Применение теории стейкхолдеров в системе управления услугами фестивалей культуры
Автор: Гордин Валерий Эрнстович, Хорева Любовь Викторовна, Дедова Мария Александровна
Журнал: Известия Санкт-Петербургского государственного экономического университета @izvestia-spgeu
Рубрика: Методология и инструментарий управления
Статья в выпуске: 5 (95), 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В статье рассматриваются вопросы применения теории стейкхолдеров в сфере управления организацией культурных событий, в частности в системе управления услугами фестивалей культуры. В основу эмпирической части исследования положен опыт организации фестивалей в России и за рубежом. В результате исследований авторами разработана методика дуального поведения стейкхолдеров как эффективный инструмент совершенствования системы управления услугами фестивалей культуры с целью усиления положительных эффектов от их проведения.
Теория стейкхолдеров, управление услугами, фестивали культуры
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14875560
IDR: 14875560
Текст научной статьи Применение теории стейкхолдеров в системе управления услугами фестивалей культуры
Любовь Викторовна Хорева – доктор экономических наук, профессор, профессор кафедры экономики и управления в сфере услуг Санкт-Петербургского государственного экономического университета.
Мария Александровна Дедова – аспирант кафедры менеджмента НИУ ВШЭ – Санкт-Петербург.
Статья поступила в редакцию 23.09.2015 г.
Для ссылок: Гордин В.Э., Хорева Л.В., Дедова М.А. Применение теории стейкхолдеров в системе управления услугами фестивалей культуры // Известия Санкт-Петербургского государственного экономического университета. 2015. № 5 (95). С. 56-65.
Статья подготовлена в рамках гранта ЦФИ НИУ ВШЭ «Исследование креативного потенциала развития культурного туризма», ТЗ № 53.
ления, на которые влияет деятельность организации. Таким образом, можно сделать вывод, что современная теория менеджмента нуждается в постоянном совершенствовании механизма учета интересов всех акторов социально-экономической деятельности для наиболее эффективного использования ресурсов и наилучшего удовлетворения запросов и потребностей различных категорий производителей и потребителей товаров и услуг. Решение данной задачи в настоящее время осуществляется, в том числе, на основе так называемой теории стейкхолдеров, применяемой в различных областях корпоративного управления.
Истоки теории стейкхолдеров можно найти в работах исследователей 30-х годов XX века. Впервые было предположено, что цели корпорации должны включать в себя вопросы обеспечения безопасности рабочих мест для наемных работников, заботу о качестве продукции для потребителей и благосостоянии местного сообщества [15]. В современном виде теория стейкхолдеров или теория заинтересованных сторон была сформулирован Эдвардом Фриманом в 1984 году в его работе «Стратегический менеджмент: концепция заинтересованных сторон» [17]. Э. Фриман предложил рассматривать стратегию развития фирмы с точки зрения различных индивидуумов и организаций, на которые она влияет или от которых зависит. В основе стратегического менеджмента компании должно лежать стремление соблюсти интересы наиболее важных стейкхолдеров [12].
Согласно теории стейкхолдеров для достижения целей компании необходимо учитывать интересы стейкхолдеров, которые могут оказываться в состоянии неформальных коалиций. С момента публикации работы Э. Фримана теория стейкхолдеров получила широкое развитие в научной литературе [8; 10; 11; 24 и др.], что способствовало появлению также различных трактовок термина «стейкхолдер». Если Э. Фриман определял стейкхолдеров фирмы с теоретической точки зрения как любую группу или индивида, оказывающего воздействие или находящегося под влиянием решений менеджмента компании, то позже исследователи обратились к более узкому подходу, характерному для практической деятельности. В рамках данного подхода к стейкхолдерам относятся только те лица и группы, с которыми фирма взаимодействует наиболее часто [12; 13].
Важно отметить, что на практике взаимодействие стейкхолдеров может носить как характер сотрудничества при условии совпадения интересов, так и конкурентной борьбы. Однако различные типы организаций, в частности, организации социального обслуживания и некоммерческие организации, учатся или предпочитают использовать стратегии сотрудничества вместо конкурентной борьбы [25; 35]. К подобному выводу приходит в своих исследованиях и Г.Б. Клейнер, утверждающий, что отношения между различными системными экономическими субъектами чаще имеют кооперационный характер [2]. Все стейкхолдеры представляют собой своего рода единое целое, они, в стремлении удовлетворить собственные интересы, определяют общую стратегию развития организации. В этой связи исследователи отмечают [29; 30] ценность теории стейкхолдеров именно для стратегического анализа и планирования на основе партнерских преимуществ [2].
