (в среднем 15,5 %), почек и мочевыделительной системы - 4,5-7,2 % (в среднем 6 %). Данные доли были от 1,5 до 9 раз выше в группе исследования, чем в контрольной. Участники, которые проживали и работали на территории вблизи аэропорта, были подвержены более высокому риску данных заболеваний. Структура заболеваемости по данным классам болезней зависит от пола и возраста в обеих группах, но решающим фактором остается экспозиция гербицидами / диоксином. Так, экспозиция гербицидами / диоксином изменила клиническую картину заболевания и привела к появлению более явных симптомов заболеваний у людей, проживающих на территориях, где ранее хранились гербициды / диоксин.
Гербициды, диоксин, горячая точка, заболевания, риски здоровью, да нанг, бьен хоа, пху кат
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142241691
IDR: 142241691 | УДК: 614.7 | DOI: 10.21668/health.risk/2024.2.05
Текст научной статьи Многолетняя экспозиция населения гербицидами / диоксином как фактор риска здоровью
Во время войны во Вьетнаме, за период с 1961 по 1971 г., американские военные применили и распылили примерно 80 млн л гербицидов, включая «эйджент оранж», «эйджент уайт», «эйджент грин», «эйджент пинк», и т. д. Среди всех гербицидов наиболее часто применялся агент «Оранж» (61 %), который содержал примерно 366 кг диоксина [1, 2]. Гербициды были распылены на территории площадью примерно 2,63 млн гектаров, что составляет 15,2 % всей территории Южного Вьетнама. В аэропортах Бьен Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат располагались американские военные и там же во время войны хранились гербициды и диоксин [3]. Агент «Оранж» / диоксин способен наносить разнообразный и комплексный ущерб организму человека и вызывать такие заболевания, как рак, повреждение кожи, болезни печени, щитовидной железы, диабет и гипертонию; он токсичен для органов дыхания, кровообращения, пищеварения, эндокринной и нервной систем, а также может вызывать мутации в генах и хромосомах, приводя к врожденным дефектам и репродуктивной дисфункции [4, 5].
Лица, проживающие вблизи аэропортов Бьен Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат, подвергаются риску экспозиции диоксином [3, 6]. В работах M. Nishijo et al. [7] показано, что концентрации диоксина в грудном молоке матерей, проживающих в районах Тханг Кхе и Сон Тра города Да Нанг, находятся в диапазоне 3,73–72,3 пг токсического эквивалента (TEQ)/г липоида, а средний уровень составляет 14,2 пг TEQ/г
липоида. Концентрации диоксина в грудном молоке были выше на тех территориях, где хранились или распылялись гербициды, чем на условно чистых территориях [8–10]. Средний TEQ в молоке матерей, проживающих в районах хранения диоксина (Пху Кат, Тханг Кхе и Сон Тра, 2008–2009), на территориях, где распылялся токсин (Кам Ло в провинции Куанг Три, 2002–2003), и на территориях, где отсутсвовало загрязнение (Кам Ксюен в провинции Ха Тинх, 2002–2003, и Ким Банг в провинции Ха Нам, 2008), составил 14,1; 10,9 и 4,09 пг/г липоида соответственно для первой беременности и 11,5; 7,56 и 2,84 пг/г липоида для второй и последующих беременностей [11].
T.T. Tuyet-Hanh et al. [12] оценили среднюю суточную дозу (ADD) диоксина в пищевых продуктах местного производства в районе Тханг Кхе города Да Нанг; она составила от 27 до 148 пг TEQ/кг массы тела в день (м.т./день), что существенно превышает допустимую суточную дозу (TDI) для диоксина (от 1 до 4 пг TEQ/кг м.т./день), рекомендованную ВОЗ [13]. Оценка риска здоровью, вызванного экспозицией аэрогенным диоксином, показала, что для людей, проживающих вблизи аэропорта Да Нанг, и рабочих, занятых на складах, суточная доза при ингаляционном воздействии на территории к северо-западу от аэропорта находилась в диапазоне 0,007–0,052 пг TEQ/кг м.т./день. К северу от аэропорта среднесуточные дозы достигали 0,006–0,129 пг TEQ/кг м.т./день. На территории, где в прошлом смешивался и загружался агент «Оранж», среднесуточные дозы составляли 0,16–0,21 пг TEQ/кг м.т./день. Следует отметить, что максимальный уровень воздействия, равный 0,61–0,82 пг TEQ/кг м.т./день, более чем на 10 % превышает допустимую суточную дозу (0,1–0,4 пг TEQ/кг м.т./день) при ингаляционном воздействии [14].
