PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в диагностике РПЖ: первый опыт применения комбинации маркеров в России
Автор: Аполихин О.И., Сивков А.В., Ефремов Г.Д., Михайленко Д.С., Шадеркин И.А., Войтко Д.А., Просянников М.Ю., Григорьева М.В.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Онкоурология
Статья в выпуске: 2, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
За последние 20 лет предложено множество новых маркеров рака предстательной железы (РПЖ), среди них - комбинация PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG. В НИИ урологии разрабатывается методика совместного определения экспрессии PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче и ткани предстательной железы (ПЖ), основанная на ПЦР с обратной транскрипцией в реальном времени. Для оценки диагностической значимости разрабатываемой методики, проанализированы две независимые выборки, представленные образцами ткани ПЖ (n=78) и мочи (n=56). Оценивали уровень сывороточного PSA, патоморфологические результаты, экспрессию PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче и ткани ПЖ. По результатам патоморфологического исследования каждая выборка разделялась на группы: РПЖ и доброкачественные изменения в ПЖ (ДГПЖ и хронический простатит). Экспрессия РСА3 в ткани и в моче у пациентов с РПЖ (Ме РСА3 в ткани 3,1 (1,2:4,9); Ме РСА3 в моче -0,04 (-0,6:2,1)) была выше, чем у пациентов с доброкачественными изменениями в ПЖ (Ме РСА3 в ткани 9,1 (6,9:10,4); Ме РСА3 в моче 4,4 (1,3:7,4)) (р
Диагностика рпж, молекулярно-генетические маркеры, рса3
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142188021
IDR: 142188021
Текст научной статьи PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в диагностике РПЖ: первый опыт применения комбинации маркеров в России
Over the past 20 years a large number of prostate cancer (PCa) markers have been proposed. A combination of PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG is among them. The real-time RT-PCR- based method for РСА3 and TMPRSS2-ERG determination in urine and prostate tissue is being developed at Russian Scientific-research Institute of Urology. Purposely to assessment of its diagnostic value, two independent samples of prostate tissue (n=78) and urine (n=56) specimens were investigated. The blood level of PSA, pathomorphological findings, PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG urinary and tissue expression were assessed. Samples were divided into groups, according to pathomorphological findings: PCa and non-cancerous prostatic changes (BPH and chronic prostatitis).
Prostate tissue РСА3 expression was significantly higher in PCa patients (Ме РСА3 in tissue 3,1 (1,2:4,9)) compared to BPH and chronic prostatitis patients (Ме РСА3 in tissue 9,1 (6,9:10,4)) (р<0,01). Urinary РСА3 demonstrated the same picture: Ме of РСА3 in urine was -0,04 (-0,6:2,1) in PCa patients and 4,4 (1,3:7,4) in patients with BPH and chronic prostatitis (р<0,01). TMPRSS2-ERG tissue expression was detected in 7 (35,0%) patients with PCa. Expression of urinary TMPRSS2-ERGwas found in 4 (14,8%) PCa patients.
We determined a cut-off score for РСА3 in prostate tissue and in urine, using ROC-analysis: ≤5,7 and ≤ 3,3 (diagnostic accuracy 88,0% and 71,4%, sensitivity 95,0% and 96,3%, specificity 86,2% and 51,7%), respectively. Area under the curve (AUC) was 0,952 for tissue РСА3 and 0,768 for urinary РСА3(р<0,0001). Therefore РСА3 is a high quality marker. TMPRSS2-ERG diagnostic efficacy was lower compared to РСА3: AUC for TMPRSS2-ERG was 0,675 in tissue and 0,574 in urine, respectively.
The method for РСА3 and TMPRSS2-ERG determination in urine and prostate tissue showed good diagnostic performance, and it could be useful for the improvement of early PCa diagnosis, particularly it could lead to optimizing costs by lowering amount of unnecessary prostate biopsies.
О.И. Аполихин, А.В. Сивков, Г.Д. Ефремов, Д.С. Михайленко, И.А. Шадеркин, Д.А. Войтко, М.Ю. Просянников, М.В. Григорьева НИИ урологии и интервенционной радиологии им. Н.А. Лопаткина – филиал ФГБУ НМИРЦ – Минздрава России
тандарт ранней диагностики рака предстательной железы (РПЖ) основывается на определении уровня сывороточного простатспеци-фического антигена (PSA) и выполнении пункционной биопсии предстательной железы (ПЖ). Длительный опыт PSA-скрининга позволил снизить смертность и повысить пятилетнюю выживаемость пациентов с РПЖ [1-3]. Однако стандартная диагностическая модель имеет ряд ограничений, приводящих к гипердиагностике (в 1,767,0% случаев) и избыточному лечению РПЖ [4].
Чувствительность и специфичность PSA-теста в отношении РПЖ (при пороговом уровне 4,0 нг/мл) не превышают 46,0% и 93,6%, соответственно [5-8]. У мужчин старшего возраста с доброкачественной гиперплазией ПЖ специфичность PSA-теста снижается до 54,0% [9]. Уровень сывороточного PSA может повышаться при определенных ситуациях, например после предшествующего пальцевого ректального исследования предстательной железы (ПРИ) [10, 11], эякуляции [12, 13], биопсии и трансуретральной резекции ПЖ [14], острой задержки мочеиспускания, при бактериальном простатите [15, 16], и снижаться на фоне приема ингибиторов 5-альфа-редук-тазы [17, 18]. В результате – лишь 25,0% биопсий, выполняемых в связи с повышением уровня сывороточного PSA, позволяют диагностировать РПЖ [19].
Клинически ненужные биопсии приводят к необоснованным материальным затратам. Кроме того, биопсия ПЖ (особенно повторная) для пациентов ассоциирована с неприятными ощущениями и психоэмоциональными переживаниями [20]. Следует отметить, что биопсия не всегда позволяет подтвердить или опровергнуть наличие РПЖ, демонстрируя ложноотрицательные результаты в 10,0-20,0% случаев [21, 22].
