Новый подход к ретроградной уретрографии у пациентов с травматической болезнью спинного мозга
Автор: Павлов А.Ю., Салюков Р.В., Цаллагова З.С., Касатонова Е.В., Котляров П.М.
Журнал: Вестник Российского научного центра рентгенорадиологии Минздрава России @vestnik-rncrr
Рубрика: Урология
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.22, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Ретроградная уретрография (РУ) является предпочтительным методом визуализации для оценки морфологического состояния уретры. Клиницисты иногда сталкиваются с неожиданными трудностями при проведении ретроградной уретрографии у пациента с травматической болезнью спинного мозга (ТБСМ). Выделены особенности диагностического подхода к патологическим изменения уретры у спинальных больных. Представлена модификация ретроградной уретрографии с использованием двухэтапного контрастирования. Исследование выполнено у 40 пациентов с ТБСМ с подозрением на уретральный стеноз или повреждение уретры. Описан ход выполнения и достигнутые результаты по визуализации заднего отдела уретры. При выполнении РУ с модификацией удалось получить убедительные данные за наличие изменений простатического и мембранозного отделов уретры, а также дифференцировать их от спазма поперечнополосатого сфинктера. Представленная модификация РУ проста, эффективна и хорошо переносится пациентами. Она может рутинно использоваться у всех пациентов с ТБСМ.
Травматическая болезнь спинного мозга, ретроградная уретрография, стриктура уретры
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149142251
IDR: 149142251
Текст научной статьи Новый подход к ретроградной уретрографии у пациентов с травматической болезнью спинного мозга
Цаллагова Земфира Сергеевна - д.м.н., профессор, ученый секретарь ФГБУ “Российский научный центр Рентгенорадиологии” МЗ РФ, ORCID: Касатонова Елена Владимировна - научный сотрудник отдела андрологии и репродукции человека НИИ урологии и интервенционной радиологии им. Н.А. Лопаткина филиала ФГБУ "НМИЦ радиологии" Минздрава России, ORCID: 0000-0003-3279-2682
Котляров Петр Михайлович - д.м.н., профессор, заведующий лабораторией лучевой диагностики заболеваний (включая молочную железу) научно-исследовательского отдела комплексной диагностики заболеваний и радиотерапии ФГБУ «Российский научный центр Рентгенорадиологии» Минздрава России, e-mail: , SPIN-код: 1781-2199, Author ID: 194339, Scopus ID: 7003497625, ORCID: Контактное лицо
У большинства пациентов с травматической болезнью спинного мозга (ТБСМ) прогрессивно развивается нейрогенная дисфункция нижних мочевыводящих путей (НДМП), которая является одним из самых разрушительных последствий травмы. НДМП имеет широкий диапазон клинических проявлений — от недержания мочи до ее хронической задержки, требующей трансуретрального дренирования мочевого пузыря. В свою очередь, трансуретральное опорожнение мочевого пузыря может иметь свои осложнения, такие как рецидивирующая инфекция нижних мочевых путей (ИМП) или повреждение уретры. Повреждение уретры возникает в результате необоснованно длительной, технически неправильной или травматичной повторной катетеризации [1]. У пациентов с нарушенной моторикой верхних конечностей такой риск может быть выше, чем в общей популяции [2]. При увеличении частоты использования катетеров пациенты сталкиваются с возможностью возникновения эрозии, свища и стриктуры уретры [3]. В частности, у пациентов с детрузорно-сфинктерной диссинергией (ДСД) уретра может быть травмирована при использовании грубых приемов для прохождения через зону спазмированного поперечнополосатого сфинктера уретры [4]. Частота возникновения ложного хода составляет 2,2% случаев наблюдений в год или от 3,1% до 5% в обсуждаемой когорте больных [5-7]. В продольном исследовании пациентов с НДНМП частота образования ложных ходов составила 5% в группе применения периодической катетеризации (ПК) мочевого пузыря и 4% в группе применения постоянных уретральных катетеров [7].
Диагностическая оценка состояния уретры показана при травмах, ее воспалительных поражениях, аномалиях, стриктурах любой этиологии и других возможных морфологических изменениях. Ретроградная уретрография (РУ) и микционная цистоуретрография (МУ) являются двумя распространенными рентгеноскопическими контрастными методами исследования, используемыми в клинической практике для оценки переднего и заднего отделов уретры. РУ/МУ остаются золотым стандартом для первоначальной диагностики и планирования реконструкции уретры. Это широкодоступные и технически несложные и информативные исследования, результаты которых могут быть воспроизведены с удовлетворительной точностью.