Для применения теории стейкхолдеров были разработаны следующие инструменты: модель Миттчела, сетевая модель и балансовая модель ресурсных отношений. В основе модели Миттчела лежит определение значимости стейкхолдеров на основе релевантных атрибутов и свойств [4]. В зависимости от наличия тех или иных свойств и атрибутов, формируются группы стейкхолдеров. Балансовая модель предполагает, что взаимодействие стейкхолдеров происходит только в целях ресурсного обмена [4]. При этом выделяются отношения ассиметричного типа в пользу целевого элемента, эквивалентного или асимметричного в ущерб целевому элементу.
В рамках сетевой модели предлагается проведение анализа взаимодействия стейкхолдеров. При этом плотность сети определяет уровень манипулирования стейкхолдерами. При низкой плотности сети происходит ограничение потоков ресурсов, что приводит к усилению влиянию того элемента, который способен их контролировать. Возможность осуществление контроля над ресурсными потоками определяется центральностью, то есть положением элемента в сети. Наличие большего числа связей и возможностей для посредничества повышает уровень вовлеченности стейкхолдера в ресурсном обмене и обеспечивает доступ к большему объему информации. Для фирмы применение сетевой модели будет способствовать определению нежелательных посредников, чьи позиции в сети необходимо ослабить [4].
Следует отметить, что в последние десятилетия существенно расширилась сфера применения теории стейкхолдеров, охватив новые отрасли и организации некоммерческого сектора. Исследования зарубежных авторов, посвященные анализу управления организацией культурных событий, в том числе и фестивалей, подтвердили применимость теории стейкхолдеров к событийному менеджменту в части изучения среды, в которой происходит формирование события, и его управленческих стратегий [5, 7, 22, 27, 28, 33, 41]. Cтейкхолдеры событий, также как и стейкхолдеры фирмы, оказывают прямое и косвенное воздействие на выбор организаторами стратегии развития события, постановку маркетинговых целей и задач, а также другие стратегические решения [18].
Среди культурных событий особое внимание исследователей получило исследование фестивалей как объектов применения теории стейкхолдеров. Организационная структура управления услугами фестивалей культуры определяется рядом факторов, в числе которых размер организации, уровень специализации и кооперации труда, характер и сложность производимых услуг. Здесь необходимо отметить, что организаторами фестивалей культуры выступают различные субъекты, такие как государственные учреждения культуры, региональные и муниципальные органы власти, а также коммерческие фирмы, общественные организации и индивидуумы.
В связи с этим превалирующим типом организационной структуры фестивалей будет органический тип, для которого характерно использование гибких управленческих структур и высокая адаптивность к изменяющимся условиям с целью совершенствования производимых услуг. Одним из характерных признаков управления услугами фестивалей культуры является активное взаимодействие с окружающей средой. Кроме того, в рамках организации фестивалей культуры находит широкое применение проектный тип организационной структуры, также характеризующийся универсальностью, простотой и экономичностью. Динамичность внешней среды в условиях проектной оргструктуры управления обеспечивает необходимость взаимодействия с широким кругом внутренних и внешних акторов.
В исследованиях по данной тематике авторы проводят категоризацию стейкхолдеров фестивалей [20; 26; 33], анализируют их роль для успешного проведения событий [37], существующие модели взаимодействия организаторов со стейкхолдерами, а также предлагают подходы к управлению стейкхолдерами в целях достижения стратегических целей фестивальной деятельности – устойчивое развитие и выживание [7; 19]. При помощи теории стейкхолдеров возможно проведение более детального анализа факторов, влияющих на возникновение фестиваля, его дальнейшего развития, а также определение его сильных и слабых сторон.
Задача по организации крупных фестивалей представляется осуществимой только в условиях сотрудничества групп или индивидуумов, разделяющих одну или несколько общих целей. Необходимо отметить, что даже в случае проведения коммерческих культурных событий, для организаторов которых характерна постановка единственной цели – получение прибыли, возникает ситуация, при которой значительное влияние на успех события будут оказывать внешние стейкхолдеры – спонсоры и партнеры, а также государственные органы власти, выполняющие регуляторную функцию [18].
В русле широкого подхода Э. Фримана к определению стейкхолдера фирмы Д. Гетс определяет стейкхолдера события как «человека или группу людей, которые могут влиять на проведение события или испытывают на себе его влияние» [21, с. 92]. Круг стейкхолдеров события, по мнению Д. Гетса [22, с. 15], очерчен теми группами или индивидуумами, кто имеет отношение к событию или его последствиям, включая всех, кто занят в организации и проведении события, спонсоров и грантодате-лей, представителей общественности, и всех тех, кто попадает под влияние события.
В рамках данной статьи авторы хотели бы уделить особое внимание именно вопросу влияния событий на стейкхолдеров или эффектов, которые стейкхолдеры получают от проведения фестивалей культуры [3, 36]. Усиление положительных эффектов и снижение действия негативных эффектов является одной из ключевых задач как для организаторов фестивалей, так и для стейкхолдеров. В связи с этим возникает необходимость поиска наиболее действенных инструментов, нацеленных на эффективное управление эффектами от проведения фестивалей. Для этого представляется важным идентифицировать основных стейкхолдеров фестивалей культуры.
