Роль D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов клюквы в профилактике рецидивов инфекции мочевыводящих путей
Автор: Москвина З.В., Болдырева М.Н., Россоловская К.А., Спивак Л.Г.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Инфекционно-воспалительные заболевания
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.17, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Профилактика инфекций мочевыводящих путей (ИМП) является актуальной проблемой в связи с их большой распространенностью. Регулярное использование антибиотиков, особенно в случаях рецидивирующей инфекции мочевых путей (РИМП), способствует формированию устойчивых штаммов микроорганизмов и развитию перекрестной антибиотикорезистентности. Именно поэтому возрастает актуальность поиска альтернативных неантибактериальных средств для лечения и профилактики воспалительных заболеваний мочевыводящих путей.
D-манноза, проантоцианидины, инфекции мочевыводящих путей, уропатогенная кишечная палочка, факторы вирулентности, адгезин fimh, профилактика, неантибактериальные средства
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142241804
IDR: 142241804 | DOI: 10.29188/2222-8543-2024-17-1-128-136
Текст научной статьи Роль D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов клюквы в профилактике рецидивов инфекции мочевыводящих путей
Инфекции мочевыводящих путей (ИМП) являются поводом для 10,5 миллионов обращений к урологам в год [1]. Российские источники свидетельствуют, что 40-50% женщин хотя бы однажды в жизни сталкивались с острым воспалением мочевого пузыря, что составляет 0,5– 0,7 эпизодов заболевания на 1 женщину [2]. При этом 8-10% женского населения в постменопаузальном периоде страдает рецидивирующими ИМП, а в пожилом возрасте эти инфекции выходят на второе место среди всех инфекций [3].
Препаратами выбора в борьбе с инфекцией мочевыводящих путей, согласно клиническим рекомендациям ведущих урологических сообществ мира, считаются про-тивомикробные препараты. В то же время их регулярное использование, особенно в случаях рецидивирующей инфекции мочевых путей, способствует формированию устойчивых штаммов микроорганизмов и развитию перекрестной антибиотикорезистентности [4-8]. В 2021 году были опубликованы результаты исследования с участием 33 732 пожилых пациентов с ИМП [9]. Одни из них получали антибиотики в течение 30 дней с целью профилактики ИМП, другие входили в контрольную группу без применения антибиотиков. В результате наблюдения оказалось, что пациенты, получавшие профилактику антибиотиками, чаще страдали от синдрома системной воспалительной реакции и сепсиса с более высокими показателями антибиотикорезистентности. У них также чаще наблюдалось развитие диареи, ассоциированной с Clostridium difficile . Авторами исследования был сделан вывод о том, что вред длительной антибиотикопрофилак-тики у пожилых пациентов может перевешивать ее преимущества.
По данным ВОЗ, бактериям семейства Enterobacte-riaceae следует уделять особенное внимание в исследованиях в связи с их растущей резистентностью к цефалоспоринам третьего поколения [10]. Таким образом, возрастает актуальность поиска альтернативных подходов для профилактики рецидивирующей ИМП. Поэтому перспективным, но все еще недостаточно изученным представляется применение таких веществ, как D-манноза и проантоцианидины клюквы.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Выполнен обзор литературы на основе данных опубликованных в базах Научной электронной библиотеки еL и PubMed . Поиск был проведен по ключевым словам: инфекции мочевых путей (urinary tract infections); D-манноза (D-mannosa); про-антоцианидины (proanthocyanidins); антибиотикорези-стентность (antibiotic resistance). Для настоящего обзора были отобраны статьи, которые отражают проблему ан-тибиотикорезистентности и возможностей неантибактериальной профилактики ИМП, а также клинические исследования, систематические обзоры и мета-анализы касающиеся эффективности и безопасности применения продуктов, содержащих D-маннозу и проантоцианидины клюквы. Всего обзор включает 64 публикаций. Проанализировано 52 зароубежные публикации и 12 – отечественных (2011-2023 гг.).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
D-манноза
Одним из методов предотвращения развития повторных эпизодов инфекции мочевыводящих путей является использование D-маннозы, представляющей собой простой сахар – альдогексозу, который обладает структурным сходством с остатками маннозы уро-плакина 1а, покрывающего поверхность эпителиальных зонтичных клеток уротелия. D-манноза способна насыщать FimH-адгезины, препятствовать прикреплению E. coli за счет механизма конкурентного ингибирования и выводить патогены с мочой [11-13].
Название «манноза» происходит от древнееврейского слова «манна». Как известно из Библии, «Манна небесная» — это спасительная пища, посланная израильтянам во время их скитаний по пустыне. В биологии слово «манна» встречается в названии растения ясень манновый (Fraxinus ornus), сок которого, образующийся при подсечке ветвей, быстро застывает на воздухе и имеет сладковатый вкус [14]. Манноза содержится в персиках, яблоках и апельсинах и, поступая в организм

человека, осуществляет гликозилирование белков [15]. N-гликозилирование белковых структур необходимо для функционирования иммуноглобулинов, из чего следует что D-манноза принимает участие в иммунорегуляции [14, 16].
Скорость всасывания D-маннозы в кровоток из желудочно-кишечного тракта после приема внутрь составляет 10% от скорости всасывания глюкозы. В норме уровень D-маннозы в крови составляет 50-100 мкмоль/л [17]. Часть D-маннозы, поступающей с пищей, метаболизируется в кишечнике, а часть выводится в неизмененном виде с мочой, при этом через час в моче обнаруживается около 25-30% от той дозы, которая была принята с пищей [18].
На сегодняшний день известны исследования, в которых проводилось изучение эффективности использования D-маннозы. Контрольные группы включали пациентов, которые не получали никакой профилактики или же использовали антибактериальные препараты для профилактики рецидивирующей инфекции мочевых путей.
В исследовании L. Domenici и соавт. пациентов, которые принимали препарат на основе D-маннозы (1,5 г D-маннозы, бикарбонат натрия, сорбит и диоксид кремния), сравнили с группой контроля, где не использовались профилактические средства. Авторы обнаружили значительное уменьшение симптомов, связанных с ИМП уменьшение частоты рецидивов инфекции и повышение качества жизни в группе, получавшей D-маннозу [11].
-
B. Kranjcec и соавт. провели исследование, в котором сравнили пациентов из трех групп: первая группа получала D-маннозу, вторая – нитрофурантоин, третья (контрольная) не получала никакой профилактики. Они обнаружили, что у пациентов, принимавших D-маннозу или нитрофурантоин в качестве профилактики РИМП частота рецидивов была значительно ниже ( р <0,0001) в сравнении с контрольной группой, при этом время до рецидива было больше в группе D-маннозы (43 дня), чем в группе антибиотиков (24 дня). Дополнительным преимуществом стало значительно меньшее количество побочных эффектов у пациентов, получавших D-маннозу, по сравнению с пациентами, принимавшими нитрофурантоин в качестве профилактики [19].
Похожие данные можно увидеть в исследовании D. Porru и соавт., которые так же отмечали большее время до развития рецидива у пациентов в группе D-маннозы (200 дней), чем в группе антибиотиков (52 дня), кроме того, пациенты, получавшие D-маннозу, реже отмечали появление ургентности [20].
