Несращения переломов ладьевидной кости и методы лечения при SNAC-синдроме
Автор: Щудло Н. А., Куттыгул Ш. К.
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Обзор литературы
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.31, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Несращение ладьевидной кости может приводить к развитию прогрессирующего коллапса запястья, - SNAC-синдрому (англ.: Scaphoid Nonunion Advanced Collapse), существенно снижающему качество жизни молодых пациентов. Высокая социальная значимость данного патологического состояния обуславливает актуальность дальнейших оригинальных исследований и анализа литературы.Цель работы - определение методов профилактики несращений ладьевидной кости и улучшения результатов лечения пациентов со SNAC-синдромом на основании анализа литературы об этиологии, диагностике и лечении заболевания.Материалы и методы. Поиск, проведённый в электронных базах eLIBRARY и Pubmed по запросам: несращение ладьевидной кости, ладьевидная кость, костная пластика, scaphoid nonunion, scaphoid, bone graft, vascularized bone graft, дал 355 результатов. Критерии включения: оригинальные статьи, систематические обзоры, мета-анализы, соответствующие теме поиска, на русском и английском языках. Критерии невключения: клинический случай, случай/контроль, а также статьи, доступные только на платной основе. Отобрано 67 статей. Хронологические рамки публикаций - с 1984 до 2024 гг.Результаты и обсуждение. Топография ладьевидной кости обуславливает высокую частоту аваскулярного некроза, замедленного сращения и несращения перелома. Для улучшения диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости в остром периоде травмы необходимо использовать комплекс клинических тестов и лучевых методов, а для определения показаний к операции - учитывать критерии нестабильности перелома. Известна тактическая классификация несращений ладьевидной кости для выбора метода хирургического лечения (остеосинтез компрессирующими винтами, некрэктомия и костные трансплантаты, либо «спасительные» операции). Единичные публикации посвящены эффективности применения аппарата Илизарова в лечении несращений ладьевидной кости без применения открытых доступов и трансплантатов. Лечение пациентов со SNAC-синдромом традиционно определяется стадией заболевания: 1 - реконструкция ладьевидной кости, резекция шиловидного отростка лучевой кости; 2-3 - четырехугольный артродез или резекция проксимального ряда костей запястья. Мета-анализы отмечают необходимость дальнейших исследований эффективности различных методов лечения. В хирургии запястья всё более широкое применение находит артроскопическая техника, улучшающая возможности диагностики и малоинвазивных операций.Заключение. Своевременное достижение сращения перелома ладьевидной кости - основной путь профилактики карпальной нестабильности и SNAC-синдрома. При выборе метода лечения пациентов с SNAC-синдромом, наряду со стадией заболевания, необходимо учитывать функциональные потребности пациента.
Несращение ладьевидной кости, ладьевидная кость, чрескожная фиксация, костный трансплантат, кровоснабжаемый костный трансплантат, snac-синдром
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142243886
IDR: 142243886 | УДК: 616.717.71-001.58-073.7-089-035(048.8) | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2025-31-1-91-100
Текст обзорной статьи Несращения переломов ладьевидной кости и методы лечения при SNAC-синдроме
Травма запястья часто приводит к переломам дистального метаэпифиза лучевой кости у пожилых людей. Молодые наиболее часто получают переломы костей запястья (ладьевидной, трёхгранной и крючковидной) либо шиловидного отростка локтевой кости. Данные переломы сопровождаются повреждениями связок, что усугубляет нарушения анатомии и биомеханики запястья и усложняет диагностику [1], а также выбор лечебной тактики [2].
Ладьевидная кость является самой крупной костью запястья, критичной для его стабилизации. Переломы ладьевидной кости нередко случаются у спортсменов и военных [3]. Несращения переломов ладьевидной кости — часто встречающееся осложнение, которое приводит к развитию SNAC-синдрома ( англ .: Scaphoid Nonunion Advanced Collapse), — артроза кистевого сустава. Как свидетельствуют обзоры последних лет, проблемы выбора методов лечения пациентов с несращением ладьевидной кости и артрозом кистевого сустава остаются дискуссионными [4, 5].
Поскольку рассматриваемые патологические состояния существенно снижают качество жизни молодых пациентов, их социальная значимость высока, что определяет актуальность дальнейших оригинальных исследований и анализа литературы.
Цель работы — определение методов профилактики несращений ладьевидной кости и улучшения результатов лечения пациентов со SNAC-синдромом на основании анализа литературы об этиологии, диагностике и лечении заболевания.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Поиск, проведённый в электронных базах eLIBRARY и Pubmed по запросам: несращение ладьевидной кости, ладьевидная кость, костная пластика, scaphoid nonunion, scaphoid, bone graft, vascularized bone graft, дал 355 результатов.
Критерии включения : оригинальные статьи, систематические обзоры, мета-анализы, соответствующие теме поиска, на русском и английском языках.
Критерии невключения : клинический случай, случай/контроль, а также статьи, доступные только на платной основе.
Для анализа отобрано 67 статей. Хронологические рамки публикаций — с 1984 до 2024 гг.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Эпидемиология переломов ладьевидной кости
Частота переломов ладьевидной кости составляет 2–7 % от всех переломов и почти 90 % от переломов костей запястья [6]. Среди пациентов с переломами ладьевидной кости преобладают молодые мужчины в возрасте от 10 до 29 лет [7, 8]. У пожилых людей переломы такой локализации встречаются редко [9]. Обзоры последних лет свидетельствуют, что данные по эпидемиологии переломов и несращений ладьевидной кости неоднородны [10].