В то время как РУ лучше визуализирует морфологические изменения передней уретры, микционные методы лучше визуализируют изменения задней уретры [8]. Микционная цистоуретрограмма не подходит пациентам без самостоятельного мочеиспускания, способности удержания мочи и может давать сомнительные результаты у пациентов с постоянным уретральным дренированием.
До 88% пациентов с ТБСМ имеют ту или иную степень дисфункции мочевого пузыря [9, 10]. Так, распространенность недержания мочи в этой когорте составляет 52,3% [11], нарушение сокращения детрузора присутствует у 35,8% [12]. Постоянное дренирование мочевого пузыря проводиться у 3,8% больных и только 13,8% пациентов с ТБСМ сохраняют нормальное произвольное мочеиспускание [13].
Конечно, нельзя недооценивать диагностическое значение уретроскопии, однако это исследование более трудоемко и опасно своими осложнениями. Информированность метода ограничена при протяженной стриктуре или облитерации уретры. КТ и МРТ более информативны при предоперационном планировании в случаях посттравматических или множественных изменений уретры [14]. Эти методы не используются у пациентов с ТБСМ и хронической болезнью почек (ХБП) из-за риска контраст-индуцированного острого повреждения почек и нефрогенного системного фиброза [15]. Конечно, эти осложнения неприменимы к РУ и микционной уретрографии, но они еще больше сужают круг диагностических возможностей, исключая проведение экскреторных методик и подчеркивают исключительную клиническую значимость ретроградной уретрографии.
Цель исследования : оптимизация выполнения ретроградной уретрографии в группе пациентов с травматической болезнью спинного мозга.
Материалы и методы
Первоначально случайным образом было отобрано и ретроспективно оценено состояние 10 пациентов мужского пола с ТБСМ, которым проведена ретроградная уретрография. Были оценены такие признаки, как наличие спазма сфинктера уретры и состояние задней уретры при исследовании. Эти результаты были обсуждены на встрече врачей физической и реабилитационной медицины, специалистов лучевой диагностики и урологов. Был предложен и утвержден модифицированный подход.
Проспективное исследование проводилось в период с января 2013 года по май 2019 года. Включены 40 пациентов мужского пола с ТБСМ, проходивших курс реабилитационного стационарного лечения в ОАО «Реабилитационном центре для инвалидов с травмой спинного мозга «Преодоление» (г. Москва), клинической базе ФГБОУ ВПО Российского университета дружбы народов и в ФГБУ «Российский научный центр рентгенорадиологии» Минздрава России. Критериями включения были мужчины старше 18 лет с ТБСМ и клиническим подозрением на морфологические изменения уретры, направленные на РУ.
Перед обследованием все испытуемые были проинформированы о порядке процедуры, значимости исследования и рисках, связанных с ним; они подтвердили, что у них нет аллергии на препараты йода и предоставили письменное информированное согласие. Исследование было одобрено локальным этическим комитетом.
Техника
Пациента укладывали на рентгенологический стол под углом 45° вправо, правая нога лежала на столе, тазобедренный и коленный суставы были слегка согнуты, а левая нога находилась в отведении, стопа опиралась на стол после сгибания бедра и колена. Наружное отверстие уретры и головку полового члена обрабатывали раствором антисептика. Для исследования применяли лубрицированный катетер Нелатона мужской (400 мм) лубрицированный Ch/Fr 14 (5354, EasiCath, Coloplast). Использовали 15 см из 40 см катетера с атравматическим кончиком. Часть с канюлей срезалась, внутренний диаметр полученного среза катетера полностью соответствовал наружному диаметру полигольного конуса стандартного шприца 20,0, который плотно одевался на катетер. На первом этапе исследования под контролем электронно-оптического преобразователя (ЭОП) окрашивали пенильную часть уретры с фиксацией на рентгенологическую пленку, заведя катетер в уретру не более, чем на 3,0-5,0 см. Затем катетер вводили дальше в мембранозную часть уретры или заводили его за наружный сфинктер уретры и выполняли вторую часть исследования, контрастируя простатический отдел уретры, в том числе и область шейки мочевого пузыря. Для исследования применялось 20,0 мл 76% урографина.