Однако есть исследования, авторы которых не обнаружили различий между группой пациентов, получавших препарат на основе D-маннозы (D-манноза N -ацетилцистеин и экстракт плодов Morinda citrifolia) и группой, принимавшей антибиотики с целью профилактики рецидивов ИМП [21].
В когортных исследованиях G. Del Popolo и F. Nelli наблюдали больных, страдающих рецидивирующей ИМП, в том числе с нейрогенным мочевым пузырем. Пациенты получали комбинацию D-маннозы с салицином (1000 мг D-маннозы + 200 мг сухого экстракта ивы) в течение 5 дней, а затем D-маннозу в сочетании с пробиотиком (затем 700 мг D-маннозы + 1×109 КОЕ Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14) в течение 7 дней. Они установили, что применение D-маннозы привело к значительному снижению ежедневной частоты мочеиспускания и сокращению частоты эпизодов недержания мочи, причем эти эффекты сохранялись в течение 1 месяца после окончания лечения [22].
-
V. Phé и соавторы сообщили, что у пациентов с рассеянным склерозом прием D-маннозы дважды в день в течение 16 недель привел к общему снижению числа подтвержденных ИМП в месяц как в группе с уретральным катетером (63%), так и в группе без катетера (75%) [23]. На сегодняшний день известны исследования, в которых проводилось изучение эффективности использования D-маннозы. Контрольные группы включали пациентов которые не получали никакой профилактики или же использовали антибактериальные препараты для профилактики рецидивирующей ИМП.
Имеется опыт использования препаратов, включающих D-маннозу, у пациенток с явной гипоэстрогенией. В 2015-2017 гг. было проведено обсервационное ретроспективное клиническое исследование, в котором приняли участие 60 пациентов с рецидивирующим циститом и раком молочной железы [24]. В одну группу (n=40) вошли пациенты, получавшие D-маннозу 500 мг, N-ацетилцистеин 100 мг и экстракт плодов Morinda citrifolia 200 мг (NDM) в течение 6 месяцев вместе с антибиотикотера-пией (фосфомицин, нитрофурантоин или ципрофлоксацин при острых эпизодах цистита). Альтернативная группа (n=20) принимала антибиотики только по мере необходимости. Через 2 месяца наблюдения только 5 (12,5%) участников группы, принимавших D-маннозу имели положительный посев мочи, в то время как у тех кто не принимал D-маннозу, положительный результат посева мочи был зафиксирован в 18 случаях (90%) [24].
-
C. Genovese и соавт. сравнили между собой группы пациентов, принимавших D-маннозу с различными растительными экстрактами (1 группа: D-манноза 420 мг+берберин, арбутин, береза (n=24), 2 группа: D-манноза 420 мг+берберин, арбутин, береза, форсколин (n=24), 3 группа D-манноза 500 мг+проантоцианидины (n= 24)). Частота рецидивов цистита оказалась меньше в 1 и во 2 группе. Однако это исследование имеет низкую степень доказательности [25].
В России также был проведен ряд исследований биологически активных добавок, в состав которых входит D-манноза [26-31]. При этом три исследования показали что частота развития рецидивов цистита оказалась ниже в группе пациентов, получавших БАДы с D-маннозой.
Известны лабораторные исследования с целью оценки потенциала D-маннозы блокировать бактериальную адгезию к уроэпителиальным клеткам для предотвращения инфекции [32, 33]. Авторы пришли к выводу, что разработка средств на основе D-маннозы предотвращающих адгезию уропатогенов, имеет большие перспективы. J. Bouckaert и соавт. обнаружили, что экзогенный бутил aльфа-D-маннозид проявляет значительно лучшее сродство к FimH, чем манноза, и, следовательно ингибирует прилипание пилей Escherichia coli 1 типа к уротелию [33]. C. N. Spaulding и соавт. исследовали персистенцию уропатогенной кишечной палочки (UPEC) в кишечнике, которая может поддерживать рецидивиро-вание ИМП. Они обнаружили, что D-манноза приводит к значительному снижению связывания FimH с кишечником мыши ( p <0,001) [32].
Несмотря на то, что D-манноза представляет собой сахар и является источником углерода, а, следовательно может способствовать росту бактерий, D. Scribano и соавт. показали, что метаболизм бактерий в присутствии D-маннозы ( in vitro ) не меняется, и она не оказывает воздействия на активность антибиотиков [34].
Проантоцианидины клюквы
Еще одним многообещающим методом профилактики рецидивирующей мочевой инфекции являются продукты из клюквы. Употребление клюквы препятствует бактериальной адгезии, содержащиеся в клюкве проантоцианидины хотя и не обладают собственной антибактериальной активностью, но препятствуют прикреплению уропатогенных Е. coli за счет блокады Р-типа фимбрий, что так же способствует угнетению образования биопленок [35, 36]. Оценку эффективности применения продуктов из клюквы затрудняет наличие различных концентраций проантоцианидинов в исследуемых продуктах, что определяет необходимость выявления оптимальной дозы проантоцианидинов клюквы для достижения антиадгезивного эффекта. Так, в одном из исследований продемонстрировано, что способность препятствовать прикреплению бактерий проантоциани-дины проявляют уже в концентрации 60 мкг/мл, особенно важно, что они имеют специфическую антиад-гезивную активность против уропатогенных бактерий [37]. Согласно клиническим исследованиям ex vivo (доза-эффект) оптимальное количество проантоцианидинов должно составлять не менее 36 мг/день [38, 39]. Исследование канадских ученых, опубликованное в 2021 году было нацелено на оценку эффективности продуктов из клюквы в профилактике рецидивирующих ИМП у женщин при использовании оптимальной дозы проантоциа-нидинов (стандартизованной на уровне 2×18,5 мг/день). В исследование были включены сексуально активные небеременные женщины в возрасте 18 лет и старше с рецидивами ИМП. Ученые обнаружили, что высокие дозы экстракта проантоцианидина два раза в день не ассоциировались со снижением числа симптоматических ИМП по сравнению с экстрактом проантоцианидина в низких дозах. Однако эта высокая доза проантоцианидинов может оказывать профилактическое воздействие на рецидив симптоматической инфекции мочевыводящих путей у женщин, перенесших менее 5 инфекций в год [40].
Многочисленные клинические испытания эффективности продуктов из клюквы показали противоречивый эффект. Метаанализ (2017 г), включавший 7 рандомизированных плацебо-контролируемых исследований стандартизированных экстрактов клюквы, проведенный у женщин с риском развития неосложненных ИМП, показал, что стандартизированные экстракты клюквы снижают риск ИМП на 26%, при этом частота нежелательных явлений одинакова в группах терапии и плацебо [41]. Однако в ранее описанном метаанализе оценивалось влияние проантоцианидинов клюквы на здоровых женщин, а коллеги из Китая в 2021 г. провели подобную оценку среди восприимчивых групп населения. По данным систематического обзора, который включал 28 РКИ (23 были плацебо-контролируемые), женщины с рецидивирующими ИМП, дети и пациенты, использующие постоянные катетеры, на 30% меньше подвержены риску развития ИМП при использовании продуктов из клюквы [42]. По данным Кокрановского обзора 2023 года, использование продуктов из клюквы для снижения риска развития инфекций мочевыводящих путей оправдано у женщин с рецидивирующими ИМП у детей и у людей, предрасположенных к ИМП после вмешательств. Имеющиеся в настоящее время данные не поддерживают использование продуктов из клюквы у пожилых людей, пациентов с проблемами опорожнения мочевого пузыря или беременных женщин [43].