На основе результатов теоретических и эмпирических исследований фестивалей культуры, проведенных при участии авторов, были идентифицированы следующие группы стейкхолдеров: организаторы; посетители; участники; туристы; местные жители; представители профильного бизнес-сообщества, в том числе туристские фирмы; информационно-туристские центры; поставщики; спон- соры; муниципальные или региональные власти; волонтеры; сотрудники учреждений культуры, принимающих участие в организации фестивалей; средства массовой информации и, в целом, медиасфера; профессиональные творческие сообщества; продюсеры, обеспечивающие интересы крупных исполнителей фестивалей; работники креативных индустрий; инфраструктурные организации, участвующие в обеспечении проведения фестиваля.
Обратимся к классификации стейкхолдеров фестивалей культуры. Исследователи выделяют несколько классификационных признаков стейкхолдеров фестивалей и других культурных событий. Одной из наиболее популярных классификаций является классификация, проведенная на основе степени вовлеченности стейкхолдеров в процесс подготовки и проведения события [20]. Стейкхолдеры в рамках этого подхода сгруппированы в пять категорий: союзники и сотрудничающие стороны, к числу таковых относятся, например, туристические агентства, профессиональные ассоциации; регуляторы, функции которых возложены на государственные органы власти; сопроизводители - в данном контексте имеются в виду люди и группы, принимающие участие в организации события; посредники, к числу которых относятся поставщики услуг и ресурсов; адресаты, т.е. те стейкхолдеры, кто получает основные эффекты от проведения фестивалей; по мнению автора классификации, эта группа включает в себя, прежде всего, посетителей и местных жителей.
Другая классификация основана на добровольном (целенаправленном) или произвольном участии стейкхолдеров в организации культурного события [14]. Это те стейкхолдеры, кто добровольно участвует в подготовке и проведении фестиваля, целенаправленно инвестируют в него различного рода ресурсы. Непроизвольные же стейкхолдеры оказываются вовлеченными посредством получения эффектов от проведения фестивалей. Отсюда вытекает другой важный аспект во взаимоотношении между стейкхолдерами - зависимость степени влияния стейкхолдеров на процесс организации события от произведенных ими инвестиций в событие.
Так, те лица или группы лиц, которые занимаются финансированием события, будут обладать большей степенью влияния по сравнению с другими стейкхолдерами [14]. Более того, некоторые исследователи указывают на тот факт, что с развитием жизненного цикла фестиваля или другого культурного события, его зависимость от спонсоров будет увеличиваться, что, в свою очередь, приведет к тому, что организаторы события потеряют собственную независимость [14]. Однако С. Рейд в своем исследовании [34] связывает влияние стейкхолдеров на процессы по организации фестиваля с численностью группы: чем она больше, тем сильнее будет оказываемое влияние. Так, например, артисты -участники фестивалей - оказываются в числе второстепенных стейкхолдеров, несмотря на то, что они являются неотъемлемой частью фестиваля.
Еще одна классификация [33] предусматривает наличие целевых (первичных) и обеспечивающих (вторичных) групп стейкхолдеров. Первичные стейкхолдеры включают в себя организаторов, спонсоров, волонтеров, поставщиков, участников, а также посетителей культурного события. Группа вторичных стейкхолдеров формируется из местного населения, органов государственной и муниципальной власти, представителей бизнес-сообщества, средств массовой информации, туристских организаций, а также специальных служб, предоставляющих, например, охранные или медицинские услуги. Значимость вторичных стейкхолдеров для организации фестиваля культуры, может быть, менее очевидна организаторам события, однако результаты эмпирических исследований [34] демонстрируют, что отсутствие вторичных стейкхолдеров негативным образом сказывается на успехе события.
С учетом результатов анализа существующих классификаций авторами разработан собственный подход к классификации и систематизации различных групп стейкхолдеров. В его основу положен тезис о лабильности роли и функций различных групп стейкхолдеров в зависимости от миссии, целей и задач фестиваля. При организации фестивалей культуры некоторые группы стейкхолдеров могут выступать как в роли первичных, так и вторичных стейкхолдеров. К первичным стейкхолдерам будут относиться те, кто испытывает на себе положительные эффекты от проводимого фестиваля, на кого изначально нацелены услуги фестиваля. К вторичным - те, чье участие в фестивале носит либо вспомогательный, обеспечивающий характер, либо те стейкхолдеры, которые испытывают положительные или отрицательные эффекты от пользования услугами фестиваля опосредованно. Важно подчеркнуть, что на разных этапах организации фестиваля первичные и вторичные стейкхолдеры могут меняться. Например, состав первичных стейкхолдеров может быть различным на стадиях планирования и под- ведения итогов фестиваля. Такие группы стейкхолдеров, как организаторы и посетители, всегда будут выступать в качестве первичных стейкхолдеров.