Функциональная анатомия и особенности кровоснабжения ладьевидной кости
Ладьевидная кость — самая крупная кость запястья, которая сочленяется с пятью соседними костями посредством преимущественно хрящевой поверхности и имеет сложную сеть креплений связочного аппарата; эти особенности предопределяют разнообразие нарушений кинематики запястья после переломов и играют существенную роль в развитии синдрома карпальной нестабильности [11].
Форма, размеры, расположение ладьевидной кости и рентгеновская плотность разных её частей индивидуально вариабельны [12]. Сужение ладьевидной кости в области талии в сочетании со сниженной костной плотностью предопределяют высокую частоту переломов (75 %) именно этой локализации [13].
Ладьевидная кость участвует в кинематике как проксимального, так и дистального ряда костей запястья, при продольной нагрузке происходит ладонная флексия ладьевидной кости, резкое разгибание и локтевая девиация запястья в сочетании с продольной нагрузкой предрасполагают к переломам, особенно при разрывах связок, переломы проксимальнее талии способствуют смещениям и ишеми-зации проксимального фрагмента [14]. Основной механизм переломов ладьевидной кости — падение на вытянутую руку. Форсированное тыльное разгибание или локтевая девиация запястья при осевой нагрузке приводят к тыльному подвывиху средне-запястных суставов и повышенному напряжению коркового слоя ладьевидной кости с ладонной стороны [15].
Переломы ладьевидной кости относят к переломам с компрометированным кровоснабжением [16]. Они характеризуются высокой частотой осложнений, таких как аваскулярный некроз, замедленное сращение и несращение, остеоартроз, существенно снижающих качество жизни пациентов.
Особенности кровоснабжения ладьевидной кости заключаются в том, что ладонная ветвь лучевой артерии кровоснабжает дистальный полюс, а ветвь тыльной запястной ветви лучевой артерии вступает в ладьевидную кость также дистально (рис. 1), являясь единственным источником кровоснабжения проксимального полюса через ретроградный внутрикостный кровоток [17].
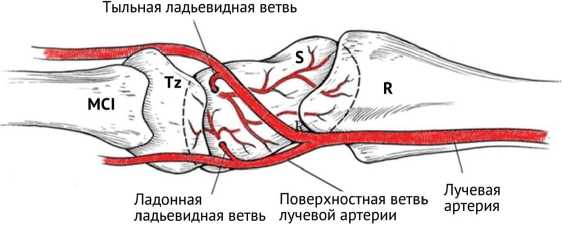
Рис. 1. Схема кровоснабжения ладьевидной кости: MCI — первая пястная кость, Tz — трапеция, S — ладьевидная кость, R — лучевая кость. Воспроизведено по T.E. Trumble et al. [18] c изменениями
Проблемы диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости
Существуют проблемы диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости, так как у 40 % пациентов в остром периоде травмы такие переломы не выявляются рентгенологически [19]. Поэтому особое значение приобретают клинические тесты, имеющие высокую чувствительность и низкую специфичность. В частности, боль при надавливании на область «анатомической табакерки» или бугорок ладьевидной кости, а также осевая нагрузка на первую пястную кость имеют 100 % чувствительность при переломах ладьевидной кости. Однако их специфичность составляет всего 9 %, 30 % и 48 % соответственно. Ограничение движений большого пальца имеет чувствительность 69 % и специфичность 66 % , поэтому при клинической диагностике важно использовать комбинацию признаков [20]. По мнению R. Grover, наиболее важными признаками являются болезненность ладьевидной кости и отёк запястья, который при переломах бывает более выраженным, чем при повреждениях мягких тканей [21].
Предпринимаются попытки разработать прогностическую формулу, включающую пять параметров: мужской пол, отёк «анатомической табакерки», болезненность «анатомической табакерки», болезненность локтевой девиации, болезненность компрессии большого пальца. Этот способ прогнозирования перелома имеет чувствительность 97 % и специфичность всего 20 % [22]. Однако, по мнению авторов, применение этой прогностической формулы снижает вероятность гиподиагностики переломов ладьевидной кости.
В последние годы при подозрении на перелом ладьевидной кости предлагается выполнять рентгенографию костей запястья в четырёх проекциях, — помимо стандартных для кисти трёх проекций, выполняется передне-задняя проекция в положении локтевой девиации [23]. Авторы указывают, что при таком методе рентгенографии не диагностируются 21,5 % переломов ладьевидной кости, но, поскольку чувствительность компьютерной томографии (КТ) составляет 81,5 %, чувствительность рентгенографии в четырёх проекциях оказывается приближенной к КТ. Алгоритм диагностики, разработанный авторами (рис. 2), наряду с рентгенографией в четырёх проекциях включает КТ и магнитную резонансную томографию (МРТ).