Ограничения стандартной диагностической модели сделали очевидной необходимость поиска дополнительных параметров при определении показаний к биопсии ПЖ. Для повышения эффективности выявления РПЖ с помощью PSA, были предложены различные диагностические стратегии, включая возрастные нормы PSA, изоформы PSA, «плотность» PSA, прирост PSA [23, 24]. За последнее двадцатилетие на основе PSA разработан ряд прогностических моделей (номограммы, таблицы, калькуляторы) для принятия решения о биопсии предстательной железы [24]. В совокупности с PSA также учитывают семейный анамнез, результаты ПРИ, ультразвуковых методов исследования и МРТ, уровни биохимических и молекулярногенетических маркеров. К наиболее специфичным в отношении РПЖ и многообещающим маркерам относят PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG [25].
РСА3 (prostate cancer antigen) демонстрирует гиперэкспрессию в 95,0% случаев РПЖ. Уровень экспрессии РСА3 в моче не зависит от локализации опухоли в предстательной железе [26] и наличия у пациента хронического простатита [27].
Экспрессия РСА3 в ткани может быть определена с помощью ПЦР с обратной транскрипцией в режиме реального времени, транскрипционноопосредованной амплификации, гибридизации РНК in situ. Специфичность тканевого РСА3 относительно РПЖ и простатической интраэпителиальной неоплазии (ПИН) высокой степени превышает 90,0% [28].
Для оценки экспрессии РСА3 в моче наиболее часто применяют единственную зарегистрированную в Европе и Северной Америке тест-систему «Progensa» (Hologic) [30-44]. В литературе также имеются данные о применении нескольких модифицированных методик, основанных на количественной полимеразной цепной реакции с обратной транскрипцией [45-48]. В результате различные авторы приводят широкий диапазон чувствительности (46,9% – 82,3%) и специфичности (55,0% – 92,0%) данного маркера в отношении РПЖ [49]. Это отчасти обусловлено и отсутствием единого мнения относительно порогового уровня для РСА3. Спорным представляется и вопрос взаимосвязи экспрессии РСА3 со степенью агрессивности РПЖ (клиническая и патоморфологиче-ская стадия, степень дифференцировки по Глисону, объем опухоли, наличие экстрапростатического роста, положительного хирургического края). Эти аспекты были подробно описаны нами ранее [50].
Мнения относительно включения оценки экспрессии РСА3 в моче в стандарт диагностики РПЖ расходятся. Управление по контролю за продуктами и лекарствами США (FDA) рекомендует учитывать результаты данного исследования для принятия решения о выполнении повторной биопсии предстательной железы у мужчин старше 50 лет. В то же время, основываясь на анализе «за-траты-эффективность», NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) не рекомендовал включе- ние РСА3 в стандартную модель обследования пациентов с подозрением на РПЖ в Великобритании [20].
Химерный ген TMPRSS2-ERG является результатом процесса слияния андроген-регулируемого гена TMPRSS2 с наиболее часто встречающимся при РПЖ представителем онкогенного ЕТS семейства факторов транскрипции ERG. Было продемонстрировано, что TMPRSS2-ERG обнаруживается у 30,0-50,0% пациентов с аденокарциномами ПЖ [51, 52].
Тканевую экспрессию TMPRSS2-ERG определяют с помощью флюоресцентной гибридизации in situ и количественной полимеразной цепной реакции с обратной транскрипцией. TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани демонстрирует высокую специфичность (до 99,0%) и чувствительность (до 86,0%) в отношении РПЖ и ПИН высокой степени [53-58].
К методам оценки экспрессии TMPRSS2-ERG в моче относят количественную полимеразную цепную реакцию с обратной транскрипцией и транскрипционно-опосредованную амплификацию. Чувствительность и специфичность маркера в моче, по различным данным составляют 37,0-69,0% и 83,0-93,0%, соответственно [35, 59-63].
В 2007 г. было предложено применять РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в комбинации, что позволило повысить диагностический потенциал обоих маркеров [59]. Дальнейшие исследования подтвердили эффективность комбинированного теста в предсказании результатов биопсии ПЖ [34, 64, 65]. Сочетанное определение РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG демонстрирует чувствительность до 93,6% и специфичность до 97,5% [34, 64, 66, 67]. Было показано, что TMPRSS2-ERG позволяет корректировать ложноотрицательные результаты РСА3 [67]. Также в литературе есть данные, указывающие, что уровень экспрессии РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче коррелирует со степенью дифференцировки опухоли по Глисону и такая комбинация может быть применена для стратификации риска РПЖ [65].
В то же время, имеется ряд не- разрешенных вопросов относительно применения комбинации РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG на практике. Отсутствует стандартизированная система для совместного определения экспрессии РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG, не определен единый подход к выполнению комбинированного исследования. Чувствительность и специфичность маркеров РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG зависят от используемого метода определения их экспрессии, в результате чего в литературе представлены различные данные о диагностической эффективности комбинации. Также требуется более детальное изучение возможности использования РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG для прогнозирования течения РПЖ. Кроме того, отсутствуют адекватные исследования клинико-экономической эффективности РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG.
В НИИ урологии им. Н.А.Ло-паткина разработана методика комбинированного определения экспрессии PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче, основанная на количественной полимеразной цепной реакции с обратной транскрипцией в режиме реального времени. В настоящей статье представлены первые результаты клинической апробации метода.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Для оценки эффективности метода определения экспрессии РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG, были сформированы и исследованы две независимые выборки, представленные образцами ткани ПЖ и мочи, полученными от пациентов с ДГПЖ, хроническим простатитом и РПЖ.
Клинический материал.
