Новый метод функционализации магнитных наночастиц, инкапсулированных углеродом
Автор: Храмцов П.В., Бочкова М.С., Тимганова В.П., Кропанева М.Д., Заморина С.А., Раев М.Б.
Журнал: Вестник Пермского университета. Серия: Биология @vestnik-psu-bio
Рубрика: Биотехнология
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Описан метод биологической функционализации магнитных железоуглеродных наночастиц. Суть метода заключается в ковалентной пришивке белков или других веществ, содержащих аминогруппы, к молекулам бычьего сывороточного альбумина, нековалентно сорбированного на углеродной поверхности наночастиц. В настоящей работе в качестве модельного белка был использован стрептавидин. Предлагаемый метод прост в реализации, все реакции проводятся в «мягких» физико-химических условиях. Синтезированные конъюгаты магнитных наноча-стиц с биомолекулами могут быть использованы в различных областях биомедицины.
Магнитные наночастицы, углеродная капсула, функционализация
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147204858
IDR: 147204858
Текст научной статьи Новый метод функционализации магнитных наночастиц, инкапсулированных углеродом
Магнитные наночастицы являются перспективной платформой для терапии и диагностики. Области их применения включают в себя медицинскую визуализацию, адресную доставку лекарственных средств, вакцинопрофилактику [Shah et al., 2014; Kang et al., 2017; Assa et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2017]. Одним из распространенных подходов к повышению стабильности и биосовместимости магнитных наночастиц является их инкапсулирование слоем углерода [Herrmann et al., 2009; Galakhov et al., 2010]. Спектр применений магнитных наночастиц, покрытых углеродной оболочкой (Mag@C) в биомедицине весьма широк. В частности, разработана технология удаления из крови токсинов и возбудителей заболеваний ex vivo [Herrmann et al., 2016]. Продемонстрирован потенциал применения Mag@C для адресной доставки противоопухолевых препаратов [Kowalczyk et al.,
2016], в фото- [Yu et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2015] и магнитотермальной терапии опухолей [Li et al., 2014; Sadhasivam et al., 2016], в качестве контрастного реагента при магниторезонансной томографии [Yu et al., 2014, Li et al., 2014]. Показана возможность контроля и усиления иммунного ответа на модельный антиген при помощи железоуглеродных наночастиц, конъюгированных с антигеном [Schreiber et al., 2010].
Разработка методов практического использования Mag@C сопряжена и с функционализацией их поверхности различными биомолекулами, полимерами и лекарственными средствами, которые придают наночастицам желаемые свойства: терапевтическую активность, повышенную стабильность, меньшую токсичность, возможность адресного взаимодействия с целевыми молекулами, например клеточными рецепторами.
Одним из распространённых способов функционализации Mag@C является модификация уг-
леродного слоя химическими группами с последующей ковалентной иммобилизацией целевых молекул. Относительно простым методом формирования гидроксильных и карбоксильных групп на поверхности углеродного слоя является обработка наночастиц кислотами [Taylor et al., 2010; Kowalczyk et al., 2016]. Karmakar с соавт. железные наночастицы, покрытые углеродом (Fe@C), инкубировали в концентрированной соляной кислоте, после чего ковалентно конъюгировали их с эпидермальным фактором роста и использовали в радиотермальной терапии опухолей [Karmakar et al., 2011]. Аналогичный подход использовали для иммобилизации ДНК-зондов на золотых наночастицах, покрытых графеном [Li et al., 2016]. В опыте [Matysiak-Brynda et al., 2017], Fe@C наночастицы, несущие гидроксильные группы, были конъюгированы с антителами к трансферрину при помощи карбодиимида в ходе разработки сенсора, детектирующего концентрацию трансферрина. В эксперименте [Mattila, 2014] обработка наночастиц УФ-излучением была использована для формирования поверхностных гидроксильных групп с последующей пришивкой к ним (3-аминопро-пил)триэтоксисилана, что приводило к образованию слоя кремния, несущего аминогруппы, поверх углеродной оболочки. В дальнейшем наличие поверхностных аминогрупп позволяет проводить ковалентную конъюгацию биомолекул при помощи реакций с производными карбодиимида, диальдегидов и т.д.