Оценка результатов. Основным оцениваемым результатом этого исследования было позитивное окрашивание задней уретры с использованием нового подхода. Дополнительно регистрировались все сообщаемые пациентами неприятные ощущения, при жалобах проводился контроль артериального давления. Статистический анализ проводили с использованием программного пакета SPSS Statistics для Windows (версия 24.0, IBM, США). Был проведен описательный анализ всех переменных путем определения частотного распределения и рассчитаны характеристические параметры количественных переменных.
Результаты и обсуждение
Основываясь на собственном опыте и представленной мировой литературе, мы сформировали следующий перечень особенностей и клинических трудностей ретроградной уретрографии (РУ) у пациентов с травматической болезнью спинного мозга (ТБСМ).
-
1. Ортопедические трудности с укладкой пациента
-
2. Повышенные риски
-
3. Особенности интерпретации исследования
Укладка пациента для ретроградной уретрографии является ключевым моментом, и пациенты должны располагаться в положении лежа на спине под углом 45°. Как правило, одно запирательное отверстие должно казаться открытым, а другое закрытым для обеспечения адекватного позиционирования пациента, что важно, например, для исключения недооценки длины стриктуры уретры [16]. Значительную сложность для правильного позиционирования больного ТБСМ и ретроградного доступа может создать наличие гетеротопического оссификата области тазобедренных суставов и спастичность нижних конечностей. Спастичность относиться к характерным признакам повреждения верхнего мотонейрона при ТБСМ, распространенность которой достигает 80%. Спастичность вызывается любым банальным сенсорным раздражителем, может сопровождаться резким повышением тонуса мышц и их неконтролируемым резким и длительным сокращением. Асимметричное напряжение сверхактивных мышц может изменить осанку и вызвать такие деформации, как кифосколиоз; сгибательные контрактуры локтя, бедра и колена или эквиноварусное поражение голеностопного сустава [17, 18]. Кроме того, сами деформации скелета и последствия остеосинтеза позвоночника могут мешать хорошей визуализации мочевыводящих путей при рентгенографии [19].
Все это создает дополнительные сложности с укладкой пациента в стандартное положение тела для рентгенологического снимка в ¾ с согнутым и приведенным правым бедром, голень которого укладывается под левое бедро. Суть техники такого исполнения уретрограммы с введением контрастного вещества заключается в выведении и натяжении пенильной части уретры вдоль мышечного массива согнутого в колене правого бедра. Это расположение позволяет контрастировать и, соответственно, визуализировать уретру на всем ее протяжении.
При укладке пациента на рентгенологическом столе для выполнения исследования спастичность была зарегистрирована у 23 (57,5 %) пациентов с нижним спастическим парапарезом. Для уменьшения явления спастичности использовались медленные пассивные движения, растяжка и отдых. Перемещение спастичной конечности в новое положение может привести к усугублению состояния и увеличению времени ожидания расслабления. В среднем длительность РУ составляла 10–12 мин, у пациентов со спастичностью время исследования достигала 15–27 минут.
Абсолютных противопоказаний к выполнению РУ нет, за исключением острого гнойного воспаления нижних мочевых путей. Единственным относительным противопоказанием является наличие у пациентов аллергии на рентгеноконтрастные вещества. К осложнениям РУ можно отнести инфекцию нижних мочевых путей (ИМП) и неприятные ощущения, связанные с исследованием [20]. Malhotra с соавторами в ретроспективном исследовании за 10 лет наблюдения не выявили высокого риска этого осложнения у пациентов, перенесших ретроградную уретрографию. Инфекцию мочевых путей после исследования они наблюдали у 2,1 %, больных. Авторы отметили, что пациенты с анатомическими изменениями уретры или нейрогенным мочевым пузырем подвержены более высокому риску осложнений [21]. Известно, что нейрогенная дисфункция нижних мочевых путей (НДНМП) и большой объем остаточной мочи являются факторами риска для ИМП при инвазивных уродинамических исследованиях [22]. При травматической болезни спинного мозга общая заболеваемость ИМП после уродинамических исследований составила 15,79%. У пациентов со стерильной мочой до ретроградной уретрографии после ее проведения ИМП выявляли в 8,6% случаях [23].
