Особенности профиля соматических мутаций и функционирования внутриклеточных сигнальных путей на различных стадиях рака мочевого пузыря и их значение для терапии
Автор: Сергиенко Сергей Александрович, Михайленко Д.С., Сафронова Н.Ю., Ефремов Г.Д., Каприн А.Д., Алексеев Б.Я.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Экспериментальная урология
Статья в выпуске: 1, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Рак мочевого пузыря (РМП) занимает одно из лидирующих мест в структуре заболеваемости и смертности среди злокачественных новообразований в мире. На данный момент имеется большое количество экспериментальных данных о нарушениях при канцерогенезе РМП на молекулярно-генетическом уровне, но лишь немногие из них рассматриваются как потенциальные предикторы ответа на проводимую терапию, пригодные для применения в клинической практике. Все больше исследований свидетельствуют о том, что РМП является генетически гетерогенным онкозаболеванием. Корреляция различных молекулярно-генетических подтипов с клинико-морфологическими данными может позволить прогнозировать течение заболевания и определять наиболее эффективные персонализированные варианты лечения. Цель работы. Анализ и обобщение современных результатов исследований молекулярно-генетических изменений на уровне последовательностей ДНК и РНК с точки зрения их прогностической ценности для выбора тактики лечения РМП. Материалы и методы...
Подтипы рака мочевого пузыря, уротелиальная карцинома, мутация, экспрессия генов, полимеразная цепная реакция, секвенирование, таргетная терапия
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142224042
IDR: 142224042 | DOI: 10.29188/2222-8543-2020-12-1-42-51
Текст научной статьи Особенности профиля соматических мутаций и функционирования внутриклеточных сигнальных путей на различных стадиях рака мочевого пузыря и их значение для терапии
Somatic mutation profiling and functioning of intracellular signaling pathways at various stages of bladder cancer and their significance for targeted therapy
S.A. Sergienko1, D.S. Mikhaylenko1–3, N.Yu. Safronova1, G.D. Efremov1, A.D. Kaprin1, B.Yа. Alekseev1
Purpose of the study. Analysis and summarization of actual studies about molecular genetic changes at the DNA and RNA sequences, and their prognostic significance for patients with BC.
Materials and methods. We used data about genetic alterations in BC and diagnostic test systems published in the PubMed, Elibrary.ru databases, as well as websites of several professional associations for writing this review. Based on the relevance of data, reliability of the sources, impact factors of journals 40 articles in peer-reviewed journals and one guide were studied during the preparation of the review.
The main part. Analysis of scientific and technical information published over the past 5 years was performed. We have identified three signaling pathways and about ten genes that are their components, mutations in which are characteristic of the main forms of BC: non-muscular- and muscle-invasive. Together with the sequencing data of tumor exomes, expression and immunohistochemical profiles these molecular genetic characteristics made it possible to improve the classification of BC and isolate new molecular subtypes. Various BC molecular subtypes are associated with prognosis, overall survival, the effectiveness of chemo- and targeted therapy, including immune control points inhibitors.
Conclusion. Certain molecular genetic alterations are already included in diagnostic and prognostic test systems (FGFR3 and TERT mutations, a number of immunohistochemical markers), but the vast majority of somatic mutations and genes expression are considered only as a starting point for finding new targeted drugs or prognostic markers. The review is aimed for urologists, oncologists, laboratory geneticists and specialists in related professions.
В России рак мочевого пузыря (РМП) занимает 13 место по распространенности среди всех онкологических заболеваний и 9 место – среди онкологических заболеваний у мужчин [1]. В мире заболеваемость РМП в среднем выше, чем в России, и занимает 11 место среди прочих онкологических патологий у обоих полов и 7 место – у мужчин [2]. В 75% случаев выявляется немышечно-ин-вазивный рак мочевого пузыря (НМРМП) на стадии Та, Т1, карцинома in situ (CIS), у оставшихся 25% диагностируется стадия Т2 и выше, а также метастатическая форма заболевания [3]. Наряду с доказанными факторами риска развития РМП (курение, работа на производстве лакокрасочных материалов, красителей, топлива) существенный вклад в возникновение и развитие этого заболевания вносят генетические факторы. С точки зрения молекулярного патогенеза РМП является в значительной мере гетерогенным заболеванием, что подразумевает не только различное клиническое течение опухолевого процесса, но и ответ на проводимую терапию. Полученные на настоящий момент данные уже позволяют разделять несколько подтипов РМП на основании иммуногистохимических и морфологических признаков [4]. Вместе с тем, все больший интерес представляют исследования молекулярногенетического профиля опухоли, который лежит в основе ее фенотипических (в том числе, патоморфоло-гических) признаков, его значения для оценки прогноза РМП и персонифицированного лечения.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
При написании обзора были использованы данные о генетических нарушениях при РМП и диагностических тест-системах, опубликованные в базах PubMed , Научной элек- тронной библиотеки , сайтах Российского общества онкоурологов ( и Европейской ассоциации урологов . Поиск в базах данных проводили по ключевым словам «gene», «bladder cancer», «mutation» и «diagnostic kit». На первом этапе были найдены 108 источников не старше 5 лет, которые имели отношение к теме обзора. Из них были исключены тезисы конференций, короткие сообщения, дублирующиеся публикации. После чего, исходя из актуальности данных, достоверности источников, импакт-факторов журналов и последовательности изложения материала в рукописи, непосредственно для цитирования в обзоре были отобраны 40 статей в научных международных рецензируемых журналах и одно руководство.
