Особенности воздействия ионов меди и стронция на ряску малую (Lemna minor L.)
Автор: Боднарь Ирина Сергеевна, Чебан Евгения Васильевна, Зайнуллин Владимир Габдуллович
Журнал: Принципы экологии @ecopri
Рубрика: Оригинальные исследования
Статья в выпуске: 2 (27) т.7, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В данной работе изучены морфометрические изменения и уровень окислительного стресса при воздействии ионов стронция и меди на лабораторную культуру ряски малой (Lemna minor L.). Медь обладает чрезвычайной реакционной способностью, поэтому более токсична для ряски, чем стронций. Показано, что угнетение удельной скорости роста относительно контроля произошло при внесении 0.6 ммоль/л стронция и 3.15 мкмоль/л меди (p ≤ 0.05). Повреждения в виде хлорозов появились при 0.3 ммоль/л стронция, 0.21 мкмоль/л меди. В градиенте концентраций при воздействии стронция изменилась окраска растений от зелено-желтой до желтой. Медь привела к побурению листовых пластинок (фрондов), корни побелели и отмерли при низких концентрациях (от 0.3 мкмоль/л). При высоких концентрациях ионов меди и стронция все растения некротически повреждены. Установлено, что при воздействии тяжелых металлов сократилась средняя площадь фрондов. Минимальная площадь наблюдалась при внесении 1.1 ммоль/л стронция и 5 мкмоль/л меди (начальная площадь уменьшилась на 23 и 42 % соответственно). Увеличение внутриклеточного уровня тяжелых металлов привело к нарушению окислительно-восстановительного баланса и накоплению активных форм кислорода. Уровень малонового диальдегида, маркера окислительного стресса, возрастал при увеличении концентрации металлов в среде (p ≤ 0.05). Медь является более редокс-активным металлом, чем стронций. Установлено, что уровень МДА статистически значимо выше по сравнению с контролем начиная с 0.63 ммоль/л стронция и 5 мкмоль/л меди (p ≤ 0.05).
Ряска малая, фитотоксичность, медь, стронций, окислительный стресс
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147231212
IDR: 147231212 | УДК: 581.1
Текст научной статьи Особенности воздействия ионов меди и стронция на ряску малую (Lemna minor L.)
Растения являются основой большинства естественных биоценозов, играют важную роль, являясь продуцентами первичных органических веществ, стоят в основании пищевой пирамиды. Воздействие на них различных поллютантов, в том числе и тяжелых металлов, приводит к снижению устойчивости биоценозов. Стронций и медь являются естественными компонентами водных и наземных экосистем. Однако из-за антропогенной деятельности концентрации этих металлов локально повышаются до уровней, которые создают потенциальный экологический риск. Стронций - щелочноземельный металл, аналог кальция, доступен для растений и хорошо переносится вверх по пищевой цепи (Кабата-Пендиас, Пендиас, 1989). Для растений этот элемент является несущественным, но может замещать кальций при его недостатке (Miller et al., 1993). Это особенно опасно при загрязнении окружающей среды радиоактивным стронцием (Kanter et al., 2010). Загрязнение почв, вод и растений стабильным стронцием вызвано длительным применением в сельском хозяйстве фосфатных удобрений, стронцийсодержащих мелиорантов и отходов промышленности (Карпова, Потатуева, 2004; Литвинович, Лаврищев, 2008). Изотоп стронция - 90Sr - причина радиоактивного загрязнения окружающей среды при ядер-ных испытаниях, утилизации радиоактивных отходов, а также при авариях на предприятиях ядерно-топливного цикла. 90Sr образует преимущественно растворимые формы и переносится водными массами на большие расстояния, поэтому потенциально опасен для водных организмов (Сапожников и др., 2006). Преобразования 90Sr в водной среде сопоставимы со стабильным стронцием (Tsukada et al., 2005; Zheng et al., 2016). Особенности воздействия стабильного изотопа на растительные организмы могут быть использованы при прогнозировании последствий загрязнения радиоактивным 90Sr.
Самый большой источник загрязнения окружающей среды медью - промышленные и сельскохозяйственные отходы (Yruela, 2009). Медь входит в состав ряда ферментов, в первую очередь - оксидоредуктаз, являющихся необходимыми участниками реакций энергетического обмена у всех аэробных организмов. Медь участвует в широком диапазоне биохимических и физиологических процессов в клетках растений, действует как кофактор Cu, Zn-супероксиддисмутазы и других ферментов. Окислительновосстановительный цикл между двумя ее ионными формами может привести к образованию активных форм кислорода (АФК). Медь потенциально является высокотоксичным тяжелым металлом ввиду возможности ошибочного связывания с неспецифическими сайтами в молекулах белков и других соединений. Кроме того, медь, будучи редокс-активным металлом, потенциально может напрямую участвовать в генерации АФК (Vidaković-Cifrek et al., 2015).
Целью данного исследования является изучение морфометрических изменений и уровня окислительного стресса у ряски малой при воздействии ионов стронция и меди.
В качестве объекта исследования выбрана ряска малая. Представители семейства рясковые ( Lemnaceae ) являются перспективным экспериментальным объектом для экотоксикологических исследований и биомониторинга в силу своей химической чувствительности. Ряска малая ( Lemna minor L. ) – однодольное покрытосеменное растение, неукорененный плейстофит, с упрощенным строением (Тахтаджян, 1982). Она широко используется для тестирования воды с природных водоемов и сточных вод на токсичность.