Пациенты с травмой спинного мозга с поражением выше Th6 сегмента имеют риск развития автономной дисрефлексии (АвтД) во время выполнения трансуретральных манипуляций: при цистоскопии, даже с применением общей анестезии [24] или при неправильном положении раздутого баллона катетера в уретре [25], при комплексном уродинамическом исследовании (КУДИ) [26]. Автономная дисрефлексия проявляется внезапной головной болью, обильным потоотделеним, повышением артериального систолического давления более чем на 20-30 мм рт. ст. выше исходного уровня. К последствиям АвтД относят сердечную аритмию, судороги, внутричерепное кровоизлияние и острый нейрогенный отек легких, ишемию миокарда [27].
В нашем исследовании при регистрации спастичности также было обращено внимание на распространенные жалобы пациентов - жжение, покалывание, ощущение «мурашек» (парестезии), сдавливающие ощущения в промежности и над лоном, вызывающие беспокойство, которые были расценены как эквивалент боли без значимых скачков артериального давления. Такие симптомы демонстрировали 11 пациентов (27,5%). Зарегистрировано 3 случая (7,5%) автономной дисрефлексии в ходе выполнения исследования, которые были купированы. Дополнительная антибиотикопрофилактика не проводилась. Четыре пациента (10%) на периодической катетеризации сообщали о наличии симптомов, указывающих на возможное обострение ИМП без гипертермии. Этим пациентам проводилась антибиотикотерапия в течение 5-7 дней.
Спазм наружного сфинктера в ответ на рероградное введение контрастного вещества – известная техническая особенность, чаще встречающаяся у молодых пациентов. Спазм мешает заполнению задней уретры и имитирует стриктуру. Дифференциальная диагностика осуществляется на основании серии снимков. При стриктуре поражение сохраняется на нескольких изображениях, сделанных во время введения контраста в уретру. Стриктура характеризуется сужением просвета, неровным контуром изображения и наличием престенотического расширения проксимальнее поражения. Давление, создаваемое силой введения, приводит к тому, что контраст может вытесняться в дренирующие венозные структуры. Такая интравазация может говорить о неправильной технике введения, может имитировать травму, но чаще характерна для стриктур уретры [16].
Обычно феномен спазма поперечнополосатого сфинктера длится очень недолго и может быть преодолен, но в случае травматической болезни спинного мозга и детрузорно-сфинктерной диссинергии (ДСД) он может сохраняться на протяжении всего исследования, не позволяя контрастировать заднюю уретру. Пациенты с ДСД могут демонстрировать постоянный спазм наружного сфинктера с ответным сужением дистальной половины или двух третей задней уретры, реже - одновременный спазм наружного сфинктера и бульбокавернозной мышцы. У пациентов с персистирующим неорганическим сужением мембранозного отдела уретры дифференцировать гипертонус поперечнополосатого сфинктера и стриктуру уретры может быть сложно [16]. ДСД проявляется как преходящее усиление активности сфинктера во время сокращения детрузора; периодические клонические сокращения; или как постоянная активность поперечнополосатого сфинктера.
Пациенты с цервикальной миелопатией на фоне ТБСМ более склонны к проявлению ДСД, чем пациенты с поражениями на нижнегрудном и поясничном уровнях спинного мозга. При микционной уретрографии во время видеоуродинамического исследования ДСД описывается как расширение проксимальной части уретры перед ее функциональным сужением в мембранозной части - зоной спазмированного поперечнополосатого сфинктера [28, 29].
Сложности с интерпретацией происходят и вследствие вторичных структурных изменений, сопровождающих нейрогенной дисфункцией нижне-выводящих мочевых путей (НДНМП). Описана типичная деформация задней уретры при пассивном мочеиспускании. Задняя стенка перерастянута, расширение проксимальной части задней уретры имитирует престенозное расширение. Уретра приобретает типичную амфорообразную форму (Рис. 1) и особенно выражена у больных, страдающих параличом нижних конечностей на протяжении относительно короткого срока - менее 5 лет [30].
Постоянный или периодически возникающий высокий тонус поперечнополосатого сфинктера уретры можно сопоставить с разновидностями ДСД (постоянной и интермитирующей). Уродинамически такое состояние сопровождается повышением запирательного давления уретры до 100-150 и более см вод ст. При РУ гипертонус поперечнополосатого сфинктера может не позволить контрастировать уретру на всем ее протяжении. В этом случае обычно контрастом заполняется и окрашивается наружная пенильная часть, обрывающаяся в мембранозном отделе в виде пламени восковой свечи (Рис. 2). В таких условиях не представляется возможным визуализировать область задней уретры, которая может иметь изменения, обусловленные первичным или вторичным стенозом, облитерацией и множественными ложными ходами.