ЧАСТО МУТИРУЮЩИЕ ГЕНЫ ПРИ РАКЕ МОЧЕВОГО ПУЗЫРЯ
На цитогенетическом уровне РМП характеризуется хромосомными аберрациями, которые представлены анеуплоидиями, делециями и инсерциями. Среди них можно упомянуть часто встречающуюся делецию 9 хромосомы, которая происходит на ранних стадиях развития уротелиальной карциномы [5]. Однако большинство описанных при РМП хромосомных аберраций не имеют прогностического значения при их определении рутинными цитогенетическими методами. Больший интерес представляет профиль точковых мутаций, которые возникают в онкогенах и генах-супрессорах, отражают процесс формирования клона злокачественных клеток РМП и прогрессию заболевания. Данные, опубликованные в международной базе данных The Сancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), продемонстрировали высокую частоту встречаемости мутаций при РМП: в среднем 8,2 на 1 млн. пар нуклеотидов [6]. Однако большинство мутаций не имеют каких-либо функциональных последствий. Чаще всего при соматических мутациях преобладает переход C:G→T:A, что в свою очередь характерно для мутаций, связанных с активностью цитидиндеаминаз APOBEC. В частности, данный механизм реализуется при возникновении точковых мутации FGFR3. Ассоциированный с экспрессией APOBEC мутационный профиль прослеживается также и при мутациях других генов, что позволяет судить о ее значительной роли в мутагенезе при РМП [7,8]. Если рассматривать частоту встречаемости мутаций в опухоли, то наиболее актуальными при РМП, в том числе, с точки зрения нарушения функции ключевых внутриклеточных сигнальных путей, контролирующих пролиферацию, являются мутации генов TP53, FGFR3, CDKN2A, PIK3CA, TERT и RB1.
Мутации гена TP53
Ген TP53 расположен у человека на коротком плече 17 хромосомы (17p13.1) и кодирует белок, негативно регулирующий клеточный цикл и апоптоз клеток. По своим характеристикам ген ТР53 представляет собой типичный ген–супрессор опухолевого роста, инактивируемый в злокачественных опухолях по двухударной модели Кнадсена. Точковые мутации TP53 могут быть представлены миссенс-мутациями, небольшими делециями или инсерциями, нонсенс-мута-циями, а также протяженными делециями [9].
Мутации гена FGFR3
Ген FGFR3 кодирует рецептор для фактора роста фибробластов 3-го типа, локализован на коротком плече 4 хромосомы в области 4р16.3, кодирует одноименный трансмембранный белок. Белки этого семейства играют важную роль в клеточной пролиферации и дифференцировке, включая позитивную регуляцию клеточного роста, онтогенез и васкуляризацию различных типов тканей [10]. Будучи трансмембранным рецептором, FGFR3 содержит лиганд-связывающий, трансмембранный и киназный домены. При канцерогенезе РМП точковые мутации затрагивают, в основном, два последних домена и представлены активирующими миссенс-мутациями. Наиболее частые из них изменяют кодоны 248 и 249, что в итоге приводит к образованию дисульфидных мостиков и, как следствие, димеризации и конститутивной активации рецепторов. Меньшая доля мутаций приходится на киназный домен, где мис-сенс-мутации также переводят рецептор в перманентно активное состояние. Отметим, что речь идет о соматических мутациях при канцерогенезе спорадического РМП у взрослых, профиль которых существенно отличается от герминальных мутаций в генах семейства FGFR, приводящих к аномалиям развития в детском возрасте [11].
Мутации гена CDKN2A
Ген CDKN2A осуществляет негативную регуляцию клеточной пролиферации, его продуктом является ингибитор циклин-зависимой киназы 2А (р16 по старой номенклатуре). Локализован CDKN2A на коротком плече 9 хромосомы (9р21.3). По своим функциям этот ген относится к генам-супрессорам, инактивируется в опухоли путем метилирования и/или мутаций. Белок p16 в норме связывается с двумя циклин-зависимыми киназами CDK4 и CDK6 и ингибирует их. Также продукт гена CDKN2A действует синэргично с ранее упомянутым опухолевым супрессором ТР53 [12,13]. Инактивирующие мутации могут быть представлены как однонуклеотидными заменами, так и делециями различной протяженности – от нескольких нуклеотидов до хромосомных фрагментов. В случае сочетания делеции CDKN2A с мутацией FGFR3, как правило, оба изменения происходят на начальных этапах развития опухоли [14].
Мутации гена PIK3CA
Ген PIK3CA находится у человека на длинном плече 3 хромосомы (3q26.32), кодирует белок p110α – основную (каталитическую) субъединицу фермента фосфатидилинозитол-3-киназы (PI3K). Как и другие киназы, PI3K фосфорилирует сигнальные молекулы, что запускает серию реакций и трансдукцию сигнала внутрь клеток. Киназа PI3K играет важную роль в регуляции нескольких внутриклеточных сигнальных путей, прежде всего, идущих от тирозинкиназных рецепторов и влияет на клеточную пролиферацию, миграцию и апоптоз [15]. Мутации PIK3CA приводят к конститутивной активации киназной субъединицы PI3K и стимулированию клеточной пролиферации. Чаще всего эти нарушения представлены активирующими миссенс-мутациями в 9 и 20 экзоне. Хотя они и являются драйверными мутациями в патогенезе многих типов опухолей, их влияние на способность клеток к неконтролируемой пролиферации не такое выраженное, как, например, у активирующих мутаций генов тирозинкиназных рецепторов (в том числе, FGFR3). Поэтому они являются лишь частью профиля активирующих точковых мутаций при РМП [16].