Образцы ткани от 78 пациентов (55-88 лет), были получены после биопсии ПЖ, трансуретральной резекции ПЖ и радикальной простатэктомии. Образцы мочи – собраны от 56 мужчин (51-85 лет) с подозрением на РПЖ (повышение уровня сывороточного PSA; данные за РПЖ при пальцевом ректальном исследовании), направленных на трансректальную биопсию ПЖ. В обеих □ выборках окончательный диагноз устанавливали на основании результатов патоморфологического исследования.
Биопсия.
Трансректальную биопсию ПЖ выполняли под контролем ультразвукового аппарата General Electric Logiq neo по стандартной схеме из 14 точек с помощью биопсийного пистолета Pro-Mag 2, иглами 16G. Полученные биопсийные столбики помещали в пробирки типа «эппен-дорф» с раствором формальдегида и направляли в патологоанатомическую лабораторию НИИ урологии для гистологического исследования.
Получение образцов мочи.
Во всех случаях сбор мочи производили перед выполнением биопсии. После проведения массажа ПЖ (по три нажатия на каждую долю) осуществляли сбор первых 20-30 мл мочи в одноразовый контейнер. В день сбора полученные образцы мочи центрифугировали в течение 15 минут при 2600-3500 g. После удаления супернатанта полученный осадок ресуспендировали и помещали в пробирку типа «эппен-дорф» 1,5 мл. К осадку добавляли 1,0 мл консервирующей «Среды РНК», пробирку герметично закрывали и оборачивали парафильмом. Полученный материал направляли в лабораторию НИИ урологии.
Выделение РНК.
Выделение тотальной РНК из образцов ткани ПЖ осуществляли с помощью набора RecoverAll™ Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit (Ambion, США) методом сорбции нуклеиновых кислот на колонке с обработкой ДНКазой, последующей отмывкой спиртовыми растворами и эллюцией РНК в ТЕ-буфер. Тотальную РНК из осадка мочи выделяли сорбентным методом с использованием набора «РИБО-сорб» (ФБУН ЦНИИ Эпидемиологии Роспотребнадзора, Россия) по инструкции производителя. Примесь геномной ДНК удаляли обработкой образцов избытком ДНКазы в соответствующем буфере при комнатной температуре в течение
40 мин (реагенты Applied Biosystems, США).
Обратная транскрипция.
Получение кДНК на РНК-матрице осуществляли методом отжига случайных олигонуклеотидов с помощью набора «High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit» (Applied Biosystems, США) в объеме реакционной смеси 20,0 мкл (для выборки образцов ткани) и 40,0 мкл (для выборки образцов мочи) в соответствии с рекомендациями фирмы-производителя.
Полимеразная цепная реакция в реальном времени (ПЦР-РВ).
Экспрессию генов РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани ПЖ и в моче определяли методом ПЦР-РВ по сравнению значений пороговых циклов Ct относительно внутреннего и тканеспецифичного контролей (гены GAPDH и KLK3, соответственно). О наличии в исходном образце мРНК свидетельствовала экспрессия эндогенного контроля GAPDH, присутствие в образце клеток предстательной железы в количестве, достаточном для проведения исследования, определяли по гену KLK3, имеющему простат-специфичную экспрессию.
Реакционная смесь содержала 1,0 мкл образца кДНК, полученного на предыдущем этапе, 8,0 мкл деионизированной воды, 1,0 мкл готовой смеси праймеров и TaqMan-зонда, 10,0 мкл концентрированного буферного раствора с полимеразой согласно протоколу производителя. Температурные параметры: 95°С в течение 10 мин, затем 47 циклов 95°С 15 с, 60°С – 1 мин. Использовали комбинации праймеров и TaqMan-зондов с красителями и MGB для ПЦР-РВ: GAPDH – huGAPDH-4326317E (VIC), KLK3 – Hs02576345_m1 (FAM), PCA3 – Hs01371939_g1 (FAM), TMPRSS2-ERG – Hs03063375_ft (FAM). Максимальное значение Ct было установлено на уровне 45 циклов. Образец считали пригодным для анализа, если в нем обнаруживали экспрессию KLK3 при значении Ct до 45 циклов. Каждый исследуемый ген в каждом образце амплифициро- вали в трех повторениях, далее определяли усредненное значение Ct по трем реакциям. ПЦР-РВ проводили в детектирующем термоциклере StepOnePlus (Applied Biosystems, США) в формате 96-луночного планшета.
Интерпретация результатов.
Для выражения экспрессии РСА3 в каждой группе пациентов вычисляли показатель ΔСt = Сt(РСА3) – Сt(KLK3). Экспрессию химерного онкогена TMPRSS2-ERG считали положительной, если во всех трех повторениях наблюдали амплификацию целевого участка кДНК этого гена при значении Ct до 45.
Расчеты. Выборка образцов ткани была разделена на две группы в соответствии с результатами биопсии ПЖ: I группа – РПЖ и II группа – доброкачественные изменения в ПЖ (ДГПЖ с ПИН различной степени, хронический простатит). Аналогичным образом на группы была разделена выборка образцов мочи. Для описательной статистики использовали медиану, 25 и 75 процентили. Различия между группами определяли с помощью критерия Манна-Уитни при уровне значимости p≤0,01 в программе MSExcel. Определение корреляции с использованием коэффициента Спирмена, а также расчет параметров диагностической значимости производили в программе MedCalc. Оптимальные пороговые уровни ΔСt = Сt(РСА3) – Сt(KLK3) в моче и в ткани предстательной железы были определены с помощью ROC-анализа в программе MedCalc.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани
Исследуемая выборка (n=78) была разделена на две группы по результатам патоморфологического заключения: I группа (n=20) – РПЖ и II группа (n=58) – доброкачественные изменения в ПЖ (ДГПЖ с ПИН различной степени, хронический простатит). Различия уровней экспрессии РСА3 (Δ Сt РСА3 – KLK3)
между I и II группами были определены как статистически значимые (табл. 1).
