Ontology Based Information Retrieval in Semantic Web: A Survey
Автор: Vishal Jain, Mayank Singh
Журнал: International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science(IJITCS) @ijitcs
Статья в выпуске: 10 Vol. 5, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In present age of computers, there are various resources for gathering information related to given query like Radio Stations, Television, Internet and many more. Among them, Internet is considered as major factor for obtaining any information about a given domain. When a user wants to find some information, he/she enters a query and results are produced via hyperlinks linked to various documents available on web. But the information that is retrieved to us may or may not be relevant. This irrelevance is caused due to huge collection of documents available on web. Traditional search engines are based on keyword based searching that is unable to transform raw data into knowledgeable representation data. It is a cumbersome task to extract relevant information from large collection of web documents. These shortcomings have led to the concept of Semantic Web (SW) and Ontology into existence. Semantic Web (SW) is a well defined portal that helps in extracting relevant information using many Information Retrieval (IR) techniques. Current Information Retrieval (IR) techniques are not so advanced that they can be able to exploit semantic knowledge within documents and give precise result. The terms, Information Retrieval (IR), Semantic Web (SW) and Ontology are used differently but they are interconnected with each other. Information Retrieval (IR) technology and Web based Indexing contributes to existence of Semantic Web. Use of Ontology also contributes in building new generation of web- Semantic Web. With the help of ontologies, we can make content of web as it will be markup with the help of Semantic Web documents (SWD’s). Ontology is considered as backbone of Software system. It improves understanding between concepts used in Semantic Web (SW). So, there is need to build an ontology that uses well defined methodology and process of developing ontology is called Ontology Development.
Information Retrieval (IR), Ontology, Data Mining, Semantic Web (SW)
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15011978
IDR: 15011978
Текст научной статьи Ontology Based Information Retrieval in Semantic Web: A Survey
Published Online September 2013 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijitcs.2013.10.06
In recent years, there was a great demand of Knowledge Management (KM) solutions and are used in organization as tools for performing many tasks. These tasks include:
-
• Document Management and Workflow Management
-
• Web Conferencing
-
• Data Warehouse and Decision Support Systems.
But these KM solutions were not uses for long time extraction purposes because these solutions are based on centralized architecture which is storehouse of central knowledge only that is accessed through standard ontology. These KM solutions are not able to access decentralized information located at different networks. After these uncertainties with KM solutions, the concept of Ontology and Semantic Web was introduced [1]. The concept of Ontology deals with various languages that are used for building Semantic Web and increases its extraction efficiency. Semantic Web (SW) is imagined as future web that uses text documents as well as semantic markup documents. We need to build a new paradigm for Information Retrieval (IR) that is compatible with all standards and provides effective and fast search. In order to maintain integrity between web search and inference, there is structure which has following points:
-
• It should support both retrieval driven and inference driven processes.
-
• Indexing words like Semantic markup should be used.
-
• Web Searching is done on basis of present generation.
-
• Inference and Retrieval are closely connected to each other.
This paper has following sections: In Section 2, we have described a brief survey on Information Retrieval (IR) technology and the evaluation of IR Along with this it also deals with various approaches, how the Information Retrieval (IR) process can be increased to get precise results in shorter amount of time. In Section
3 shows description of Semantic Web (SW) and technologies comes under SW. In Section 4, gives details about the use of ontology in Semantic Web and ontology based retrieval techniques. Section 5 concludes the paper and the last Section displays list of References, which are being referred to survey this approach. .
-
II. Information Retrieval
Definition: - Information Retrieval (IR) is defined as process of identifying and retrieving unstructured documents containing the specific information stored in them. Unstructured documents are written in natural language. E.g. videos, photos, and audio etc. IR mainly focuses on retrieval of natural language text. It addresses retrieval of documents from an organized well defined huge collection of documents on web. Information Retrieval (IR) technology is major factor responsible for handling annotations in Semantic Web (SW). Traditional text Search Engines are not optimal for finding the relevant documents. It is produced by various approaches of ontologies and Semantic data. These purely text based Search Engines fails because of following reasons:
-
• Improper style of natural languages: - There are chances that syntax of languages is not appropriate.