Цель исследования – изучение структуры заболеваемости и рисков для здоровья населения, проживающего вблизи аэропортов Да Нанг, Бьен Хоа и Пху Кат (далее – группа исследования), и для населения, проживающего в районе Сон Тра на удалении от аэропорта Да Нанг (далее – контрольная группа).
Материалы и методы. В группу исследования были включены участники, проживающие на трех территориях: Бьен Хоа (БХ), Тханг Кхе-Да Нанг (TK) и Пху Кат (ПК). Всего 1039 человек, в настоящее время проживающих на территориях вблизи аэропортов Да Нанг, Бьен Хоа и Пху Кат и мест, где армия США в прошлом хранила гербициды / диоксин. Контрольная группа состояла из 400 человек, проживающих в районе Сон Тра города Да Нанг.
Участники исследования отбирались по критериям места проживания, которое должно было находиться на одной из выбранных территорий наблюдения, и времени проживания на данной территории, которое должно было составлять не менее пяти лет. Возраст участников исследования варьировался от 18 до 69 лет. При включении в исследо- вание предпочтение отдавалось женщинам, поскольку одной из целей было изучение репродуктивного здоровья, а также потому, что женщины, как правило, склонны давать более распространенные ответы о заболеваниях членов семьи.
Территория БХ была исследована в июле 2020 г. в рамках четырех административных районов города Бьен Хоа: Тан Фонг, Трунг Дунг, Куанг Винх и Буу Лонг.
Территория TK была исследована в марте 2021 г. в рамках четырех административных районов провинции Тханг Кхе: Хоа Кхе, Ан Кхе, Чинх Жиан и Тхак Жиан.
Территория ПК была исследована в апреле 2022 г. в рамках двух административных районов: Кат Тан в Пху Кат и Нхон Тханх города Ан Нхон, провинция Бин Дин.
Территория проживания контрольной группы была исследована в октябре 2021 г. в рамках трех административных районов: Ан Хай Донг, Ан Ха Тай и Пхуок Май района Сон Тра.
Данное исследование является поперечным, описательным, биомедицинским (при помощи анкетирования и личных интервью изучались существующие риски экспозиции диоксином, состояние здоровья, а также некоторые заболевания и нарушения здоровья, которые могут быть вызваны экспозицией диоксином). Для анализа данных исследования применялись статистические методы.
Анкета состояла из 85 вопросов для сбора общих данных, данных о состоянии здоровья, анамнезе, акушерском анамнезе, экспозиции боевыми токсинами, рационе и других факторах риска, которые могут быть связаны с экспозицией гербицидами / диоксином.
Данные были обработаны при помощи программы Excel. Статистический анализ проводился в программе IBM SPSS Statistics 20 согласно традиционным методам биомедицинской статистики. Результаты представлены как: среднее ( X ), стандартное отклонение ( SD ), доля (%); статистическая значимость p < 0,05.
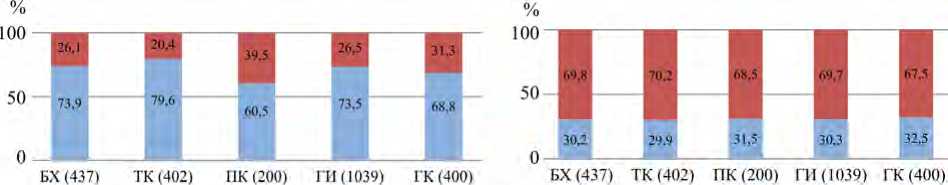
Согласно данным, приведенным на рис. 1, доля участников в возрасте 45–69 лет была сходна во всех подгруппах и группах исследования: люди данного возраста составляли большую часть как группы исследования (ГИ), так и группы контроля (ГК) (ГИ: 73,5 % и ГК: 68,8 %), что полностью совпадает с критериями отбора участников. Между долями участников одной и той же возрастной группы (45–69 лет или 18–44 лет) не было статистически значимых различий в обеих группах исследования. Кроме того, сходным был и средний возраст участников в ГИ (51,95 ± 11,58 г.) и ГК (50,47 ± 12,21 г.), и между группами также не было статистически значимых различий по данному критерию. Таким образом, распределение участников по возрасту гарантирует сопоставимость ГИ и ГК.