С целью совершенствования процесса управления услугами фестивалей культуры авторами разработана методика дуального поведения стейкхолдеров, в основу которой положен тезис о двойственной роли многих групп стейкхолдеров фестивалей: в рамках фестивалей культуры стейкхолдеры могут выступать как в роли потребителей, так и в роли производителей услуг.
Теоретическое обоснование методики дуального поведения стейкхолдеров лежит в рамках концепции сопроизводства (co-production), которая получила развитие в теории маркетинга услуг в начале 2000-х годов [8; 32; 39] или участия потребителей в создании ценности (value co-creation) [9; 31; 39; 40]. С. Варго и Р. Лаш [40, c. 44] проводят различие между этими концепциями, используя термин «сопро-изводство» для производства товаров, а «участие в создание ценности» для производства услуг. В рамках данного исследования различий между концепциями не проводится, так как услуги фестивалей культуры рассматриваются с точки зрения организации управления.
Концепция сопроизводства подразумевает участие потребителей в одном или нескольких этапах производственной цепочки услуги. В рамках подхода, разработанного авторами, стейкхолдеры фестиваля, выступающие преимущественно в роли потребителей услуг, рассматриваются как участники процесса производства комплексной системы услуг фестиваля. При этом некоторые из стейкхолдеров частично задействованы в производстве услуг, как, например, в случае, когда посетители фестиваля участвуют в формировании программы события (основные услуги фестиваля, связанные с его творческой концепцией), другие – являются производителями отдельных видов услуг в рамках фестиваля, например, вспомогательных (творческие услуги, но дополняющие по своему характеру основные услуги) или обеспечивающих (услуги по обеспечению безопасности, медицинской помощи, транспорта и т.п.), участвуя в производстве системы услуг (см. рис. 1).
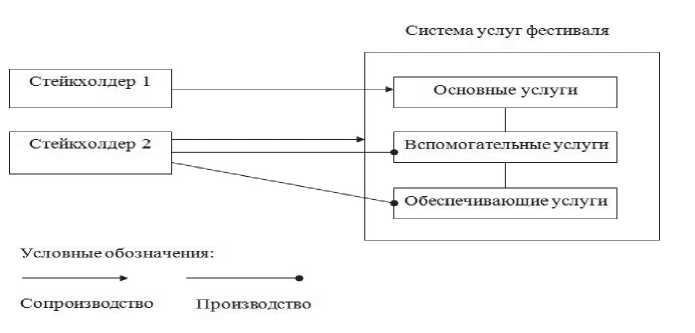
Составлено авторами.
Рис. 1. Сопроизводство и производство услуг фестиваля
Участие потребителя в производстве услуги позволяет повысить степень ее кастомизации [16], таким образом, стейкхолдеры, участвуя в производстве услуг фестиваля, повышают уровень их соответствия собственным запросам и нуждам, что, в свою очередь, приводит к формированию положительных эффектов фестиваля.
Далее будут рассмотрены результаты проведенных эмпирических исследований, положенных авторами в основу методики дуального поведения стейкхолдеров.
В ходе проекта Лаборатории экономики культуры НИУ ВШЭ – Санкт-Петербург, реализованного в 2012–2013 гг. при участии авторов, были исследованы услуги, оказываемые организаторами и участниками российских фестивалей военно-исторической реконструкции другим участникам фестивалей [23]. Участие в фестивалях военно-исторической реконструкции является популярным хобби или серьезным досугом (serious leisure) [38]. В рамках фестивалей военно-исторической реконструкции сложилась своя внутренняя система предоставления услуг. Так, были выделены следующие типы услуг:
-
1) оплачиваемые, бартерные и бесплатные услуги;
-
2) материальные и нематериальные услуги (услуги по изготовлению аутентичных предметов оружия, быта, одежды, с одной стороны, и консультационные и коммуникационные услуги, с другой);
-
3) услуги разным категориям потребителей: членам одного клуба, членам других клубов и сторонним посетителям фестивалей, например, туристам.
Результаты опроса участников фестивалей показали, что они не только активно пользуются услугами товарищей, но также предлагают свои услуги одноклубникам и реконструкторам из других клубов, а также в небольшой мере оказывают услуги туристам, посещающим фестивали. Среди наиболее популярных услуг, оказываемых реконструкторами, выделяются: производство одежды, включая ткачество, консультационные услуги, изготовление кожаных изделий, ковка предметов оружия и быта, изготовление стрел, изготовление предметов быта.
