Роль общих для человека и микробиоты метаболитов триптофана при тяжелых заболеваниях и критических состояниях (обзор)
Автор: Гецина Мария Львовна, Черневская Екатерина Александровна, Белобородова Наталья Владимировна
Журнал: Клиническая практика @clinpractice
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.11, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Растущий интерес к метаболитам, циркулирующим в крови, связан с накоплением фактологического материала об участии низкомолекулярных соединений, в том числе микробного происхождения, в развитии ряда тяжелых заболеваний и состояний. В данном обзоре прослежено влияние большого класса природных химических соединений - метаболитов триптофана - на различные патологические процессы. Для поиска научных статей по ключевым словам, включающим названия индольных соединений и методы их детекции, а также нозологию ряда заболеваний и критических состояний, использованы базы данных PubMed за последние 10 лет. Научный материал представлен по разделам, в которых приведены данные об изучении метаболитов триптофана при самых разных группах заболеваний, таких как рак, сердечно-сосудистая патология, заболевания почек, кишечника, психические расстройства, атеросклероз и др. Особое внимание уделено роли индольных соединений, попадающих в системный кровоток в результате микробной биотрансформации триптофана, серотонина и других, которые можно отнести к общим метаболитам человека и микробиоты...
Обзор, триптофан, индольные метаболиты, уремия, колоректальный рак, атеросклероз, воспаление кишечника, шизофрения, депрессивные расстройства, метаболомный подход, биомаркеры, критическое состояние
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143170837
IDR: 143170837 | DOI: 10.17816/clinpract19068
Текст обзорной статьи Роль общих для человека и микробиоты метаболитов триптофана при тяжелых заболеваниях и критических состояниях (обзор)
Низкомолекулярные метаболиты являются промежуточными и конечными продуктами основных метаболических путей, отражают степень экспрессии генов, функциональную активность клеточных ферментов и другое, что позволяет рассматривать их в качестве вероятных участников патологических процессов и нередко как кандидатные биомаркеры различных состояний. Современные лабораторные технологии позволили установить, что ряд классов низкомолекулярных соединений в крови человека имеет исключительно микробное происхождение, то есть является продуктом метаболизма микробиоты [1], а другие соединения имеют общую структуру как у человека, так и у бактерий, то есть являются общими метаболитами [2]. В здоровом организме низкомолекулярные соединения, представляющие собой метаболиты нормальной микрофлоры кишечника, определяются в крови в относительно стабильных концентрациях, что свидетельствует об адекватности биохимических процессов, направленных на поддержание гомеостаза. При этом многие метаболиты непосредственно вовлечены в механизмы жизнедеятельности человека. При избыточном поступлении микробных метаболитов из кишечника во внутреннюю среду организма человека они подвергаются нейтрализации в печени с формированием сульфатов, конъюгатов и других водорастворимых компонентов для выведения с мочой. При различных заболеваниях естественные взаимодействия метаболитов бактерий с организмом человека приобретают искаженный характер, гармоничная в норме интеграция эндогенных метаболических путей человека и микробиоты разрушается, что может приобретать патологическую картину со стороны разных органов и систем. Большое внимание в литературе уделено таким метаболитам микробиоты, как летучие короткоцепочечные жирные кислоты
(short certain fatty acids, SCFA). Доказано, что они являются важным энергетическим субстратом для энтероцитов, обеспечивают функционирование локального иммунологического барьера, препятствуют развитию воспаления кишечной стенки и др. [3]. Микробные метаболиты ароматической структуры, продукты микробной биодеградации аминокислоты тирозина играют важную роль в развитии септического шока и полиорганной недостаточности [4].