Мужчины ■ Женщины
Рис. 2. Распределение участников исследования по полу, %
■ Возрастная подгруппа 45-69 лет ■ Возрастная подгруппа 18-44 лет
Рис. 1. Распределение участников исследования по возрасту, %
Соотношение полов, как показано на рис. 2, соответствует критериям отбора участников исследования, поскольку именно женскому полу был отдан приоритет, и поэтому доля участниц женского пола выше, чем доля участников мужского пола. Доля женщин в каждой группе (67,5–69,8 %) статистически значимо превышает долю мужчин (30,2–32,5 %), p = 0,000. Доли женщин в ГИ и ГК являются схожими: 69,7 и 67,5 % соответственно.
В предыдущих исследованиях была установлена взаимосвязь между некоторыми заболеваниями и возрастом и полом [15–17]. В рамках данного исследования изучалась и сравнивалась структура заболеваемости по полу и возрасту в группах исследования и контроля. В фокусе внимания находились заболевания систем и органов, наиболее подверженных токсическому воздействию гербицидов / диоксина, включая печень, нервную систему, иммунную систему, гормональную систему, органы дыхания, легкие, и т. д. [5, 18].
Гипертония и сахарный диабет являются основными заболеваниями, вызываемыми экспозицией диоксином, согласно рекомендациям Национальной академии наук, машиностроения и медицины от 2018 г.
Согласно результатам, приведенным на рис. 3, распространенность гипертонии в ГИ составляет 23,0–33,6 % (среднее значение – 29,6 %); диабета – 3,50–13,0 % (среднее значение – 9,62 %). Средний уровень распространенности гипертонии превышает среднее значение данного показателя для Вьетнама в целом в 1,57 раза; диабета – в 2,35 раза (18,9 и 4,1 % соответственно) [19]. В частности, более высокий уровень распространенности гипертонии, по сравнению с контрольными данными, был обнаружен во всех трех подгруппах ГИ: БХ, ТК и ПК (19 и 6,0 % соответственно). Заболеваемость по всем
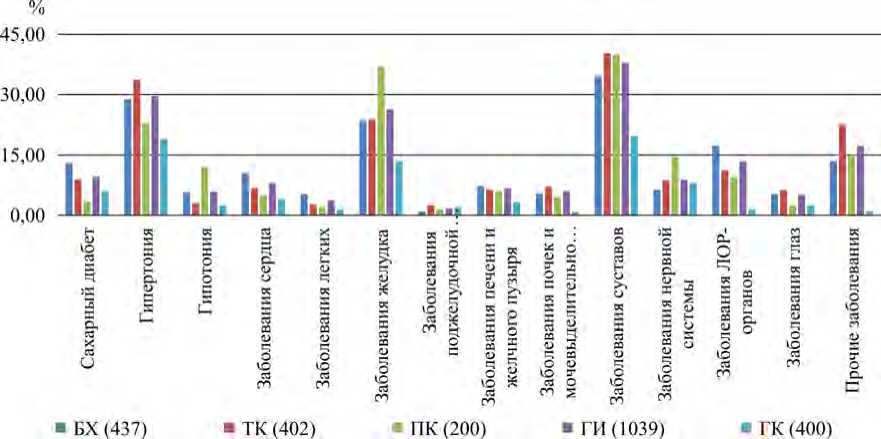
Рис. 3. Структура заболеваемости (с указанием вклада в %) в ГИ и ГК
анализируемым классам болезней была в 1,1–17,3 раза выше в ГИ, чем в ГК, во всех возрастных группах от 18 до 69 лет. Таким образом, результаты нашего исследования указывают на более высокие риски для здоровья населения, экспонированного гербицидами / диоксином и / или проживающего и работающего вблизи территорий, загрязненных высокими концентрациями гербицидов / диоксина.