Среди преимуществ, которые получают реконструкторы, предоставляя услуги, были отмечены: усиление персональных связей в сообществе реконструкторов; усиление единства в клубе; повышение социального статуса; материальные выгоды. Таким образом, участники фестивалей, являясь и производителями, и потребителями услуг, испытывают на себе положительные социокультурные и экономические эффекты фестивалей, что также приводит к формированию устойчивых связей для взаимодействия в рамках развития движения реконструкторов.
Следует подчеркнуть, что до недавнего времени подавляющее большинство фестивалей реконструкторов носило негосударственный характер, и государственные органы управления культурой оказывали им минимальную поддержку. В этих условиях, одним из важнейших эффектов фестивалей реконструкторов было формирование и поддержание уникальной атмосферы социума, в которой участники легко меняли свои роли и выступали в различных качествах: соорганизаторов, участников – артистов, зрителей, потребителей специфических услуг, предоставляемых другими участниками фестивалей. Именно возможность постоянных «перевоплощений» является для участников данных фестивалей одним из главных эффектов.
Другой пример основан на исследовании акции «Ночь музеев», которая проводится ежегодно в более, чем в 160 странах. В Санкт-Петербурге она впервые была организован в 2008 году и за последние годы приобрела огромную популярность (в 2014 г. на акции побывало более 100 тыс. посетителей). В рамках исследовательского проекта Лаборатории экономики культуры НИУ ВШЭ – Санкт-Петербург, реализованного в 2012–2013 гг., при участии авторов были проведены опросы посетителей акции, а также проведены глубинные интервью с представителями музеев и других учреждений, ответственных за организацию и проведение «Ночи музеев».
Всего было проведено 62 интервью. Характеризуя структуру выборки менеджеров учреждений культуры, отметим, что в нее вошли сотрудники учреждений разной ведомственной принадлежности, как государственные, так и частные, находящиеся в различных районах города и отличающиеся по расположению к основным туристским маршрутам [1]. По результатам интервью с менеджерами музеев и других учреждений было выявлено, что они являются не только производителями основных услуг для посетителей акции, формируя специальные программы, но также и потребителями ее услуг, создание которых становится возможным благодаря формату «Ночи музеев», то есть благодаря заданным организаторами «правилам игры».
К данным «правилам» относятся: общая тема всех мероприятий фестиваля, время проведения мероприятий, требования по организации работы с посетителями, ожидающими в очереди возможности входа в музей. В ходе интервью менеджеры отметили, что участие в фестивале способствует развитию креативного потенциала сотрудников учреждений, освоению новых пространств, которые прежде не использовались (внутренние дворы, близлежащие территории и т.п.), поиску дополнительных ресурсов (в том числе, трудовых) и повышению эффективности их распределения, а также развитию внешних коммуникаций и обмена опыта с другими учреждениями культуры и организациями, принимающими участие в акции.
Данный пример характерен тем, что здесь потребителями услуг, которые создаются организаторами акции, становятся ее участники, сами предоставляющие разнообразные услуги посетителям акции. Тем самым, в данном случае мы имеем дело с дуальностью поведения одной из ключевых групп стейкхолдеров, которые заинтересованы в положительных эффектах и как производители услуг, и как потребители.
Следующие два примера связаны с музыкальными джазовыми фестивалями «Пори Джаз» (г. Пори, Финляндия) и «Сентябрь в Тихвине» (г. Тихвин, Россия). В 2013 году в рамках реализации исследовательских проектов Лаборатории экономики культуры НИУ ВШЭ – Санкт-Петербург при участии авторов были проведены интервью со 111 стейкхолдерами фестиваля «Пори Джаз» и 11 стейкхолдерами фестиваля «Сентябрь в Тихвине». Целью интервью было узнать об эффектах, получаемых стейкхолдерами от проведения фестивалей на основе получаемых и производимых ими услуг. Список респондентов для интервью создавался с учетом необходимости охвата как можно большего числа стейкхолдеров фестиваля. В таблице в качестве примера представлен список стейкхолдеров, принявших участие в интервью в г. Пори.
Масштабы изученных фестивалей различны, однако в рамках обоих фестивалей организаторы предоставляют услуги таким группам стейкхолдеров, как участники, спонсоры, а также местные учреждения культуры. Так, спонсорам фестиваля «Сентябрь в Тихвине» предлагаются спонсорские пакеты, включающие в себя размещение логотипа спонсора на сайте фестиваля, в СМИ – информационных партнерах фестиваля и получение благодарственных писем от Администрации Тихвинского городского поселения, являющейся организатором фестиваля. Кроме того, в рамках фестиваля проводится закрытое мероприятие – Jam session в одном из ресторанов города, на которое спонсоры получают приглашение, что позволяет им в неформальной обстановке пообщаться с организаторами и участниками фестиваля.