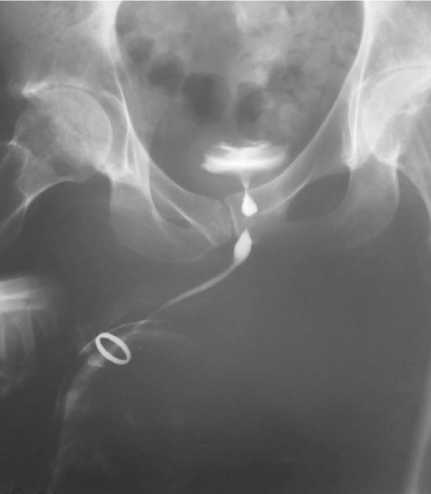
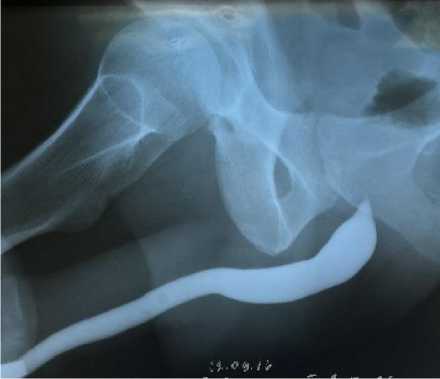
Рис. 1. Уретрограмма пациента с нижнегрудным уровнем ТБСМ с типичным амфорообразным контуром задней части уретры. Визуализируется пристенотическое расширение уретры перед поперечнополосатым сфинктером и расширение простатического отдела уретры перед внутренним сфинктером мочевого пузыря.
Рис. 2. Уретрограмма пациента с цервикальным уровнем поражения спинного мозга, демонстрирующая сложность визуализации задней части уретры, из-за спазма поперечнополосатого сфинктера. Зона мембранозного отдела уретры и поперечнополосатого сфинктера приставлена сужением уретры в виде «пламени восковой свечи».
Модификация стандартной техники позволила визуализировать заднюю уретру в 100% (N=40) случаев. На уретрограммах у 6 (15%) пациентов выявлена стриктура уретры. Стриктура передней уретры выявлена у 3(7,5%) человек; задней - у 2 (5%). В одном случае была визуализирована комбинированная стриктура переднего и заднего отделов уретры (Рис. 3). Уретральный свищ диагностирован у 1 больного, множественные ложные ходы - у 2 (5%) (Рис. 4), дивертикул уретры - у 2 (5%) (Рис. 5). На остальных рентгенограммах патологических изменений выявлено не было.
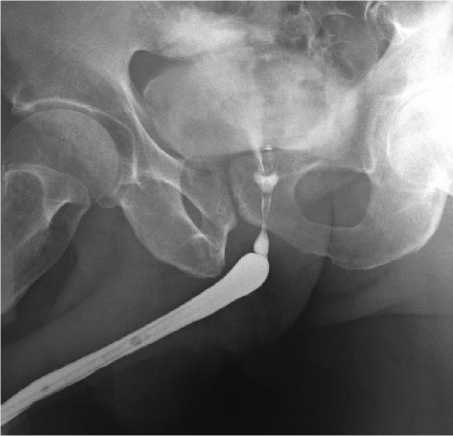
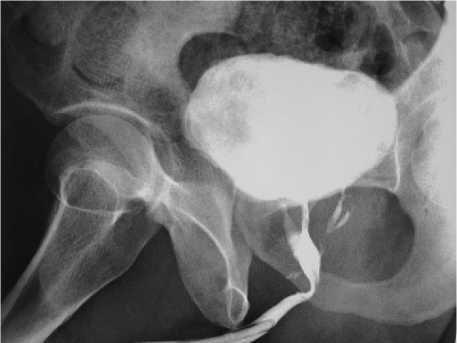
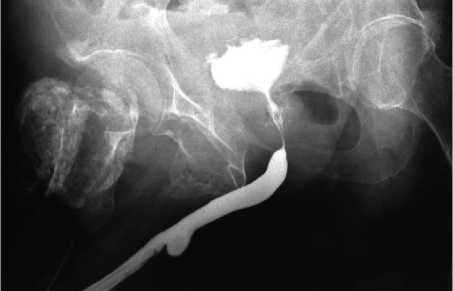
Рис. 3. Уретрограмма по модифицированной методике с контрастированием стриктуры мембранозного отдела уретры и сужением шейки мочевого пузыря.