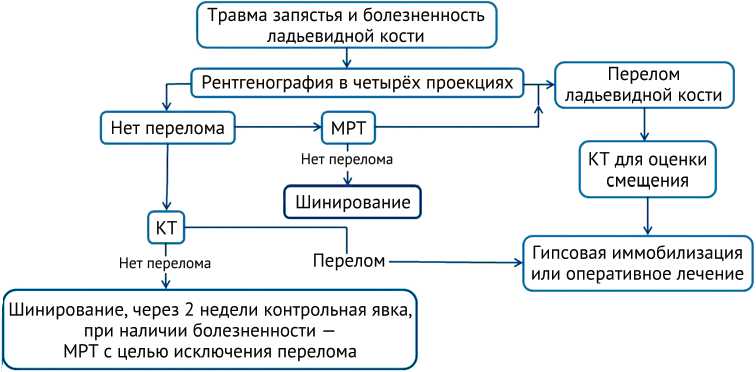
Рис. 2. Алгоритм диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости по H.C. Bäcker, C.H. Wu, R.J. Strauch [23]
Ранее для повышения информативности метода рентгенографии в выявлении нестабильных переломов ладьевидной кости предлагалось выполнять четыре проекции обоих запястий, причём обе прямые проекции в девиантном положении кисти — локтевом и лучевом [24].
Классификации переломов ладьевидной кости
В мировой литературе выявлено 13 классификаций переломов ладьевидной кости, которые учитывают локализацию перелома, ориентацию его плоскости, стабильность или смещение [25]. По данным авторов, наиболее цитируемой является классификация Herbert. Согласно этой классификации, большинство переломов ладьевидной кости нестабильны, к стабильным относятся только переломы типа A (рис. 3).
По мнению других авторов, в клинической практике целесообразно использовать более упрощённый классификационный подход разделения переломов ладьевидной кости на проксимальные, дистальные и переломы талии, при этом необходимо указывать наличие и величину смещения, а также давность травмы [17]. В соответствии с упрощённой классификацией локализации переломов разработано три алгоритма их лечения [26].
Тип А: Стабильные свежие переломы
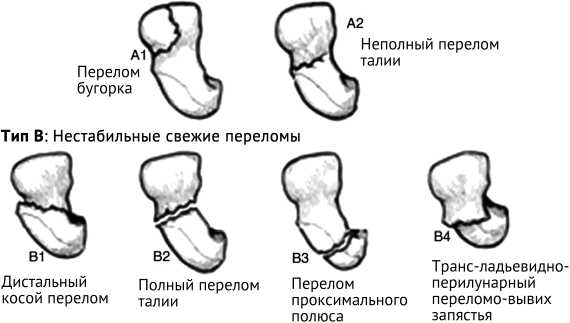
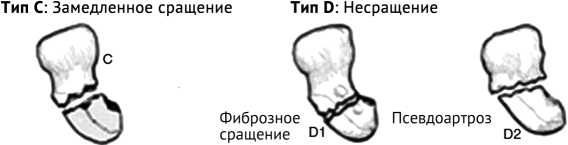
Рис. 3. Зарисовка классификационной схемы переломов костей запястья по Herbert. Воспроизведена с изменениями по T.G. Sommerkamp [8]
Смещения более 1 мм ассоциированы с 55 %-ной частотой несращений и 50 %-ной частотой аваску-лярных некрозов; смещённые переломы, которые срастаются спонтанно, требуют длительной иммобилизации; неправильные сращения или несращения часто сопровождаются болевым синдромом и приводят к остеоартрозу запястья [27]. Смещённые переломы ладьевидной кости условно классифицируют на минимально смещённые (≤ 0,5 мм), средне смещённые (0,5–1,5 мм), сильно смещённые (≥ 1,5 мм) [28]. Смещение перелома, как правило, является признаком его нестабильности, но нестабильными могут быть и несмещённые переломы. Основные критерии нестабильности: смещения более 1 мм, синдром разгибательной нестабильности вставочного сегмента (DISI), — ладьевидно-полулунный угол более 60° и латеральный внутри-ладьевидный угол более 35°, а также оскольчатые переломы и переломы ладьевидной кости как часть перилунарного повреждения [26]. Артроскопически верифицированные разрывы ладьевидно-полулунной связки более чем в 25 % сочетаются с несмещёнными переломами ладьевидной кости, которые также относят к нестабильным [29].
Причины несращений переломов ладьевидной кости и методы их лечения
Если сращение перелома ладьевидной кости не достигается в течение 3 месяцев, это расценивается как замедленное сращение, если же не достигается через 6 месяцев — как несращение. Основными причинами несращения переломов ладьевидной кости считают несвоевременную диагностику и нарушения васкуляризации [30], а также неадекватную по качеству и срокам иммобилизацию перелома [31].
Среди причин несращения переломов ладьевидной кости авторы выделяют факторы, связанные с пациентом (подразумевая его некомплаентность), ятрогенные и биологические факторы [32].
При анализе эпидемиологии несращений переломов 18 локализаций более чем у 300 тыс. пациентов установлено, что при средней частоте несращений 4,9 % частота несращений переломов ладьевидной кости была наибольшей и составила 15,5 %; риск несращений был повышен при открытых и множественных переломах, большом массо-ростовом коэффициенте, курении и алкоголизме [33].
При лечении пациентов с переломами ладьевидной кости методом открытой репозиции и внутренней фиксации установлено, что факторами несращения являются срок оперативного лечения более 31 дня с момента травмы и объём фрагмента ладьевидной кости менее 38 % от объёма кости в целом [34].
Клиника несращений переломов ладьевидной кости характеризуется вариабельностью, наиболее часто регистрируют выраженный болевой синдром, проявления капсулита, контрактуры кистевого сустава и снижение высоты кистевого сустава. Патоморфологические изменения кистевого сустава проявляются в виде дистрофически-деструктивных, продуктивно-репаративных и воспалительных процессов [35].