-
• High level unclear concepts: - Some concepts which are used in document but present Search Engines can’t find those words.
-
• Timely Scenario: - Keywords matching is not used to find timely specified documents.
IR deals with fusion of streams of output documents produced from multiple retrieval methods. They are combined to form single ranked stream which is shown to user. There are two methods for solving user queries:
-
• By submitting a given query to multiple document collections.
-
• By submitting a given query through multiple IR methods.
The architecture of Information Retrieval Engine is based on ONTOLOGY BASED MODEL which represents the content of resource from given ontology. It has following parts:
V OMC (Ontology Manager Component):- It is used by Indexer, Search Engine and GUI.
V INDEXER: - It indexes documents and creates metadata.
V SEARCH ENGINE
V GUI supports user in query formation.
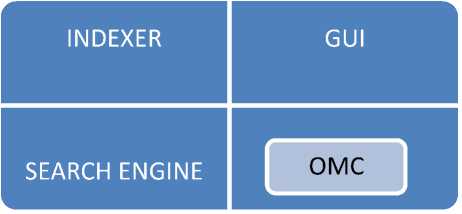
Fig. 1: IR Architecture [2]
-
2.1 Evaluation of Information RetrievalPerformance
There are two methods for evaluating performance as listed below:
-
• It is evaluated on concept of Relevance. Relevance means that user should be satisfied with the results produced with respect to given query.
-
• Precision (P) and Recall (R) are two measures to evaluate performance where Precision (P) = Relevant items retrieved / Total number of items retrieved. Recall (R) = Relevant items retrieved / Total relevant items in document
In 1979, Van Rigs berg proposed a formula for measuring Precision and Recall as:
E = 1 – 1 / [$(1/P) + (1-$) 1/R]
where E = Effectiveness measure
P = Precision
R = Recall
$ = parameter that describes importance to P and R.
If $ = 0, then user has no importance to Precision
If $ = ½, then P = R
If $ = 1, then No Recall
We can improve Information Retrieval effectiveness by:
-
• Use concept of co-occurrence to measure the strength of semantic relations between words.
-
• Make use of background knowledge into search process. Background knowledge signifies use of Thesaurus.
Thesaurus defines the set of standard terms or words that are used to search a document and set of relations between these terms. It gives hint related to words which are typed in search box.
Information Model: - It is defined as model for representing documents and user query in system. This model is based on ontology based model and contains the matter of subject as combination of instances and temporal intervals i.e. it combines Conceptual Part and Temporal Part.
Conceptual Part is represented by Information model using IR engines that are built on Vector Space Model. It involves Temporal Vector Space Model. This model is used to find similarity between sets of time intervals.
Temporal Vector Space Model: - It defines that if we choose discrete time representation, we can represent keywords used in query as terms. Temporal signifies terms which are viewed in space. But this model has not worked effectively due to following reasons:
-
• It has large number of level of details that are represented by large time intervals and requires large time.
-
• Traditional time intervals do not produce results with full certainty.
Solution: - Fuzzy Temporal Model
Fuzzy Model is extension of Vector Space Model. It uses Fuzzy time intervals in various application domains like business news or history.
-
III. Semantic Web
The idea of Semantic Web (SW) as envisioned by Tim Bermers Lee came into existence in 1996 with the aim to translate given information into machine understandable form. The Semantic Web (SW) is an extension of current www in which documents are filled
by annotations in machine understandable markup language [21]. It is defined as framework of expressing information because we can develop various languages and approaches for increasing IR effectiveness. Semantic Web uses documents called Semantic Web Documents (SWD’s) that are written in SW languages like OWL, DAML+OIL. SW is an XML (Extensible Markup Language) application.
Its aim is to maintain coordination between users and software agents so that they can find answers to their queries clearly. For maintaining this, we have to maintain Semantic Web Inference Engine which process query and produces results in following manner:
-
• Given query acts as input to Inference Engine.
-
• This query leads to production of semantic markup documents for retrieving information.
-
• The system has to prove this query if we want to produce Inference.
-
• We cannot use output of engine as search query. The given query is encoded as a text query that is identified by search engines.
-
• After identification, query is submitted to one or more web pages.