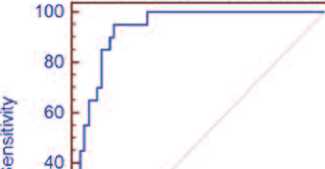
С помощью ROC-анализа определен наиболее оптимальный пороговый уровень тканевого РСА3 ≤ 5,7 , которому соответствовали диагностическая точность 88,0%, чувствительность 95,0% (95% ДИ 75,1-99,9) и специфичность 86,2% (95% ДИ 74,693,9) (рис.1). Рассчитан показатель площади под ROC-кривой (area under the curve, AUC) для РСА3 в ткани ПЖ – AUC 0,952 (р<0,0001). Это соответствует диагностической модели высокого качества.
Д_С(_РСАЗ___KLK3 е ткани
U)
20 ■
0H ... 1 ... 1 ... 1 ... I ... г О 20 40 60 80 100
100-Speoficity
Рис. 1. ROC-кривая РСА3 в ткани предстательной железы
Определена статистически значимая корреляция между уровнем экспрессии РСА3 в ткани и уровнем сывороточного PSA (р<0,01).
Экспрессия TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани была выявлена у 7 пациентов с РПЖ. TMPRSS2-ERG продемон- стрировал диагностическую точность 83,3%, чувствительность 35,0% (95% ДИ 15,4-59,2) и специфичность 100% (95% ДИ 93,8-100). Показатель AUC для TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани составил 0,675 (р<0,0014), что характерно для диагностических моделей среднего качества (рис. 2).
TMPRSS2 ERG в ткани
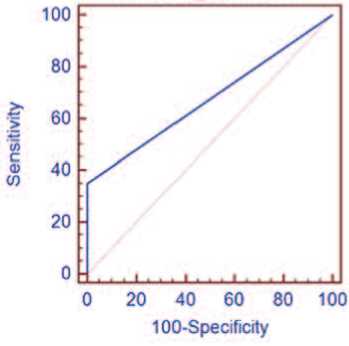
Рис. 2. ROC-кривая TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани предстательной железы
РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче
В соответствии с результатами патоморфологического заключения, исследуемые (n=56) были разделены на две группы: I группа (n=27) – РПЖ и II группа (n=29) – доброкачественные изменения в ПЖ (ДГПЖ с ПИН различной степени, хронический простатит). Результаты обследования представлены в таблице 2. Уровень экспрессии РСА3 в I группе был достоверно выше, чем во II (р<0,01).
Выявлена статистически значимая корреляция между уровнем экс- прессии РСА3 в моче и уровнем сывороточного PSA (р<0,01).
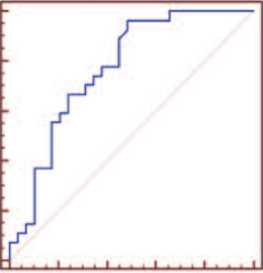
С использованием ROC-анализа, был определен наиболее оптимальный пороговый уровень для значения Δ Сt РСА3 – KLK3 ≤ 3,3, которому соответствовали диагностическая точность 71,4%, чувствительность 96,3% (95% ДИ 81,0-99,9) и специфичность 51,7% (95% ДИ 32,5-70,6) (рис. 3). Показатель AUC РСА3 в моче составил 0,768 (р<0,0001), что соответствует диагностической модели хорошего качества.
РСА 3/KLK 3 в моче
I 60 й § 40
О
О 20 40 60 80 100
100-Speafiaty
Рис. 3. ROC-кривая РСА3 в моче
Экспрессия химерного гена TMPRSS2-ERG была выявлена у 4 пациентов с РПЖ. Диагностическая точность, чувствительность и специфичность TMPRSS2-ERG в моче составили 59,0%, 14,8% (95% ДИ 4,2-33,7) и 100% (95% ДИ 88,1-100), соответственно. Рассчитан показатель AUC, равный 0,574 (р=0,0335),
Таблица 1. Краткая характеристика пациентов (выборка образцов ткани)
|
Показатели |
I - пациенты с РПЖ (n=20) Ме (25%:75%) |
II - пациенты с доброкачественными изменениями в ПЖ (n=58) Ме (25%:75%) |
Уровень значимости ( р ) |
|
Возраст |
66,5 (62,5:76,0) |
67 (62,0:73,0) |
р >0,05 |
|
Сывороточный PSA (нг/мл) |
10,2 (8,6:26,0) |
6,3 (3,9:7,8) |
р <0,05 |
|
Δ Сt РСА3 - KLK3 |
3,1 (1,3:4,9) |
9,1 (6,9:10,4) |
р <0,01 |
Таблица 2. Краткая характеристика пациентов (выборка образцов мочи)
|
Показатели |
I - пациенты с РПЖ (n=27) Ме (25%:75%) |
II - пациенты с доброкачественными изменениями в ПЖ (n=29) Ме (25%:75%) |
Уровень значимости ( р ) |
|
Возраст |
63,0 (60,5:70,0) |
62,0 (59,0:66,0) |
р >0,05 |
|
Сывороточный PSA (нг/мл) |
7,5 (5,8:9,6) |
6,2 (4,8:8,4) |
р >0,05 |
|
ΔСt РСА3 - KLK3 |
-0,04 (-0,7:2,1) |
4,4 (1,3:7,4) |
р <0,01 |
что характерно для диагностических моделей низкого качества (рис. 4). Н
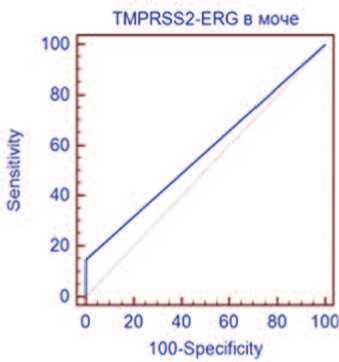
Рис. 4. ROC-кривая TMPRSS2-ERG в моче
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
В настоящем исследовании продемонстрирована высокая диагностическая значимость РСА3 в ткани. При этом, диагностическая эффективность TMPRSS2-ERG была значительно ниже, в сравнении с РСА3, что сопоставимо с результатами других авторов [67].