Предложена тактическая классификация несращений переломов ладьевидной кости [36] (табл. 1).
Таблица 1
Тактическая классификация несращений J.F. Slade et al., 2005 [36]
|
Группа |
Характеристика |
|
I |
Пациенты с переломами, пролеченные через 4–12 недель после травмы |
|
II |
Фиброзное сращение: линия перелома минимальна, нет кист и склероза |
|
III |
Минимальный склероз: костная резорбция занимает ≤ 1 мм интерфейса несращения |
|
IV |
Кисты и склероз: костная резорбция > 1 ≤ 5 мм интерфейса несращения |
|
V |
Деформация и псевдоартроз — костная резорбция > 5 мм интерфейса |
|
VI |
Артроз запястья — несращение с признаками лучезапястного и среднезапястного артроза |
Согласно этой классификации, пациентам I–III групп показан остеосинтез компрессирующими винтами, пациентам IV–V групп — некрэктомия и костные трансплантаты, пациентам VI группы — «спасительные» операции.
Имеются единичные публикации, посвящённые применению компрессирующих кортикальных винтов из человеческой аллокости в лечении пациентов с переломами и псевдоартрозами ладьевидной кости. Винты из аллокости обеспечивают высокий процент сращения, низкую частоту осложнений и не требуют удаления [37].
Для лечения несращений ладьевидной кости применяют различные костные трансплантаты: традиционные некровоснабжаемые, и несвободные или свободные кровоснабжаемые (на сосудистой ножке). По данным некоторых авторов, несвободные кровоснабжаемые трансплантаты в лечении пациентов с псевдоартрозами и дефектами костей дают очень высокий процент сращений — 96,3 % [38]. Однако эти данные противоречивы: по данным M.A. Chang et al., сращение достигалось у 68 % пациентов [39], по данным C. Hirche — у 75 % [40]. Некоторые авторы указывают на ещё более низкую частоту сращения — 27 %, что, по их мнению, связано с аваскулярным некрозом проксимального полюса ладьевидной кости у многих пациентов [41].
Систематический обзор 48 публикаций [42] показал, что частота сращений при применении кровоснабжаемых и некровоснабжаемых трансплантатов при данной патологии достоверно не различалась. Практически одинаковый процент сращений достигнут при применении трансплантатов из лучевой кости и гребня подвздошной кости, однако последний давал большее количество осложнений. Фиксация винтами и спицами Киршнера также приводила к одинаковым показателям частоты сращения, но пациентов с фиксацией винтами мобилизовали раньше.
По данным мета-анализа публикаций на материале от 1500 пациентов [43], кровоснабжаемые трансплантаты не имеют достоверных преимуществ в плане повышения частоты сращения по сравнению с некровоснабжаемыми, то есть сопоставимые результаты достигаются при применении менее инвазивного варианта операции.
Анализ результатов лечения и операционного гистологического материала 35 пациентов, у которых применяли некровоснабжаемые трансплантаты, показал, что «инфаркт» проксимального полюса развивается экстремально редко, поэтому и кровоснабжаемые трансплантаты показаны также редко [44]. Сообщается об успешном применении артроскопической техники в лечении несращений переломов ладьевидной кости костными трансплантатами, фиксированными спицами Киршнера [45], однако процедура имеет ограничения, — несращения проксимальной и средней трети ладьевидной кости без интракарпальной деформации и остеоартрита.
В последние годы в качестве первого этапа лечения пациентов с несращениями используют фиксацию двумя винтами без применения костных трансплантатов, даже при наличии кист и большом внутри-ладьевидном угле («горбатой деформации») [30].
Пациентам, которые по тем или иным причинам не соглашаются на операцию, назначают консервативное лечение, — электрическую или ультразвуковую костную стимуляцию в сочетании с гипсовой иммобилизацией [46].
В обзоре данных Embase и Pubmed за 2000–2023 гг. отмечены отличные результаты применения артроскопических способов фиксации костных трансплантатов и способа Fisk – Fernendez (трансплантата гребня подвздошной кости с внутренней фиксацией). Ультразвуковое лечение также показывает эффективность, хотя доказательства ограничены [47].
Единичные публикации посвящены лечению несращений ладьевидной кости с применением аппарата и метода Илизарова. В группе из 18 пациентов у 14 получены хорошие и отличные результаты, продолжительность иммобилизации в аппарате не превышала 9 недель [31]. Аналогичные результаты получены другой группой авторов, применявших компрессирующие спицы с напайками, период иммобилизации в этом исследовании не превышал 6 недель [48]. Преимущества данного подхода состоит в том, что он не требует применения открытых хирургических доступов и костных трансплантатов. Следует отметить, что у пациентов этих групп не было «горбатой деформации», карпальной нестабильности, прогрессирующего коллапса или аваскулярного некроза.
Независимо от того, какой метод лечения несращений ладьевидной кости выбран, для успешного результата он должен обеспечить сохранение кровоснабжения, стабильную фиксацию, костный трансплантат для замещения дефекта и стимуляции сращения, которое должно быть достигнуто до наступления дегенеративных изменений [49].
Прогрессирующий коллапс на фоне несращения ладьевидной кости (SNAC–синдром)
Отсутствие лечения у пациентов с несращениями ладьевидной кости неизбежно приводит к дегенеративным изменениям суставов запястья. По данным более чем 30-летнего наблюдения пациентов с последствиями переломов ладьевидной кости, установлено, что при сросшихся переломах остеоартроз развился только у одного пациента из 57 (менее 2 %), а при несращениях многократно чаще — у 5 пациентов из 9 [50].