Лечение препаратами клюквы хорошо переносится – частота отказа от приема клюквенного сока из-за его плохих органолептических свойств минимальна при использовании капсул [44]. Необходимо отметить, что про-антоцианидины предотвращают развитие резистентности к антибиотикам и подавляют образование биопленок [45]. Канадские ученые показали потенцирующее действие проантоцианидинов клюквы как in vitro , так и in vivo в отношении антибактериальных препаратов, используемых против E. coli, Proteus mirabilis и Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ученые выделили два механизма, которые позволяют микробным клеткам становиться более уязвимыми: повышение проницаемости мембран бактериальных клеток и снижение активности насосов оттока многих лекарств, в том числе антибиотиков [46]. В 20182020 гг. в Румынии было проведено исследование, которое доказало, что сочетание D-маннозы с экстрактом клюквы может влиять на механизм антибактериальной устойчивости. Пациенты с неосложненной инфекцией мочевыводящих путей наблюдались в двух группах: одни получали только антибактериальную терапию
Таблица 1. Основные характеристики клинических исследований лечения и профилактики рецидивирующего ИМП с применением D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов
Table 1. Main characteristics of clinical trials of RINMP treatment and prevention using D-mannose and proanthocyanidins
|
Год исследования Year of study |
Дизайн исследования Study design |
Исследуемое вещество Test substance |
Группа(ы) сравнения Comparison group(s) |
Размер выборки. Пол Sample size. gender |
Результаты Results |
|
L. Domenici и соавт. [11] |
РКИ RCS |
3,0 г D-маннозы /сутки (3 дня), затем 1,5 г/сутки 3.0 g D-mannose/day (3 days), then 1.5 g/day |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
43 Женщины Women |
Уменьшение частоты рецидивов инфекции, уменьшение симптомов, связанных с ИМП в группе, получающей D-маннозу Reduced infection recurrence rate and UTI-related symptoms in the D-mannose group |
|
B. Kranjceс и соавт. [19] |
РКИ RCS |
2,0 г D-маннозы /сутки 2.0 g D-mannose/day |
|
308 Женщины Women |
Частота рецидивов в группе D-маннозы и антибиоти-копрофилактики одинакова, однако время до развития рецидива больше в группе с D-маннозой The relapse rate in the D-mannose and antibiotic prophylaxis group is the same, but the time to relapse is longer in the D-mannose group |
|
D. Porru и соавт. [20] |
РКИ RCS |
3,0 г D-маннозы (2 нед), затем по 2,0 г/сутки 3.0 g D-mannose (2 weeks), then 2.0 g/day |
Антибиотикопрофи-лактика Antibiotic prophylaxis |
60 Женщины Women |
В группе D-маннозы большее время до развития рецидива In the D-mannose group there was a longer time to relapse |
|
G. Palleschi и соавт. [21] |
РКИ RCS |
1,0 г D-маннозы /сутки + N-ацетилцистеин и экстракт плодов Morinda citrifolia 1.0 g D-mannose/day + N-acetylcysteine and Morinda citrifolia fruit extract |
Антибиотикопрофи-лактика Antibiotic prophylaxis |
80 Женщины (38) Women Мужчины (42) Men |
Частота рецидивов одинаковая в группах сравнения The relapse rate is the same in the comparison groups |
|
G. Del Popolo и соавт. [22] |
Когортное Cohort |
3,0 г D-маннозы /сутки + сухой экстракт ивы (5дн), затем 1,4 г D-маннозы/сутки + Lactobacillus acidophilus 3.0 g D-mannose / day + dry willow extract (5 days), then 1.4 g D-mannose/day + Lactobacillus acidophilus |
85 Женщины (68) Women Мужчины (17) Men |
Снижение частоты и эпизодов недержания мочи Reduced frequency and episodes of urinary incontinence |
|
|
V. Phé и соавт. [23] |
Когортное Cohort |
3,0 г D-маннозы /сутки 3.0 g D-mannose/day |
22 Женщины (18) Women Мужчины (4) Men |
Снижению числа подтвержденных ИМП Reducing the number of confirmed UTIs |
|
|
D. Marchiori и соавт. [24] |
Ретроспектив-ное Retrospective |
1,0 г D-маннозы /сутки (60 дней) + N-ацетилцистеин и экстракт плодов Morinda citrifo-lia, затем 500 мг D-маннозы /сутки + N-ацетилцистеин и экстракт плодов Morinda citrifolia 1.0 g D-mannose/day (60 days) + N-acetyl-cysteine and Morinda citrifolia fruit extract, then 500 mg D-mannose/day + N-acetylcysteine and Morinda citrifolia fruit extract 0.5 g D-mannose/day + proanthocyanidins |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
60 Женщины Women |
Уменьшение бактериурии и дизурических симптомов в группе, получающей профилактику Reduction of bacteriuria and dysuric symptoms in the group receiving prophylaxis |
|
C. Genovese и соавт. [25] |
РКИ RCS |
0,5 г D-манноза /сутки + проантоцианидины 0.5 g D-mannose/day + proanthocyanidins |
Group 1: D-mannose 0.42 g + berberine, arbutin, birch, Group 2: D-mannose 0.42 g + berberine, arbutin, birch, forskolin |
72 Женщины Women |
В группе пациентов, получавших D-маннозу + проантоцианидин частота рецидивов выше In the group of patients receiving D-mannose + proanthocyanidin, the relapse rate was higher и |
|
Год исследования Year of study |
Дизайн исследования Study design |
Исследуемое вещество Test substance |
Группа(ы) сравнения Comparison group(s) |
Размер выборки. Пол Sample size. gender |
Результаты Results |
|
А.Н. Берников и соавт. [26] |
РКИ RCS |
2,0 г D-маннозы + проантоцианидины+ витамин D (БАД Уронекст) 2.0 g D-mannose + proanthocyanidins+vitamin D (Dietary supplement Uronext) |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
111 Женщины Women |
Снижение частоты рецидивов, улучшение качества жизни в группе пациентов, получающих Уронекст Reduced relapse rate, improved quality of life in the group of patients receiving Uronext |
|
К.П. Тевлин и соавт. [27] |
РКИ RCS |
2,0 г D-маннозы + проантоцианидины+ витамин D (БАД Уронекст) 2.0 g D-mannose + proanthocyanidins+vitamin D (Dietary supplement Uronext) |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
60 Женщины Women |
Снижение частоты рецидивов, улучшение качества жизни в группе пациентов, получающих Уронекст Reduced relapse rate, improved quality of life in the group of patients receiving Uronext |
|
И.С. Шорманов и соавт. [28] |
РКИ RCS |
0,48 г D-маннозы/сут + проантоцианидины + экстракт толокнянки 0.48 g D-mannose/day + proanthocyanidins + extract bearberry |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
60 Женщины Women |
Снижение частоты рецидивов, улучшение качества жизни в группе пациентов, получающих профилактику Reduced relapse rate, improved quality of life in the group of patients receiving prophylaxis |
|
F. Vicariotto и соавт. [50] |
Когортное Cohort |