Участников фестиваля в г. Тихвин лично приглашает его художественный руководитель и идейный вдохновитель И.В. Володин. В период проведения фестиваля участники фестиваля записывают новые музыкальные композиции вместе с его руководителем и договариваются о новых творческих проектах. Для музыкантов – это услуга, которую они получают в рамках фестиваля. Необходимо также отметить и услугу, заключающуюся в возможности общения с профессиональными музыкантами, которую могут получать в рамках фестиваля ученики Детской школы искусств им. Н.А. Римского-Корсакова. Однако потенциал этой услуги реализуется пока в весьма ограниченном объеме и заключается в выступлении учеников школы на фестивале.
Таблица
Список стейкхолдеров, принявших участие в интервью в г. Пори (Финляндия)
|
Группа стейкхолдеров |
Количество интервью |
|
Внешние эксперты в сфере событийного менеджмента |
2 |
|
Волонтеры |
11 |
|
Местные жители |
41 |
|
Организаторы фестиваля |
3 |
|
Представители академического сообщества и практики событийного менеджмента |
6 |
|
Представители индустрии гостеприимства (владельцы ресторанов, баров, менеджеры отелей и т.п.) |
13 |
|
Представители креативных индустрий г. Пори |
2 |
|
Представители медицинской службы |
1 |
|
Представители муниципальной власти г. Пори |
4 |
|
Представители некоммерческих учреждений культуры г. Пори |
4 |
|
Представители региональной власти региона Сатакунта |
2 |
|
Представители СМИ |
1 |
|
Спонсоры фестиваля |
1 |
|
Торговцы уличных палаток |
14 |
|
Участники фестиваля (музыканты) |
6 |
|
Итого |
111 |
Что касается фестиваля «Пори Джаз», то объем и качество реализации услуг спонсорам, участникам и исполнителям находится на более высоком уровне. За время своего существования фестиваль «Пори Джаз» сформировал комплексную систему спонсорства, в которой основное место занимают продукты, предлагаемые фестивалем своим спонсорам. Это, прежде всего, ко-брендинг, используемый как во время фестиваля и его отдельных мероприятий, так и для дальнейшего продвижения продукции спонсоров. Благодаря высокому уровню узнаваемости бренда фестиваля – 92% финнов знают про фестиваль [1] – фестиваль не испытывает сложностей в поиске спонсоров. Спонсорам предоставляется уникальное право продавать свою продукцию на фестивале (только одна компания продает ту или иную категорию товаров), также им предоставляется возможность ко-брендинга с логотипом «Пори Джаз».
Следующий пример основан на экспертном опросе менеджеров культурных событий Санкт-Петербурга, проведенном при участии авторов Лабораторией экономики культуры НИУ ВШЭ – Санкт-Петербург в декабре 2012 года. Опрос был нацелен на выявление партнерских связей и оценку уровня взаимодействия менеджеров культурных событий, в частности, фестивалей культуры, и представителей туристского бизнеса. Несмотря на то, что в целом сотрудничество между оргкомитетами мероприятий и турфирмами развито в очень слабой степени, менеджеры отметили, что его интенсификация будет способствовать привлечению дополнительного числа посетителей: непосредственно туристов – клиентов турфирм, дополнительной рекламе фестиваля, развитию спонсорского сотрудничества с другими субподрядчиками (отели, транспортные компании), а также продвижению собственных или совместных брендов. Таким образом, круг услуг, которые представители турбизнеса способны предоставлять организаторам событий на взаимовыгодной основе, довольно широк, но, к сожалению, пока сотрудничество между этими двумя категориями стейкхолдеров не налажено.
Участие стейкхолдеров в роли производителей и потребителей услуг фестивалей культуры способно, с одной стороны, увеличить спектр потребляемых культурных услуг в целом, а, с другой стороны, усилить эффекты от проведения фестиваля. Результаты проведенных эмпирических исследований продемонстрировали, что усилению положительных эффектов от проведения фестивалей будет способствовать применение организаторами методики дуального поведения стейкхолдеров. Далее мы рассмотрим основные составляющие методики.
На первом этапе организаторы определяют перечень услуг, которые будут предназначены для ключевых стейкхолдеров фестиваля. Эти услуги преимущественно являются основными и способствуют продвижению творческой концепции, главной идеи и миссии фестиваля. Так, для посетителей организаторы предусматривают разнообразную программу мероприятий в рамках фестиваля, то есть именно посетители выступают в качестве получателей услуг. При этом участники фестиваля, в свою очередь, являются производителями услуг, непосредственно создавая творческий продукт фестиваля, выступая с концертами и спектаклями или представляя другие виды исполнительских или изобразительных искусств.