Материалы
В работе использована лабораторная культура ряски малой Института биологии КНЦ УрО РАН. Растения культивировали в среде Штейнберга (Steinberg, 1946). Культивирование проводили в климатической камере при температуре 24 ± 0.1 °С, фотопериодичности 16 ч свет / 8 ч темнота, 70 % влажности. Интенсивность света 8000 люкс, представлена холодно-белым светом люминесцентных ламп. При проведении эксперимента колонии, состоящие из 2–4 фрондов, отбирали из материнской культуры и переносили в стерилизованные стеклянные чашки. Каждая экспериментальная емкость содержала 9-12 пластинок. Воздействие проводили в течение 7 дней, в соответствии с рекомендациями OECD (2006). Определяли морфометрические показатели: удельную скорость роста, повреждения (хлорозы и некрозы), площадь фрондов. В работе в качестве источника ионов стронция использовали - Sr(NO3)2, ионов меди - СиС12^2Н2О. Используемые концентрации стронция от 0 до 1.58 ммоль/л, меди – от 0 до 12.6 мкмоль/л. В качестве контроля применяли растения, выращенные на среде Штейнберга.
Методы
Средняя удельная скорость роста - лога-рифметическое увеличение темпа роста – количества фрондов для каждой параллели опытных и контрольных групп (OECD, 2006).
д._= (In (Nj) - In (Ni))/1, где μi-j – средняя удельная скорость роста от времени i до времени j,
N . - переменная теста в опыте во время. / ' ,
Ni - переменная теста в контроле во время i, t – период времени от i до j.
Для определения времени удвоения ( Td ) числа фрондов для проверки на соответствие критерию достоверности (удвоение в контроле менее чем за 60 часов) использовали следующую формулу:
Td = ln2 / μ .
Расчет площади фронда проводили по фотографиям, до воздействия и через семь дней после (OECD, 2006). Изображения проанализированы с помощью программного обеспечения Image J ( NIH, USA). В работе использовали отношение площадей до и после воздействия: S2 / S1 , где S1 - площадь в начале эксперимента, мм; S2 - площадь через 7 дней, мм.
Для определения уровня малонового диальдегида (МДА) ряску предварительно содержали в экспериментальном растворе в течение четырех дней (Uruç Parlac, Demirezen, 2012). МДА определяли следующим образом: 50 мг растительного материала гомогенизировали в 1.5 мл 20 % трихлоруксусной кислоте с кварцевым песком, центрифугировали при 10 000 g в течение 15 минут. К отобранным 0.3 мл супернатанта добавили 1.2 мл 0.5 % тиобарбитуровой кислоты в 20 % трихлоруксусной кислоте. Реакционную смесь инкубировали 30 минут при 95 °С, затем быстро охладили для того, чтобы остановить реакцию, центрифугировали 15 мин при 10 000 g. Оптическую плотность супернатанта определяли при 532 нм и 600 нм. В качестве контроля использовали раствор тиобарбитуровой кислоты в трихлоруксусной кислоте. Содержание МДА определяли по формуле:
Cx =(E532 — E600)• Ve / k• ms• Va, где Сx – содержание МДА, нмоль/л сырой массы; E – оптическая плотность раствора; Ve- объем экстракта, взятый для анализа, мл; k – коэффициент молярной экстинкции МДА: 156 мМ-1хсм-1; ms - масса образца для экстракции (Молекулярно-генетические и биохимические методы…, 2012).
Статистическую обработку проводили с использованием программного пакета Statistica 6.0. Статистическую значимость отличий между параметрами в опыте и контроле определяли с помощью критерия Стьюдента, Манна – Уитни, одностороннего дисперсионного анализа.
Результаты
Торможение роста – это основной ответ растительных организмов на воздействие тяжелых металлов, интегральная характеристика многих происходящих процессов. Однофакторный дисперсионный анализ данных показал, что имеется прямая зависимость между содержанием ионов металлов в растворе и удельной скоростью роста лабораторной культуры ряски малой (р ≤ 0.05). Наименьшая эффективная наблюдаемая концентрация, при которой происходило угнетение роста, для стронция составила 0.6 ммоль/л, для меди 3.15 мкмоль/л (рис. 1, 2). Удельная скорость роста снизилась при 0.179, 0.95, 1.1, 1.27 ммоль/л стронция на 25.3, 34, 45 и 48.3 % соответственно по сравнению с контролем. Воздействие меди в концентрациях 5, 6.3, 9.45, 12.6 мкмоль/л привело к снижению темпа роста ряски относительно контроля на 59.5, 58, 83.3, 79.3 % соответственно. При максимальных исследуемых концентрациях скорость роста относительно контроля уменьшилась на 73.3 % для 1.58 ммоль/л стронция и на 80 % для 12.6 мкмоль/л меди.