В связи с отсутствием стандартизированного подхода к оценке экспрессии РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче, различные исследователи применяли несколько видов методик в своих работах: «Progensa» и набор для исследования экспрессии TMPRSS2-ERG компании «Hologic», количественная ПЦР с обратной транскрипцией в реальном времени с различными модификациями праймеров и зондов. Кроме того, размеры выборок также были неодинаковы, в связи с чем результаты, представленные в литературе, вариабельны.
По данным ряда авторов, РСА3 в моче является эффективным маркером при выявлении РПЖ, а диагностическая эффективность TMPRSS2-ERG в моче ниже среднего уровня, в связи с чем определение этого маркера носит вспомогательный характер [33-35, 65], что также соответствует результатам нашего исследования.
Относительно низкая чувствительность TMPRSS2-ERG может быть обусловлена его встречаемостью лишь примерно в половине случаев аденокарцином ПЖ. Кроме того, следует учитывать нестабильность простатической мРНК в образцах мочи. При этом TMPRSS2-ERG, обладающий 98% специфичностью, способен усилить диагностический потенциал РСА3, что было продемонстрировано другими авторами [64, 67].
В нашем исследовании у всех пациентов с гиперэкспрессией TMPRSS2-ERG также наблюдали гиперэкспрессию РСА3, в связи с чем оценку диагностической значимости комбинации маркеров на этом этапе работы не проводили.
При пороговом значении ≤ 3,3 тест РСА3 в моче продемонстрировал 14 ложноположительных результатов (25,0% всей группы). Следует отметить, что во всех 14 случаях уровень сывороточного PSA превышал референсные значения, что может отражать как истинную долю ложноположительных результатов теста, так и возможные ложноотрицательные результаты биопсии (рис. 5). Зарегистрирован всего 1 ложноотри-
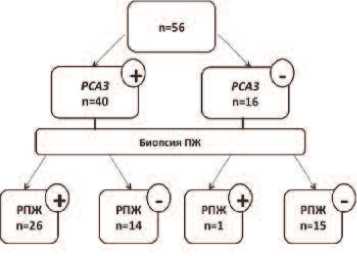
Рис.5. Ложноположительные и ложноотрицательные результаты РСА3 в моче цательный случай (1,8%), что подтверждает высокую чувствительность теста.
ВЫВОДЫ
Настоящей работой продемонстрирована эффективность разрабатываемой в НИИ урологии методики для определения экспрессии РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани ПЖ и моче. Использование данной комбинации способно существенно улучшить качество ранней диагностики РПЖ.
В клинической практике определение РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в ткани ПЖ важно для уточнения па-томорфологического диагноза. Выявление гиперэкспрессии указанных генов в материале первичной отрицательной биопсии свидетельствует о высокой вероятности наличия РПЖ и является показанием для выполнения повторной биопсии.
Гиперэкспрессия РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в моче у пациентов с повышенным уровнем PSA – жесткий аргумент в пользу решения вопроса о первичной и, что более важно, повторной биопсии ПЖ. Разрабатываемый метод позволяет уменьшить число «ненужных» биопсий и, соответственно, может способствовать оптимизации экономических затрат при диагностике РПЖ, в том числе в ходе программ массового скрининга. □
Резюме:
Список литературы PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в диагностике РПЖ: первый опыт применения комбинации маркеров в России
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2014. American Cancer Society, 2014. Р.19.
- Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ,Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H, Zappa M, Denis LJ, Recker F, Paez A, Määttänen L, Bangma CH, Aus G, Carlsson S, Villers A, Rebillard X, van der Kwast T, Kujala PM, Blijenberg BG, Stenman U, Huber A, Taari K, Hakama M, Moss SM, de Koning HJ, Auvinen A. Prostate-Cancer Mortality at 11 Years of Follow-up.//N Engl J Med. 2012. Vol. 366. P. 981-990.
- Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Carlsson S, Tammela T, Määttänen L, Auvinen A, Kwiatkowski M, Recker F, Roobol MJ. Screening for prostate cancer decreas-es the risk of developing metastatic disease: findings from the European Ran-domized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC).//Eur Urol. 2012. Vol. 62. P. 745-752.
- Loeb S, Bjurlin MA, Nicholson J, Tammela TL, Penson DF, Carter HB, Carroll P, Etzioni R. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer. // Eur Urol. 2014. Vol. 65, N 6. P.1046-1055.
- Gann PH, Hennekens CH, Stampfer MJ. A prospective evaluation of plasma prostate-specific antigen for detection of prostatic cancer.//JAMA.1995. Vol. 273, N 4. P. 289-294.
- Thompson IM, Ankerst DP, Chi C, Lucia MS, Goodman PJ, Crowley JJ, Parnes HL, Coltman CA. Operating characteristics of prostate-specific antigen in men with an initial PSA level of 3.0 ng/ml or lower.//JAMA. 2005. Vol. 294, N 1. P. 66-70.
- Ankerst DP, Thompson IM. Sensitivity and specificity of prostate-specific antigen for prostate cancer detection with high rates of biopsy verification.//Arch Ital Urol Androl.2006. Vol. 78, N 4. P. 125-129.