На следующем этапе происходит разработка системы услуг, которые могут быть произведены другими категориями стейкхолдеров, в том числе и посетителями фестиваля. Такие услуги могут носить вспомогательный или даже обеспечивающий характер. Так, например, стимулирование посетителей фестиваля к распространению информации о событии сделает их одним из основных производителей услуг по созданию информационных поводов и продвижению бренда фестиваля и места его проведения. В настоящее время эта услуга имеет широкое распространение благодаря социальным сетям и интернет-сервисам, в которых посетители фестивалей размещают разнообразную информацию, способствующую формированию положительного имиджа фестиваля и, таким образом, повышению удовлетворенности фестивалем различных групп стейкхолдеров.
Наконец, на третьем, последнем, этапе организаторам необходимо спланировать производство услуг для тех стейкхолдеров, которые являются ключевыми производителями услуг. К их числу относятся участники фестивалей, спонсоры, предприятия сферы гостеприимства.
Таким образом, организаторы фестиваля создают систему, в которой значительная часть стейкхолдеров получает на фестивале услуги, удовлетворяющие их собственные потребности, что способствует устойчивому развитию фестиваля. На рисунке 2 схематично изображены основные этапы формирования системы услуг фестивалей культуры при помощи методики дуального поведения стейкхолдеров.
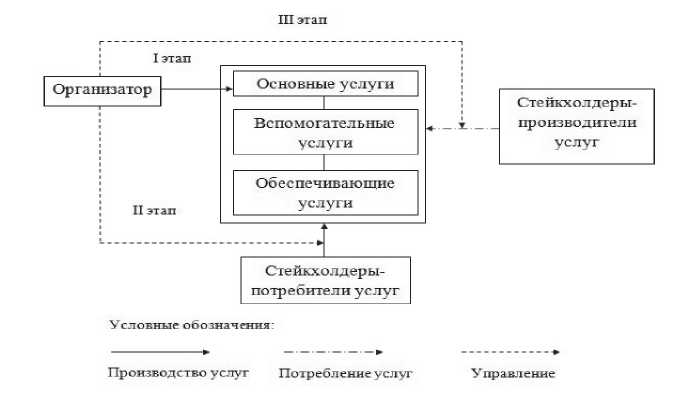
Составлено авторами.
Рис. 2. Формирование системы услуг фестиваля при помощи методики дуального поведения стейкхолдеров
На наш взгляд, методика дуального поведения стейкхолдеров, являясь развитием теории сопроиз-водства услуг, может стать действенным инструментом усиления позитивных эффектов от проведения фестивалей культуры на основе более активного вовлечения различных групп посетителей, гостей и участников фестивалей в систему производства и потребления услуг. Как выявлено авторами в ходе исследований, стейкхолдеры фестивалей одновременно могут выступать и в роли производителей, и в роли потребителей услуг. Следует подчеркнуть, что предложенный методический подход к организации и проведению фестивалей носит достаточно универсальный характер и применим для фестивалей культуры различных жанров и масштабов.
Список литературы Применение теории стейкхолдеров в системе управления услугами фестивалей культуры
- Гордин В.Э., Хорева Л.В., Дедова М.А. Совершенствование музейного менеджмента на основе развития событийной деятельности//Известия Санкт-Петербургского государственного экономического университета. 2014. № 4. С. 73-82.
- Клейнер Г. Б. Ресурсная теория системной организации экономики//Российский журнал менеджмента. 2011. № 3. С. 3-28.
- Матецкая М.В., Дедова М.А. Актуальные подходы к оценке прямых и косвенных эффектов культурных событии//Журнал новой экономической ассоциации. 2014. № 24. С. 190-194.
- Петров М.А. Теория заинтересованных сторон: пути практического применения//Вестник СПбГУ. Серия 8. 2004. № 16. Вып. 2. С. 51-68.
- Allen J. Festival and special event management. Milton: John Wiley & Sons Australia, 2011. 20 р.
- Anderson J.W. Corporate social responsibility. New York: Quorum Books, 1989.
- Andersson T.D., Getz D. Stakeholder Management Strategies of Festivals//Journal of Convention & Event Tourism. 2008. Vol. 9. № 3. P. 199-220.
- Benpaudi N., Leone R.P. Psychological implications of customer participation in co-production//Journal of Marketing. 2003. Vol. 67. P. 14-28.
- Berthon P., John J. From entities to interfaces: Delineating value in customer-firm interactions/In Lusch R.F., Vargo S.L. (Eds.) The service dominant logic of marketing: Dialog, debate and directions. NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2006.
- Brenner S.N., Cochran P. The stakeholder theory of the firm: Implications for business and society theory and research. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the International Association for Business and Society, Sundance, UT, 1991.