Особого внимания при ряде заболеваний заслуживают серотонин и другие индольные метаболиты, обладающие собственной биологической активностью, попадающие в системный кровоток, в том числе в результате микробной биотрансформации триптофана и других индольных соединений. Триптофан является одной из незаменимых аминокислот, индольное кольцо триптофана синтезируется в природе микроорганизмами и растениями, и не может быть синтезировано организмом человека. В организм человека триптофан поступает с пищей, поэтому считается, что содержание триптофана можно регулировать с помощью диеты [5]. Однако, оказалось, что управлять метаболизмом триптофана и его производными значительно сложнее.
ОБЩИЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ О МЕТАБОЛИЗМЕТРИПТОФАНА
Триптофан играет важную роль в метаболизме человека. Образование производных триптофана происходит двумя основными путями, которые могут быть названы индольным и кинурениновым (рис. 1) [6]. Индольный путь превращения триптофана (условно делится на серотониновый и микробный) ведет к образованию нейротрансмиттера серотонина, «гормона сна» — мелатонина, а также целого ряда других метаболитов, содержащих индольное кольцо, например триптамина, который подвергается дальнейшей биотрансформации с образованием индолуксусной, индолпропановой
Рис. 1. Схема метаболизма триптофана: (1) триптофан 5-гидроксилаза; (2) триптофан 2,3-диоксигена-за; (3) декарбоксилаза ароматик-L-амино-кислоты; (4) индолэтиламин N-метилтрансфераза; (5) кинуренин формамидаза; (6) кинуренин 3-монооксидаза; (7) альдегид дегидроксилаза, митохондриальная; (8) альдегид дегидроксилаза митохондриальная или альдегидоксидаза; (9) серотонин N-ацетилтрансфераза; (10) ацетилсеротонин O-метилтрансфераза (цит. по [6])
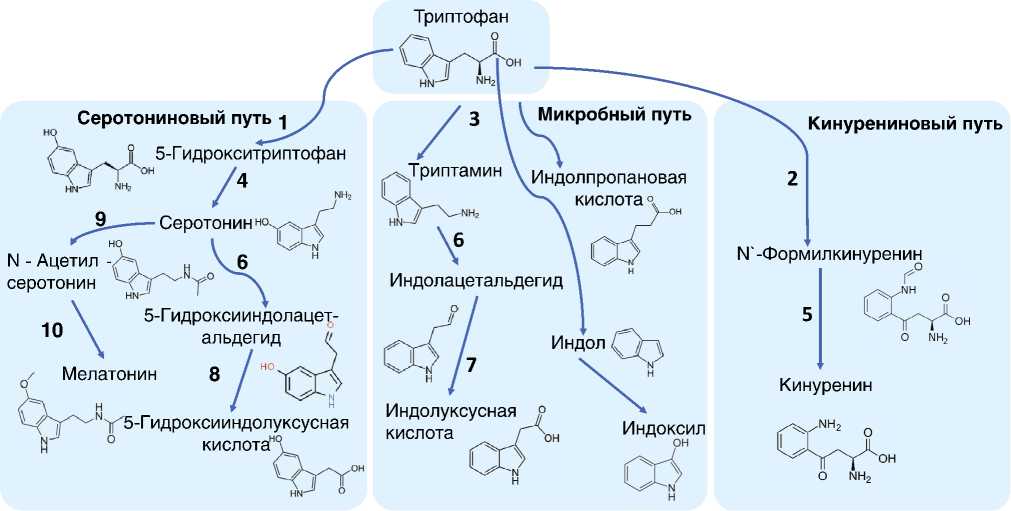
кислот, индола и индоксила. Кинурениновый путь сопровождается разрушением индольного кольца триптофана и приводит к образованию L-кинуренина, кинуреновой и хинолиновой кислот или кофермента никотинамидадениндинуклеотида (НАД+). На образование кинуренина расходуется б о льшая часть поступающего триптофана и лишь 5–10% идет на образование серотонина и мелатонина [5]. Часть поглощенного с пищей триптофана уходит на бактериальную деградацию (4–6%), в результате чего образуются индольные кислоты (например, 3-индолпропановая) и индол. В результате метаболизма серотонина появляется, в частности, 5-гид-роксииндолуксусная кислота [7].