Остеоартроз лучезапястного и среднезапястного суставов обозначается как прогрессирующий коллапс запястья или SNAC–синдром, который в первую очередь поражает лучезапястный сустав в области шиловидного отростка, вызывая сужение суставной щели (стадия 1). Затем развиваются костные кисты ладьевидной кости и поражается вся ладьевидная ямка (стадия 2), средне-запястный остеоартроз и сужение щели полулунно-головчатого сустава (стадия 3) и диффузное поражение головчатой кости (стадия 4) [51].
Специальное исследование показало, что надёжность этой классификации невелика [52], однако другие классификации не разработаны.
Частота SNAC зависит от локализации перелома ладьевидной кости. Так, у шести пациентов с несраще-нием проксимальных переломов частота SNAC составила 85,7 %, у восьми пациентов с несращением переломов талии — 40,0 % и у восьми с несращениями дистальных переломов — 33,3 % [53].
Выбор метода хирургического лечения определяется, прежде всего, стадией заболевания. Для SNAC I реконструкция ладьевидной кости в сочетании с резекцией шиловидного отростка ладьевидной кости является многообещающим методом. При более тяжелых стадиях для снижения болевого синдрома и сохранения функции запястья выполняют операции денервации, резекции проксимального ряда костей запястья и частичный артродез. Тотальный артродез и тотальная артропластика применяют при панартрите и неудачах «спасительных операций» [54]. Для SNAC I выявлена высокая эффективность артро-скопически ассистируемой костной трансплантации без резекции шиловидного отростка [55].
По мнению некоторых авторов, при SNAC II и III успешное применение костных трансплантатов позволяет приостановить прогрессирование артроза, поэтому следует предпочесть этот метод четырёхстороннему артродезу [56].
Авторы мета-анализа 40 публикаций (1730 пациентов) о затратности и эффективности основных операций [57] пришли к выводу, что четырёхугольный артродез с фиксацией винтами и резекция проксимального ряда костей запястья имеют низкий уровень осложнений и являются эффективными. Четырёхугольный артродез c фиксацией пластинами и спицами Киршнера не соответствует стандартам затратности и эффективности.
Из 10 пациентов со SNAC IV, пролеченных методом четырёхугольного артродеза с применением спиц Киршнера, у семи достигнуты хорошие результаты по модифицированной шкале Mayo, интраоперационных осложнений не было [58].
Однако некоторые авторы на основании результатов лечения шести пациентов делают вывод о том, что применение ретроградных винтов при четырёхугольном артродезе является золотым стандартом [59].
Сравнительный мета-анализ отдалённых функциональных результатов резекции проксимального ряда костей запястья и четырёхугольного артродеза, выполненный на основе 7 исследований на 1059 запястьях, показал, что резекция проксимального ряда костей запястья обеспечивает больший объём движений и меньшую частоту осложнений. Сила кистевого схвата и частота конверсии в тотальный артродез не имеют значимых отличий [60].
Однако если дегенеративный процесс захватывает средне-запястный сустав, одна резекция проксимального ряда костей запястья противопоказана. Для замещения суставной поверхности головчатой кости при резекции проксимального ряда костей запястья применяют пирокарбоновые импланты [61].
В качестве альтернативы четырёхстороннему артродезу применяют частичный артродез, он позволяет стабилизировать именно те компоненты запястья, которые поражены дегенеративными изменениями и вызывают болевой синдром, в то время как интактные суставы остаются мобильными [62]. Авторы считают, что этот подход позволяет уменьшить частоту осложнений и улучшить функциональные результаты по сравнению с четырёхсторонним артродезом.
Сравнительно недавно разработаны менее инвазивные по сравнению с четырёхугольным артродезом методики, которые названы одноколонным (головчато-полулунным) артродезом [63] и двухколонным артродезом, который помимо головчато-полулунного артродеза включает артродез между трёхгранной и крючковидной костью [64]. Анализ результатов применения этих методик у 78 пациентов показал сращение в 95 % случаев, приемлемую частоту осложнений, достоверное снижение болевого синдрома и улучшение функциональных показателей, однако у трёх пациентов выполнена конверсия в тотальный артродез запястья, у одного — в тотальную артропластику запястья [65].
Сравнительный анализ результатов частичного межзапястного артродеза и резекции проксимального ряда костей запястья показал, что через 3,5 года у всех пациентов с резекцией проксимального ряда костей запястья отмечали прогрессирование остеоартроза, в группе с частичным артродезом — только у 19 %. Объём движений и сила кистевого схвата сопоставимы у мужчин и лучше после ограниченного артродеза у женщин [66]. Авторы делают вывод о необходимости дальнейших сравнительных исследований эффективности разных методик лечения.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Расположение ладьевидной кости обуславливает высокую распространенность ее переломов среди переломов костей запястья. Особенности кровоснабжения ладьевидной кости способствуют частым случаям аваскулярного некроза, а также замедленному сращению и несращению перелома. Диагностика перелома ладьевидной кости представляет сложную задачу в остром периоде, так как рутинная рентгенография может упустить до 40 % случаев перелома. Для улучшения прогноза результата лечения необходимо ввести в рядовую практику специфические клинические тесты, такие как надавливание в области «анатомической табакерки» и осевая нагрузка на первый палец. Разработка прогностических формул на основе нескольких параметров, включая пол, отек и болезненность, может значительно снизить количество случаев гиподиагностики, несмотря на низкую специфичность тестов. Для повышения точности диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости необходимо применять многоуровневый подход, который сочетает клинические данные, различные методы визуализации и алгоритмы диагностики.