0,5 г D-маннозы/сут+ экзопо-лисахариды Str. thermophilus +проантоцианидины + L. plantarum and L. paracasei 0.5 g D-mannose/day + exopolysaccharides Str. thermophilus + proanthocyanidins + L. plantarum and L. paracasei |
35 Женщины Women |
Уменьшение типичных симптомов цистита, снижение уровня нитритурии и лейкоцитарной эстеразы Reduction of typical symptoms of cystitis, reduction of nitrituria and leukocyte esterase levels |
|
|
V. DE Leo и соавт. [49] |
РКИ RCS |
0,5 г D-маннозы/сут + проантоцианидины + экстракт прополиса 0.5 g D-mannose/day + proanthocyanidins + extract propolis |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
150 Женщины Women |
Снижение дизурических симптомов в группе пациентов, получающих профилактику Reduction of dysuric symptoms in the group of patients receiving prophylaxis |
|
А.И. Неймарк и соавт. [29] |
РКИ RCS |
2,0 г D-маннозы + проантоцианидины+витамин D (БАД Уронекст) 2.0 g D-mannose + proanthocyanidins+vitamin D (Dietary supplement Uronext) |
Без профилактики Without prevention |
86 Женщины Women |
Снижение частоты обострений посткоитального цистита в группе пациентов, получающих Уронекст Reduced frequency of exacerbations of postcoital cystitis in the group of patients receiving Uronext |
|
М.Н. Слесаревская и соавт. [30] |
Когортное Cohort |
2,0 г D-маннозы + проантоцианидины+витамин D (БАД Уронекст) 2.0 g D-mannose + proanthocyanidins+vitamin D (Dietary supplement Uronext) |
67 Женщины Women |
Уменьшение клинических симптомов, лейко-цитурии, бактериурии у женщин с РИНМП Reduction of clinical symptoms, leukocyturia, bacteriuria in women with RINUS |
|
|
А.С. Аль-Шукри и соавт. [31] |
2,0 г D-маннозы + проантоцианидины+витамин D (БАД Уронекст) 2.0 g D-mannose + proanthocyanidins+vitamin D (Dietary supplement Uronext) |
Только антибактериальная терапия Antibacterial therapy only |
120 Женщины Women Мужчины Men |
Снижение уровня обсеменeнности мочевого катетер в группе пациентов, получавших антибиотик + Уронекст Reduced level of urinary catheter contamination in the group of patients receiving antibiotic + Uronext |
(триметоприм + сульфаметоксазол), у вторых антибактериальную терапию сочетали с экстрактом клюквы и D-маннозой. Авторы проанализировали подгруппы больных с резистентностью к выбранному антибиотику. Ожидаемо, что частота излеченности в подгруппе, получавшей только триметоприм+сульфаметоксазол, была низкой (37,5%), а в группе, где антибиотик назначался совместно с экстрактом клюквы и D-маннозой, процент вылеченных пациенток составлял около 90%, и был схож с результатами в группе, где отмечалась чувствительность к использованному антибактериальному препарату [47].
Еще одно интересное исследование, доказывающее антиадгезивный эффект клюквы, проведено в Германии [48]. Образцы мочи пациентов, употреблявших экстракт клюквы, проанализировали на способность последнего препятствовать бактериальной адгезии, а также на содержание уромодулина (белка Тамма-Хорсфолла). Образцы в которых было отмечено нарушение прикрепления уропатогенов, содержали повышенное количество уромоду-лина, который был расценен как фактор неспецифической защиты.
В попытке найти максимально эффективное решение лечения и профилактики рецидивирующего ИМП проводилось изучение комбинации D-маннозы экстрактов клюквы и прополиса. Такое сочетание зарекомендовало себя как эффективное средство для профилактики рецидивов мочевых инфекций у женщин в перименопаузе (n=150). Полную ремиссию мочевых симптомов наблюдали у 92 (60%) пациенток [49].
Другие ученые проанализировали воздействие экстракта клюквы в сочетании с D-маннозой и пробиотиками Lactobacillus plantarum LP01 и Lactobacillus paracasei LPC09 и пришли к выводу, что такая комбинация значительно уменьшила симптомы острого цистита: дизурию частое мочеиспускание, сильные позывы к мочеиспусканию и рези внизу живота [50].
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Положительное действие продуктов на основе D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов для уменьшения симптомов и профилактики ИМП продемонстрировано во многих исследованиях, часто эти вещества комбинируют другими (табл. 1).
В 2020 году испанскими коллегами опубликовано рандомизированное клиническое исследование с двойным ослеплением [51]. Исследование было направлено на сравнительное изучение эффективности и безопасности в профилактике ИМП пищевой добавки, основным ингредиентом которой являлась D-манноза, и препарата с активным ингредиентом проантоцианидинами. В эксперимент были включены 283 женщины с рецидивирующей ИМП. В результате оказалось, что в профилактике рецидивирующих ИМП, вызванных кишечной палочкой у женщин, пероральный прием препарата на основе 2000 мг D-маннозы является более эффективным, чем прием 240 мг проантоцианидинов.
Результаты сравнительных клинических исследований двух методов профилактики ИМП на основе использования D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов клюквы вызвали интерес в научной среде. Все чаще можно слышать мнение, что польза от назначения антибиотиков при цистите более не превышает вред от них, поэтому необходимо развивать и внедрять в клиническую практику новые стратегии лечения и профилактики неосложненной ИМП [52].
На сегодняшний день известно множество различных неантибактериальных методов профилактики. В первую очередь необходимо упомянуть о поведенческой терапии – мочеиспускание после коитуса, повышенное потребление воды [53, 54], включение в рацион продуктов богатых витамином С [55, 56], применение фитопрепаратов [57]. Доказана эффективность иммуностимулирующего средства, содержащего бактериальный лизат 18 штаммов E coli [58, 59]. Положительно зарекомендовало себя внутрипузырное введение гиалуроновой кислоты и хондроитин сульфата с целью восстановления гликоза-мингликанового слоя слизистой мочевого пузыря [6062]. Также используются пробиотики на основе лактобактерий (Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1, Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14), способные конкурентно вытеснять патогенные микроорганизмы, а у женщин в постменопаузальном периоде с успехом применяются вагинальные эстрогены [63]. В борьбу за предотвращение ре- цидива ИМП вступают различные средства, и приходится делать выбор в пользу наиболее подходящей их комбинации. Знание механизмов действия D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов клюквы, которые оказывают свой антиадгезивный эффект, взаимодействуя с различными типами фимбрий, позволяет предположить, что сочетание этих веществ принесет гораздо большую пользу и способно максимально заблокировать адгезию патогенных бактерий (рис. 1).