Несмотря на растущий интерес к клинической значимости индольных соединений, в международной базе данных метаболома человека [8] достаточно скудно представлены cведения об изменениях концентраций в крови тех или иных метаболитов триптофана при различных заболеваниях. Даны лишь сведения преимущественно о шизофрении и уремии, что суммировано в табл. 1.
Соотношение уровней кинуренина и триптофана в сыворотке позволяет оценивать продукцию и активность ключевого фермента индол-амин-2,3-диоксигеназы. Этот внутриклеточный несекретируемый фермент способен индуциро- вать катаболизм триптофана с образованием целого ряда продуктов, оказывающих существенное влияние на функции иммунной системы. Изменение активности индоламин-2,3-диоксигеназы может рассматриваться как информативный биомаркер, имеющий прогностическую значимость при оценке течения и исхода для целого ряда заболеваний и состояний, таких как сепсис, внебольничная пневмония, стенокардия, острый инфаркт миокарда и др. [17].
Нарушение метаболизма триптофана приводит к образованию иммуноактивных кинуренинов, что влияет на работу Т-клеток и связано c развитием аутоиммунных реакций [18]. В качестве последствий могут рассматриваться не только уменьшение содержания триптофана, но и производство иммуноактивных кинуренинов, которые могут действовать как лиганды арилуглеводородного рецептора [19]. Изменение уровней метаболитов кинуренинового пути связывают с психическими расстройствами и нарушениями функций желудочно-кишечного тракта [20]. Таким образом, регуляция биодоступности циркулирующего триптофана и его метаболитов может зависеть от состава микробиоты кишечника, что в свою очередь отражается на состоянии иммунореактивности и влияет на работу различных органов и систем.
<линическая’2п20
п эакти ка Том 11 №1
Таблица 1
Концентрации индольных соединений (метаболитов триптофана) в норме и при различных заболеваниях по базе данных Humane Metabolom Data Base (HMDB) [8]
|
Индольные соединения / метаболиты триптофана |
Норма, кровь, мкМ |
Источник |
Заболевания |
Отклонения от нормы при заболеваниях, кровь, мкМ |
Источник |
|
Триптофан |
54,5±9,7 81,3±3,36 |
[9] [10] |
Шизофрения Эпилепсия |
101±4,48 37,2 (34,3–40,1) |
[10] [11] |
|
Серотонин |
0,85±0,077 |
[10] |
Шизофрения |
0,61±0,096 |
[10] |
|
Кинуренин |
1,6±0,1 1,74±0,121 |
[12] [10] |
Шизофрения |
2,35±0,162 |
[10] |
|
Индолуксусная кислота |
2,85 0,05 |
[13] [14] |
Уремия |
13,7 |
[13] |
|
Индол-3-пропановая кислота |
0,481 |
[15] |
Нет данных |
- |
- |
|
5-Гидроксииндолуксусная кислота |
0,0516 |
[16] |
Шизофрения |
0,0475 |
[16] |
|
Индоксил сульфат |
2,49±1,36 |
[13] |
Уремия |
21,11±12,20 |
[13] |
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания
Эффекты серотонина в организме определяются его взаимодействием с различными типами центральных и периферических 5-гидрокситриптами-новых рецепторов (5-HТ-рецепторы). В настоящее время выделено 7 основных видов серотониновых рецепторов и множество подвидов, причем активация этих рецепторных структур может вызывать как снижение, так и повышение сосудистого тонуса, т.е. серотонин является модулятором тонуса гладкой мускулатуры. Серотонинергическая сигнальная система участвует в регуляции некоторых жизненно важных функций организма и является мишенью множества фармакологически активных веществ — антидепрессантов, анксиолитиков, ноотропов, противорвотных, прокинетиков, противомигренозных и других групп лекарственных средств. Изучаются возможности коррекции сосудистой недостаточности с помощью аналога эндогенного серотонина — отечественного фармакопейного препарата серотонина адипината; показано его стойкое нормализующее действие на сосудистый тонус [21].