Мутации гена TERT
Рассмотренные в предыдущих разделах частые точковые мутации в ключевых онкогенах происходят непосредственно в кодирующих последовательностях генов. Однако такие мутации могут быть обнаружены и в промоторе, в частности, в гене TERT. Этот ген находится на коротком плече 5 хромосомы (5p15.33) и кодирует большую субъединицу фермента теломеразы. Теломераза осуществляет матричный синтез структур, называемых теломерами, которые состоят из повторяющихся участков ДНК и располагаются на концах хромосом. Теломеры защищают хромосомы от деградации во время репликации генома и от аберрантных хромосомных перестроек с негомологичным соединением концов. По мере исчерпания репликативного потенциала клетки, теломеры на концах хромосом становятся короче и клетка может вступить в апоптоз. В норме это происходит со всеми дифференцированными клетками за исключением клеток зародышевой линии, в которых активна теломераза. В большинстве типов клеток иммуногистохимически теломераза либо не обнаруживается, либо имеет место фоновое окрашивание. Гиперэкспрессия теломеразы отмечается во многих опухолевых клетках и рассматривается как существенный этап перехода к бесконтрольному делению. Мутации TERT при РМП представлены, в основном, однонуклеотидными заменами в двух участках промотора, которые создают дополнительные сайты связывания транскрипционных факторов и способствуют экспрессии гена [17,18].
Мутации гена RB1
Ген RB1 находится на длинном плече 13 хромосомы (13q14.2), кодирует одноименный белок – фактор ретинобластомы (назван так по типу опухолей, в которых ген был впервые выделен и охарактеризован). Этот белок является классическим опухолевым супрессором, осуществляющим негативную регуляцию клеточного деления. В норме он ингибирует фактор E2F и препятствует продвижению по клеточному циклу дальше S-стадии. Герминальные мутации RB1 приводят, в основном, к развитию ретинобластомы, тогда как соматические – встречаются во многих типах опухолей и в части случаев РМП, демонстрируя один из наиболее частых видов повреждений генов-супрессоров в канцерогенезе [19,20]. Мутации в перечисленных выше онкогенах и генах-супрессорах приводят к разбалансировке регуляции клеточного деления. Позитивная и негативная регуляция клеточной пролиферации уротелия – сложный многоступенчатый процесс, но в нем выделяют несколько основных сигнальных путей со своими рецепторами и вторичными мессенджерами, активация/ инактивация которых играют ведущую роль в развитии РМП.
НАРУШЕНИЯ ФУНКЦИИ ОСНОВНЫХ СИГНАЛЬНЫХ ПУТЕЙ ПРИ РАКЕ МОЧЕВОГО ПУЗЫРЯ
Путь FGFR3/RAS
Мутация FGFR3 вызывает конститутивную активацию пути RAS/MAPK. Этот путь рассматривают как один из основных механизмов, запускающих пролиферацию уротелиальных клеток. Приблизительно в 10% случаев РМП обнаруживают мутации в генах семейства RAS: HRAS, KRAS и NRAS. Нарушение функции пути
RAS/MAPK вследствие мутаций FGFR3 или генов RAS неизменно ассоциировано с высокой пролиферативной активностью опухолей. Мутация FGFR3 встречается примерно в 80% НМРМП. Для этих опухолей характерны частые рецидивы, немышечно-инвазивный характер роста и благоприятный прогноз. Встречаемость мутаций существенно ниже при мышечно-инвазивном РМП (МИРМП), составляя 10 – 20% случаев [20-23].
Путь PIK3/AKT/MTOR
Путь PIK3/AKT/MTOR также регулирует скорость деления клеток и условно берет начало от киназы PIK3. В свою очередь, эта киназа активируется под действием рецепторных тирозинкиназ, таких как ERBB2, ERBB3 и FGFR3. Мутация гена рецептора эпидермального фактора роста 2-го типа ERBB2 встречается в 12% случаев МИРМП. Делеция или пониженная экспрессия PTEN, который является негативным регулятором пути PIK3/AKT/MTOR, наблюдается во многих случаях МИРМП, тогда как нарушение функции генов AKT1, TSC1 и других, занимающих нижележащие позиции в пути PIK3/AKT/MTOR, встречаются реже [6,24].
Путь TP53/RB1
Данный путь играет важную роль в негативной регуляции клеточного цикла, в отличие от двух описанных выше сигнальных каскадов. Мутации TP53 и RB1 чаще встречаются при инвазии РМП: карциноме in situ и МИРМП. Согласно данным TCGA путь TP53/RB1 инактивирован у 89% больных МИРМП. Показано, что CDKN2A, который непосредственно связан с путем TP53/RB1, подвергается мутациям или протяженным делециям в 7-22% случаев РМП [14,25].Различная вовлеченность мутантных форм онкогенов и генов-супрессоров в ключевые сигнальные пути, регулирующие деление уротелиальных клеток, связана с разными путями молекулярного патогенеза подтипов РМП.
РАЗЛИЧИЯ В ПУТЯХ МОЛЕКУЛЯРНОГО ПАТОГЕНЕЗА ОПУХОЛЕЙ МОЧЕВОГО ПУЗЫРЯ
В общем виде существуют два альтернативных пути молекулярного патогенеза РМП, ассоциированных с неинвазивными и инвазивными формами этого заболевания. В первом случае для неинвазивных опухолей характерна ведущая роль сигнальных путей FGFR3/RAS и PIK3/AKT/MTOR. В частности, обнаруживают мутации FGFR3 и HRAS на стадии предраковых изменений (гиперплазии) и развитии немышечно-инвазивных папиллярных опухолей. Такие первичные опухоли, как правило, склонны к частому рецидивированию, но редко переходят в инвазивную форму, имеют относительно благоприятный прогноз общей выживаемости.
В дальнейшем в части случаев НМРМП возможно приобретение опухолью мутаций PIK3CA, STAG2 и инактивация CDKN2A, что активирует переход опухоли в инвазивную форму и ассоциировано со снижением уровня дифференцировки (G2-3, high-grade). В инвазивных опухолях на первое место выходят множественные хромосомные аберрации вследствие хромо-трипсиса, инактивация сигнального пути TP53/RB1. В этом случае предраковым состоянием выступает дисплазия, CIS, а в качестве ранних точковых мутаций – нарушения в гене-супрессоре TP53, а также RB1. Эти опухоли характеризуются агрессивным течением, инвазивным характером роста, склонностью к прогрессированию. В редких случаях возможны сочетанные нарушения всех трех сигнальных путей (рис. 1) [26,27].