Функциональные группы на углеродной поверхности наночастиц могут быть введены при помощи реакций с солями диазония [Zlateski et al., 2014]. Этот метод был использован для иммобилизации ферментов β-глюкозидазы, α-химотрипсина и липазы B на частицах Co@C. Ковалентная иммобилизация обеспечила более высокую стабильность иммобилизированных ферментов в сравнении с нековалентной сорбцией. В работе [Herrmann et al., 2016] тиол-модифицированные наночастицы Fe3C@C были ковалентно покрыты слоем ПЭГ, несущим концевую малеимидную группу, которую в дальнейшем использовали для пришивки IgG. В недавно опубликованной статье [Kasprzak et al., 2017] был предложен экологически чистый, быстрый метод ковалентной функционализации Fe@C, основанный на механохимиче-ской реакции, позволяющий вводить в структуру поверхности наночастиц углеводы, а также гидроксильные и карбоксильные группы.
Другой подход состоит в формировании на поверхности наночастиц полимерного слоя, содержащего множество функциональных групп, например, аминогрупп, к которым ковалентно пришивается целевая молекула при помощи кросслинкера. Подобный метод использован в работе [Fuhrer et al., 2011]: на кобальтовые наночастицы, покрытые углеродом, сорбировали полиэтилени-мин, к аминогруппам которого пришивали бета- циклодекстрин при помощи гексаметил диизоцио-ната. Yu с соавт. продемонстрировали способ иммобилизации терапевтического средства доксорубицина на частицах Fe5C2@C при помощи последовательной сорбции на их поверхности слоев молекул с противоположным зарядом: 1-й слой – положительно заряженный дофамин, 2-й слой – негативно заряженный бычий сывороточный альбумин, 3-й слой – положительно заряженный доксорубицин [Yu et al., 2016].
В этой статье описан подход к функционализации железных наночастиц, покрытых слоем углерода, основанный на ковалентной пришивке целевой биомолекулы (стрептавидина) к молекулам БСА, сорбированным на поверхности наночастиц.
Материалы и методы
Материалы
Наночастицы Fe@C были любезно предоставлены сотрудниками лаборатории прикладного магнетизма Института физики металлов имени М.Н. Михеева (зав. лаб. М.А. Уймин). Процедура синтеза наночастиц описана в работе [Galakhov et al., 2010]. Химические реактивы, использованные в работе: нитроцеллюлозная мембрана с размером пор 0,45 мкм (Bio-Rad, США), БСА (Sigma-Aldrich, США), глицерин, глутаровый альдегид, натрий фосфорнокислый одно- и двухзамещенный (Panreac, Испания), Sepharose 6B-CL (GE Healthcare, США), стрептавидин (ProspecBio, Израиль). БСА был модифицирован биотином по методике, описанной в статье [Goding, 1980].
Приборы: спектрофотометр Shimadzu UV-VIS UVmini 1240 (Япония), ультразвуковой дезинтегратор MSE Soniprep 150 (Великобритания), анализатор частиц Malvern ZetaSizer NanoZS (Великобритания).
Буферные растворы: 0.15М раствор NaCl, за-буференный 0.015М Na-фосфатами, содержащий 0.1% азида натрия рН 7.25 (ФБ), ФБ+0,1% Tween-20 (ФБТ), ФБТ+1% БСА (ФБТБ).