К негативным эффектам серотонина относятся тахикардия с предшествующей краткой рефлекторной брадикардией, повышение сократимости предсердий, развитие предсердных аритмий [22] и легочной артериальной гипертензии через воздействие на сократимость гладких мышц и ремоделирование сосудов [23]. Кроме того, повышенный уровень серотонина в плазме крови выявлен при синдроме внезапной детской смерти. В образцах сыворотки крови, взятых у детей, умерших в результате развития этого синдрома (n=61), уровни серотонина были достоверно выше, чем у других детей (n=15), которые умерли от других причин (177 и 91 нг/мл соответственно, p=0,014). При сравнении этих же групп детей обнаружены также различия в сывороточных концентрациях 5-гидроксиин-долуксусной кислоты (70 и 36 нг/мл соответственно, p=0,09). Полученные данные могут иметь потенциальное клиническое значение, позволяя заблаговременно оценить риск синдрома внезапной детской смерти [24].
Но не только серотонин можно использовать в качестве маркера, отражающего состояние сердечно-сосудистой системы. Исследователи использовали потенциально связанные с температурными изменениями ключевые воспалительные пути, оцениваемые по уровню триптофана, катаболитов триптофана (включая кинуренины) и активности индоламин-2,3-диоксигеназы у пациентов, выживших после остановки сердца. Известно, что управляемая гипотермия у таких пациентов значимо улучшает неврологический прогноз, однако повышает риск возникновения инфекционных осложнений. Отмечено, что снижение сывороточных уровней триптофана и повышение активности индоламин-2,3-диоксигеназы при гипотермии связано с неблагоприятным исходом, вероятно, по причине увеличения чувствительности к инфекционным осложнениям и сепсису под воздействием низких температур, в то время как у пациентов с благоприятным исходом сохранялась тенденция к более высоким значениям триптофана и низкой активности индоламин-2,3-диоксигеназы [25].
Содержание триптофана и индольных производных существенно уменьшается и в случаях осложненного атеросклероза, коррелируя с лодыжечно-плечевым индексом — показателем, отражающим состояние кровообращения в нижних конечностях. Была найдена обратная корреляция с прогрессирующим атеросклерозом для индола, индол-3-пропионовой кислоты и концентрации ин-дол-3-альдегида, в то время как для соотношения кинуренина к триптофану — положительная корреляция. При многофакторном анализе соотношение кинуренин–триптофан достоверно ассоциировалось с послеоперационными кардиальными осложнениями [26].
Заболевания кишечника
Отличительной особенностью метаболомных исследований в гастроэнтерологии является их фокус на микробных метаболитах. Показано, что метаболиты триптофана 3-индолуксусная и индолпропановая кислоты имеют преимущественно бактериальное происхождение и в незначительных концентрациях присутствуют не только в сыворотке, но и моче здоровых людей. У пациентов с язвенным колитом и целиакией в крови обнаружено достоверное повышение 3-индолуксусной кислоты, что может быть обусловлено повышением метаболической активности клостридий в отношении ароматических аминокислот. Выявленное повышение 3-индолпропановой кислоты у пациентов с целиакией, по сравнению с пациентами с язвенным колитом и здоровыми добровольцами, авторы объясняют возможной разницей в количестве/ метаболической активности Clostridium sporogenes у пациентов этих двух групп [27].