Наиболее полно охарактеризовать профиль мутаций в опухоли в настоящее время позволяют методы высокопроизводительного секвенирования (NGS – next generation sequencing). Благодаря им можно проводить одновременный анализ панелей из нескольких десятков протяженных интересующих исследователя генов или даже всего опухолевого экзома (совокупности кодирующих последовательностей всех генов). В массив геномных данных также вносят свой вклад результаты исследований на экспрессионных и гибридизационных микрочипах высокой плотности. Эти данные могут быть соотнесены с иммуногистохимическими и морфологическими характеристиками опухоли.
Экспрессионный анализ НМРМП
Транскриптомный анализ 460 случаев НМРМП показал, что эти опухоли можно разделить на три подтипа (классы 1–3), которые значительно различаются по своим клинико-патологическим признакам, включая продолжительность выживаемости без прогрессирования. Исследовано 345 случаев на стадии Та, 112 – Т1 и 3 – Тis. Класс 1 включал наибольшее число Та опухолей, отличался наилучшим прогнозом. Класс 2 чаще был представлен опухолями Т1, низкой дифференцировкой и имел худший прогноз. Отмечен высокий уровень экспрессии KRT20, часто встречающийся при CIS. В целом, экспрессионный спектр 2 класса схож с мышечно-инвазивными опухолями. Мутации, ассоциированные с APOBEC, также ассоциировались с плохим прогнозом. Опухоли класса 3 (n = 129) включали экспрессию KRT5, KRT15 и CD44 и имели промежуточный прогноз среди прочих НМРМП [28,29].
Мутационный и экспрессионный анализ МИРМП
Комплексная молекулярная характеристика МИРМП позволила разделить его на подтипы, связанные с клинико-патологическими признаками. РМП в соответствии с этой новой молекулярной классификацией был разделен на два основных подтипа – люминальный и базальный. D. Lindgren и соавт. впервые идентифицировали базальный подтип МИРМП, который был связан с низкой выживаемостью [30]. W. Choi
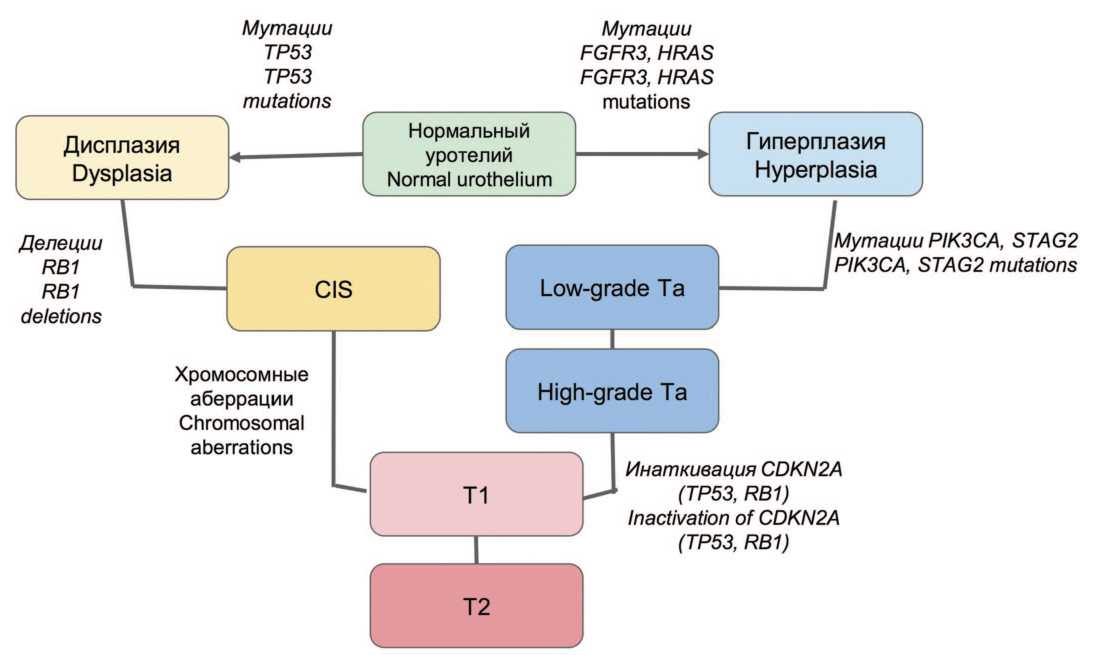
Рис. 1. Молекулярный патогенез рака мочевого пузыря
Fig. 1. Molecular pathogenesis of bladder cancer
гене

экспериментальная и клиническая урология № 1 2 0 2 0
и соавт. продемонстрировали, что, хотя базальный подтип МИРМП агрессивен в контексте инвазии и метастазирования, он демонстрирует хороший ответ на неоадъювантную химиотерапию (НеоХТ). Он также характеризуется экспрессией белков CK5/6, CD44 и EGFR, но не KRT20 или маркеров дифференцировки уротелия. Эти авторы отметили, что люминальный подтип МИРМП часто имеет мутации FGFR3, экспрессию KRT20 и маркеры дифференцировки уротелия (GATA3, уроплакины и ERBB2, но не CK5/6, CD44, TP63 или EGFR). Они также идентифицировали TP53-подобный подтип МИРМП, который устойчив к НеоХТ [31]. В 2014-2016 гг. данные TCGA использовались для классификации МИРМП на четыре подтипа экспрессии (кластеры I-IV). Кластеры I и II имеют общие черты МИРМП люминального типа, включая дифференцировку уротелиальных клеток и экспрессию GATA3 и FOXA1. Высокие уровни экспрессии семейства E-кадгерина (CDH1) и малой интерферирующей РНК miR-200, которые ингибируют эпителиально-мезенхимальный переход (ЭМП), также обнаружены в кластерах I и II. Кластер I (папиллярный подтип) характеризуется папиллярной морфологией, частыми мутациями FGFR3 и низкими уровнями экспрессии miR-99a-5p и miR-100-5p, которые снижают экспрессию FGFR3. Кластер III (базальный/плоскоклеточный подтип) демонстрирует особенности базального типа МИРМП, включая плоскоклеточную дифференцировку и экспрессию маркеров стволовых клеток. Класс IV, соответствующий подтипу, характеризующемуся ЭМП, экспрессирует на низком уровне E-кадгерин и членов семейства miR-200. Что касается ответа на лечение, то кластер TCGA II / TP53-подоб-ный люминальный подтип чувствителен к атезо-лизумабу (ингибитору PD-L1), но не к НеоХТ. Таким образом, пациенты с опухолями, соответствующими кластеру TCGA II / TP53, могут избежать неоправданной НеоХТ и получить лечение в необходимом объеме цистэктомии или иммунотерапии [32]. Еще в одном классификационном исследовании были выделены четыре кластера мутационных профилей экспрессии Msig1-4 (APOBEC-a и -b, ERCC2 и C>T-at-CpG), которые были ассоциированы с общей выживаемостью. Пациенты с кластером MSig1, APOBEC и высокой мутационной нагрузкой имели пятилетнюю выживаемость 75% по сравнению с кластером MSig2 с самой низкой мутационной нагрузкой (пятилетняя выживаемость в нем составила 22%). Кластер MSig4 был представлен мутациями ERCC2 (49% мутаций против 17% для других MSig). Высокая выживаемость пациентов из первого кластера может быть результатом более эффективного противоопухолевого иммунного ответа на опухоли с высокой мутационной нагрузкой [33].