-
• Then some of these web pages must be extracted to retrieve markup. These markups may be irrelevant, useful or unauthorized.
-
• FILTERS are used to make these markups relevant and fully trusted.
-
• After filtering, these facts will be passed to inference engine and the whole process repeats.
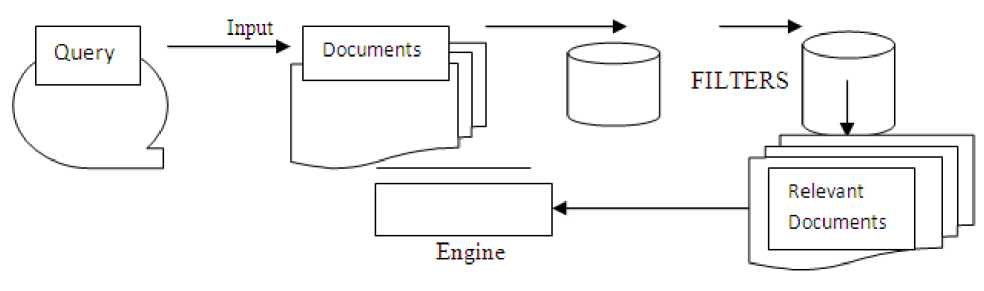
Fig. 2: SW Inference Engine
-
3.1 Semantic Web (SW) Technologies
SW technologies are listed below:-
V XML: - XML is extensible language that allows users to create their own tags to documents. It provides syntax for content structure within documents. XML Schema: - It is language for defining XML documents. XML document is a tree.
V RDF: - It stands for Resource Description
Framework. It is simple language to express data models which refers to objects and their relationships. These models are called RDF Models.
Both XML and RDF deal with Metadata which is data about other data. Raw data is stored in some repository called as Database Storage. Then Information Extraction techniques like KM solutions generate metadata.
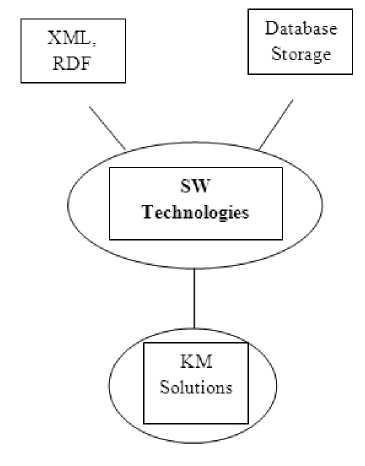
Fig. 3: Semantic Web Technologies
-
3.2 How to Build Semantic Web
Building a Semantic Web is a sophisticated task. It has certain requirements, challenges etc.
Requirements: - Semantic Web is build only if standards/rules must be defined within syntactic as well as semantic form of documents. Both Syntactic and Semantic are different from each other. Syntactic refers to pointing to rules of syntax. Syntax must be correct. Semantic means what it means.
For exchanging information, there must always be Exchange format and requirements for exchange format are as follows:
V Universal Expressive Power: - It is not possible to require all users. So, web based exchange format is necessary.
V Syntactic Interoperability: - It means that applications must be able to read data and presents information. It is about naming part of document.
V Semantic Interoperability: - It defines that data that is exchanged should be understandable. It is about defining semantic mappings between terms within data.
We can use XML and RDF as XML fulfills first two requirements i.e. Power requirement and Syntactic Interoperability. XML does not fulfill requirement of semantic interoperability because:
-
V XML only describe grammars.
-
V No way to make data understandable.
-
V No way to find semantic content from particular domain as XML focus on structure of document.
-
V No interpretation of data.
-
3.3 Challenges faced in Building Semantic Web
Using RDF can fulfill all three requirements. RDF model consists of Resource, Property and Object that satisfies Power requirement. RDF parsers are available that analysis data in form of symbols either in natural languages and machine language, thus leading to Syntactic Interoperability. RDF model also provides object – attribute structure that gives semantic units also, so it fulfills Semantic Interoperability.
The current Semantic web languages like RDF, OWL are not built on top of www. RDF can refer to syntax of XML but it cannot use XML Syntax properly. So, there is Semantic discontinuity at Semantic Web. There are few differences between RDF and XML.