Методы
Конъюгирование железоуглеродных наночастиц осуществляли следующим образом. В 2%-ный раствор БСА в ФБ вносили 500 мг Fe@C, массовая доля наночастиц в суспензии составляла 5%. Суспензию перемешивали на ротационном встряхива-теле при комнатной температуре (КТ) в течение 72 ч., а затем обрабатывали ультразвуком в течение 30 мин. без перерывов и помещали на хранение при 4°С. В день эксперимента 5%-ную суспензию перемешивали встряхиванием, и из нее готовили 1%-ную суспензию наночастиц в 2% БСА. 5 мл полученной суспензии озвучивали в течение получаса на холоде, неразрушенные агрегаты удаляли коротким центрифугированием на 1600 g. К 4 мл 1%-ной суспензии добавляли 4 мл 25%-ного рас- твора глутарового альдегида в 0.15М NaCl, забу-ференного натрий-фосфатами до рН 7.25. Смесь перемешивали на роторном смесителе в течение 40 мин., после чего наночастицы отмывали от избытка глутаральдегида ФБ при помощи 4 циклов центрифугирования (20000g, 15 мин.) и декантации. К осадку добавляли 4 мл ФБ, затем смесь озвучивали 30 мин. на холоде, неразрушенные агрегаты удаляли коротким центрифугированием на 1600 g. К суспензии добавляли 500 мкл раствора стрептавидина с концентрацией 2 мг/мл в ФБ. После 16часовой инкубации при 4°С наночастицы отмывали от избытка стрептавидина описанным методом до конечной концентрации свободного стрептавидина менее 5 нг/мл. К осадку наночастиц добавляли 2.5 мл ФБ, смесь озвучивали в течение 5 мин. на холоде, неразрушенные агрегаты удаляли коротким центрифугированием на 1600 g, после чего к суспензии добавляли БСА и глицерин до конечных концентраций 1 и 20% соответственно.
Концентрацию наночастиц в суспензии оценивали спектрофотометрически по изменению поглощения при длине волны 450 нм. Для регистрации потерь наночастиц в ходе синтеза и расчёта выхода конъюгата использовали показатель суммарной оптической плотности (СОП) образца, который рассчитывали следующим образом: СОП = ОП450 нм × Vобразца.
Размеры наночастиц оценивали при помощи измерения обратного динамического светорассеяния. Для этого суспензию разводили в ФБ до оптической плотности 0.4–0.5 ОЕ. Распределение час-
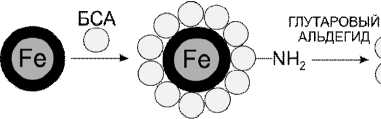
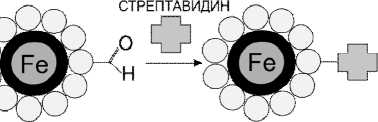
Рис. 1 . Схема конъюгирования железоуглеродных наночастиц, инкапсулированных углеродом, со стрептавидином
тиц по размерам оценивали по показателям интенсивности светорассеяния (средний диаметр [z-average], средние пиков интенсивности светорассеяния) и количества частиц (приведены средние значения для пиков распределения).
Функциональную активность наночастиц оценивали по взаимодействию с биотинилированным БСА (БСА-Bi) в формате прямого дот-анализа на нитроцеллюлозной мембране. На полоски из нитроцеллюлозной мембраны размером 6×80 мм сорбировали по 5 мкл 10-кратных разведений БСА-Bi и БСА в ФБ, начиная с концентрации 100 мкг/мл. Полоски высушивали, помещали в пластиковые ванночки, блокировали 60 мин. в 2 мл ФБТБ, промывали трехкратно ФБТ, после чего в ванночки вносили конъюгат Fe@C-Str, разведенный в ФБТБ 1/15. Тест-полоски инкубировали в растворе конъюгата 15 мин. при температуре +37°С (все остальные процедуры проводили при комнатной температуре), затем промывали ФБТ и высушивали. Наличие реакции оценивали визуально по наличию окрашивания точек на тест-полосках.
Результаты
Синтезированы конъюгаты железных наночастиц, покрытых углеродом, со стрептавидином. Принцип конъгирования заключается в ковалентной пришивке стрептавидина к молекулам БСА, нековалентно сорбированным на поверхности наночастиц. Схема синтеза изображена на рис. 1.
Размеры Fe@C оценивали на трех стадиях их таральдегидом и обработанные ультразвуком.
функционализации: 3. Частицы Fe@C-Str.
-
1. Озвученные частицы Fe@C-БСА. Результаты оценки размеров частиц суммиро-
-
2. Частицы Fe@C-БСА, активированные глу- ваны в таблице.