Кластеризация по уровню экспрессии мРНК позволила идентифицировать пять различных молекулярных подтипов РМП (люминально-папиллярный, люминально-инфильтративный, люминальный, базально-плоскоклеточный и нейрональный), которые можно использовать для стратификации пациентов в соответствии с прогнозируемым ответом на лечение (рис. 2). Например, люминально-папиллярный,
Мышечно-инвазивный рак мочевого пузыря __ Muscle-invasive bladder cancer _______
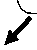
Люминальный
ИГХ: KRT20+, GATA3+, F0XA1 +
Luminal
INC: KRT20+ , GATA3+, F0XA1 +
Базальный / плоскоклеточный
Basal / squamous
Нейрональный
Neuronal
Папиллярный люминальный Papillary-lumina[
Инфильтративный люминальный Infiltrative-luminal
Люминальный Luminal
химерные гены, амплификация онкогенов.
Папиллярный рак SHH+, редко - CIS.
FGFR3 mutation, chimeric genes, amplification of oncogenes.
Papillary cancer,

Маркеры 3MT(TWIST1, ZEB1), семейство miR-200. Средняя экспрессия PD-L1, CTLA-4, миофибробластных маркеров. Нет мутаций ТР53.

ЕМТ markers (TWIST1, ZEB1), miR-200 family. Medium expression of the PD-L1, CTLA-4, myofibroblast markers. NoTP53 mutations.
уроплакинов, KRT20, SNX31
Uroplakins’ expression,

плоскоклеточный. Основные кератины, по ИГХ: KRT5,6,14+, GATA3-, F0XA1-, высокая экспрессияР0-Ь1, CTLA4

Often female; squamous cell. Basal keratinous markers, ICH: KRT5,6,14+, GATA3-, F0XA1-, high expression
PLEKHG4B.
Амплификация химерного гена E2F3/SOX4. Интенсивная пролиферация опухолевых клеток.
S0X2, DLX6, MS11, and PLEKHG4B expression. Amplification of the chimeric gene E2F3/SOX4.
Intensive tumor cell _ proliferation ,
Рис. 2. Молекулярные подтипы мышечно-инвазивного рака мочевого пузыря
Fig. 2. Molecular subtypes of the muscle-invasive bladder cancer люминально-инфильтративный и люминальный подтипы экспрессируют люминальные маркеры, включая GATA3, FOXA1, уроплакин и KRT20. В свою очередь, базально-плоскоклеточный подтип характеризуется повышенной экспрессией KRT5, KRT6 и KRT14 и сниженной экспрессией GATA3 и FOXA1. Люминально-папиллярный подтип (35%) характеризуется папиллярной морфологией и имеет лучшие показатели общей выживаемости. Он характеризуется мутациями FGFR3. Этот подтип редко представлен CIS, имеет низкую мутационную нагрузку и уровень метилирования, высокую частоту делеций CDKN2A. Такие опухоли имеют высокую экспрессию miR-200, CDH1 и ERBB2, но низкие уровни экспрессии miR-99a-5p и miR-100-5p. Люминально-инфильтративный подтип (19%) имеет мезенхимальный профиль экспрессии. Эти опухоли характеризуются ЭМП и умеренно экспрессируют маркеры ответа на таргетные иммунопрепараты PD-L1 и CTLA4. Люминальный подтип (6%) имеет высокий уровень экспрессии уроплакинов (UPK1A и UPK2), KRT20 и SNX31. Базально-плоскоклеточный подтип (35%) соответствует ранее определенному базальному подтипу, который связан с плоскоклеточной дифференцировкой и экспрессией кератинов. Этот подтип преимущественно обнаруживается у женщин и имеет высокий уровень экспрессии базальных маркеров (CD44, KRT5, KRT6A и KRT14), маркеров плоскоклеточной дифференцировки (TGM1, DSC3 и PI3) и мишеней для таргетной иммунотерапии PD-L1 и CTLA4. Подтип часто представлен CIS, характеризуется мутациями SHH и TP53. Нейрональный подтип (5%) характеризуется худшим клиническим исходом из всех подтипов. Отмечают повышенную экспрессию генов нейроэндокринной и нейрональной дифференцировки, высокий пролиферативный индекс, большое количество мутаций TP53 и RB1 [6,34,35].