-
IV. Ontology
The term Ontology can be defined in different ways as:
Ontology is abbreviated as FESC (Formal, Explicit, and Specification of Shared Conceptualization):
Formal: - It specifies that it should be machine understandable.
Explicit: - It defines type of constraints used in model.
Shared: - It means that ontology is shared by group. It is not restricted to individuals.
Conceptualization: - It refers model of some phenomenon to identify relevant concepts of that phenomenon.
Ontology is very useful in increasing Information Retrieval performance. Ontology deals with occurrence of events, their instances and user defined relations between concepts. This represents background knowledge on Semantic level where Semantic level is defined as set of semantic entities including their concepts and relations instead of simple words which are used in thesaurus [21, 22]. Semantic level specifies relations between entities and also holds the facts and rules about domain problem. Following points describes the role of ontology in development of Semantic Web:
-
• Ontology is considered as backbone of Software.
Since SW translates the given data into machine understandable language using concept of ontologies.
-
• Ontology development is a cooperative process; it allows different peoples to express their views on given domain.
-
• It gives complete description of problem that can be communicated among people and application systems.
-
• The use of ontologies has overcome the limitations of keyword based search and led to development of Semantic Web.
-
• Various ontology models are used for exploitation of domain ontologies and knowledge bases to support semantic web development.
-
• Ontology language editors help to build Semantic Web.
-
• Ontologies are metadata schemes providing a controlled vocabulary of concepts.
It is not possible to convert from full text based systems to semantic based systems in one step. It involves use of gradual approach which provides smooth relations between them. Since ontologies store the domain knowledge in much effective way than thesaurus. So, we can say that ontologies measure the rate of increase in IR system. Accuracy in ontology models is directly related to effectiveness in Information Retrieval systems.
Table 1: Difference between XML and RDF
|
Extensive Markup Language (XML) |
Resource Description Framework (RDF) |
|
1. It is based on tree model. |
1. It is based on directed graph model. |
|
2. Edges have no labels but they are ordered. |
2. Edges have labels but they are unordered. |
|
3. Use of XML leads to semi structured databases. |
3. Use of RDF leads to model theory. Model theory is semantic theory which provides relation between expressions and interpretations. |
There are some problems in ontology languages and to avoid them, we have developed a prototype with following points:
-
• In ontology based model, quality of results was not as much as accurate due to lack of information.
-
• Large cost is required in creating ontology language.
-
• There are limited facts and axioms related to ontologies.
-
4.1 Ontology Based Retrieval Techniques
So, imperfections in ontology and metadata should be considered properly. We can create new ontologies by demonstrating the use of semantic information in domain by avoiding imperfections and assumptions about the quality of ontologies and metadata. Ontology has also contributed to the use of Data Mining. We can also generate ontology on databases. Data Mining is a technology that is used for identifying patterns and ways from large quantities of data or other information repositories. Data Mining is also known as Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD). It is multi level field i.e. it includes different areas like database system, information retrieval, machine learning etc. There are two goals of Data Mining:
Prediction: - It involves use of some variables or records in database to predict future values of other variables.
Description: - It finds useful patterns describing the given data.
Building ontology needs attention of domain experts that represents concepts and relationships between them for a given domain. Ontology can be built manually as well as automatically. Various researchers have contributed to this scenario:
-
• Clerkin et.al discovered ontology automatically with the help of concept of clustering algorithm. It is useful in case where no expert knowledge exists and it uses agents for building ontology [3].
-
• Blaschke et.al proposed methodology that makes use of iterative information extraction for building ontology [4].
-
• Formal Concept Analysis (FCA) is a technique that is used to abstract data as conceptual structures [5].
-
• Quan et.al proposed concept of Fuzzy logic into FCA to deal with uncertainty of data by designing framework called as Fuzzy Formal Concept Analysis (FFCA) for building ontology [6].
-
• Wrobel et.al built ontology on basis of output of data mining results. It uses Semantic web languages like RDF, RDFs, DAML+OIL etc [7].