- Wolf AM, Wender RC, Etzioni RB, Thompson IM, D'Amico AV, Volk RJ, Brooks DD, Dash C, Guessous I, Andrews K, DeSantis C, Smith R.A. American Cancer Society guideline for the early detection of prostate cancer: update 2010.//CA Cancer J Clin.2010. Vol. 60, N 2. P. 70-98.
- Sershon PD, Barry MJ, Oesterling JE. Serum prostate-specific antigen discriminates weakly between men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and patients with organ-confined prostate cancer. // Eur Urol. 1994. Vol. 25. P. 281-287.
- Chybowski FM, Bergstralh EJ, Oesterling JE. The effect of digital rectal examination on the serum prostate specific antigen concentration: results of a randomized study.//J Urol.1992. Vol. 148, N 1. P. 83-86.
- Effect of digital rectal examination on serum prostate-specific antigen in a primary care setting. The Internal Medicine Clinic Research Consortium.//Arch Intern Med.1995. Vol. 155, N 4. P. 389-392.
- Herschman JD, Smith DS, Catalona WJ. Effect of ejaculation on serum total and free prostate-specific antigen concentrations. // Urology. 1997. Vol. 50, N 2. P. 239-243.
- Tchetgen MB, Song JT, Strawderman M, Jacobsen SJ, Oesterling JE. Ejaculation increases the serum prostate-specific antigen concentration. // Urology. 1996. Vol. 47, N 4. P. 511-516.
- Tchetgen MB, Oesterling JE. The effect of prostatitis, urinary retention, ejaculation, and ambulation on the serum prostate-specific antigen concentration. // Urol Clin North Am. 1997. Vol. 24, N 2. P. 283-291.
- Kawakami J, Siemens DR, Nickel JC. Prostatitis and prostate cancer: implications for prostate cancer screening. // Urology. 2004. Vol. 64, N 6. P. 1075-1080.
- Simardi LH, Tobias-MacHado M, Kappaz GT, Goldenstein TP, Potts JM, Wroclawski ER. Influence of asymptomatic histologic prostatitis on serum prostate-specific antigen: a prospective study. // Urology. 2004. Vol. 64, N 6. P. 1098-1101.
- Guess HA, Heyse JF, Gormley GJ. The effect of finasteride on prostate-specific antigen in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. // Prostate. 1993. Vol. 22, N 1. P. 31-37.
- Roehrborn CG, Marks LS, Fenter T, Freedman S, Tuttle J, Gittleman M, Mor-rill B, Wolford ET. Efficacy and safety of dutasteride in the four-year treat-ment of men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. // Urology. 2004. Vol. 63, N 4. P. 709-715.
- Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H, Zappa M, Denis LJ, Recker F, Berenguer A, Määttänen L, Bangma CH, Aus G, Villers A, Rebillard X, van der Kwast T, Blijenberg BG, Moss SM, de Koning HJ, Auvinen A. Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. // N Engl J Med. 2009. Vol. 360, N 13. P. 1320-1328.
- Diagnosis and monitoring of prostate cancer: PROGENSA PCA3 assay and Prostate Health Index (PHI). National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2014. P. 39-41.
- Stroumbakis N, Cookson MS, Reuter VE, Fair WR. Clinical significance of repeat sextant biopsies in prostate cancer patients.//Urology. 1997. Vol. 49, Suppl 3A. P113-118.
- Ellis WJ, Brawer MK. Repeat prostate needle biopsy: who needs it?//J Urol. 1995. Vol. 153, N 5. P. 1496.
- Adhyam M, Gupta AK. A Review on the clinical utility of PSA in cancer prostate. // Indian J Surg Oncol. 2012. Vol. 3, N 2. P. 120-129.
- Louie KS, Seigneurin A, Cathcart P, Sasieni P. Do prostate cancer risk models improve the predictive accuracy of PSA screening? A meta-analysis. // Ann Oncol. 2015. Vol. 26, N 5. P. 848-864.
- Salagierski M, Schalken JA. Molecular diagnosis of prostate cancer: PCA3 and TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion. // J Urol. 2012. Vol. 187. P. 795-801.
- Schilling DA, Hennenlotter J, von Weyhern CH, Kuehs U, Joerg T, Pelzer A, Stenzl A. Does the PCA3 score depend on tumor localization within the prostate? -A morphometric computer animated analysis.//J Urol. 2009. Vol. 181, Suppl. 4. P. 655.
- Vlaeminck-Guillem V, Bandel M, Cottancin M, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Bohbot JM, Sednaoui P. Chronic prostatitis does not influence urinary PCA3 score//Prostate. 2012. Vol. 72, N 5. P. 549-554.
- Warrick JI, Tomlins SA, Carskadon SL, Young AM, Siddiqui J, Wei JT, Chin-naiyan AM, Kunju LP, Palanisamy N. Evaluation of tissue PCA3 expression in prostate cancer by RNA in situ hybridization - a correlative study with urine PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG. // Mod Pathol. 2014. Vol. 27, N 4. P. 609-620.
- Albino G, Capoluongo E, Rocchetti S, Palumbo S, Zuppi C, Cirillo-Marucco E. Evaluation of the diagnostic and predictive power of PCA3 in the prostate cancer. A different best cut-off in each different scenario. Preliminary results.//Arch Ital Urol Androl.2014. Vol. 86, N 4. P. 306-310.
- Capoluongo E, Zambon CF, Basso D, Boccia S, Rocchetti S, Leoncini E, Palumbo S, Padoan A, Albino G, Todaro A, Prayer-Galetti T, Zattoni F, Zuppi C, Plebani M. PCA3 score of 20 could improve prostate cancer detection: results obtained on 734 Italian individuals. // Clin Chim Acta. 2014. Vol. 429. P. 46-50.
- Gittelman MC, Hertzman B, Bailen J, Williams T, Koziol I, Henderson RJ, Efros M, Bidair M, Ward JF. PCA3 molecular urine test as a predictor of repeat prostate biopsy outcome in men with previous negative biopsies: a prospective multicenter clinical study. // J Urol. 2013. Vol. 190, N 1. P. 64-69.