АКТИВИРУЮЩИЕ МУТАЦИИ И ГИПЕРЭКСПРЕССИРОВАННЫЕ ГЕНЫ КАК ПОТЕНЦИАЛЬНЫЕ МИШЕНИ ДЛЯ ТАРГЕТНЫХ ПРЕПАРАТОВ ПРИ РАКЕ МОЧЕВОГО ПУЗЫРЯ
Накопление экспериментальных данных о мутациях и профилях экспрессии различных подтипов РМП, функционировании внутриклеточных сигнальных путей может иметь значение не только для классификации опухолей, но и для разработки новых противоопухолевых агентов, совершенствовании схем назначения уже существующих таргетных препаратов.
Ингибиторы PD-L1
На поверхности опухолевых клеток экспрессируется лиганд PD-L1, кодируемый геном CD274, который соединяется с рецептором PD-1, кодируемым геном
CD279, на поверхности Т-лимфоцита и тем самым предотвращает его цитотоксическое действие на клетки опухоли. В исследовании IMvigor210 у пациентов с метастатическим РМП (n=119), которым была противопоказана полихимиотерапия с цисплатином, в качестве первой линии терапии применялся атезоли-зумаб. Атезолизумаб является гуманизированным моноклональным антителом G1, который ингибирует PD-L1, разрывая связь с рецептором PD-1. В результате Т-лимфоцит получает возможность выполнять свои функции по элиминации опухолевой клетки. Пациентов разделили на группы, основываясь на уровне экспрессии белка PD-L1 на иммунных клетках (IC-index): IC0 – экспрессия PD-L1 <1%, IC1 – экспрессия PD-L1 ≥1 и <5%, IC2/3 – экспрессия PD-L1 ≥5%. Конечная точка исследования – частота объективных ответов (ОО), согласно критериям RECIST version 1.1. При медиане наблюдения 17,2 мес. была достигнута частота ОО 23% (95% ДИ 16-31) среди всех групп. При разделении на группы были получены следующие результаты: IC0 – 21%, IC1 – 21%, IC1/2/3 – 24%, IC2/3 – 28%. Медиана ОВ составила 15,9 месяцев. На данный момент продолжается клиническое исследование 2 фазы IMvigor211, в котором оценивается эффективность атезолизумаба во второй линии терапии. Пока не достигнута конечная точка общей выживаемости (ОВ) [36].
Ингибиторы PD-1
В исследовании KEYNOTE-012 оценивали эффективность пембролизумаба у пациентов с метастатическим РМП, которым невозможно проведения цисплатин-содержащей химиотерапии. Пембролизу-маб является высокоселективным гуманизированным моноклональным иммуноглобулином G4, который ингибирует рецептор PD-1. Механизм действия препарата схож с атезолизумабом: при блокировании рецептора PD-1 разрывается связь с лигандом PD-L1/PD-L2. В исследовании принимали участие только пациенты с экспрессией PD-L1 в строме или с экспрессией PD-L1 в ≥1% опухолевых клеткок. Частота объективных ответов составила 24%, а медиана ОВ 9,3 месяцев [37]. В исследовании KEYNOTE-045 оценивалась эффективность пембролизумаба во второй линии терапии. Показано преимущество в ОВ для группы пембролизумаба по сравнению со второй линией химиотерапии. При уровне экспрессии PD-L1 ≥10% ОВ у больных, получавших пембролизумаб, составила 8, а у больных, получавших химиотерапию – 5,2 месяцев [38].
Ингибиторы с-МЕТ
Белок с-МЕТ является продуктом протоонкогена МЕТ, который часто гиперэкспрессируется в разных типах эпителиальных опухолей. с-МЕТ представляет собой тирозинкиназный рецептор, активируемый лигандом HGF (фактором роста гепатоцитов). При активации запускаются внутриклеточные сигнальные пути, направленные на стимуляцию клеточной пролиферации. Показана связь между активацией с-МЕТ и PDGFR. Гиперэкспрессия МЕТ встречается в 60% случаев местнораспространенного и метастатического РМП и характеризуется неблагоприятным прогнозом. Ингибиторы c-MET находятся на разных стадиях клинических испытаний [39].