Еще одним метаболитом кишечной микробиоты является 5-гидроксииндолуксусная кислота (5-HIAA), ее повышенные уровни (>20 мкМ) в моче наблюдаются при аппендиците и гастроэнтерите [28]. Источником 5-HIAA в данных ситуациях является вазоспастический медиатор 5-гидрок-ситриптамин, который во время воспалительных процессов выделяется из энтерохромаффинных клеток и метаболизируется до конечного продукта [29]. Некоторые авторы считают, что если содержание 5-HIAA не увеличивается, аппендицит может быть исключен с высокой степенью достоверности [30]. Показано, что ее содержание снижается при гангренозном аппендиците и в случае перфо- рации червеобразного отростка [31], при этом ряд авторов отмечает, что уменьшение концентрации 5-HIAA может быть предупреждающим признаком перфорации [32]. Однако другие авторы не поддерживают эту идею и считают, что диагностическая значимость при остром аппендиците не столь велика, приводя данные сравнения 5-HIAA с другими показателями воспаления (уровень лейкоцитов/ нейтрофилов и С-реактивного белка) в крови [33].
Колоректальный и другие виды рака
В патогенезе онкологических заболеваний лежат нарушения различных метаболических путей — гликолиза, цикла трикарбоновых кислот, мочевины, аргинина, пролина, метаболизма жирных кислот, а также нарушения метаболизма, связанные с микробиотой кишечника. При изучении диагностической значимости и корреляции с диагнозом объектом исследования чаще служит сыворотка крови. Например, у пациентов с диагнозом колоректального рака было исследовано 249 метаболитов сыворотки крови, из которых только 72 значимо отличались при сравнении с показателями здоровых добровольцев, из них 5 относились к метаболитам триптофана — 5-гидрокситриптамин, триптофан, индоксил сульфат, индоксил, N-ацетил-5-гидрок-ситриптамин — и имели тенденцию к уменьшению концентрации по сравнению со здоровыми [34]. Предметом исследования могут быть метаболиты и других биологических субстратов, например кишечного содержимого, однако авторы отмечают, что эти данные сложнее интерпретировать, так как количественный и качественный состав фекальных метаболитов отличается большей вариабельностью [35]. В моче метаболит триптофана 5-гидроксиин-долуксусная кислота расценена как хороший биомаркер для ранней диагностики опухолей тонкой кишки [36]. При колоректальном раке снижение индолпропановой кислоты в кишечном содержимом находится в сильной корреляционной связи с ростом актинобактерий в кишечной микробиоте [37].
Метаболомный анализ может быть информативен не только для ранней диагностики, но и для мониторинга онкологического процесса. В зависимости от стадии колоректального рака содержание метаболитов в сыворотке крови меняется. Так, для бензойной кислоты выявлена самая сильная статистически значимая обратная корреляция со стадией заболевания. Показано, что содержание 3-ин-долуксусной кислоты также снижалось по мере прогрессирования заболевания [38].
<линическая’2п20 п эакти ка Том 11 №1
Таблица 2
Изменение метаболитов триптофана при раковых заболеваниях пищеварительного тракта
|
Вещество |
Диагноз |
Изменение |
Источник |
|
Индоксил сульфат |
Колоректальный рак |
↓ |
[34] |
|
Триптофан |
Колоректальный рак |
↓ |
|
|
3-Индолпропановая кислота |
Лейкоплакия и рак полости рта |
↑ |
[39] |
|
3-Индолуксусная кислота |
Колоректальный рак |
↓ |
[38] |
|
Тирозин |
|||
|
Триптофан |
|||
|
3-Индоксил сульфат |
Примечание. ↓ / ↑ — понижение/повышение показателя.
У пациентов с диагнозом лейкоплакии и рака полости рта в качестве исследуемого материала использовали слюну, из которой было выделено пять прогностически значимых метаболитов — гамма-аминомасляная кислота, фенилаланин, валин, н-эйкозановая и молочная кислота. Среди метаболитов отмечали существенное увеличение концентрации 3-индолпропановой кислоты [39]. В табл. 2 отражена динамика метаболитов триптофана при раковых заболеваниях.