Ontology Retrieval techniques include Query Expansion and Indexing. It is known that combination of results produced by simple queries gives better view as compared to using single query result [8, 9, 10]. It is called as Query Expansion. It is so because any algorithm has its merits and demerits and it is not always suggested to find optimal method. To find optimal method, there is need to use Ranking algorithm [11]. The given query is extracted in following manner as:
-
• The query entered by user contains terms which may or may not be relevant. It is made relevant by use of Filters.
-
• Then filtered query process applies various ontology based rules to create a separate query which executes independently using full text search engine.
-
• After applying rules, we get transformed query corresponding to transformation.
-
• The query is executed and ranked results are produced.
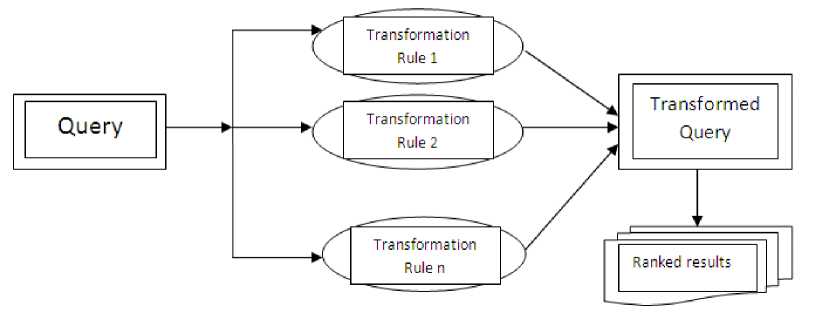
Fig. 4: Query Extraction Process
Ontology is generated from given databases that help in performing process of data mining. Following figure illustrates the process [24].
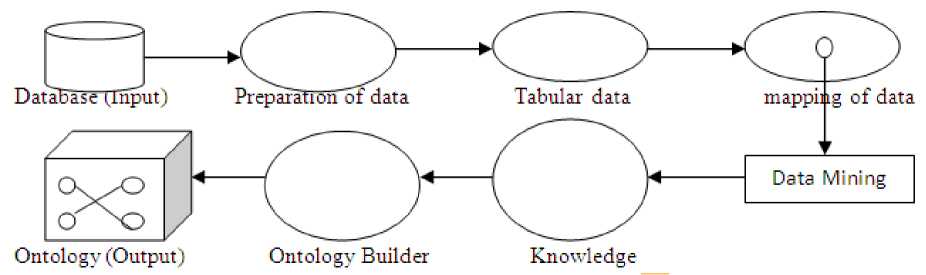
Fig. 5: Ontology Generation
-
V. Conclusion
In The above paper has given a new way to users for extracting information from the web. Since, there is large number of documents present on web and to retrieve information from them is very difficult task. It generates the concept of Information Retrieval and Semantic Web. Semantic Web is termed as next generation of current World Wide Web. It used Semantic markup documents for extracting information from web documents. It generates annotations and metadata from original data by translating them into knowledgeable representation documents. The traditional search engines failed to understand the structure and semantics of Semantic Web documents. These engines expect documents to be unstructured text but there are various documents involved in Information Retrieval (IR) process. The paper described the role of ontology in development of Semantic Web. Ontology is considered as backbone of every software system. Building ontology needs attention of domain experts that represents all concepts and relationships. There are various algorithms used to extract and discover knowledge from given structured data. It is found that semantic markup within documents leads to greater number of relevant documents as compared with text documents. We have created semantic foundation for semantic web that extends as www. Semantic foundation includes use of XML, trees, graphs, model theory and XML schemas. XML is considered as major source of semantic information for Semantic Web. It also acts as standard format for writing documents on web. The main issue of using XML is that it does not represent ontology information. It is represented by using SWOL (Semantic Web ontology language). The concept of knowledge stored in ontologies and semantic metadata is used for task of Information Retrieval.
Acknowledgement
I ,Vishal Jain would like to give my sincere thanks to Prof. M. N. Hoda, Director, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s Institute of Computer Applications and Management (BVICAM), New Delhi for giving me opportunity to do P.hD from Lingaya’s University, Faridabad.
Список литературы Ontology Based Information Retrieval in Semantic Web: A Survey
- Vishal Jain, Gagandeep Singh, Dr. Mayank Singh, “Implementation of Multi Agent Systems with ontology in Data Mining”, “International Journal Of Research In Computer Application & Management (IJRCM), Vol. No. 3, Issue No.1 ISSN 2231-1009”, January 2013, pp 111-117.