Ингибиторы FGFR3
Частота мутаций FGFR3 при НМРМП достигает 60% случаев, а при метастатическом РМП составляет лишь 15%. Однако НМРМП представляет основную форму РМП, встречающуюся у 80% пациентов с этим заболеванием, что делает его одной из наиболее перспективных мишеней для разработки таргетных ингибиторов [6, 11]. Кроме того, мутация FGFR3 характерна для люминально-инфильтративного подтипа РМП, который имеет низкую частоту ответа на иммунную терапию. Этот фактор делает необходимым поиск альтернативных точек воздействия на опухолевые клетки. Эрдафитиниб является ингибитором 4 изоформ рецепторов семейства FGFR. Во 2 фазе клинического исследования пациентам, резистентным к химио- и иммунотерапии, при наличии мутации FGFR3/FGFR2 назначался эрдафитиниб. Частота объективных ответов составила 42%, в отдельных случаях длительность стабилизации процесса составляла более одного года [40]. Как было отмечено выше, применение атезолизумаба и пембролизумаба в первой линии у больных с метастатическим РМП увеличивает общую выживаемость при наличии гиперэкспрессии PD-L1. В настоящее время одобрено использование пембролизумаба во второй линии терапии метастатического РМП. Сейчас согласно клиническим рекомендациям профессиональных сообществ пембролизумаб рекомендован независимо от типа опухоли, если она имеет статус MSI-H, свидетельствующий о высокой частоте мутаций в ге- номе вследствие инактивации генов репарации неспаренных оснований. Проблема в том, что при РМП таких опухолей не более 1%, поэтому и критерий MSI-H не имеет практического значения. Ожидается, что даже еще лучшим предиктором, чем MSI-Н, будет определяемая NGS высокая мутационная нагрузка, но эта гипотеза пока проверяется в ходе реализации научноисследовательских проектов [41].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Таким образом, можно выделить условно три сигнальных пути и около десяти генов, являющихся их компонентами, мутации в которых характерны для двух основных форм РМП: НМРМП и МИРМП. В совокупности с данными секвенирования опухолевых эк-зомов, экспрессионными и иммуногистохимическими профилями эти молекулярно-генетические характеристики позволили усовершенствовать классификацию РМП и привели к необходимости выделения новых молекулярных подтипов. Различные молекулярные подтипы РМП ассоциированы с прогнозом, общей выживаемостью, эффективностью химио- и таргетной терапии, в том числе, ингибиторами иммунных контрольных точек. Основной вопрос, который в связи с изложенным выше ставится сейчас перед прикладными генетическими и иммуногистохимическими исследованиями – в каком виде и в какой мере полученные результаты могут быть имплементированы в практическую онкоурологию? Некоторые молекулярно-генетические характеристики уже сейчас входят в состав диагностических и прогностических тест-систем (мутации FGFR3, TERT, ряд иммуногистохимических маркеров), но основной массив соматических мутаций и изменений в уровне экспрессии генов представляет собой пока лишь отправную точку для поиска новых таргетных препаратов, либо нуждается в дополнительной валидации в качестве потенциальных прогностических маркеров.
ЛИТЕРАТУPA/REFERENC ES
Список литературы Особенности профиля соматических мутаций и функционирования внутриклеточных сигнальных путей на различных стадиях рака мочевого пузыря и их значение для терапии
- Злокачественные новообразования в России в 2017 году (заболеваемость и смертность). [Под ред. А.Д. Каприна, В.В. Старинского, Г.В. Петровой]. МНИОИ им. П.А. Герцена - филиал ФГБУ "НМИЦ радиологии" Минздрава России, 2018, 250 с.
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin 2018;68(6):394-24. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492
- Comperat E., Larre S., Roupret M., Neuzillet Y., Pignot G., Quintens H., et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of urothelial bladder cancer in patients less than 40 years old. Virchows Arch 2015; 466(5):589-94. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-015-1739-2
- Burger M., Catto JW, Dalbagni G., Grossman HB, Herr H., Karakiewicz P., et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2013;63(2):234-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.07.033
- Zhang X., Zhang Y. Bladder cancer and genetic mutations. Cell Biochem Biophys 2015;73(1):65-9. DOI: 10.1007/s12013-015-0574-z
- Robertson AG, Kim J., Al-Ahmadie H., Bellmunt J., Guo G., Cherniack AD, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cell 2017;171(3):540-56.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.007
- Lawrence MS, Stojanov P., Polak P., Kryukov GV, Cibulskis K., Sivachenko A., et al. Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature 2013;499(7457):214-8. 10.1038/ Nature12213.
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12213
- Shi MJ, Meng XY, Lamy P., Banday AR, Yang J., Moreno-Vega A., et al. APOBEC-mediated mutagenesis as a likely cause of FGFR3 S249C mutation over-representation in bladder cancer. Eur Urol 2019;76(1):9-13.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.03.032
- Apollo A., Ortenzi V., Scatena C., Zavaglia K., Aretini P., Lessi F., et al. Molecular characterization of low grade and high grade bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2019;14(1):e0210635.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210635
- Hafner C., Di Martino E., Pitt E., Stempfl T., Tomlinson D., Hartmann A., et al. FGFR3 mutation affects cell growth, apoptosis and attachment in keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res 2010;316(12):2008-16. 10.1016/ j.yexcr.2010.04.021.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.04.021
- Mikhaylenko DS, Alekseev BY, Zaletaev DV, Goncharova RI, Nemtsova MV. Structural alterations in human fibroblast growth factor receptors in carcinogenesis. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2018;83(8): 930-43. 10.1134/ S0006297918080059.
- DOI: 10.1134/S0006297918080059
- Baker DJ, Childs BG, Durik M., Wijers ME, Sieben CJ, Zhong J., et al. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 2016;530(7589):184-9.
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16932
- He S., Sharpless NE. Senescence in health and disease. Cell 2017;169(6):1000-11.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.015
- Downes MR, Weening B., van Rhijn BW, Have CL, Treurniet KM, van der Kwast TH. Analysis of papillary urothelial carcinomas of the bladder with grade heterogeneity: supportive evidence for an early role of CDKN2A deletions in the FGFR3 pathway. Histopathology 2017;70(2):281-9. 10.1111/his. 13063.
- DOI: 10.1111/his.13063
- Graupera M., Guillermet-Guibert J., Foukas LC, Phng LK, Cain RJ, Salpekar A., et al. Angiogenesis selectively requires the p110alpha isoform of PI3K to control endothelial cell migration. Nature 2008;453(7195): 662-6.
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06892
- Segovia C., Martinez-Fernandez M., Duenas M., Rubio C., Lopez-Calderon FF, Costa C., et al. Opposing roles of PIK3CA gene alterations to EZH2 signaling in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2017;8(6):10531-42.
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14453
- Descotes F., Kara N., Decaussin-Petrucci M., Piaton E., Geiguer F., Rodriguez-Lafrasse C., et al. Non-invasive prediction of recurrence in bladder cancer by detecting somatic TERT promoter mutations in urine. Br J. Cancer 2017;117(4):583-7.