Критические состояния, травма, сепсис
Обсуждается необходимость разработки индивидуального подхода к коррекции метаболизма, приводящего к более эффективному лечению пациентов, находящихся в критических состояниях [40]. У пациентов с внебольничной пневмонией с неблагоприятным клиническим исходом изучали отношения концентраций триптофана к серотонину и триптофана к кинуренину в корреляции с С-ре-активным белком, прокальцитонином, упрощенной шкалой оценки полиорганной недостаточности qSOFA [quick Sequential (Sepsis-related) Organ Failure Assessment] и шкалой оценки тяжести пневмонии, но пришли к выводу, что данных о значимости изменения индоламин-2,3-диоксигеназы для прогнозирования исхода пока недостаточно [41].
Изучение метаболомного профиля сыворотки при черепно-мозговой травме позволило выявить снижение концентрации индол-3-пропановой кислоты в сыворотке крови [42], в то время как содержание другого индольного производного серотонина, а именно мелатонина, повышалось в крови после черепно-мозговой травмы у детей, что, возможно, связано с ответом на окислительный стресс или воспаление, вызванным травмой [43]. Уровень мелатонина в крови впоследствии умерших паци- ентов с тяжелой черепно-мозговой травмой был выше, чем у выживших, и найдена корреляция его с уровнями малонового диальдегида (показателя перекисного окисления липидов) и общей антиоксидантной активности, отражающей тяжесть повреждения головного мозга [44]. Ранее также была обнаружена связь повышенных концентраций мелатонина в крови с показателем смертности у септических пациентов [45]. Однако в экспериментальной работе на мышах показано, что мелатонин способствует удалению поврежденных митохондрий с помощью аутофагии, что подавляет индуцированное черепно-мозговой травмой воспаление и ослабляет секрецию воспалительных цитокинов [46]. Прием экзогенного мелатонина после черепно-мозговой травмы способствовал улучшению показателей сна и не оказывал побочных эффектов [47], у пациентов в отделении реанимации и интенсивной терапии усиливал общую антиоксидантную активность крови благодаря своим иммуномодулирующим и антиоксидантным свойствам [48].
Нарушение функции почек, уремия
Микроорганизмы толстого кишечника продуцируют соединения, которые обычно выводятся почками. Нарушение функции почек приводит к накоплению в организме больного некоторых соединений, которые оказывают токсическое влияние на жизненно важные органы, поэтому их часто называют потенциальными уремическими токсинами [49]. В число уремических токсинов входят фенилацетил-1-глутамин, 5-гидроксииндол, индок-силглюкуронид, п-крезол сульфат, индоксил сульфат. Некоторые из них, например индоксил сульфат, п-крезол сульфат и триметиламин-N-оксид, участвуют в разрушении эпителиального барьера кишечника, тем самым облегчая попадание токси- нов в кровоток. Часть триптофана под действием триптофаназы — фермента кишечной микробиоты, в частности Escherichia coli, — превращается в индол. Далее часть индола удаляется вместе с каловыми массами, а часть всасывается и с током крови попадает в печень, где после окисления и сульфатирования превращается в индоксил сульфат. При хронической болезни почек концентрация индоксил сульфата в крови постепенно повышается [50]. Попадание уремических токсинов в кровоток сказывается на состоянии сердечно-сосудистой системы. Так, при сердечно-сосудистых заболеваниях увеличение в крови концентрации 3-индолук-сусной кислоты выше 3,73 мкМ/л коррелирует с более высокой смертностью [51]. В эксперименте на крысах показано, что индол и индоксил вызывают значительные гемодинамические изменения, действие которых нивелируется через центральный и периферические механизмы с участием серотониновых рецепторов [52].
Один из основных методов борьбы с хронической почечной недостаточностью — это проведение гемодиализа с целью уменьшения количества токсинов в крови. Для оценки эффективности проводят метаболомный анализ сыворотки до и после процедуры гемодиализа, оценивая содержание таких уремических токсинов, как индоксил сульфат, 3-индолуксусная и гиппуровая кислота [53].