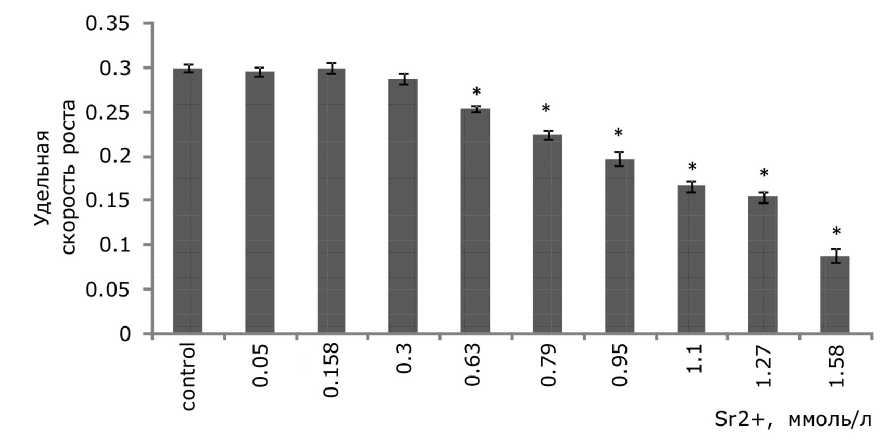
Рис. 1. Изменение удельной скорости роста ряски малой в зависимости от содержания ионов стронция в среде для культивирования. * – отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 1. The change in the specific growth rate of duckweed depending on the concentration of strontium ions in the culture medium. * - the differences are significant in comparison with controls ( p ≤ 0.05), the Student's test
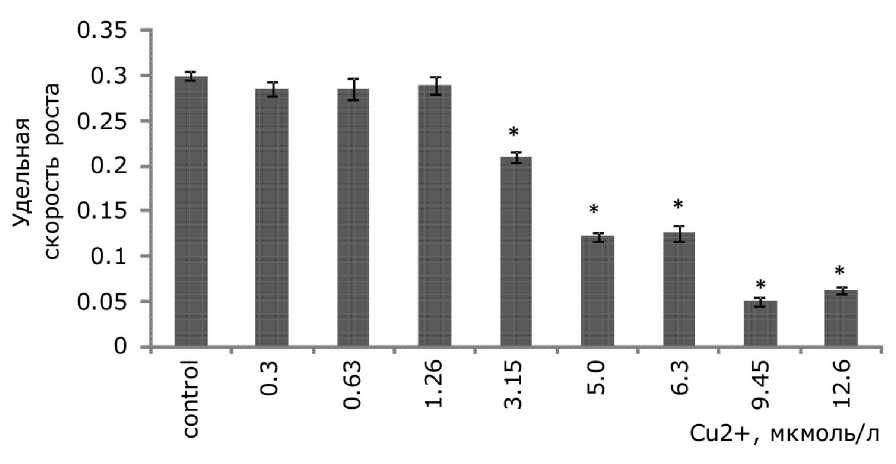
Рис. 2. Изменение удельной скорости роста ряски малой в зависимости от содержания ионов меди в среде для культивирования. * – отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем (p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 2. The change in the specific growth rate of duckweed depending on the concentration of copper ions in the culture medium. * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls (p ≤ 0.05), the Student's test
При воздействии тяжелых металлов появились повреждения поверхности зеленых пластинок в виде хлорозов и некрозов. Уровень поврежденных растений увеличивался с возрастанием концентрации металла в растворе (р ≤ 0.05). Повреждения в виде хлорозов появились при 0.3 ммоль/л стронция, 0.211 мкмоль/л меди (рис. 3, 4). Высокий уровень растений с хлорозами и некрозами (свыше 60 % от общего числа растений) наблюдался при культивировании ряски с добавлением 0.948 ммоль/л стронция и 5 мкмоль/л меди. Основным типом повреж- дений при высоких концентрациях являлись некрозы. Для обоих тяжелых металлов наименьшие эффективные наблюдаемые концентрации, при которых возникли повреждения листовой поверхности, ниже, чем те, что привели к угнетению удельной скорости роста.
В градиенте концентрации при воздействии стронция произошло изменение цвета фрондов от зелено-желтого до желтого. Воздействие меди привело к бурой окраске листьев, корни белели и отпадали уже при концентрации 0.3 мкмоль/л.
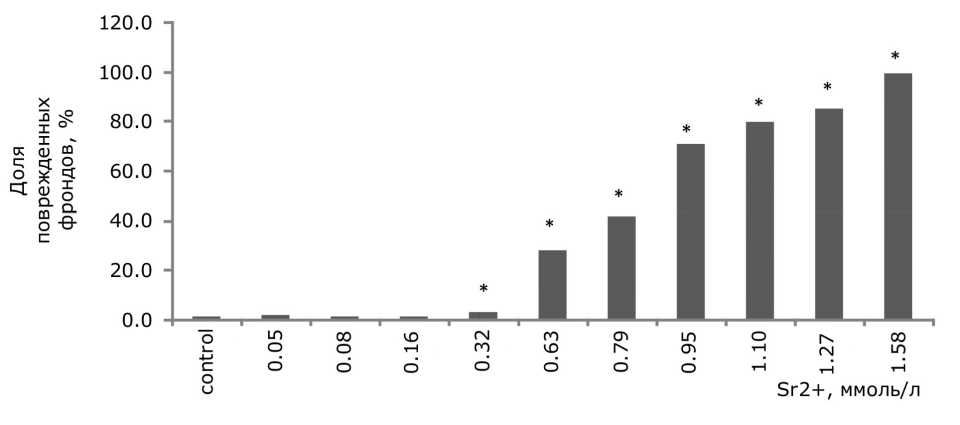
Рис. 3. Доля поврежденных фрондов ряски малой в зависимости от содержания ионов стронция в среде для культивирования. * – отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Манна – Уитни
Fig. 3. Fraction of damaged duckweed fronds, depending on the content of strontium ions in the culture medium. * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls ( p ≤ 0.05), Mann – Whitney’s test
При воздействии рассматриваемых тяжелых металлов на ряску малую произошло снижение площади поверхности фрон-дов. Площадь уменьшалась по сравнению с контрольными растениями начиная с 0.316 ммоль/л стронция и 0.63 мкмоль/л меди (рис. 5, 6). Минимальная площадь фрондов наблюдалась при концентрации стронция 1.1 ммоль/л, меди – 5 мкмоль/л, средняя площадь листовой пластинки (фронда) сократилась на 23 и 42 % соответственно по сравнению с изначальной до воздействия тяжелых металлов. Зависимость между концентрацией ионов металлов и изменением площади поверхности фронда нелинейная. При увеличении концентрации исследуемых веществ в растворе средняя площадь уменьшалась, при воздействии высоких концентраций оставалась прежней, так как рост новых растений почти полностью подавлен, и остаются лишь родительские растения с изначальной площадью листовой поверхности.