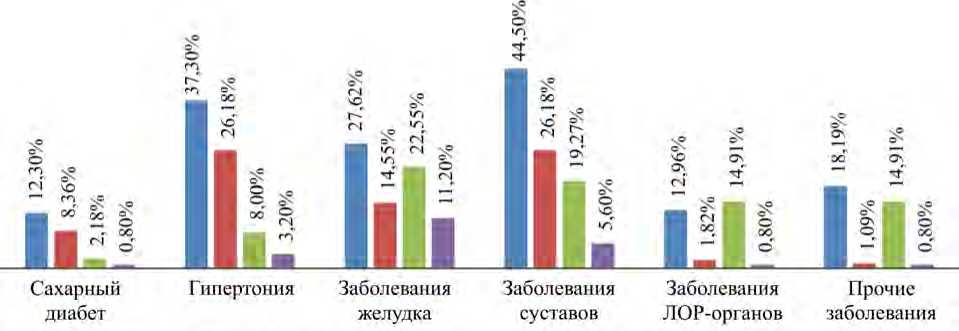
Как показано на рис. 6, распространенность диабета и гипертонии в возрастной подгруппе 45–69 лет ГИ (12,3 и 37,3 % соответственно) и ГК (8,36 и 26,2 % соответственно) выше, чем в среднем во Вьетнаме в 2015 г. (4,1 и 20,3 % соответственно) [19]. И наоборот, распространенность данных заболеваний в возрастной подгруппе 18–44 лет ГИ (2,18 и 8,0 % соответственно) и ГК (0,8 и 3,2 % соответственно) была ниже, чем в целом по стране. Таким образом, результаты исследования, приведенные на рис. 3–5 , указывают на более высокие риски диабета и гипертонии для экспонированного населения в возрасте 45–69 лет, по сравнению с таковыми для населения в возрасте 18–44 лет.
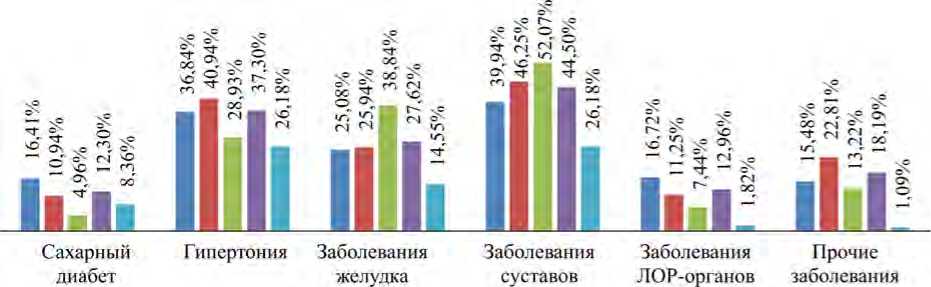
■ БХ (323)
■ ТК(320) ■ ПК(121) ■ ГИ (764) ■ ГК (275)
Рис. 4. Структура заболеваемости в возрастной подгруппе 45–69 лет
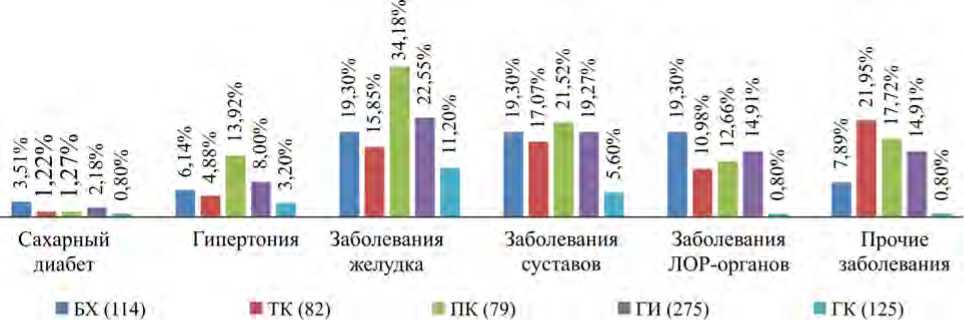
Рис. 5. Структура заболеваемости в возрастной подгруппе 18–44 лет
■ ГИ 45-69 лет (764)
■ ГК 45-69 лет (275)
ГИ 18-44 лет (275)
■ ГК 18-44 лет (125)
Рис. 6. Сравнение структуры заболеваемости между возрастными подгруппами 18–44 и 45–69 лет
Участники исследования, как в ГИ, так и в ГК, чаще болели диабетом и гипертензией в старшем возрасте; распространенность данных заболеваний была выше на территориях, расположенных вблизи областей с загрязнением диоксином. В особенности наиболее низкие уровни заболеваемости диабетом, гипертонией и болезнями суставов были обнаружены в