Рис. 4. Уретрограмма по модифицированной методике, на которой визуализированы множественные ложные ходы уретры.
Рис. 5. Уретрограмма по модифицированной методике с контрастированием дивертикула уретры.
Заключение
Вследствие функциональных и структурных изменений, наблюдаемых при НДНМП у пациентов с ТБСМ, затруднениями с использованием микционных и экскреторных рентгенологических методик, трудностями с их техническим выполнением, существует необходимость создания у этой когорты больных специального подхода к ретроградной уретрографии. Новый подход с применением двухэтапного контрастирования позволяет визуализировать заднюю уретру у всех пациентов. Стоит обращать внимание на «красные флаги» автономной дисрефлексии при проведении ретроградной уретрографии: возникновение парестезии, потливости, внезапной головной боли, повышение систолического артериального давления более чем на 20-30 мм рт. ст. от базового значения. При появлении гипертермии после исследования должна быть исключена инфекция мочевых путей.
Список литературы Новый подход к ретроградной уретрографии у пациентов с травматической болезнью спинного мозга
- Mundy A.R., Andrich D.E. Urethral strictures. BJU Int. 2011. V. 107. No. 1. P. 6-26. DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09800.x.
- Cornejo-Davila V., Duran-Ortiz S., Pacheco-Gahbler C. Incidence of Urethral Stricture in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury Treated With Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterization. Urology. 2017. V. 99. P. 260-264. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.08.024.
- Casey J.T., Erickson B.A., Navai N., et al. Urethral reconstruction in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction. J Urol. 2008. V. 180. No. 1. P. 197-200. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.03.056.
- Cohen A.J., Cheng P.J., Song S., et al. Multicenter urethroplasty outcomes for urethral stricture disease for patients with neurogenic bladder or bladder dysfunction requiring clean intermittent catheterization. Transl Androl Urol. 2021. V. 10. No. 5. P.2035-2042. DOI: 10.21037/tau-20-988.
- Hollingsworth J.M., Rogers M.A., Krein S.L., et al. Determining the noninfectious complications of indwelling urethral catheters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2013. V. 159. No. 6. P. 401-410. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-6-201309170-00006.
- Hakansson M.A., Neovius K., Norrback M., et al. Health care utilization and complications rates among users of hydrophilic-coated catheters. Urol Nurs. 2015. V. 35. No. 5. P.239-247. DOI:10.7257/1053-816x.2015.35.5.239.
- Singh R., Rohilla R., Sangwan K., et al. Bladder management methods and urological complications in spinal cord injury patients. Indian J Orthop. 2011. V. 45. No. 2. P. 141-147. DOI:10.4103/0019-5413.77134.
- Ramanathan S., Raghu V., Ramchandani P. Imaging of the adult male urethra, penile prostheses and artificial urinary sphincters. Abdom Radiol. 2020. V. 45. No. 7. P. 2018-2035. DOI: 10.1007/s00261 -019-02356-x.
- Dorsher P.T., Mcintosh P.M. Neurogenic bladder. Adv Urol. 2012. V. 2012. Article ID 816274. DOI:10.1155/2012/816274.
- Blanes L., Lourenço L., Carmagnani M.I., et al. Clinical and socio-demographic characteristics of persons with traumatic paraplegia living in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2009. V. 67. No. 2B. P.388-390. DOI:10.1590/s0004-282x2009000300003.
- Ruffion A., Castro-Diaz D., Patel H., et al. Systematic review of the epidemiology of urinary incontinence and detrusor overactivity among patients with neurogenic overactive bladder. Neuroepidemiology. 2013. V. 41. No. 3-4. P. 146-155. DOI:10.1159/000353274.
- Sacomani C., Trigo-Rocha F., Gomes C., et al. Effect of the trauma mechanism on the bladder-sphincteric behavior after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2003. V. 41. No. 1. P. 12-15. DOI: 10.1038/sj.sc.3101354.