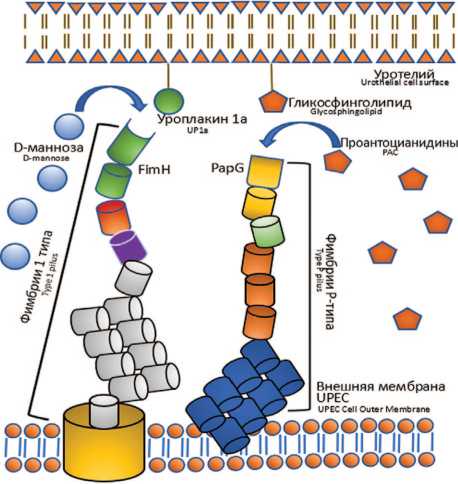
Рис. 1. Механизм действия D-маннозы и проантоцианидино Fig. 1. Mechanism of action of D-mannose and proanthocyanidins
На российском рынке представлена биологически активная добавка Уронекст, которая содержит комбинацию трех активных компонентов в оптимальной дозировке, что обеспечивает продукту комплексное действие. В состав комплекса входят: Cran-Max® 500 мг – вы-сокоочищенный 100% натуральный экстракт клюквы обладающей стандартизованной активностью (36 мг про-антоцианидинов); D-манноза в максимальной эффективной и безопасной суточной дозировке 2000 мг; витамин D3 500 МЕ, помогающий поддерживать нормальную работу иммунной системы и способствующий синтезу антимикробных пептидов, защищающих уротелий [64].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Научные знания о метафилактике рецидивирующего ИМП включают множество разных подходов – поведенческие методы, неантибактериальные средства (фитопрепараты, биологические активные добавки) и антибактериальные препараты. Учитывая рост антибио-тикорезистентности, во всем мире уделяется большое внимание поиску эффективных и безопасных методов неантибактериальной профилактики рецидивирующего ИМП. В клинических исследованиях подтверждена эффективность назначения D-маннозы и проантоциани-динов клюквы для профилактики рецидивирующего
ИМП. Необходимы дальнейшие надежно спланированные клинические исследования совместного примене- ния различных профилактических методов для контроля над инфекцией мочевых путей.
ЛШАТШШШШЩ
ПШАТШ/1ШИИШ blind study. BMC Infect Dis 2010;10(1):94.
Сведения об авторах:
Москвина З.В. – аспирант Института урологии и репродуктивного здоровья человека ФГАОУ ВО «Первый Московский государственный медицинский университет имени И.М.Сеченова» Минздрава России (Сеченовский университет); Москва, Россия;
Болдырева М.Н. – д.м.н., ведущий научный сотрудник ФГБУ «ГНЦ Институт иммунологии» ФМБА России; Москва, Россия; РИНЦ Author ID 277583,
Россоловская К.А. – аспирант кафедры акушерства и гинекологии №1 Института клинической медицины им. Н.В. Склифосовского Первого Московского государственного медицинского университета им. И.М. Сеченова (Сеченовский Университет); Москва, Россия; РИНЦ Author ID 1236452,
Спивак Л.Г. – д.м.н., профессор Института урологии и репродуктивного здоровья человека ФГАОУ ВО «Первый Московский государственный медицинский университет имени И. М. Сеченова» Минздрава России (Сеченовский университет); Москва, Россия; РИНЦ Author ID 659929,
Вклад авторов:
Москвина З.В. – литературный обзор, написание текста, 25%
Болдырева М.Н. – дизайн публикации, определение научного интереса, 25%
Россоловская К.А. – литературный обзор, написание текста, 25%
Спивак Л.Г. – дизайн публикации, определение научного интереса, 25%
Конфликт интересов: Авторы заявляют об отсутствии конфликта интересов.
Финансирование: Исследование проведено при поддержке АО «Петровакс».
Статья поступила: 12.11.23
Результаты рецензирования: 14.12.23
Исправления получены: 23.01.24
Принята к публикации: 30.01.24
Information about authors:
Moskvina Z.V. – postgraduate student of the Institute of Urology and Human Reproductive Health of the Federal State Autonomous EducationalInstitution of Higher Education «First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov» of the Ministry of Health of Russia (Sechenov University), Moscow, Russia,
Boldyreva M.N. – Dr. Sci., Leading Researcher of the FederalState Budgetary Institution «SSC Institute of Immunology» FMBA of Russia; Moscow, Russia; RSCI Author ID 277583,
Rossolovskaya K.A.– postgraduate student of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology No. 1 of the Institute of Clinical Medicine named after. N.V. Sklifosovsky «First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov» (Sechenov University); Moscow, Russia;
RSCI Author ID 1236452,
Spivak L.G.– Dr. Sci., Professor of the Institute of Urology and Human Reproductive Health of the Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education «FirstMoscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov» of the Ministry of Health of Russia (Sechenov University); Moscow, Russia; RSCI Author ID 659929,
Authors’ contributions:
Moskvina Z.V. – literature review, text writing, 25%
Boldyreva M.N. – publication design, determination of scientific interest, 25%
Rossolovskaya K.A. – literature review, text writing, 25%
Spivak L.G. – publication design, determination of scientific interest, 25%
Conflict of interest. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Financing. The study was supported by JSC Petrovax.
Received: 12.11.23
Peer review: 14.12.23
Corrections received: 23.01.24
Accepted for publication: 30.01.24
э ЛОНГИДАЗА
Бовгиалуронидаза азоксиме
СВОБОДА
ОТ ФИБРОЗА

Лонгидаза® в составе комплексной терапии способствует:
-
♦ снижению выраженности спаечного процесса в очагах хронического воспаления1
-
♦ уменьшению выраженности симптомов хронического простатита2
-
♦ профилактике рецидивов хронического простатита2
-
♦ повышению биодоступности антибиотиков за счет разрушения биопленок3
-
♦ уменьшению выраженности симптомов приДГПЖ4
3000 ME
ЛОНГИДАЗА8 5
Бовгиалуронидаза азоксимер ==:
Суппозитории вагинальные и ректальные
10 суппозиториев \
^ Petrovax
ООО «НПО Петровакс Фарм»
142143, Московская область, г. Подольск, с. Покров, Сосновая ул., д. 1. Тел./факс: +7 (495) 730-75-45/60, email: ,
-
1 Инструкция по медицинскому применению препарата Лонгидаза® ЛСР-002940/07 от 11.08.2022.
-
2 Кульчавеня Е.В. и др. Новые возможности применения гиалуронидазы при хроническом простатите // Журнал Урология, № 2. 2020.
-
3 Тризна Е.Ю., Байдамшина Д.Р., Виницкий А.А., Каюмов А.Р. Влияние in vitro изолированного и сочетанного с антибактериальными средствами применения бовгиалуронидазы азоксимер на целостность бактериальной биопленки и жизнеспособность микроорганизмов // Экспериментальная и клиническая фармакология. 2020; 83 (2): 38-44. Trizna Е., Baidamshina D. et al. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13 (11): 1740.