Заболевания центральной нервной системы и депрессивные расстройства
Метаболическая активность микробиома кишечника может влиять на развитие депрессивного расстройства [54]. Влияние метаболитов триптофана на психическое здоровье человека можно оценить лабораторными методами по их уровню в моче пациентов. Например, тяжелая форма депрессивного расстройства характеризуется снижением триметиламиноксида, индоксил сульфата, м-гидроксифенилацетата, 3-гидроксифенилуксус-ной кислоты, а также повышением уровней п-гид-роксифенил ацетата, изобутирата, пальмитиновой кислоты, лактата и глицина. При умеренном депрессивном расстройстве были обнаружены только два соединения — изобутират и триметил-аминоксид. При шизофрении наблюдается нарушение метаболизма триптофана по кинурениновому пути: в плазме крови отмечают уменьшение концентрации кинурениновой кислоты, а после терапии — нормализацию ее уровня [55]. Для оценки вероятности возникновения острой дисфункции головного мозга показан прогностический потенциал концентрации серотонина в плазме или активности ацетилхолинэстеразы при поступлении в отделение интенсивной терапии [56]. Уменьшение концентрации тромбоцитарного серотонина является дифференциальным признаком шизофрении с симптомами депрессии [57]. У женщин с послеродовой депрессией отмечают снижение уровня нейротрансмиттеров (серотонин, дофамин, норэпинефрин), но, по мнению авторов, развитие депрессии у этих пациентов может быть следствием других причин, не связанных с родами [58].
У пациентов с рассеянным склерозом выявлены молекулярные механизмы, с помощью которых микробиота регулирует иммунный ответ, а именно: триптофан метаболизируется кишечной микробиотой в агонисты рецептора ароматических углеводородов, которые воздействуют на астроциты, ограничивают воспаление в центральной нервной системе [59].
Влияние микробиотына проницаемость кишечника
Интересно, что продукты биодеградации ароматических аминокислот тирозина, фенилаланина и триптофана, регулируют непосредственно степень проницаемости кишечника. В частности, индолпропановая кислота, продукт метаболизма Clostridium sporogenes , при уменьшении концентрации в системном кровотоке повышает проницаемость кишечного барьера с последующими нарушениями в иммунной системе человека [1, 60]. Однако, даже острая нехватка самого триптофана не нарушает проницаемости кишечника и он влияет значимо на содержание метаболитов в крови [61].
Коррекцию метаболической активности микробиоты кишечника предлагают использовать для восстановления психического здоровья. Термин «психобиотики» появился не так давно, он выделяет группу пробиотиков, обладающих способностью к коррекции психического состояния [62]. Ряд экспериментальных работ показывает эффективность приема различных штаммов микроорганизмов ( Lactobacillus helveticus , Lactobacillus casei , Bifidobacterium longum и др.) для снижения уровня стресса, тревожности, улучшения эмоционального состояния [63]. Необходимы большие плаце-боконтролируемые исследования, позволяющие оценить психобиотический потенциал различных штаммов, их эффективность и безопасность для человека.
циническая'™™ Том 121 №01
Арилуглеводородный рецептор (aryl hydrocarbon receptor, AHR) является основным регулятором иммунной функции в желудочно-кишечном тракте. Резидентная микробиота способна влиять на пути AHR-зависимой передачи сигналов через производство множества биологически активных молекул, которые действуют как агонисты арилуглеводородного рецептора, такие как индол или индол-3-альдегид [64]. Индол-пировиноградная кислота рассматривается как предшественник индол-3-ацетальдегида, индол-3-альдегида и ин-дол-3-уксусной кислоты, агонистов арилуглеводородного рецептора. На модели колита у мышей показана способность данной кислоты снижать воспаление, активируя работу AHR-рецептора [65]. При хроническом заболевании почек уремические токсины индоксил сульфат (IS) и индол-3-уксусная кислота микробного происхождения могут быть вовлечены в воспалительный сигнальный путь [66]. Так, индол-3-уксусная кислота влияет на функцию арилуглеродного рецептора, что приводит к экспрессии тканевого фактора в эндотелиальных клетках и повышает риск тромбоза [67].