Однофакторный дисперсионный анализ показал, что при увеличении концентрации ионов тяжелых металлов в растворе уровень МДА у ряски малой повысился (p ≤ 0.05). Стронций и медь спровоцировали развитие окислительного стресса у растений. Уровень МДА при воздействии стронция статистически значимо выше по сравнению с контролем начиная с 0.63 ммоль/л, меди – с 5 мкмоль/л (рис. 7, 8). Концентрация МДА при воздействии стронция достигла 46 ± 1.6 нмоль/г сырой массы, что в 3.6 раза выше, чем в контроле. При воздействии меди в высоких концентрациях уровень МДА выше и составлял 63.45 ± 2.2 нмоль/г сырой массы, что в 5.4 раза выше, чем в контроле.
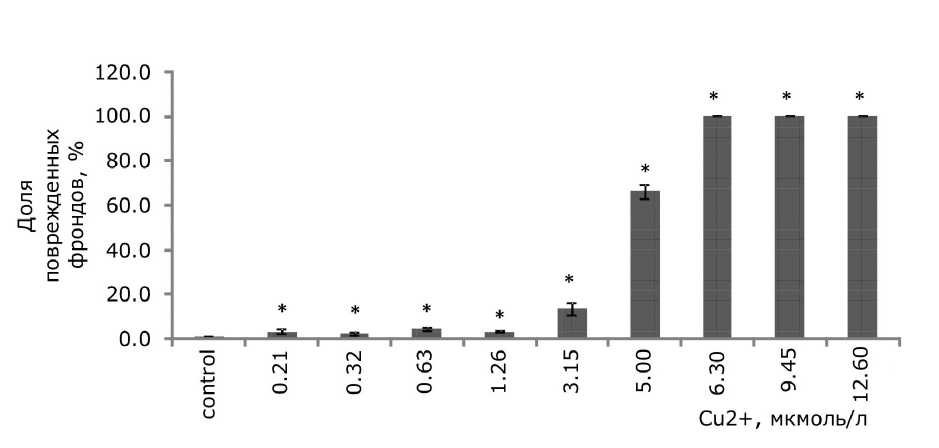
Рис. 4. Доля поврежденных фрондов ряски малой в зависимости от содержания ионов меди в среде для культивирования. * – отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем (p ≤ 0.05), критерий Манна –
Уитни
Fig. 4. Fraction of damaged duckweed fronds depending on the content of copper ions in the culture medium. * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls (p ≤ 0.05), Mann-Whitney’s test
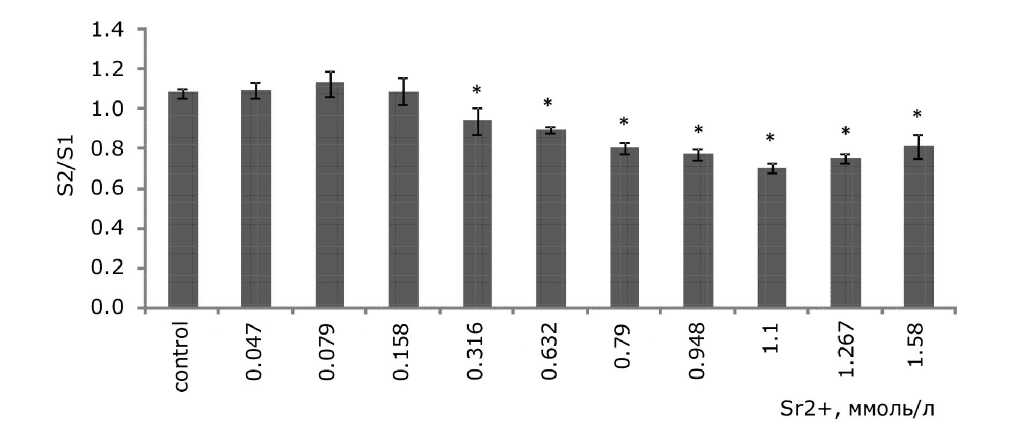
Рис. 5. Изменение площади фрондов ряски малой в зависимости от концентрации ионов стронция в растворе ( S2 / S1 – отношение площадей фрондов, S1 – первоначальная площадь фрондов, мм; S2 – площадь фрондов через 7 дней, мм). * – отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 5. Change in the area of the duckweed fronds as a function of the concentration of strontium ions in the solution ( S2 / S1 is the ratio of the fronds areas , S1 is the original area of the fronds, mm; S2 is the area of the fronds after 7 days, mm). * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls ( p ≤ 0.05), the Student's test
Обсуждение
Тяжелые металлы относятся к одним из самых распространенных загрязнителей окружающей среды. На разных видах высших растений показано, что воздействие токсичных концентраций меди (3–100 ммоль/л) приводило к снижению биомассы, изменению содержания воды, хлорозам, некрозам, ингибированию роста побегов, удлинению корней, сокращению скорости прорастания семян, уменьшению содержания хлорофилла и изменению структуры хлоропластов и мембран тилакоидов в листьях шпината, риса, пшеницы (Ahsan et al., 2007; Baszynski et al., 1988; Lidon, Henriques, 1993; Ciscato et al., 1997; Pätsikkä et al., 1998; Quartacci et al., 2000; Panou-Filotheou et al., 2001). Ряска малая является активным аккумулятором тяжелых металлов, что используется в экоток-сикологических экспериментах. В данном исследовании показано, что уже при 0.315 мкмоль/л меди произошло снижение удельной скорости роста лабораторной культуры ряски малой относительно контроля. Видимые повреждения листовой поверхности в виде хлорозов появились при более низкой концентрации 0.2 мкмоль/л. Для изменения площади листовой поверхности требуется 0.63 мкмоль/л меди. Характерными особенностями действия меди является бурая окраска фрондов и потеря растениями корней начиная с 0.3 мкмоль/л.