Для выбора метода хирургического лечения несращений переломов ладьевидной кости (остеосинтез компрессирующими винтами, некрэктомия и костные трансплантаты либо «спасительные» операции) применима известная тактическая классификация. Тактика лечения пациентов с SNAC-синдромом традиционно определяется в зависимости от стадии заболевания: при SNAC 1 показаны реконструктивные вмешательства на ладьевидной кости с резекцией шиловидного отростка лучевой кости, при прогрессировании заболевания SNAC 2–3 с целью купирования болевого синдрома выполняют спасательные операции (четырехугольный артродез и резекция проксимального ряда). Следует отметить, что в хирургии запястья находит всё более широкое применение артроскопия.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
В целом, проблема диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости требует мультидисциплинарного подхода и применения комплексных методов, чтобы улучшить исходы для пациентов и снизить риск гиподиагностики. SNAC–синдром — это состояние, которое влияет на качество жизни, так как приводит к ограничению диапазона движений, стойкому болевому синдрому, снижению силы хвата запястья.
Методы лучевой диагностики крайне важны для диагностики переломов ладьевидной кости и их последствий, но в случае развития SNAC–синдрома окончательное определение стадии заболевания происходит во время операции. Своевременное достижение сращения перелома ладьевидной кости является профилактикой карпальной нестабильности. Для этого разработаны различные хирургические методы лечения, выбор которых необходимо осуществлять с учётом тактической классификации несращений.
При развитии артроза запястья некоторые авторы считают необходимым исчерпать возможности консервативного лечения до того, как предлагать хирургическое лечение. При выборе хирургического метода при SNAC–синдроме, наряду со стадией заболевания, необходимо учитывать функциональные потребности пациента. Мета-анализы отмечают необходимость дальнейших исследований для оценки эффективности различных методов лечения. В хирургии запястья находит всё более широкое применение артроскопическая техника, улучшающая возможности диагностики и малоинвазивного лечения.
Список литературы Несращения переломов ладьевидной кости и методы лечения при SNAC-синдроме
- Shahabpour M, Abid W, Van Overstraeten L, De Maeseneer M. Wrist Trauma: More Than Bones. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2021;105(1):90. doi: 10.5334/jbsr.2709.
- Czarnecki P, Siemionow M, Baek GH, et al. Hand and wrist - what the hand surgeon wants to know from the radiologist. Pol J Radiol. 2024;89:e70-e79. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2024.135304.
- D'Itri L, Gattuso MS, Cobisi CD, et al. Bilateral Scaphoid Fractures: A Systematic Literature Review. J Pers Med. 2024;14(4):424. doi: 10.3390/jpm14040424.
- Gray RRL, Halpern AL, King SR, Anderson JE. Scaphoid fracture and nonunion: new directions. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2023;48(2_ suppl):4S-10S. doi: 10.1177/17531934231165419.
- Maris S, Apergis E, Apostolopoulos A, et al. Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC) and Scaphoid Nonunion Advanced Collapse (SNAC): A Review of Treatment Options for Stage II. Cureus. 2024;16(4):e59014. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59014.
- Rhemrev SJ, Ootes D, Beeres FJ, et al. Current methods of diagnosis and treatment of scaphoid fractures. Int J Emerg Med. 2011;4:4. doi: 10.1186/1865-1380-4-4.
- Van Tassel DC, Owens BD, Wolf JM. Incidence estimates and demographics of scaphoid fracture in the U.S. population. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35(8):1242-1245. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.05.017.
- Sommerkamp TG. Hand and Wrist Injuries in Baseball: Scaphoid Fractures. In: Lourie GM. (ed.) Hand and Wrist Injuries in Baseball. Springer, Cham. Publ.; 2022:21-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-81659-9_2.
- Alsawadi A, Stanton J. Scaphoid fracture in the elderly: a review. Hand Surg. 2012;17(2):295-298. doi: 10.1142/S0218810412300021.
- J0rgsholm P, Ossowski D, Thomsen N, Björkman A. Epidemiology of scaphoid fractures and non-unions: A systematic review. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2020;52(5):374-381. English. doi: 10.1055/a-1250-8190.
- Bulstra AE, Doornberg JN, Buijze GA, Bain GI. Anatomy of the Scaphoid Bone and Ligaments. In: Scaphoid Fractures: Evidence-Based Management: Evidence-Based Management. Elsevier Inc. Publ.; 2018:21-34. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-48564-7.00003-4.
- Ahrend MD, Teunis T, Noser H, et al. 3D computational anatomy of the scaphoid and its waist for use in fracture treatment. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02330-8.
- Haisman JM, Rohde RS, Weiland AJ; American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Acute fractures of the scaphoid. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(12):2750-2758. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200612000-00026.
- Berger RA. The anatomy of the scaphoid. Hand Clin. 2001;17(4):525-532.
- Sauerbier M, Germann G, Dacho A. Current Concepts in the Treatment of Scaphoid Fractures. Eur J Trauma. 2004;30(2):80-92. doi: 10.1007/s00068-004-1408-7.