возрастной подгруппе 18–44 лет в ГК, где они составили 0,8; 3,2 и 5,6 % соответственно. В той же самой возрастной подгруппе ГИ данные уровни были выше в 2,73; 2,50 и 3,44 раза соответственно (2,18; 8,0 и 19, 3 % соответственно). Заболеваемость была выше минимального обнаруженного уровня в возрастной подгруппе 45–69 лет ГК в 3,83; 3,27; 1,36 раза соответственно (8,36; 26,2 и 26,2 % соответственно), а наивысшие показатели были обнаружены в возрастной подгруппе 45–69 лет ГИ – в 1,47; 1,42 и 1,70 раза выше минимального обнаруженного уровня (12,3; 37,3 и 44,5 % соответственно).
Как показано на рис. 7 некоторые характеристики заболеваемости являются сходными в ГИ и ГК. Например, доли мужчин с диабетом (12,9 и 10,8 % соответственно) и гипертонией (42,9 и 26,9 % соответственно) были выше, чем доли женщин с теми же заболеваниями в той же группе (диабет: 12,0 и 7,14 % соответственно, гипертония: 34,7 и
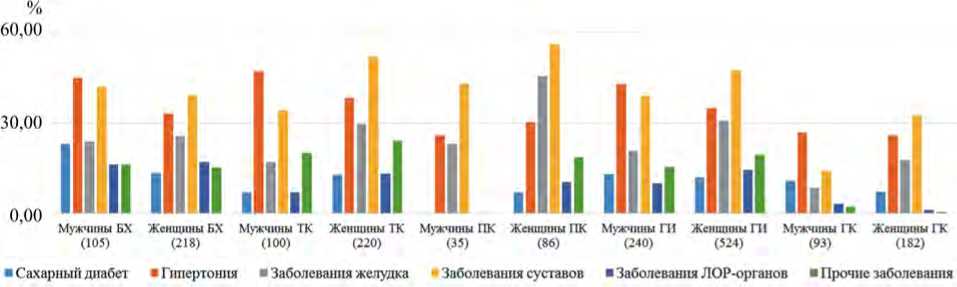
Рис. 7. Сравнение уровней заболеваемости среди мужчин и женщин в возрасте 45–69 лет
40.00
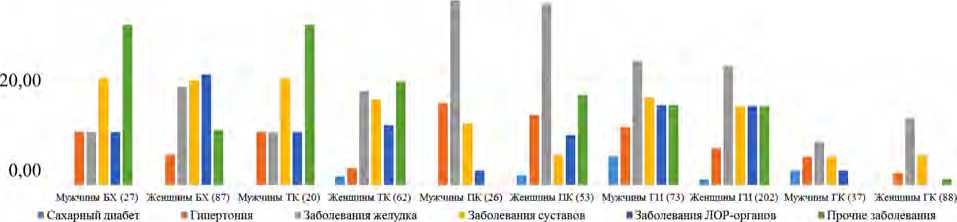
Рис. 8. Сравнение уровней заболеваемости среди мужчин и женщин в возрасте 18–44 лет
Таким образом, результаты статистического анализа, приведенные на рис. 7 и 8, говорят о том, что экспозиция гербицидами / диоксином населения, проживающего и / или работающего вблизи трех аэропортов Бьен Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат, являлась основным фактором повышенного риска заболеваемости в ГИ.