-
4 Кузьменко А.В., Кузьменко В.В., Гяургиев ТА., Винник Ю.Ю. Наблюдательное рандомизированное исследование эффективности и безопасности препарата Лонгидаза® при терапии больных с симптомами нижних мочевыводящих путей на фоне доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы //Урология. 2021; 6: 57-65. pvx/lg-uro/3OO124R лрс -002940/07 от 11,08.2022
ИНФОРМАЦИЯ ПРЕДНАЗНАЧЕНА ДЛЯ СПЕЦИАЛИСТОВ ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ
Список литературы Роль D-маннозы и проантоцианидинов клюквы в профилактике рецидивов инфекции мочевыводящих путей
- Simmering JE, Tang F, Cavanaugh JE, Polgreen LA, Polgreen PM. The Increase in Hospitalizations for Urinary Tract Infections and the Associated Costs in the United States, 1998–2011. Open Forum Infect Dis 2017;4(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofw281.
- Гаджиева З.К., Казилов Ю.Б. Особенности подхода к профилактик рецидивирующей инфекции нижних мочевыводящих путей. Урология 2016;(3S3):65–76. [Gadzhieva Z.K., Kazilov Yu.B. The features in preventing recurrent lower urinary tract infection. Urologiya = Urologiia 2016;(3S3):65–76. (In Russian)].
- Плеханов А.Н., Дамбаев А.Б. Инфекция мочевых путей: эпидемиология, этиология, патогенез, факторы риска, диагностика. Бюллетень восточно-сибирского научного центра Сибирского отделения Российской Академии Медицинских Наук 2016;107(1):70–4. [Plekhanov A.N., Dambaev A.B. Urinary tract infection: epidemiology, etiology, pathogenesis, risk factors, diagnosis. Byulleten' Vostochno-Sibirskogo Nauchnogo Tsentra Sibirskogo Otdeleniya Rossiyskoy Akademii Meditsinskikh Nauk = Bulletin Of The East Siberian Research Center Of The Siberian Branch Of The Russian Academy Of Medical Sciences 2016;107(1):70–4. (In Russian)].
- Набока Ю.Л., Алькина А.К., Коган М.И., Гудима И.А., Ибишев Х.С., Джалагония К.Т., Черницкая М.Л. Мониторинг микробиоты и антибиотикорезистентности уропатогенов в одном урологическом стационаре. Вестник урологии 2020;8(3):47–57. [Naboka Yu.L., Alkina A.K., Kogan M.I., Gudima I.A., Ibishev Kh.S., Jalagonia K.T., Chernitskaya M.L. Monitoring of microbiota and antibiotic resistance of uropathogens in one urological hospital. Vestnik urologii = Herald of Urology 2020;8(3):47–57. (In Russian)].
- Raeispour M, Ranjbar R. Antibiotic resistance, virulence factors and genotyping of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2018;7:118. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-018-0411-4.
- Sherchan JB, Dongol A, Humagain S, Joshi A, Rana Magar S, Bhandari S. Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Bacteria Causing Urinary Tract Infection. J Nepal Health Res Counc 2022;20(1):218–24. https://doi.org/10.33314/jnhrc.v20i01.4142.
- Baines G, Banjoko A, Brair A, Gray J, Desai N, Cardozo L, et al. Antibiotic resistance in urinary tract infections: A re-visit after five years and experience over two sites. Post Reprod Health 2020;26(2):91–100. https://doi.org/10.1177/2053369120910039.
- Палагин И.С., Сухорукова А.В., Дехнич А.В., Эйдельштейн М.В., Перепанова Т.С., Козлов Р.С. и др. Состояние антибиотикорезистентности возбудителей внебольничных инфекций мочевыводящих путей в России, Беларуси и Казахстане: результаты многоцентрового международного исследования «Дармис-2018». Урология 2020;(1):19–31. [Palagin I.S., Sukhorukova A.V., Dekhnich A.V., Eidelshtein M.V., Perepanova |T.S., Kozlov R.S., et al. Current state of antibiotic resistance of pathogens causing community-acquired urinary tract infections in Russia, Belarus and Kazakhstan: results of the international multicenter study «DARMIS-2018». Urologiya = Urologiia 2020;(1):19–31. (In Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/urology.2020.1.19-31.
- Langford BJ, Brown KA, Diong C, Marchand-Austin A, Adomako K, Saedi A, et al. The Benefits and Harms of Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Urinary Tract Infection in Older Adults. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2021;73(3):782–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab116.
- World Healht Organization. Prioritization of pathogens to guide discovery, research and development of new antibiotics for drug-resistant bacterial infections, including tuberculosis. [Electronic resource]. URL: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-EMP-IAU-2017.12.
- Domenici L, Monti M, Bracchi C, Giorgini M, Colagiovanni V, Muzii L, et al. D-mannose: a promising support for acute urinary tract infections in women. A pilot study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2016;20(13):2920–5.
- Terlizzi ME, Gribaudo G, Maffei ME. UroPathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) Infections: Virulence Factors, Bladder Responses, Antibiotic, and Non-antibiotic Antimicrobial Strategies. Front Microbiol 2017;15(8):1566. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01566.
- Bouckaert J, Berglund J, Schembri M, de Genst E, Cools L, Wuhrer M, et al. Receptor binding studies disclose a novel class of high-affinity inhibitors of the Escherichia coli FimH adhesin. Mol Microbiol 2004;55(2):441–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.13652958.2004.04415.x.
- Торшин И.Ю., Аполихина И.А., Громов А.Н., Громова О.А.Torshin IYu, Apolikhina IA, Gromov AN, Gromova OA. О свойствах D-маннозы: противовоспалительные и противоопухолевые эффекты. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2020;12(2):164–170. [Torshin I.Yu., Apolikhina I.A., Gromov A.N., Gromova O.A. Torshin IYu, Apolikhina IA, Gromov AN, Gromova OA. About the properties of D-mannose: anti-inflammatory and antitumor effects. Eksperimental'naya i klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2020;12(2):164–70. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2020-12-2-164-170. (In Russian)].
- Medus ML, Gomez GE, Zacchi LF, Couto PM, Labriola CA, Labanda MS, et al. N-glycosylation Triggers a Dual Selection Pressure in Eukaryotic Secretory Proteins. Sci Rep 2017;7(1):8788. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09173-6.
- Zhang D, Chia C, Jiao X, Jin W, Kasagi S, Wu R, et al. D-mannose induces regulatory T cells and suppresses immunopathology. Nat Med 2017;23(9):1036–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/нм.4375.
- Alton G, Kjaergaard S, Etchison JR, Skovby F, Freeze HH. Oral ingestion of mannose elevates blood mannose levels: a first step toward a potential therapy for carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type I. Biochem Mol Med 1997;60(2):127–33. https://doi.org/10.1006/bmme.1997.2574.
- Ganda OP, Soeldner JS, Gleason RE, Cleator IG, Reynolds C. Metabolic effects of glucose, mannose, galactose, and fructose in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1979;49(4):616–22. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-49-4-616.
- Kranjčec B, Papeš D, Altarac S. D-mannose powder for prophylaxis of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: A randomized clinical trial. World J Urol 2014;32(1):79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-013-1091-6.