В силу своей реакционной способности медь показала себя токсичнее стронция по всем рассматриваемым морфологическим параметрам. Стронций привел к угнетению скорости роста ряски малой с 0.6 ммоль/л и возрастанию доли растений с хлорозами относительно контроля начиная с 0.3 ммоль/л (р ≤ 0.05). При воздействии стронция (0.316– 1.58 ммоль/л) сократилась площадь листовой поверхности (фрондов). Медь обладает чрезвычайной реакционной способностью, поэтому более токсична для растений, чем стронций. Медь имеет высокое сродство SH-группам, стронций подобно кальцию не образует прочных соединений с тиолами. При реакции ионов металлов с cульфгидрильными группами образуются нерастворимые, слабо диссоциирующие меркаптиды, что является причиной осаждения белков. Показано, что независимо от вида растений Сu2+ при одинаковом заряде иона с Cd2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Zn2+ оказывается токсичнее, поскольку име- ет наивысшую плотность заряда, высокую электроотрицательность, что обуславливает способность меди оттягивать электроны и образовывать комплексы с биологически важными соединениями (Евсеева, 2006).
Характерная особенность действия стронция, наблюдаемая и у ряски, – это увеличение длины корней. Рост корней при избытке стронция объясняется излишней растяжимостью клеток. Одним из механизмов действия тяжелых металлов на растяжение клеток может быть изменение пластичности клеточных оболочек. Чем больше сродство металла к карбоксильным группам уроновых кислот, входящих в состав оболочек, тем в большей степени снижается их эластичность. Стронций, поглощаясь в зоне растяжения и накапливаясь в апопласте, образует менее прочные по сравнению с кальцием связи с уроновыми кислотами, в результате чего пластичность оболочек может несколько увеличиваться, в том числе и благодаря конкуренции с ионами кальция, аналогом которого он является (Кожевникова и др., 2009).
Механизмы токсического действия меди активно изучаются. Предположительно, медь мешает биосинтезу фотосинтетического аппарата, модифицирующих пигментов и белкового состава фотосинтетических мембран (Lidon, Henriques, 1991; Maksymiec et al., 1994; Pätsikkä et al., 2002) Медь негативно влияет на фотосистему II (ФСII). Медь ингибирует рост и нарушает клеточные процессы, такие как фотосинтез и дыхание (Marschner, 1995; Prasad, Strzalka, 1999; Yruela, 2005). Замена центрального Mg-иона хлорофилла медью приводит к ингибированию фотосинтеза (Küpper et al., 2003; Küpper, Kroneck, 2005). При высоких уровнях медь сильно фитотоксична и может привести к задержке роста, хлорозам, некрозам и депигментации листьев. На молекулярном уровне происходит связывание сульфгидрильных групп белков, что отрицательно сказывается на поглощениии эссенциальных элементов и процессах переноса в клетке (Vidacovic-Cifrek et al., 2015).
Тяжелые металлы реагируют с функциональными группами белков, что приводит к изменению конформации белков и потере активности многих ферментов, а значит, нарушает метаболизм клеток (Иванов и др., 2001). Это влечет ингибирование активности или разрушение структур с перемеще-
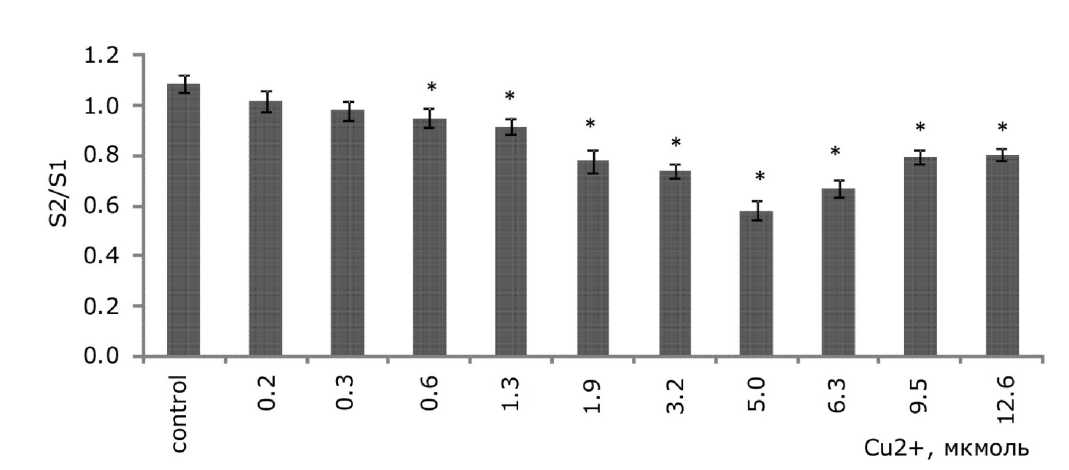
Рис. 6. Изменение площади фрондов ряски малой в зависимости от концентрации ионов меди в растворе ( S2 / S1 - отношение площадей фрондов, S1 - первоначальная площадь фрондов, мм; S2 - площадь фрондов через 7 дней, мм). * - отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем ( p < 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 6. Change in the area of duckweed fronds as a function of the concentration of copper ions in the solution ( S2/S1 is the ratio of the fronds areas; S1 is the original area of the fronds, mm; S2 is the area of the fronds after 7 days, mm). * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls ( p ≤ 0.05), the Student's test
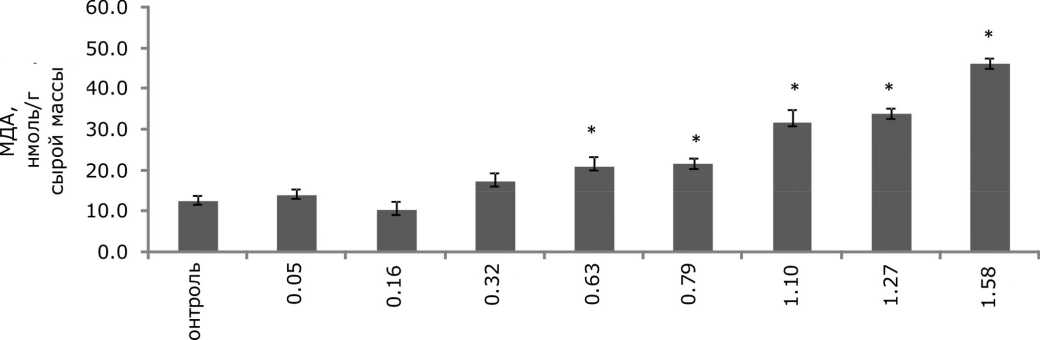
Sr2+, ммоль/л
Рис. 7. Изменение содержания малонового диальдегида в клетках ряски малой в зависимости от концентрации ионов стронция в среде для культивирования. * - отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Манна – Уитни