Для дальнейшего прояснения влияния экспозиции диоксином на структуру заболеваемости в анализируемых группах население, подвергающееся экспозиции гербицидами / диоксином, было разделено на подгруппы, одна из которых была подвержена воздействию обоих факторов (ЭД – подгруппа экспозиции диоксином), а вторая была экспонирована только гербицидами (БЭД – подгруппа без экспозиции диоксином). Далее, поскольку подгруппа ЭД состояла в основном из людей в возрасте 45–69 лет, в составе подгруппы БЭД была отдельно выделена подгруппа людей того же возраста. Результаты сравнения данных подгрупп приведены в таблице.
В ГИ распространенность диабета, гипертонии и заболеваний суставов была от 1,67 до 2,74 раза выше в подгруппе ЭД, чем в подгруппе БЭД, а также в 1,45–2,13 раза выше, чем в подгруппе БЭД в возрасте 45–69 лет.
Схожие различия были зафиксированы в ГК, где распространенность всех шести анализируемых классов заболеваний была от 2,31 до 18,7 раза выше в подгруппе ЭД, чем в подгруппе БЭД, а также в 1,67–19,2 раза выше, по сравнению с соответствующими данными подгруппы БЭД в возрасте 45–69 лет. Таким образом, экспозиция гербицидами / диоксином создавала повышенные риски для здоровья в подгруппе ЭД.
С целью выявления влияния продолжительности проживания вблизи трех аэропортов Бьен Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат на территориях, где ранее складировались или распылялись гербициды / диоксин, участников исследования разделили на три подгруппы с длительностью проживания от 5 до 25 лет, от 25 до 45 лет и свыше 45 лет.
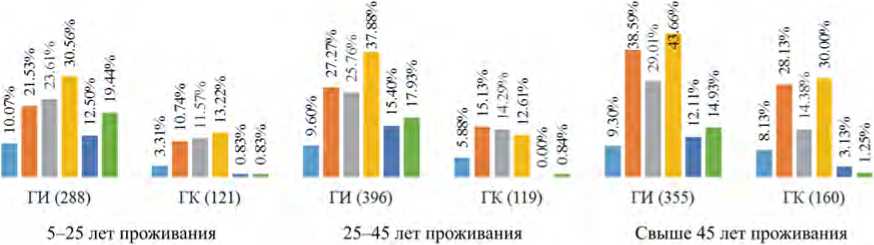
Как показано на рис. 9, распространенность всех шести анализируемых классов болезней была выше во всех подгруппах ГИ, чем в ГК. В особенности в подгруппе с длительностью проживания от 5 до 25 лет она была в 2,0–23,5 раза выше; от 25 до 45 лет – в 1,63–21,3 раз выше; более 45 лет – в 1,14–11,9 раза выше.
Структура заболеваемости согласно факторам экспозиции диоксином, %
Сахарный диабет
Заболевания суставов
■ Гипертония
■ Заболевания ЛОР-органов
• Прочие заболевания
Рис. 9. Структура заболеваемости в разрезе длительности проживания в опасной зоне
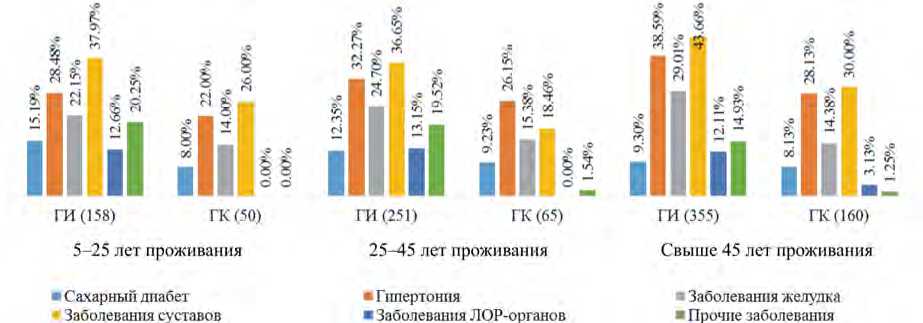
Рис. 10. Структура заболеваемости в возрастной подгруппе 45–69 лет в разрезе длительности проживания
Выводы. Уровни заболеваемости в группе исследования (как в целом, так и по возрастным подгруппам 18–44 и 45–69 лет) были выше, чем в контрольной группе. В рамках данного исследования выявлены приоритетные классы болезней с более высокими уровнями заболеваемости, включая диабет, гипертонию, болезни опорно-двигательного аппарата, заболевания ЛОР-органов.