Динамика изменения размеров наночастиц в процессе конъюгирования со стрептавидином
|
Стадия |
Индекс полидисперсности |
Интенсивность светорассеяния |
Количество частиц |
|||||
|
Средний диаметр, нм |
Средний размер, 1-й пик, нм |
Средний размер, 2-й пик, нм |
Средний размер, 3-й пик, нм |
Средний размер, 1-й пик, нм |
Средний размер, 2-й пик, нм |
Средний размер, 3-й пик, нм |
||
|
1 |
0.512 |
382 |
736 (80.4%)* |
128 (17.2%) |
4988 (2.4%) |
83 (95.4%) |
396 (4.6%) |
– |
|
2 |
0.275 |
225 |
314 (98.9%) |
4815 (1.1%) |
– |
91 (100%) |
– |
– |
|
3 |
0.391 |
196 |
315 (93.3%) |
3757 (6.7%) |
– |
79 (100%) |
– |
– |
*Процент интенсивности светорассеяния/количества частиц пика от суммарной интенсивности/количества частиц пробы.
Анализ данных светорассеяния говорит о сни- жении средней интенсивности светорассеяния на- ночастиц, при том, что большая часть частиц име- за (рис. 2).
ла размеры в районе 100 нм на всех стадиях сните-
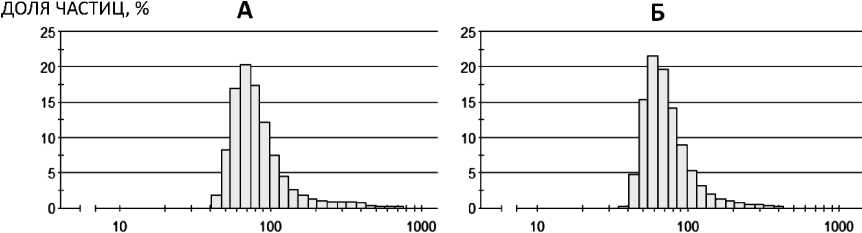
ДИАМЕТР ЧАСТИЦ, НМ
Рис. 2. Распределение наночастиц по размеру: Fe@C-БСА (А) и Fe@C-Str (Б)
Выход синтеза оценивали по изменению суммарной оптической плотности суспензии наночастиц. Исходная СОП для 4 мл раствора Fe@C-БСА составила 728, конечная СОП для 3.3 мл раствора Fe@C-Str – 719, таким образом, выход синтеза составил 98%.
Визуально конъюгат Fe@C-Str представлял собой оптически плотную, однородную суспензию наночастиц, спустя сутки хранения при +4°С на дне флакона образовался осадок агрегировавших наночастиц, при этом даже спустя неделю хранения в осадок выпали не все частицы, не было отмечено видимого изменения плотности надосадочной жидкости в сравнении с исходной суспензией.
Способность Fe@C-Str связываться с биотинилированными молекулами была подтверждена при помощи дот-анализа на нитроцеллюлозной бумаге. Конъюгированные со стрептавидином наночастицы взаимодействовали с БСА-Bi в концентрации 10 мкг/мл и более, при этом взаимодействия с БСА не было выявлено (рис. 3).
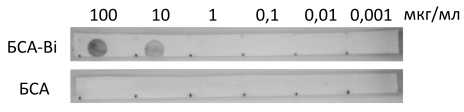
Рис. 3 . Оценка функциональной активности Fe@C-Str методом дот-анализа на нитроцеллюлозных полосках.
В верхней части рисунка указаны концентрации сорбированных на мембрану белков в соответствии с участками их сорбции на тест-полосках
Разработанный метод позволяет функционализировать магнитные наночастицы, покрытые углеродом, белками, а также другими соединениями, содержащими химические группы, способные формировать стабильные ковалентные связи с альдегидными группами глутаральдегида. Стоит отметить, что данный метод может быть модифицирован путем применения других бифункциональных сшивающих агентов, что позволит расширить спектр молекул, доступных для конъюгирования.
Предлагаемая методика функционализации магнитных наночастиц достаточно оперативна, не требует жестких физико-химических условий и сложного, дорогостоящего оборудования, все реакции проводятся в водной среде. Задача, которую необходимо решить в будущем, – это повышение устойчивости суспензии наночастиц к агрегации.
Исследование выполнено за счет гранта Российского научного фонда (проект №17-15-01116).