Fig. 7. Change in the concentration of malondialdehyde in duckweed cells, depending on the concentration of strontium ions in the medium for cultivation. * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls ( p ≤ 0.05), Mann – Whitney’s test
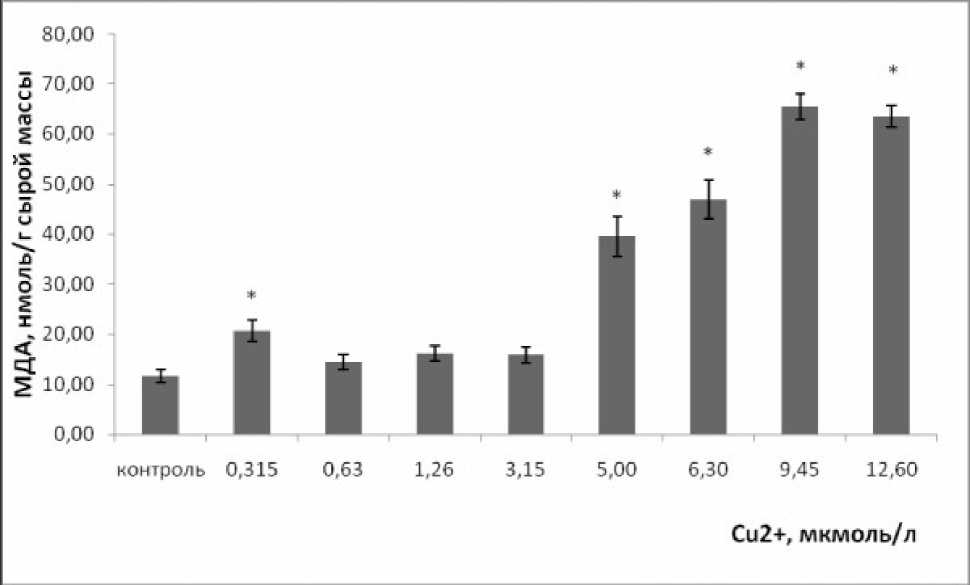
Рис. 8. Изменение содержания малонового диальдегида в клетках ряски малой в зависимости от концентрации ионов меди в среде для культивирования. * – отличия достоверны по сравнению с контролем ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Манна – Уитни
Fig. 8. Change in the concentration of malondialdehyde in duckweed cells, depending on the concentration of copper ions in the medium for cultivation. * – the differences are significant in comparison with controls ( p ≤ 0.05), Mann – Whitney’s test
нием существенных элементов, таких как цинк, магний, кальций, железо, вызывая дополнительные эффекты дефицита (Su et al., 2007). При замене кальция на стронций, ион которого имеет сходные с ионом кальция физико-химические свойства, он не играет функциональной роли, свойственной последнему (Костюк, 1986). Sr2+ передвигается преимущественно по апопласту. В дополнение к апопластному пути со стронцием связаны различные кальциевые каналы (White, 2001; White et al., 2002).
Одной из причин токсичности тяжелых металлов является развитие в клетках окислительного стресса, вызванного образованием избыточного количества активных форм кислорода (АФК), обладающих чрезмерно высокой реакционной способностью. АФК представляют серьезную угрозу, так так могут подавлять активность ферментов, вызывать повреждения нуклеиновых кислот, плазмолеммы. При низких концентрациях АФК выполняют роль ключевых сигнальных молекул, участвуют в регуляции важнейших биологических процессов, экспрессии генов (Marschner, Cakmak, 1989). Переходные металлы, такие как медь, катализируют об- разование гидроксильных радикалов (OH*) от неферментативной химической реакции между супероксидом (O2*) и перекисью H2O2 (реакция Хабера – Вайса) (Halliwell, Gutteridge, 1984). Следовательно, избыток меди может вызвать окислительный стресс у растений, увеличение содержания высокотоксичных свободных радикалов, изменения в активности и содержании некоторых антиоксидантов (De Vos et al., 1992; Luna et al., 1994; Stohs, Bagchi, 1995; Gupta et al., 1999). Высокий уровень окислительного стресса приводит к повреждению клеточных мембран, фотосинтетических пигментов, белков, нуклеиновых кислот и липидов, в конечном итоге к гибели клетки (Sasmaz, 2016). Окислительный стресс является причиной перекисного окисления липидов (ПОЛ), возникает целый каскад последовательных свободнорадикальных реакций с образованием различных химических соединений (спиртов, альдегидов, кетонов), обладающих высокой биологической активностью и токсичностью. В результате ПОЛ нарушается структура клеточных мембран, снижается их пластичность, изменяется проницаемость. Помимо перекисного окисления липидов, при воздействии меди происходит снижение содержания липидов и изменение состава жирных кислот тилакоидных мембран (Sadmann, Böger, 1980; Luna et al., 1994; Maksymiec et al., 1994). В результате этих изменений было обнаружено изменение текучести мембран (Quartacci et al., 2000). При распаде жирных кислот, сопровождающем ПОЛ, первоначально образуются диеновые коньюгаты, а затем такие метаболиты, как малоновый диальдегид. МДА – продукт разложения полинасыщенных жирных кислот биомембран, и его увеличение показывает, что растения находятся в стадии высокого уровня окислительного стресса (Загоскина, Назаренко, 2016). При средних и высоких концентрациях меди (от 5 до 12.6 мкмоль/л) уровень МДА у ряски выше, чем у контрольных растений. При данных концентрациях у ряски малой темпы роста сократились более чем на 60 % относительно контрольных растений, доля поврежденных растений в культуре выше 60 %, на 40 % уменьшилась площадь листовой поверхности (фронда). При воздействии стронция уровень МДА у растений повысился при концентрациях на два порядка выше, чем у меди, – от 0.632 до 1.58 ммоль/л. При данных концентрациях у растений также наблюдались морфометрические изменения, снизилась удельная скорость роста, площадь фрондов, увеличилась доля растений с хлорозами и некрозами.