Уровни заболеваемости по шести приоритетным классам болезней были в 1,1–2,7 раза выше среди населения, экспонированного агентом «Оранж», чем среди неэкспонированного населения в группе исследования, и в 2,3–18,7 раза выше, чем в контрольной группе.
Чем выше была длительность периода проживания и работы на территориях вблизи аэропортов Бьен
Хоа, Да Нанг и Пху Кат, тем выше был риск заболеваний: уровень заболеваемости в группе исследования в подгруппе с длительностью проживания 25–45 лет был в 1,1–1,3 раза выше, а в подгруппе с длительностью проживания 45 лет и более – в 1,2–1,8 раза выше, чем таковой в подгруппе с длительностью проживания 5–25 лет. В каждой из этих подгрупп в группе исследования уровни заболеваемости были выше, чем в контрольной группе: в 2,0–23,5 раза в подгруппе с длительностью проживания 5–25 лет, в 1,6–21,3 раза – в подгруппе 25–45 лет и в 1,1–11,9 раза выше в подгруппе с длительностью проживания на опасной территории более 45 лет.
Уровень заболеваемости населения в группах исследования и контрольной зависит от длительности проживания, пола и возраста. Однако основным фактором, определяющим различия в структуре заболеваемости, является экспозиция гербицидами / диоксином на территории проживания. Экспозиция гербицидами / диоксином, остатки которых загрязняют территории вблизи исследуемых аэропортов в течение последних 50 лет, является одним из вредных факторов, оказывающих влияние на структуру заболеваемости в группе исследования, а также приводящих к подъему уровней заболеваемости некоторыми нозологиями.
Одобрение комитета по этике и согласие на участие в исследовании. Данное исследование было одобрено Сове- том по этике биомедицинских исследований Совместного Российско-Вьетнамского тропического научно-исследовательского и технологического центра (Код: 18/2020/VREC, Сертификат одобрения № 1987/CN-TTNDVN, выдан 01.07.2020) и осуществлялось под соответствующим контролем.
Финансирование. Исследование было профинансировано в рамках гранта Совместного Российско-Вьетнамского тропического научно-исследовательского и технологического центра под номером M-3.3.
Список литературы Многолетняя экспозиция населения гербицидами / диоксином как фактор риска здоровью
- The extent and patterns of usage of Agent Orange and other herbicides in Vietnam / J.M. Stellman, S.D. Stellman, R. Christian, T. Weber, C. Tomasallo // Nature. - 2003. - Vol. 422. - P. 681-687. DOI: 10.1038/nature01537
- Young A.L. The History, Use, Disposition and Environmental Fate of Agent Orange. - NY: Springer New York, 2009. - 339 p. DOI: 10.1007/978-0-387-87486-9
- Predictors for dioxin accumulation in residents living in Da Nang and Bien Hoa, Vietnam, many years after Agent Orange use / D.T. Pham, H.M. Nguyen, T.G. Boivin, A. Zajacova, S.V. Huzurbazar, H.L. Bergman // Chemosphere. - 2015. -Vol. 118. - P. 277-283. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.064
- Veterans and Agent Orange: Update 2014 / Committee to Review the Health Effects in Vietnam Veterans of Exposure to Herbicides (Tenth Biennial Update); Board on the Health of Select Populations; Institute of Medicine; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. - Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2016. - 1114 p. DOI: 10.17226/21845
- The Relationship of Dioxin Levels in Serum of 9-Year-Old Vietnamese Children and Their Mothers' Breast Milk / H.D. Manh, T. Kido, T. Takasuga, M. Yamashita, L.M. Giang, H. Nakagawa // Toxics. - 2022. - Vol. 10, № 4. - P. 155. DOI: 10.3390/toxics10040155
- Nishijo M. Dioxin and Dioxin-like Compounds and Human Health // Toxics. - 2023. - Vol. 11, № 6. - P. 512. DOI: 10.3390/toxics11060512
- Impact of perinatal dioxin exposure on infant growth: a cross-sectional and longitudinal studies in dioxin-contaminated areas in Vietnam / M. Nishijo, P.T. Tai, H. Nakagawa, S. Maruzeni, N.T.N. Anh, H.V. Luong, T.H. Anh, R. Honda [et al.] // PLoS One. - 2012. - Vol. 7, № 7. - P. e40273. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040273