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.210
- Allory Y., Beukers W., Sagrera A., Flandez M., Marques M., van der Keur KA, et al. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutations in bladder cancer: high frequency across stages, detection in urine, and lack of association with outcome. Eur Urol 2014;65(2):360-6. 10.1016/ j.eururo.2013.08.052.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.08.052
- Yin M., Grivas P., Emamekhoo H., Mendiratta P., Ali S., Hsu J., et al. ATM/RB1 mutations predict shorter overall survival in urothelial cancer. Oncotarget 2018;9(24):16891-8.
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24738
- Hurst CD, Knowles MA. Bladder cancer: Multi-omic profiling refines the molecular view. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15(4):203-4. 10.1038/ nrclinonc.2017.195.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.195
- Galsky MD. Bladder cancer in 2017: Advancing care through genomics and immune checkpoint blockade. Nat Rev Urol 2018;15(2): 71-2.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.199
- van Rhijn BW, van der Kwast TH, Liu L., Fleshner NE, Bostrom PJ, Vis AN, et al. The FGFR3 mutation is related to favorable pT1 bladder cancer. J. Urol 2012; 187(1):310-4.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.09.008
- Kompier LC, Lurkin I., van der Aa MN, van Rhijn BW, van der Kwast T.H., Zwarthoff EC. FGFR3, HRAS, KRAS, NRAS and PIK3CA mutations in bladder cancer and their potential as biomarkers for surveillance and therapy. PLoS One 2010;5(11):e13821.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013821
- Kim PH, Cha EK, Sfakianos JP, Iyer G., Zabor EC, Scott SN, et al. Genomic predictors of survival in patients with high-grade urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 2015;67(2):198-201. 10.1016/ j.eururo.2014.06.050.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.06.050
- Nordentoft I., Lamy P., Birkenkamp-Demtroder K., Shumansky K., Vang S., Hornshoj H., et al. Mutational context and diverse clonal development in early and late bladder cancer. Cell Rep 2014;7(5):1649-63.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.038
- Van Batavia J., Yamany T., Molotkov A., Dan H., Mansukhani M., Batourina E., et al. Bladder cancers arise from distinct urothelial sub-populations. Nat Cell Biol 2014;16(10):982-91.
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3038
- Glaser AP, Fantini D., Shilatifard A., Schaeffer EM, Meeks JJ. The evolving genomic landscape of urothelial carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol 2017;14(4):215-29.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.11
- Jung S., Wu C., Eslami Z., Tanguay S., Aprikian A., Kassouf W., et al. The role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of flat urothelial lesions: a study using CK20, CK5/6, P53, Cd138, and Her2/Neu. Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18(1):27-32.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2013.10.006
- Hedegaard J., Lamy P., Nordentoft I., Algaba F., Hoyer S., Ulhoi BP, et al. Comprehensive transcriptional analysis of early-stage urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016; 30(1):27-42.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.004
- Lindgren D., Frigyesi A., Gudjonsson S., Sjodahl G., Hallden C., Chebil G., et al. Combined gene expression and genomic profiling define two intrinsic molecular subtypes of urothelial carcinoma and gene signatures for molecular grading and outcome. Cancer Res 2010;70(9):3463-72.
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4213
- Choi W., Porten S., Kim S., Willis D., Plimack ER, Hoffman-Censits J., et al. Identification of distinct basal and luminal subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with different sensitivities to frontline chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 2014;25(2):152-65.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.009
- Rosenberg JE, Hoffman-Censits J., Powles T., van der Heijden MS, Balar AV, Necchi A., et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016;387(10031):1909-20. 10.1016/ S0140-6736(16)00561-4.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00561-4
- Roberts SA, Lawrence MS, Klimczak LJ, Grimm SA, Fargo D, Stojanov P, et al. An APOBEC cytidine deaminase mutagenesis pattern is widespread in human cancers. Nat Genet 2013;45(9):970-6. 10.1038/ ng.2702.
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2702
- Knowles MA, Hurst CD. Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat Rev Cancer 2015;15(1):25-41.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3817
- Kim J., Akbani R., Creighton CJ, Lerner SP, Weinstein JN, Getz G., et al. Invasive bladder cancer: genomic insights and therapeutic promise. Clin Cancer Res 2015;21(20):4514-24.
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1215
- Powles T., Duran I., van der Heijden MS, Loriot Y., Vogelzang NJ, De Giorgi U., et al. Atezolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with platinum-treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (IMvigor211): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018;391:748.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33297-X
- O'Donnell PH, Plimack ER, Bellmunt J., Berger R., Montgomery RB, Heath K., et al. Pembrolizumab (Pembro; MK-3475) for advanced urothelial cancer: Results of a phase IB study. J. Clin Oncol 2015;33(7)suppl:296.
- DOI: 10.1200/jco.2015.33.7_suppl.296
- Bellmunt J., de Wit R., Vaughn DJ, Fradet Y., Lee JL, Fong L., et al. Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl J. Med 2017;376(11):1015-26.
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1613683
- Kim YW, Yun SJ, Jeong P., Kim SK, Kim SY, Yan C., et al. The c-MET network as novel prognostic marker for predicting bladder cancer patients with an increased risk of developing aggressive disease. PLoS One 2015;10(7):e0134552.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134552
- News. Erdafitinib Efficacious in Bladder Cancer. Cancer Discov 2018;8(8):OF6.
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2018-085
- Михайленко Д.С., Сергиенко С.А., Заборский И.Н., Сафиуллин К.Н., Серебряный С.А., Сафронова Н.Ю. и др. Роль молекулярно-генетических изменений в прогнозе эффективности адъювантной внутрипузырной терапии немышечно-инвазивного рака мочевого пузыря. Онкоурология 2018;14(4): 124-38.
- DOI: 10.17650/1726-97762018-14-4-124-138