Список литературы Новый метод функционализации магнитных наночастиц, инкапсулированных углеродом
- Fuhrer R. et al. Immobilized P-cyclodextrin on surface-modified carbon-coated cobalt nanomagnets: Reversible organic contaminant adsorption and enrichment from water//Langmuir. 2011. Vol. 27 (5). P. 1924-1929
- Galakhov V.R. et al. Characterization of carbon-encapsulated nickel and iron nanoparticles by means of X-ray absorption and photoelectron spectroscopy//Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2010. Vol. 114 (51). P. 22413-22416
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas//Journal of Immunological Methods. 1980. Vol. 39 (4). P. 285-308
- Herrmann I.K. et al. High-strength metal nanomag-nets for diagnostics and medicine: Carbon shells allow long-term stability and reliable linker chemistry//Nanomedicine. 2009. Vol. 4 (7). P. 787798
- Herrmann I.K. et al. In vivo risk evaluation of carbon-coated iron carbide nanoparticles based on short-and long-term exposure scenarios//Nanomedicine. 2016. Vol. 11 (7). P. 783-796
- Kang T. et al. Surface design of magnetic nanoparti-cles for stimuli-responsive cancer imaging and therapy//Biomaterials. 2017. Vol. 136. P. 98114
- Karmakar A. et al. Radio-frequency induced in vitro thermal ablation of cancer cells by EGF function-alized carbon-coated magnetic nanoparticles//Journal of Materials Chemistry. 2011. Vol. 21 (34). P. 12761-12769
- Kasprzak A. et al. Grinding-induced functionalization of carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles//Green Chemistry. 2017. Vol. 19 (15). P. 3510-3514
- Kowalczyk A. et al. Conformational control of human transferrin covalently anchored to carbon-coated iron nanoparticles in presence of a magnetic field//Acta Biomaterialia. 2016. Vol. 45 P. 367-374
- Lee H.-J. et al. Photothermal cancer therapy using graphitic carbon-coated magnetic particles prepared by one-pot synthesis//International Journal of Nanomedicine. 2015. Vol. 10. P. 271-282
- Li X. et al. One-pot synthesis and functionalisation of Fe2O3@C-NH2 nanoparticles for imaging and therapy//IET Nanobiotechnology. 2014. Vol. 8 (2). P. 93-101
- Li Y. et al. Functionalization of multilayer Carbon shell-encapsulated gold nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensing and DNA immobilization//Carbon. 2016. Vol. 100. P. 165-177
- Mattila P. et al. Scalable synthesis and functionaliza-tion of cobalt nanoparticles for versatile magnetic separation and metal adsorption//Journal of Nanoparticle Research. 2014. Vol. 16 (9). art. no. 2606
- Matysiak-Brynda E. et al. Novel ultrasensitive im-munosensor based on magnetic particles for direct detection of transferrin in blood//Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical. 2017. Vol. 249. P. 105113
- Sadhasivam S. et al. Carbon encapsulated iron oxide nanoparticles surface engineered with polyethylene glycol-folic acid to induce selective hyperthermia in folate over expressed cancer cells//International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2015. Vol. 480 (1-2). P. 814
- Schreiber H.A. et al. Using carbon magnetic nanopar-ticles to target, track, and manipulate dendritic cells//Journal of Immunological Methods. 2010. Vol. 356 (1-2). P. 47-59
- Shah M.A.A. et al. Nanoparticles for DNA vaccine delivery//Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology. 2014. Vol. 10 (9). P. 2332-2349
- Shen Z. et al. Iron oxide nanoparticle based contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging//Molecular Pharmaceutics. 2017. Vol. 14 (5) P. 13521364
- Taylor A. et al. Functionalization of carbon encapsulated iron nanoparticles//Journal of Nanoparticle Research. 2010. Vol. 12 (2). P. 513-519
- Yu J. et al. Multifunctional Fe5C2 nanoparticles: a targeted theranostic platform for magnetic resonance imaging and photoacoustic tomography-guided photothermal therapy//Advanced Materials. 2014. Vol. 26 (24). P. 4114-4120
- Yu J. et al. Multistimuli-regulated photochemother-mal cancer therapy remotely controlled via Fe5C2 nanoparticles//ACS Nano. 2016. Vol. 10 (1). P. 159-169
- Zlateski V. et al. Efficient magnetic recycling of cova-lently attached enzymes on carbon-coated metallic nanomagnets//Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2014. Vol. 25 (4). P. 677-684
- Assa F. et al. Chitosan magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery systems//Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 2017. Vol. 7 (4). P. 492-509