- Brummer J.J. Corporate responsibility and legitimacy: An interdisciplinary analysis. New York: Greenwood Press, 1991. МЕТОДОЛОГИЯ И ИНСТРУМЕНТАРИЙ УПРАВЛЕНИЯ
- Clarkson M.A. Stakeholder framework for analyzing and evaluating corporate social performance//Academy of Management Review. 1995. Vol. 20. № 1. P. 92-117.
- CornellB., Shapiro A.C. Corporate stakeholders and corporate finance//Financial Management. 1987. № 16. Р. 5-14.
- Crespi-Vallbona M., Richards G. The meaning of cultural festivals. Stakeholders perspectives in Catalunya//International journal of cultural policy. 2007. № 13. P. 103-122.
- Dodd E.M. For whom are corporate managers trustees?//Harvard Law Review. 1932. № 45. Р. 1145-1163.
- Etgar M. A descriptive model of the consumer co-production process//Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science. 2008. Vol. 36. P. 97-108.
- Freeman R.E. Strategic management: A stakeholder approach. Boston: Pitman, 1984.
- Getz D., Andersson T. Festival stakeholders: exploring relationships and dependency through a four-country comparison//Journal of hospitality & tourism research. 2010. Vol. 34. № 4. P. 531-556.
- Getz D., Andersson T. Sustainable festivals: On becoming an institution//Event Management. 2009. Vol. 12. № 1. P. 1-17.
- Getz D., Andersson T., Larson M. Festival stakeholder roles: Concepts and case studies//Event Management. 2007. Vol. 10. № 2. P. 103-122.
- Getz D. Event Tourism: Definition, Evolution and Research//Tourism Management. 2007. Vol. 29. № 3. P. 403-428.
- Getz D. Festivals, special events, and tourism. NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1991.
- Gordin V.E., Dedova M. Social Entrepreneurship in the Informal Economy: a Case Study of Re-enactment Festivals//Journal of Enterprising Communities. 2015. Vol. 9. № 1. P. 6-16.
- Hill C.W.L., Jones T.M. Stakeholder-agency theory//Journal of Management Studies. 1992. № 29. Р. 131-154.
- Kramer R. A third sector in the new millennium?//Voluntas. 2000. Vol. 11. № 1. P. 1-23.
- Larson M. A political approach to relationship marketing: Case study of the Storsjoyran Festival//International Journal of Tourism Research. 2002. № 2. P. 119-143.
- Long P. After the Event: Perspectives on Organizational Partnerships in the Management of a Themed Festival Year//Event Management. 2000. № 6. P. 45-59.
- Lovendahl B.R. Learning Effects: The Case of the Lillehammer Olympic Winter Games 1994/In Mossberg L.L. (ed.) Evaluation of Events: Scandinavian Experiences. NY: Cognizant Communication Corporation, 2000.
- Mitchell R.K., Agle B.R., Wood D.J. Toward a theory of stakeholder identification and salience: Defining the principle of who and what really counts//Academy of Management Review. 1997. Vol. 22. № 4. P. 853-886.
- Payne A., Ballantyne D., Christopher M. A stakeholder approach to relationship marketing strategy//European Journal of Marketing. 2005. Vol. 39. № 7/8. P. 855-871.
- Payne A.F., Storbacka K., Frow P. Managing the co-creation of value//Journal of the academy of marketing science. 2008. Vol. 36. №. 1. P. 83-96.
- Pralahad C.K., Ramaswamy V. The future of competition: Co-creating unique value with customers. Boston, Mass: Harvard Business School Press, 2004.
- Reid S., Arcodia C. Understanding the role of the stakeholder in event management//Journal of Sport & Tourism. 2002. Vol. 7. № 3. P. 20-22.
- Reid S. Event stakeholder management: developing sustainable rural event practices//International Journal of Event and Festival Management. 2011. Vol. 2. № 1. P. 20-36.
- Reilly T. Collaboration in action: An uncertain process//Administration in Social Work. 2001. Vol. 25. № 1. P. 53-74.
- Richards G., Palmer R. Eventful Cities. London: Routledge, 2012.
- Spiropoulos S., Gargalianos D., Sotiriadou K. The 20th Greek festival of Sydney: A stakeholder analysis//Event Management. 2006. Vol. 9. № 4. P. 169-183.
- Stebbins R.A. Amateurs, Professionals, and Serious Leisure. Montreal: McGill-Queen's University Press, 1992.
- Vargo S., Lusch R. Evolving to a new dominant logic for marketing//Journal of Marketing. 2004. Vol. 68. P. 1-17.
- Vargo S.L., Lusch R.F. Service-dominant logic: What it is, what it is not, what it might be/In Lusch R.F., Vargo S.L. (Eds.) The service dominant logic of marketing: Dialog, debate and directions. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2006.
- Watt M.D. Event Management in Leisure and Tourism. Harlow, Essex, England: Longman, 1998.