- Vannabouathong C, Schemitsch E, Petrisor B, Bhandari M. Closed Limb Fractures With Compromised Vascularization: A Narrative Review. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;12:1179544119836742. doi: 10.1177/1179544119836742.
- Tysver T, Jawa A. Fractures in brief: scaphoid fractures. Clin OrthopRelatRes. 2010;468(9):2553-2555. doi: 10.1007/s11999-010-1261-4.
- Trumble TE, Salas P, Barthel T, Robert KQ 3rd. Management of scaphoid nonunions. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(6):380-391. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200311000-00002.
- Nguyen Q, Chaudhry S, Sloan R, et al. The clinical scaphoid fracture: early computed tomography as a practical approach. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008;90(6):488-491. doi: 10.1308/003588408X300948.
- Parvizi J, Wayman J, Kelly P, Moran CG. Combining the clinical signs improves diagnosis of scaphoid fractures. A prospective study with follow-up. J Hand Surg Br. 1998;23(3):324-327. doi: 10.1016/s0266-7681(98)80050-8.
- Grover R. Clinical assessment of scaphoid injuries and the detection of fractures. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21(3):341-343. doi: 10.1016/ s0266-7681(05)80197-4.
- Mallee WH, Walenkamp MMJ, Mulders MAM, et al. Detecting scaphoid fractures in wrist injury: a clinical decision rule. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(4):575-581. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03383-w.
- Bäcker HC, Wu CH, Strauch RJ. Systematic Review of Diagnosis of Clinically Suspected Scaphoid Fractures. J Wrist Surg. 2020;9(1):81-89. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1693147.
- Herbert TJ, Fisher WE. Management of the fractured scaphoid using a new bone screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984;66(1):114-123. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.66B1.6693468.
- Ten Berg PW, Drijkoningen T, Strackee SD, Buijze GA. Classifications of Acute Scaphoid Fractures: A Systematic Literature Review. J Wrist Surg. 2016;5(2):152-159. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1571280.
- Clementson M, Björkman A, Thomsen NOB. Acute scaphoid fractures: guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(2):96-103. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190025.
- Szabo RM, Manske D. Displaced fractures of the scaphoid. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(230):30-38.
- Clementson M, J0rgsholm P, Besjakov J, et al. Union of Scaphoid Waist Fractures Assessed by CT Scan. J Wrist Surg. 2015;4(1):49-55. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1398472.
- J0rgsholm P, Thomsen NO, Björkman A, et al. The incidence of intrinsic and extrinsic ligament injuries in scaphoid waist fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35(3):368-374. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2009.12.023.
- Gray RRL, Halpern AL, King SR, Anderson JE. Scaphoid fracture and nonunion: new directions. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2023;48(2_suppl):4S-10S. doi: 10.1177/17531934231165419.
- Bumbasirevic M, Tomic S, Lesic A, et al. The treatment of scaphoid nonunion using the Ilizarov fixator without bone graft, a study of 18 cases. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:57. doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-6-57.
- Yin Y, Xu K, Zhang N, et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Features of Scaphoid Fracture Nonunion: A Hospital-Based Study in Beijing, China. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(10):2455-2461. doi: 10.1111/os.13478.
- Zura R, Xiong Z, Einhorn T, et al. Epidemiology of Fracture Nonunion in 18 Human Bones. JAMA Surg. 2016;151(11):e162775. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.2775.
- Prabhakar P, Wessel L, Nguyen J, et al. Factors Associated with Scaphoid Nonunion following Early Open Reduction and Internal Fixation. J Wrist Surg. 2020;9(2):141-149. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3402769.
- Григоровский В., Страфун С., Тимошенко С. Гистопатология тканей кистевого сустава и некоторые клинико-морфологические корреляции у больных с последствиями переломов ладьевидной кости. Гений ортопедии. 2017;23(1):30-37. doi: 10.18019/10284427-2017-23-1-30-37.
- Slade JF 3rd, Merrell GA, Geissler WB. Geissler WB. Fixation of acute and selected nonunion scaphoid fractures. In: Geissler WB. (ed.) Wrist Arthroscopy. New York: Springer; 2005:112-124.
- Sailer S, Lechner S, Floßmann A, et al. Treatment of scaphoid fractures and pseudarthroses with the human allogeneic cortical bone screw. A multicentric retrospective study. J Orthop Traumatol. 2023;24(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s10195-023-00686-7.
- Губочкин Н.Г., Микитюк С.И., Иванов В.С. Пересадка кровоснабжаемых костных трансплантатов для лечения ложных суставов и дефектов костей. Гений ортопедии. 2014;(4):5-10.
- Chang MA, Bishop AT, Moran SL, Shin AY. The outcomes and complications of 1,2-intercompartmental supraretinacular artery pedicled vascularized bone grafting of scaphoid nonunions. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31(3):387-396. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.10.019.
- Hirche C, Heffinger C, Xiong L, et al. The 1,2-intercompartmental supraretinacular artery vascularized bone graft for scaphoid nonunion: management and clinical outcome. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(3):423-429. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.10.028.
- Straw RG, Davis TR, Dias JJ. Scaphoid nonunion: treatment with a pedicled vascularized bone graft based on the 1,2 intercompartmental supraretinacular branch of the radial artery. J Hand Surg Br. 2002;27(5):413. doi: 10.1054/jhsb.2002.0808.
- Pinder RM, Brkljac M, Rix L, et al. Treatment of Scaphoid Nonunion: A Systematic Review of the Existing Evidence. J Hand Surg Am. 2015;40(9):1797-1805.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.05.003.