Заключение
Увеличение внутриклеточного уровня тяжелых металлов привело к нарушению окислительно-восстановительного баланса в растительной клетке и накоплению активных форм кислорода. В силу большей реакционной способности медь токсичнее стронция. Высокий уровень окислительного стресса сопровождался значительным увеличением доли растений с хлорозами и некрозами, сокращению площади фрондов, низкой удельной скорости роста растений.
Список литературы Особенности воздействия ионов меди и стронция на ряску малую (Lemna minor L.)
- Евсеева Т. И., Белых Е. С., Майстренко Т. А. Закономерности индукции цитогенетических эффектов у растений при действии тяжелых металлов [Regularities in the induction of cytogenetic effects in plants under the action of heavy metals] // Вестник Института биологии. 2005. № 1. С. 2-;11.
- Загоскина Н. В., Назаренко Л. В. Активные формы кислорода и антиоксидантная система растений [Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant system of plants] // Вестник МГПУ. Сер.: Естественные науки. 2016. № 2. С. 9-;23.
- Иванов В. Б., Быстрова Е. И., Сергин И. В. Сравнение влияния тяжелых металлов на рост корня в связи с проблемой специфичности и избирательности их действия [Comparison of the influence of heavy metals on root growth in connection with the problem of specificity and selectivity of their action] // Физиология растений. 2001. Т. 48. С. 606-;630.
- Кабата-Пендиас А., Пендиас Х. Микроэлементы в почвах и растениях [Microelements in soils and plants]. М.: Мир, 1989. 439 с.
- Карпова Е. А., Потатуева Ю. А. Последствия применения различных форм фосфорных удобрений: стронций в системе дерново-подзолистая почва -; растения [Consequences of application of various forms of phosphorus fertilizers: strontium in the sod-podzolic soil system -; plants] // Агрохимия. 2004. С. 91-;96.
- Кожевникова А. Д., Серегин И. В., Быстрова Е. И., Беляева А. И., Катаева М. Н., Иванов В. Б. Влияние нитратов свинца, никеля и стронция на деление и растяжение клеток корня кукурузы [Effect of lead, nickel and strontium nitrates on the division and extension of corn root cells] // Физиология растений. 2009. Т. 56. № 2. С. 268-;277.
- Костюк П. Г. Кальций и клеточная возбудимость [Calcium and cellular irritability]. М.: Наука, 1986. 255 с.
- Литвинович А. В., Лаврищев А. В. Стронций в системе удобрения (мелиоранты)-почва-растения-животные (человек) [Strontium in the system of fertilizer (meliorants)-soil-plants-animals (human)] // Агрохимия. 2008. № 5. С. 73-;86.
- Молекулярно-генетические и биохимические методы в современной биологии растений [Molecular-genetic and biochemical methods in modern plant biology] / Под ред. Вл. В. Кузнецова, В. В. Кузнецова, Г. А. Романова. М.: БИНОМ, 2011. С. 348-;349.
- Сапожников Ю. А., Алиев Р. А., Калмыков С. Н. Радиоактивность окружающей среды [Environmental Radioactivity]. М.: БИНОМ, 2006. 286 с.
- Тахтаджян А. Л. Жизнь растений [Plant life]. М.: Просвещение, 1982. Т. 6. С. 493-;500.
- Ahsan N., Lee D.-G., Lee S.-H., Kang K. Y., Lee J. J., Kim P. J., Yoon H.-S., Kim J.-S., Lee B.-H. Excess copper induced physiological and proteomic changes in germinating rice seeds // Chemosphere. 2007. Vol. 67. P. 1182-;1193.
- Baszynski T., Tukendorf A., Ruszkowska M., Skórzynska E., Maksymiec W. Characteristics of the photosynthetic apparatus of copper nontolerant spinach exposed to excess copper // Journal of Plant Physiology. 1988. Vol. 132. P. 708-;713.
- Ciscato M., Valcke R., van Loven K., Clijsters H., Navari-Izzo F. Effects of in vivo copper treatment on the photosynthetic apparatus of two Triticum durum cultivars with different stress sensitivity // Physiologia Plantarum. 1997. Vol. 100. P. 901-;908.
- De Vos C. H. R., Schat H., De Waal M. A. M., Voojis R., Ernst W. H. O. Increased resistance to copper-induced damage of the root cell plasmalemma in copper tolerant Silene cucubalus // Physiologia Plantarum. 1991. Vol. 82. P. 523-;528.
- Gupta M., Cuypers A., Vangronsveld J., Clijsters H. Copper affects the enzymes of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and its related metabolites in the roots of Phaseolus vulgaris // Physiologia Plantarum. 1999. Vol. 106. P. 262-;267.
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. C. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease // The Biochemical Journal. 1984. Vol. 219. P. 1-;14.