- 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in breast milk increases autistic traits of 3-year-old children in Vietnam / M. Nishijo, T.T. Pham, A.T.N. Nguyen, N.N. Tran, H. Nakagawa, L.V. Hoang, A.H. Tran, Y. Morikawa [et al.] // Mol. Psychiatry. -2014. - Vol. 19, № 11. - P. 1220-1226. DOI: 10.1038/mp.2014.18
- Impacts of Perinatal Dioxin Exposure on Motor Coordination and Higher Cognitive Development in Vietnamese Preschool Children: A Five-Year Follow-Up / N.N. Tran, T.T. Pham, K. Ozawa, M. Nishijo, A.T.N. Nguyen, T.Q. Tran, L.V. Hoang, A.H. Tran [et al.] // PLoS One. - 2016. - Vol. 11, № 1. - P. e0147655. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147655
- Dwernychuk L.W. Dioxin hot spots in Vietnam // Chemosphere. - 2005. - Vol. 60, № 7. - P. 998-999. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.052
- Dioxin concentrations in breast milk of Vietnamese nursing mothers: a survey four decades after the herbicide spraying / P.T. Tai, M. Nishijo, T. Kido, H. Nakagawa, S. Maruzeni, R. Naganuma, N.T.N. Anh, Y. Morikawa [et al.] // Environ. Sci. Technol. - 2011. - Vol. 45, № 15. - P. 6625-6632. DOI: 10.1021/es201666d
- Environmental health risk assessment of dioxin in foods at the two most severe dioxin hot spots in Vietnam / T.T. Tuyet-Hanh, N.H. Minh, L. Vu-Anh, M. Dunne, L.-M. Toms, T. Tenkate, M.-H.N. Thi, F. Harden // Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. - 2015. - Vol. 218, № 5. - P. 471-478. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2015.03.014
- World Health Organization. Assessment of the health risks of dioxin: re-evaluation of the Tolerable Daily Intake (TDI). Executive summary. - Geneva: WHO European Centre for Environment and Health, International Programme on Chemical Safety, 1998. - 28 p.
- Ambient air monitoring around the dioxin remediation site in Da Nang, Vietnam, using passive air samplers / T.K. Sau, N.X. Truong, T.T.T. Hanh, B. Le Hung, N.D. Thang, T. Le Lan Anh // Environ. Monit. Assess. - 2021. - Vol. 193, № 7. - P. 434. DOI: 10.1007/s10661-021-09223-7
- Choi H.M., Kim H.C., Kang D.R. Sex differences in hypertension prevalence and control: Analysis of the 2010-2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey // PLoS One. - 2017. - Vol. 12, № 5. - P. e0178334. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178334
- Diaz A., Belena A., Zueco J. The Role of Age and Gender in Perceived Vulnerability to Infectious Diseases // Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. - 2020. - Vol. 17, № 2. - P. 485. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17020485
- Higher Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes in Men Than in Women Is Associated With Differences in Visceral Fat Mass / A. Nordström, J. Hadrevi, T. Olsson, P.W. Franks, P. Nordström // J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. - 2016. - Vol. 101, № 10. -P. 3740-3746. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2016-1915
- The American people's dioxin report: technical support document. - Falls Church, VA: Center for Health Environment and Justice, 1999.
- Announcing the results of the national investigation of risk factors for non-communicable disease in 2015 [Электронный ресурс] // Vietnam General Department of Preventive Medicine. - 2015. - URL: https://vncdc.gov.vn/cong-bo-ket-qua-dieu-tra-quoc-gia-yeu-to-nguy-co-benh-khong-lay-nhiem-nam-2015-nd14421.html (дата обращения: 09.02.2024).
- Veterans and Agent Orange: Update 11 (2018) / National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice; Committee to Review the Health Effects in Vietnam Veterans of Exposure to Herbicides (Eleventh Biennial Update). - Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2018. DOI: 10.17226/25137