- Fujihara Y, Yamamoto M, Hidaka S, et al. Vascularised versus non-vascularised bone graft for scaphoid nonunion: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and comparative studies. JPRAS Open. 2022;35:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2022.12.001.
- Rancy SK, Swanstrom MM, DiCarlo EF, et al. Success of scaphoid nonunion surgery is independent of proximal pole vascularity. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2018;43(1):32-40. doi: 10.1177/1753193417732003.
- Lamon B, Ardouin L, Bellemere P, et al. Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion: A Retrospective Study of 42 Cases. J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2021;26(4):545-554. doi: 10.1142/S242483552150051X.
- Kawamura K, Chung KC. Treatment of scaphoid fractures and nonunions. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(6):988-997. doi: 10.1016/j. jhsa.2008.04.026.
- Aldairi MM, Sindi GJ. Treatment of scaphoid fracture non-union: a systematic review of the current evidence. IJMDC. 2024; 8(1):305-314. doi: 10.24911/IJMDC.51-1697184483.
- Bari M, Konchada S, Pradhan S, et al. Management of Scaphoid Nonunion (SNU) With Ilizarov Ring Fixator Using Two Olive Wire Compression Without Bone Grafting: A Case Series. Cureus. 2022;14(11):e31646. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31646.
- Eggli S, Fernandez DL, Beck T. Unstable scaphoid fracture nonunion: a medium-term study of anterior wedge grafting procedures. J Hand Surg Br. 2002;27(1):36-41. doi: 10.1054/jhsb.2001.0651.
- Duppe H, Johnell O, Lundborg G, et al. Long-term results of fracture of the scaphoid. A follow-up study of more than thirty years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(2):249-252. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199402000-00012.
- Vender MI, Watson HK, Wiener BD, Black DM. Degenerative change in symptomatic scaphoid nonunion. J Hand Surg Am. 1987;12(4):514-519. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(87)80198-3.
- Penteado FT, Dos Santos JB, Caporrino FA, et al. Scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse classifications: a reliability study. J Hand Microsurg. 2012;4(1):12-15. doi: 10.1007/s12593-012-0062-2.
- Moritomo H, Tada K, Yoshida T, Masatomi T. The relationship between the site of nonunion of the scaphoid and scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse (SNAC). J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(5):871-876. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.81b5.9333.
- Meier R. Treatment options for scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse. Unfallchirurg. 2019;122(3):211-218. (In German). doi: 10.1007/ s00113-019-0631-y.
- Lee YK, Jung YR. Arthroscopy-assisted bone grafting for the treatment of SNAC stage I without radial styloidectomy. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(32):e29930. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029930.
- De Cheviegne C. Long-Term Results of Scaphoid Grafting in 52 SNAC Wrists: Should We Cut Down on Salvage Procedures? J Hand Surg. 2018;43(9):54-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2018.06.104.
- Daar DA, Shah A, Mirrer JT, et al. Proximal Row Carpectomy versus Four-Corner Arthrodesis for the Treatment of Scapholunate Advanced Collapse/Scaphoid Nonunion Advanced Collapse Wrist: A Cost-Utility Analysis. PlastReconstrSurg. 2019;143(5):1432-1445. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005558.
- El-Mowafi H, El-Hadidi M, Boghdady GW, Hasanein EY. Functional outcome of four-corner arthrodesis for treatment of grade IV scaphoid non-union. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007;73(5):604-611.
- Ghargozloo D, Tomarchio A, Ballerini M, et al. High results and lower cost in four-bone arthrodesis with retrograde screws. Med Glas (Zenica). 2022;19(1):75-78. doi: 10.17392/1450-21.
- Chammas PE, Hadouiri N, Chammas M, et al. Proximal row carpectomy generates better mid- to long-term outcomes than four-corner arthrodesis for post-traumatic wrist arthritis: A meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022;108(7):103373. doi: 10.1016/j. otsr.2022.103373.
- Bastard C, Goubier JN, Teboul F. Proximal Row Carpectomy with Resurfacing Capitate Pyrocarbon Implant with Bone Graft for Scaphoid Nonunion Advanced Collapse III Wrist with Total Intramedullary Bone Resorption of the Capitate: A Case Report. J Orthop Case Rep. 2018;8(4):35-37. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1148.
- Hegazy G. Capitolunate Arthrodesis for Treatment of Scaphoid Nonunion Advanced Collapse (SNAC) Wrist Arthritis. J Hand Microsurg. 2015;7(1):79-86. doi: 10.1007/s12593-015-0182-6.
- Goubier JN, Teboul F. Capitolunate arthrodesis with compression screws. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2007;11(1):24-28. doi: 10.1097/ bth.0b013e31802caa87.
- Wang ML, Bednar JM. Lunatocapitate and triquetrohamate arthrodeses for degenerative arthritis of the wrist. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(6):1136-1141. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.03.023.
- Solgard L, Gvozdenovic R. Single- and Bicolumn Limited Intercarpal Fusion: A Solution for the SLAC or SNAC Wrist. J Wrist Surg. 2023;13(1):16-23. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1762932.
- Gvozdenovic R, Schioedt MA, Solgaard L, et al. Limited intercarpal fusion versus proximal row carpectomy in the treatment of SLAC or SNAC wrist, results after 3.5 years. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):681. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04177-7.