- Kanter V., Hausen A., Michalke B., Draxi S., Schäffner A. Caesium and strontium accumulation in shoots of Arabidopsis thaliana: genetic and physiological aspects genetic and physiological aspects // Journal of Experimental. 2010. Vol. 61. № 14. P. 3995-;4009.
- Küpper H., Kroneck P. M. H. Heavy metal uptake by plants and cyanobacteria // Metal Ions in Biological Systems. 2005. Vol. 44. P. 97-;144.
- Küpper H., Šetlík I., Šetliková E., Ferimazova N., Spiller M., Küpper F. C. Copper-induced inhibition of photosynthesis: limiting steps of in vivo copper chlorophyll formation in Scenedesmus quadricauda // Functional Plant Biology. 2003. Vol. 30. P. 1187-;1196.
- Lidon F. C., Henriques F. S. Limiting step in photosynthesis of rice plants treated with varying copper levels // Journal of Plant Physiology. 1991. Vol. 138. P. 115-;118.
- Lidon F. C., Henriques F. S. Changes in the thylakoid membrane polypeptide patterns triggered by excess Cu in rice // Photosynthetica. 1993. Vol. 28. P. 109-;117.
- Luna C. M., González A., Trippi V. S. Oxidative damage caused by excess of copper in oat leaves // Plant & Cell Physiology. 1994. Vol. 35. P. 11-;15.
- Maksymiec W., Russa R., Urbanik-Sypniewska T., Baszynski T. Effect of excess Cu on the photosynthetic apparatus of runner bean leaves treated at two different growth stages // Physiologia Plantarum. 1994. Vol. 91. P. 715-;721.
- Marschner H., Cakmak I. High light intensity enhances chlorosis and necrosis in leaves of Zn, K and Mg deficient plants // J. Plant. Physiol. 1989. Vol. 134. P. 308-;315.
- Marschner H. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Boston, 1995. 889 p.
- Miller E. K., Blum J. D., Friedland A. J. Determination of soil exchangeablecation loss and weathering rates using Sr isotopes // Nature. 1993. Vol. 362. P. 438-;441.
- OECD Guidelines for the testing chemicals. Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Paris, 2006.
- Panou-Filotheou H., Bosabalidis A. M., Karataglis S. Effects of copper toxicity on leaves of oregano (Origanum vulgare hirtum) // Annals of Botany. 2001. Vol. 88. P. 207-;214.
- Pätsikkä E., Aro E.-M., Tyystjärvi E. Increase in the quantum yield of photoinhibition contributes to copper toxicity in vivo // Plant Physiology. 1998. Vol. 117. P. 619-;627.
- Pätsikkä E., Kairavuo M., Sersen F., Aro E-M., Tyystjärvi E. Excess copper predisposes photosystem II to photoinhibition in vivo by outcompeting iron and causing decrease in leaf chlorophyll // Plant Phisiolog. 2002. Vol. 129. P. 1359-;1367.
- Prasad M. N. V., Strzalka K. Impact of heavy metals on photosynthesis // Heavy metal stress in plants. 1999. P. 117-;138.
- Quartacci M. F., Pinzino C., Sgherri C. L. M., Dalla Vecchia F., Navari-Izzo F. Growth in excess copper induces changes in the lipid composition and fluidity of PSII-enriched membranes in wheat // Physiologia Plantarum. 2000. Vol. 108. P. 87-;93.
- Sadmann G., Böger P. Copper-mediated lipid peroxidation processes in photosynthetic membranes // Plant Physiology. 1980. Vol. 66. P. 797-;800.
- Sasmaz M., Obek E., Sasmaz A. Bioaccumulaton of uranium and thorium by Lemna minor and Lemna gibba in Pb-Zn-Ag tailing water // Bull. Environ Contam Toxicol. 2016. Vol. 96. № 3. P. 832-;837.
- Steinberg R. Mineral requirement of Lemna minor // Plant Physiol. 1946. Vol. 21. P. 42-;48.
- Stohs S. J., Bagchi D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions // Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 1995. Vol. 18. P. 321-;336.
- Su Y., Maruthi B., Sridhar B., Han F. X., Diehl S. V., Monts D. L. Effect of bioaccumulation of Cs and Sr natural isotopes on foliar structure and plant spectral reflectance of Indian mustard (Brassica Juncea) // Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007. Vol. 180. P. 65-;74.
- Tsukada H., Takeda A., Takahashi T., Hasegawa H., Hisamatsu S., Inaba J. Uptake and distribution of 90Sr and stable Sr in rice plants // J. Environ. Radio. 2005. Vol. 81. P. 221-;231.
- Uruç Parlac K., Demirezen Yilmaz D. Response of antioxidant defences to Zn stress in three duckweed species // Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2012. № 85. P. 52-;58.
- Vidaković-Cifrek Ž., Tkalec M., Šikić S., Tolić S., Lepeduš H., Pevalek-Kozlina B. Growth and photosynthetic responses of Lemna minor exposed to cadmium in combination with zinc or copper // Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2015. Vol. 66. P. 141-;152.
- White P. J. The pathways of calcium movement to the xylem // Journal of Experomental Botany. 2001. Vol. 52. P. 891-;899.
- White P. J., Bowen H. C., Demidchik V., Nichols C., Davies J. M. Genes for calcium-permeable channels in the plasma membrane of plant root cells // Biochimica et Biophisica Acta (BBA). 2002. Vol. 1564. P. 299-;309.
- Yruela I. Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions // Funct. Plant Biol. 2009. Vol. 36. P. 409-;430.
- Yruela I. Copper in plants // Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology. Vol. 17. P. 145-;146.
- Zheng G., Pemberton R., Li P. Bioindicating potential of strontium contamination with Spanish moss Tilandsia usneoides // Journal of Environmental Radioactivity. 2016. Vol. 152. P. 23-;27.