- Porru D, Parmigiani A, Tinelli C, Barletta D, Choussos D, Di Franco C, et al. Oral D-mannose in recurrent urinary tract infections in women: a pilot study. J Clinic Urol 2014;7(3):208–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1569-9056(13)61373-1.
- Palleschi G, Carbone A, Zanello PP, Mele R, Leto A, Fuschi A, et al. Prospective study to compare antibiosis versus the association of N-acetylcysteine, D-mannose and Morinda citrifolia fruit extract in preventing urinary tract infections in patients submitted to urodynamic investigation. Archivio Italiano di Urologia e Andrologia 2017;89(1):45-50. https://doi.org/10.4081/aiua.2017.1.45.
- Del Popolo G, Nelli F. Recurrent bacterial symptomatic cystitis: A pilot study on a new natural option for treatment. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2018;90(2):101–3. https://doi.org/10.4081/aiua.2018.2.101.
- Phé V, Pakzad M, Haslam C, Gonzales G, Curtis C, Porter B, et al. Open label feasibility study evaluating D-mannose combined with home-based monitoring of suspected urinary tract infections in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurourol Urodyn 2017;36(7):1770–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23173.
- Marchiori D, Zanello PP. Efficacy of N-acetylcysteine, D-mannose and Morinda citrifolia to Treat Recurrent Cystitis in Breast Cancer Survivals. In Vivo 2017;31(5):931–6. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11149.
- Genovese C, Davinelli S, Mangano K, Tempera G, Nicolosi D, Corsello S, и др. Effects of a new combination of plant extracts plus d-mannose for the management of uncomplicated recurrent urinary tract infections. Journal of Chemotherapy 2018;30(2):107–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/1120009X.2017.1393587.
- Берников А.Н., Ходырева Л.А., Арефьева О.А. Российское проспективное исследование по изучению эффективности и безопасности Уронекст® в параллельных группах у женщин с обострением хронического рецидивирующего цистита. АБВ-пресс 2022:60. [Ernikov A.N., Khody-reva L.A., Arefieva O.A. Russian prospective study to study the effectiveness and safety of Uronext® in parallel groups in women with exacerbation of chronic recurrent cystitis. ABV-press 2022:60].
- Тевлин К.П., Ханалиев Б.В., Тевлин Д.К. Свойства и безопасность комбинированной биологически активной добавки Уронекст в комплексном лечении острого (обострение хронического) цистита у женщин с бактериальным вагинозом. Consilium Medicum 2021;23(7):571–8. [Tevlin K.P., Khanaliev B.V., Tevlin D.K. Properties and safety of the combined dietary supplement Uronext in the complex treatment of acute (exacerbation of chronic) cystitis in women with bacterial vaginosis. Consilium Medicum 2021;23(7):571–8. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.26442/20751753.2021.7.201061.
- Шорманов И.С., Соловьев А.С., Чирков И.А., Щедров Д.Н., Красняк С.С., Шадеркин И.А. Возможности препаратов на основе D-маннозы и растительных компонентов в лечении и профилактике рецидивирующих инфекций нижних мочевых путей у женщин. Урологические ведомости 2022;12(1):13–20. [Shormanov I.S., Solovyov A.S., Chirkov I.A., Shchedrov D.N., Krasnyak S.S., Shaderkin I.A. Opportunities of drugs based on D-mannose and herbal components in the treatment and prevention of recurrent lower urinary tract infections in women. Urologicheskiye vedomosti = Urology reports 2022;12(1):13–20. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.17816/uroved84084.
- Неймарк А.И., Неймарк Б.А., Ноздрачев Н.А., Ковалева Ю.С, Раздорская М.В., Мельник М.А. Возможности профилактики посткоитального цистита. Урология 2022;(3):33-40. [Neimark A.I., Neimark B.A., Nozdrachev N.A., Kovaleva Yu.S., Razdorskaya M.V., Melnik M.A. Possibilities for the prevention of postcoital cystitis. Urologiya = Urologiia 2022;(3):33-40. (In Russian)]. https://dx.doi.org/10.18565/urology.2022.3.33-41.
- Слесаревская М.Н., Кузьмин И.В., Краева Л.А., Смирнова Е.В. Эффективность комбинированной биологически активной добавки Уронекст у женщин с рецидивирующими циститами: клинико-микробиологическое исследование. Экспериментальная и клиническая урология 2022;15(2):140-8. [Slesarevskaya M.N., Kuzmin I.V., Kraeva L.A., Smirnova E.V. The effectiveness of the combined dietary supplement Uronext in women with recurrent cystitis: a clinical microbiological study. Eksperimental'naya i klinicheskaya urologiya = Experimental and Clinical Urology 2022;15(2):140-8. (In Russian)]. https://doi.org/10.29188/2222-8543-2022-15-2-140-148.
- Аль-Шукри А.С., Максимова А.В., Дуб Н.И., Костюков С.В., Манченко А.А., Майоров И.Д., и соавт. Профилактика развития катетер-ассоциированных инфекций мочевыделительной системы у пациентов в раннем послеоперационном периоде. Урология 2023;(2):10-6. [Al-Shukri A.S., Maksimova A.V., Dub N.I., Kostyukov S.V., Manchenko A.A., Mayorov I.D., et al. Prevention of the development of catheter-associated urinary system infections in patients in the early postoperative period. Urologiya = Urologiia 2023;(2):10-6. (In Russian)]. https: //dx.doi.org/10.18565/urology.2023.2.00-00.
- Spaulding CN, Klein RD, Ruer S, Kau AL, Schreiber HL, Cusumano ZT, et al. Selective depletion of uropathogenic E. coli from the gut by a FimH antagonist. Nature 2017;546(7659):528–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22972.
- Bouckaert J, Berglund J, Schembri M, De Genst E, Cools L, Wuhrer M, et al. Receptor binding studies disclose a novel class of high-affinity inhibitors of the Escherichia coli FimH adhesin. Mol Microbiol 2004;55(2):441–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.13652958.2004.04415.x.
- Scribano D, Sarshar M, Prezioso C, Lucarelli M, Angeloni A, Zagaglia C, et al. d-Mannose Treatment neither Affects Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Properties nor Induces Stable FimH Modifications. Molecules 2020;25(2)316. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020316.
- Blumberg JB, Camesano TA, Cassidy A, Kris-Etherton P, Howell A, Manach C, et al. Cranberries and Their Bioactive Constituents in Human Health. Advances in Nutrition 2013;4(6):618–32. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.113.004473.
- Gupta K, Chou MY, Howell A, Wobbe C, Grady R, Stapleton AE. Cranberry Products Inhibit Adherence of P-Fimbriated Escherichia Coli to Primary Cultured Bladder and Vaginal Epithelial Cells. Journal of Urology 2007;177(6):2357–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.01.114.
- Howell AB, Reed JD, Krueger CG, Winterbottom R, Cunningham DG, Leahy M. A-type cranberry proanthocyanidins and uropathogenic bacterial anti-adhesion activity. Phytochemistry 2005;66(18):2281–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.05.022.