- Ochiai A, Okihara K, Kamoi K, Oikawa T, Shimazui T, Murayama S, Tomita K, Umekawa T, Uemura H, Miki T. Clinical utility of the prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3) urine assay in Japanese men undergoing prostate biopsy.//BJU Int. 2013. Vol. 111, N 6. P. 928-933.
- Stephan C, Jung K, Semjonow A, Schulze-Forster K, Cammann H, Hu X, Meyer HA, Bögemann M, Miller K, FriedersdorffF. Comparative assessment of urinary prostate cancer antigen 3 and TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion with the serum [-2]proprostate-specific antigen-based prostate health index for detection of prostate cancer. // Clin Chem. 2013. Vol. 59, N 1. P. 280-288.
- Leyten GH, Hessels D, Jannink SA, Smit FP, de Jong H, Cornel EB, de Reijke TM, Vergunst H, Kil P, Knipscheer BC, van Oort IM, Mulders PF, Hulsber-genvan de Kaa CA, Schalken JA. Prospective multicentre evaluation of PCA3 and TM-PRSS2-ERG gene fusions as diagnostic and prognostic urinary bi-omarkers for prostate cancer. // Eur Urol. 2014. Vol. 65, N 3. P. 534-542.
- Cornu JN, Cancel-Tassin G, Egrot C, Gaffory C, Haab F, Cussenot O. Urine TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcript integrated with PCA3 score, genotyping, and biological features are correlated to the results of prostatic biopsies in men at risk of prostate cancer. //Prostate. 2013. Vol. 73, N 3. P. 242-249.
- Perdonà S, Bruzzese D, Ferro M, Autorino R, Marino A, Mazzarella C, Perru-olo G, Longo M, Spinelli R, Di Lorenzo G, Oliva A, De Sio M, Damiano R, Altieri V, Terracciano D. Prostate health index (phi) and prostate cancer antigen 3 (PCA3) significantly improve diagnostic accuracy in patients undergoing prostate biopsy. // Prostate. 2013. Vol. 73, N 3. P. 227-235.
- Augustin H, Mayrhofer K, Pummer K, Mannweiler S. Relationship between prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3) and characteristics of tumor aggressiveness. // Prostate. 2013. Vol. 73, N 2. P. 203-210.
- Ramos CG, Valdevenito R, Vergara I, Anabalon P, Sanchez C, Fulla J. PCA3 sensitivity and specificity for prostate cancer detection in patients with abnormal PSA and/or suspicious digital rectal examination. First Latin American experience.//Urol Oncol. 2013. Vol. 31, N 8. P. 1522-1526.
- Ferro M, Bruzzese D, Perdonà S, Mazzarella C, Marino A, Sorrentino A, Di Carlo A, Autorino R, Di Lorenzo G, Buonerba C, Altieri V, Mariano A, Macchia V, Terracciano D. Predicting prostate biopsy outcome: prostate health index (phi) and prostate cancer antigen 3 (PCA3) are useful biomarkers. //Clin Chim Acta. 2012. Vol. 413, N 15-16. P. 1274-1278.
- Durand X, Xylinas E, Radulescu C, Haus-Cheymol R, Moutereau S, Ploussard G, Forgues A, Robert G, Vacherot F, Loric S, Allory Y, Ruffion A, de la Taille A. The value of urinary prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3) scores in predicting pathological features at radical prostatectomy. // BJU Int. 2012. Vol. 110, N 1. P. 43-49.
- Auprich M, Augustin H, Budäus L, Kluth L, Mannweiler S, Shariat SF, Fisch M, Graefen M, Pummer K, Chun FK. A comparative performance analysis of total prostate-specific antigen, percentage free prostate-specific antigen, pros-tate-specific antigen velocity and urinary prostate cancer gene 3 in the first, se-cond and third repeat prostate biopsy. // BJU Int. 2012. Vol. 109, N 11. P. 1627-1635.
- de la Taille A, Irani J, Graefen M, Chun F, de Reijke T, Kil P, Gontero P, Mottaz A, Haese A. Clinical evaluation of the PCA3 assay in guiding initial biopsy decisions. // J Urol. 2011. Vol. 185, N 6. P. 2119-2125.
- Durand X, Moutereau S, Xylinas E, de la Taille A. Progensa™ PCA3 test for prostate cancer. // Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2011. Vol. 11, N 2. P. 137-144.
- Nyberg M, Ulmert D, Lindgren A, Lindström U, Abrahamsson PA, Bjartell A. PCA3 as a diagnostic marker for prostate cancer: a validation study on a Swe-dish patient population. // Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2010. Vol. 44, N 6. P. 378-383.
- Hessels D, Klein Gunnewiek JM, van Oort I, Karthaus HF, van Leenders GJ, van Balken B. DD3(PCA3)-based molecular urine analysis for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. // Eur Urol. 2003. Vol. 44. P. 8-15.
- Van Gils MP, Hessels D, Van Hooij O, Jannink SA, Peelen WP, Hanssen SL. The time-resolved fluorescence-based PCA3 test on urinary sediments after digital rectal examination; a Dutch multicenter validation of the diagnostic performance. // Clin Cancer Res. 2007. Vol. 13. P. 939-943.
- Сидоренков А.В., Говоров А.В., Пушкарь Д.Ю., Павлов К.А., Шкопоров А.Н., Хохлова Е.В., Корчагина А.А., Григорьев М.Э., Чехонин В.П. Российская тест-система РСА3: первые результаты//Экспериментальная и клиническая урология. 2014. N 2. С. 44-49.