- Yildiz N., Akkoç Y. Neurogenic Bladder Turkish Research Group. Neurogenic bladder in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury: treatment and follow-up. Spinal Cord. 2014. V. 52. No. 6. P. 462-467. DOI: 10.1038/sc.2014.41.
- Mikolaj F., Karolina M., Oliwia K., et al. Retrograde urethrography, sonouretrography and magnetic resonance urethrography in evaluation of male urethral strictures. Should the novel methods become the new standard in radiological diagnosis of urethral stricture disease? Int Urol Nephrol. 2021. V. 53. No. 12. P. 2423-2435. DOI: 10.1007/s11255-021-02994-5.
- Mehdi A., Taliercio J.J., Nakhoul G. Contrast media in patients with kidney disease: An update. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020. V. 87. No. 11. P. 683-694. DOI:10.3949/ccjm.87a.20015.
- Galgano S.J., Sivils C., Selph J.P., et al. The Male Urethra: Imaging and Surgical Approach for Common Pathologies. Cur Probl Diagn Radiol. 2021. V. 50. No. 3. P. 410-418. DOI:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2020.06.005.
- Kessler T.M., Traini L.R., Welk B., et al. Early neurological care of patients with spinal cord injury. World J Urol. 2018. V. 36. No. 10. P. 1529-1536. DOI:10.1007/s00345-018-2343-2.
- Белова А.Н., Балдова С.Н. Нейромодуляция и спинальная спастичность. Трудный пациент. 2013. Т. 11. №. 12. С. 33-37.
- NaЪЪout P., S^odov G., Culkin D.J. Surgical Management of Urolithiasis in Spinal Cord Injury Patients. Curr Urol Rep. 2014. V. 15. No. 6. Article ID 408. DOI:10.1007/s11934-014-0408-3.
- Maciejewski C., Rourke K. Imaging of urethral stricture disease. Transl Androl Urol. 2015. V. 4. No. 1. P. 2-9. DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.02.03.
- Malhotra N.R., Green J.R., RigsЪy C.K., et al. Urinary tract infection after retrograde urethrogram in children: A multicenter study. J Pediatr Urol. 2017. V. 13. No. 6. P. 623.e1-623.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2017.04.026.
- Cameron A.P., Campeau L., Brucker B.M., et al. Best practice policy statement on urodynamic antibiotic prophylaxis in the non-index patient. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. V. 36. No. 4. P. 915-926. DOI:10.1002/nau.23253.
- Böthig R., Fiebag K., Thietje R., et al. Morbidity of urinary tract infection after urodynamic examination of hospitalized SCI patients: the impact of bladder management. Spinal Cord. 2013. V. 51. No. 1. P. 70-73. DOI: 10.1038/sc.2012.107.
- Vaidyanathan S., Soni B., Selmi F., et al. Are urological procedures in tetraplegic patients safely performed without anesthesia? a report of three cases. Patient Saf Surg. 2012. V. 20. No. 6. Article ID 3. DOI: 10.1186/1754-9493-6-3.
- Vaidyanathan S., Soni B.M., Oo T., et al. Missed signs of autonomic dysreflexia in a tetraplegic patient after incorrect placement of urethral Foley catheter: a case report. Patient Saf Surg. 2014. V. 8. Article ID 44. DOI: 10.1186/s13037-014-0044-3.
- Vírseda-Chamorro M, Salinas-Casado J., Gutiérrez-Martín P., et al. Risk factors to develop autonomic dysreflexia during urodynamic examinations in patients with spinal cord injury. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. V. 36. No. 1. P. 171-175. DOI:10.1002/nau.22906.
- Ho C.P., Krassioukov A.V. Autonomic dysreflexia and myocardial ischemia. Spinal Cord. 2010. V. 48. No. 9. P. 714-715. DOI: 10.1038/sc.2010.2.
- Liu N., Fougere R., Zhou M.W., Nigro M.K. Autonomic dysreflexia severity during urodynamics and cystoscopy in individuals with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2013. V. 51. No. 11. P. 863-867. DOI:10.1038/sc.2013.113.
- FeloneyM.P., Leslie S.W. Bladder Sphincter Dyssynergia. Book. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2022. Адрес доступа https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562166/ (дата доступа 20.08.2022).
- Madersbacher H. The Neuropathic Urethra: Urethrogram and Pathophysiologic Aspects. Eur Urol. 1977. V. 3. No. 6. P. 321-332. DOI:10.1159/000472129.