- Howell AB, Botto H, Combescure C, Blanc-Potard AB, Gausa L, Matsumoto T, et al. Dosage effect on uropathogenic Escherichia coli anti-adhesion activity in urine following consumption of cranberry powder standardized for proanthocyanidin content: a multicentric randomized doubleblind study. BMC Infect Dis 2010;10(1):94. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-10-94.
- Lavigne JP, Bourg G, Combescure C, Botto H, Sotto A. In-vitro and in-vivo evidence of dose-dependent decrease of uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence after consumption of commercial Vaccinium macrocarpon (cranberry) capsules. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2008;14(4):350–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01917.x.
- Babar A, Moore L, Leblanc V, Dudonné S, Desjardins Y, Lemieux S, et al. High dose versus low dose standardized cranberry proanthocyanidin extract for the prevention of recurrent urinary tract infection in healthy women: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. BMC Urol 2021;21(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-021-00811-w.
- Fu Z, Liska D, Talan D, Chung M. Cranberry Reduces the Risk of Urinary Tract Infection Recurrence in Otherwise Healthy Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Nutr 2017;147(12):2282–8. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.117.254961.
- Xia J yue, Yang C, Xu D feng, Xia H, Yang L gang, Sun G ju. Consumption of cranberry as adjuvant therapy for urinary tract infections in susceptible populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. PLoS One 2021;16(9):e0256992. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256992.
- Williams G, Hahn D, Stephens JH, Craig JC, Hodson EM. Cranberries for preventing urinary tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2023;4(4):CD001321. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001321.pub6.
- Сычев Д.А. Применение препаратов клюквы в урологической практике: взгляд клинического фармаколога. Эффективная фармакотерапия. Урология и Нефрология 2011;(2):44–8. [Sychev D.A. The use of cranberry preparations in urological practice: the view of a clinical pharmacologist. Effektivnaya farmakoterapiya. Urologiya i Nefrologiya = Effective pharmacotherapy. Urology and Nephrology 2011;(2):44–8. (In Russian)].
- Ulrey RK, Barksdale SM, Zhou W, van Hoek ML. Cranberry proanthocyanidins have anti-biofilm properties against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014;14(1):499. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-499.
- Maisuria VB, Okshevsky M, Déziel E, Tufenkji N. Proanthocyanidin Interferes with Intrinsic Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms of Gram‐Negative Bacteria. Advanced Science 2019;6(15):1802333. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201802333.
- Rădulescu D, David C, Turcu FL, Spătaru DM, Popescu P, Văcăroiu IA. Combination of cranberry extract and D-mannose - possible enhancer of uropathogen sensitivity to antibiotics in acute therapy of urinary tract infections: Results of a pilot study. Exp Ther Med 2020;20(4):3399–406. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8970.
- Scharf B, Sendker J, Dobrindt U, Hensel A. Influence of Cranberry Extract on Tamm-Horsfall Protein in Human Urine and its Antiadhesive Activity Against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Planta Med 2019;85(2):126–38. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0755-7801.
- DE Leo V, Cappelli V, Massaro MG, Tosti C, Morgante G. Evaluation of the effects of a natural dietary supplement with cranberry, Noxamicina® and D-mannose in recurrent urinary infections in perimenopausal women. Minerva Ginecol 2017;69(4):336–41. https://doi.org/10.23736/ S0026-4784.17.04074-6.
- Vicariotto F. Effectiveness of an association of a cranberry dry extract, D-mannose, and the two microorganisms Lactobacillus plantarum LP01 and Lactobacillus paracasei LPC09 in women affected by cystitis: a pilot study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2014;48(Suppl 1):S96-101. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000000224.
- Salinas-Casado J, Méndez-Rubio S, Esteban-Fuertes M, Gómez-Rodríguez A, Vírseda-Chamorro M, Luján-Galán M, et al. Large study (283 women) on the effectiveness of Manosar®: 2 g of d-mannose + 140 mg of proanthocyanidins (PAC), of prolonged release. Arch Esp Urol 2020;73(6):491–8.
- Garofalo L, Nakama C, Hanes D, Zwickey H. Whole-Person, Urobiome-Centric Therapy for Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection. Antibiotics 2022;11(2):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ antibiotics11020218.
- Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Cox ME, Stapleton AE. Voided Midstream Urine Culture and Acute Cystitis in Premenopausal Women. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;369(20):1883–91. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1302186.
- Eckford SD, Keane DP, Lamond E, Jackson SR, Abrams P. Hydration monitoring in the prevention of recurrent idiopathic urinary tract infections in pre-menopausal women. Br J Urol 1995;76(1):90–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410x.1995.tb07839.x.
- Castelló T, Girona L, Gómez MR, Mena Mur A, Garcia L. The possible value of ascorbic acid as a prophylactic agent for urinary tract infection. Spinal Cord 1996;34(10):592–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1996.105.
- Ochoa-Brust GJ, Fernández AR, Villanueva-Ruiz GJ, Velasco R, Trujillo-Hernández B, Vásquez C. Daily intake of 100 mg ascorbic acid as urinary tract infection prophylactic agent during pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2007;86(7):783–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016340701273189.
- Wagenlehner FM, Abramov-Sommariva D, Höller M, Steindl H, Naber KG. Non-Antibiotic Herbal Therapy (BNO 1045) versus Antibiotic Therapy (Fosfomycin Trometamol) for the Treatment of Acute Lower Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: A Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Randomized, Multicentre, Non-Inferiority Phase III Trial. Urol Int 2018;101(3):327–36. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493368.
- Beerepoot MAJ, Geerlings SE, van Haarst EP, van Charante NM, ter Riet G. Nonantibiotic Prophylaxis for Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Urol 2013;190(6):1981–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2013.04.142.
- Taha Neto KA, Nogueira Castilho L, Reis LO. Oral vaccine (OM-89) in the recurrent urinary tract infection prophylaxis: a realistic systematic review with meta-analysis. Actas Urol Esp 2016;40(4):203–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acuro.2015.04.008.
- Costantini E, Lazzeri M, Pistolesi D, Del Zingaro M, Frumenzio E, Boni A, et al. Morphological Changes of Bladder Mucosa in Patients Who Underwent Instillation with Combined Sodium Hyaluronic Acid-Chondroitin Sulphate (Ialuril®). Urol Int 2013;91(1):81–8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000345047.
- Madersbacher H, van Ophoven A, van Kerrebroeck PEVA. GAG layer replenishment therapy for chronic forms of cystitis with intravesical glycosaminoglycans-A review. Neurourol Urodyn 2013;32(1):9–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22256.
- Damiano R, Cicione A. The role of sodium hyaluronate and sodium chondroitin sulphate in the management of bladder disease. Ther Adv Urol 2011;3(5):223–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756287211418723.
- Perrotta C, Albert X, Aznar M. Oestrogens for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008;16(2):CD005131. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005131.pub2.
- Mohanty S, Kamolvit W, Hertting O, Brauner A. Vitamin D strengthens the bladder epithelial barrier by inducing tight junction proteins during E. coli urinary tract infection. Cell Tissue Res 2020;380(3):669-73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03162-z.