- Ng CF, Yeung R, Chiu PK, Lam NY, Chow J, Chan B. The role of urine prostate cancer antigen 3 mRNA levels in the diagnosis of prostate cancer among Hong Kong Chinese patients. // Hong Kong Med J. 2012. Vol.18, N 6. P. 459-465.
- Yong L, Xin G, Peng H, Chan M. Prostate cancer antigen 3 test for prostate biopsy decision: a systematic review and meta analysis.//Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. Vol. 127, N 9. P.1768-1774.
- Сивков А.В., Ефремов Г.Д., Михайленко Д.С., Григорьева М.В. Комбинация маркеров РСА3 и TMPRSS2-ERG в ранней диагностике рака предстательной железы (обзор литературы).//Экспериментальная и клиническая урология. 2014. N 3. C. 20-26.
- Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. // Science. 2005. Vol. 310. P. 644-648.
- Attard G, Clark J, Ambroisine L, Fisher G, Kovacs G. Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. // Oncogene. 2008. Vol. 27. P. 253-263.
- Hermans KG, van Marion R, van Dekken H, Jenster G, van Weerden W M, Trapman J. TMPRSS2:ERG fusion by translocation or interstitial deletion is highly relevant in androgen-dependent prostate cancer, but is bypassed in late-stage androgen receptor-negative prostate cancer.// Cancer Res. 2006. Vol. 66. P. 10658-10663.
- Perner S, Demichelis F, Beroukhim R, Schmidt FH, Mosquera JM, Setlur S. TMPRSS2:ERG fusion-associated deletions provide insight into the heterogeneity of prostate cancer. // Cancer Res. 2006. Vol. 66. P. 8337-8341.
- Iljin K, Wolf M, Edgren H, Gupta S, Kilpinen S, I.Skotheim R. TMPRSS2 fusions with oncogenic ETS factors in prostate cancer involve unbalanced genomic rearrangements and are associated with HDAC1 and epigenetic reprogramming. // Cancer Res. 2006. Vol. 66, N 21. P. 10242-10246.
- Wang J, Cai Y, Ren C, Ittmann M. Expression of variant TMPRSS2/ERG fusion messenger RNAs is associated with aggressive prostate cancer.//Cancer Res. 2006. Vol. 66. P. 8347-8351.
- Yoshimoto M, Joshua AM, Chilton-Macneill S, Bayani J, Selvarajah S, Evans AJ. Three-color FISH analysis of TMPRSS2/ERG fusions in prostate cancer indicates that genomic microdeletion of chromosome 21 is associated with re-arrangement.//Neoplasia. 2006. Vol. 8. P. 465-469.
- Clark J, Merson S, Jhavar S, Flohr P, Edwards S, Foster CS. Diversity of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts in the human prostate. // Oncogene. 2007. Vol. 26. P. 2667-2673.
- Hessels D, Smit FP, Verhaegh GW, Witjes JA, Cornel EB, Schalken JA. Detection of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts and prostate cancer antigen 3 in urinary sediments may improve diagnosis of prostate cancer. // Clinical Cancer Res. 2007. Vol. 13. P. 5103-5108.
- Nguyen PN, Violette P, Chan S, Tanguay S, Kassouf W, Aprikian A, Chen JZ. A panel of TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcript markers for urine-based prostate cancer detection with high specificity and sensitivity. // Eur Urol. 2011. Vol. 59, N 3. P.407-414.
- Laxman B, Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Morris DS, Wang L, Helgeson BE, Shah RB, Rubinb MA, Wei JT, Chinnaiyan AM. Noninvasive detection of TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcripts in the urine of men with prostate cancer. // Neoplasia. 2006. Vol. 8, N 10. P. 885-888.
- Bories PN, Younes P, Zerbib M, Denjean L, Popovici T, Cynober L, Delongchamps N.B. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion transcripts in matched urine and needle rinse material after biopsy for the detection of prostate cancer.//Clin Chem. 2013. Vol. 59.P. 245-251.
- Tomlins SA, Aubin SM, Siddiqui J, Lonigro RJ, Sefton-Miller L, Miick S, Williamsen S, Hodge P, Meinke J, Blase A, Penabella Y, Day JR, Varambally R, Han B, Wood D, Wang L, Sanda MG, Rubin MA, Rhodes DR, Hollenbeck B, Sakamoto K, Silberstein JL, Fradet Y, Amberson JB, Meyers S, Palanisamy N, Rittenhouse H, Wei JT, Groskopf J, Chinnaiyan AM. Urine TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcript stratifies prostate cancer risk in men with elevated serum PSA. // Sci Transl Med. 2011. Vol. 3, N 94. P. 72.
- Salami SS, Schmidt F, Laxman B, Regan MM, Rickman DS, Scherr D, Bueti G, Siddiqui J, Tomlins SA, Wei JT, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA, Sanda MG. Combining urinary detection of TMPRSS2: ERG and PCA3 with serum PSA to predict diagnosis of prostate cancer. // Urol Oncol. 2011. Vol. 31, N 5. P. 566-571.
- Lin DW, Newcomb LF, Brown EC, Brooks JD, Carroll PR, Feng Z, Gleave ME, Lance RS, Sanda MG, Thompson IM, Wei JT, Nelson PS. Urinary TMPRSS2:ERG and PCA3 in an active surveillance cohort: results from a baseline analysis in the canary prostate active surveillance study. // Clin Cancer Res. 2013. Vol. 19. P. 2442-2450.
- Laxman B, Morris DS, Yu J. A first-generation multiplex biomarker analysis of urine for the early detection of prostate cancer.//Cancer Res. 2008 Vol. 68. P. 645.
- Robert G, Jannink S, Smit F, Aalders T, Hessels D, Cremers R, Mulders PF, Schalken JA. Rational basis for the combination of PCA3 and TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion for prostate cancer diagnosis. // Prostate. 2012. Vol. 73, N 2. P. 113-120.