- Gagandeep Singh, Vishal Jain, “Information Retrieval (IR) through Semantic Web (SW):An Overview”, “In proceedings of CONFLUENCE 2012- The Next Generation Information Technology Summit at Amity School of Engineering and Technology”, September 2012, pp 23-27.
- Clerkin, P. Cunningham and C. Hayes, “Ontology Discovery for the Semantic Web using Hierarchical Clustering, Trinity College Dubin”, “TCD-CS-2002-25”.
- Blaschke, C. Valencia, “Automatic Ontology Construction from the Literature”, “Genome Informatics Vol.13”, 2002, pp 201-213.
- Ganter, B. Stumme, G.Wille, “Formal Concept Analysis: Foundations and Applications. Lecture notes on Artificial Intelligence”, “Springer- Verlag. ISBN 3-540-27891-5”, 2005.
- Quan, T.T Hui, Cao T.H, “Automatic generation of ontology for scholarly semantic web”, “In proceedings of Lecture notes in Computer Science Vol. 3298”, pp 726-740.
- O. Wrobel, A. Hui, J.M. Joller, “Data Mining for Ontology Building: Semantic Web Overview”, “Diploma Thesis- Department of Computer Science WS2002/2003, Nanyang Technological University”.
- Urvi Shah, James Mayfield, “Information Retrieval on the Semantic Web”, “ACM CIKM International Conference on Information Management”, Nov 2002.
- S. Luke, L. Spector, D. Rager and J. Hendler, “An Introduction to Ontology”, “In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Autonomous Agents (Agents 97)”, pages 59-66, 1997.
- Berners Lee, J. Lassila, “Ontologies in Semantic Web”, “Scientific American”, May 2001, pp 34-43.
- Assilis, Kotis and George A. Vourus, “Semantic Retrieval and ranking of Semantic Web documents using free- form queries”, “Int. J. Metadata, Semantics and Ontologies, Vol.3, No.2”, 2008.
- U. Fayyad, R. Uthuruswamy, “Data Mining and Knowledge discovery in databases”, “Communications of the ACM, 39(11)”, 1996, pages 1-15.
- Chandrasekaran B, Josephon J.R, “What are ontologies, and why do we need them?”, “IEEE Intelligent Systems”, pp 20-26, 1999.
- Dayal U, Kuno H, “Making the Semantic Web Real”, “IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, Vol.26, No.4”, pp 4-7, 2003.
- Uschold, M. And Gr Ninger, “Ontologies: Principles, Methods and Applications”, “Knowledge Engineering Review, Vol.11 No.2”, pp 93-137.
- J. Mayfield, “Ontologies and text retrieval”, “Knowledge Engineering Review”, 2007.
- Stojanovic, N. Studer, R. Stojanovic, “An approach for ranking of query results in the Semantic Web”, “The Semantic Web – ISWC”, 2003, pp 500-516.
- Goetz Graze, “Query Evaluation techniques for large databases”, “In Proceedings of ACM COMPUTING SURVEYS”, 2003.
- Berners-Lee and Fischetti, “Weaving the Web: The Original Design of the World Wide Web by its inventor”, “Scientific American”, 2005.
- J. Kopena, A.Joshi, “DAMLJessKB: A tool for reasoning with Semantic Web”, “IEEE Intelligent Systems”, 2006.
- Jeremy, Lan, Dollin, “Implementing the Semantic Web Recommendations”, “In proceedings of the 13th international conference World Wide Web”, 2004.
- Gabor Nagypal, “Improving Information Retrieval Effectiveness by Using Domain Knowledge Stored in Ontologies”, “The Semantic Web, Scientific American 284”, 2001, pp 34-43.
- Kaushal Giri, “Role of Ontology in Semantic Web”, “IEEE Intelligent Systems Vol.16 (2)”, 2001, pp 72-79.
- M. Preethi, Dr. J. Akilandeswari, “Combining Retrieval with Ontology Browsing”, “International Journal of Internet Computing (IJIC), Vol.1, Issue-1”, 2011.