О МЕТОДАХ ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЯИНДОЛЬНЫХ СОЕДИНЕНИЙ
Основными методами скринингового метаболомного анализа являются газовая хрома- то-масс-спектрометрия и жидкостная хрома-то-масс-спектрометрия [68, 69], также используют ядерно-магнитную резонансную спектроскопию и другие аналитические методы [70]. Важную роль в трактовке результатов играют методы подготовки пробы к анализу [71–74]. Экстракцию анализируемых компонентов проводят методом жид-кость-жидкостной экстракции с применением диэтилового эфира или методом твердофазной экстракции [75, 76].
Методы масс-спектрометрии не так широко распространены в клинической лабораторной практике. Ряд индольных соединений (серотонин, мелатонин, 5-гидроксииндолуксусная кислота, триметиламиноксид) можно определять методом иммуноферментного анализа, однако на сегодняшний день тест-системы в основном валидированы только для научных исследований.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Таким образом, в системном кровотоке обнаруживается целый ряд индольных соединений, играющих важную роль в патогенезе и диагностике ряда заболеваний. Представленные в обзоре основные закономерности по изменению содержания индольных соединений в крови обобщены на рис. 2. Немаловажно, что б о льшая часть их является метаболитами микробиоты. Целенаправленная регу-
Рис. 2. Основные изменения, характерные для триптофана и его метаболитов при тяжелых заболеваниях и критических состояниях
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания
3-Индолпропановая кислота
Индол
Триптофан
3-Индолуксусная кислота
Заболевания центральной нервной системы
Кинурениновая кислота
Серотонин
Индоксил сульфат
Черепно-мозговая травма. Сепсис
Мелатонин
Триптофан
3-Индолпропановая кислота
Заболевания кишечника
3-Индолуксусная кислота Серотонин
3-Индолпропановая кислота 5-Гидроксииндолуксусная кислота
\
Онкология
3-Индолпропановая кислота
Триптофан
Индоксил сульфат
3-Индолуксусная кислота
Болезни почек, уремия 3-Индолуксусная кислота Индоксил сульфат 3-Индолпропановая кислота Серотонин ляция в системе метаболом/микробиом открывает новые перспективы для лечебного воздействия на патологический процесс через микробиоту человека. До сих пор доказательная база не столь велика, исследования в этом направлении продолжаются и открывают огромное поле для дальнейшего научного поиска.
ИСТОЧНИК ФИНАНСИРОВАНИЯ
Исследование проведено без спонсорской поддержки.
Список литературы Роль общих для человека и микробиоты метаболитов триптофана при тяжелых заболеваниях и критических состояниях (обзор)
- Wikoff WR, Anfora AT, Liu J, et al. Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites. PNAS. 2009;106(10):3698-3703. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812874106
- Beloborodova NV, Olenin AY, Pautova AK. Metabolomic findings in sepsis as a damage of host-microbial metabolism integration. J Crit Care. 2018;43:246-255. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.09.014
- Cani PD, Van Hul M, Lefort C, et al. Microbial regulation of organismal energy homeostasis. Nat Metab. 2019;(1):34-46. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-018-0017-4
- Beloborodova NV, Sarshor YN, Bedova AY, et al. Involvement of aromatic metabolites in the pathogenesis of septic shock. shock. 2018;50(3):273-279. DOI: 10.1097/shk.0000000000001064
- Palego L, Betti L, Rossi A, Giannaccini G. Tryptophan biochemistry: structural, nutritional, metabolic, and medical aspects in humans. J Amino Acids. 2016;2016:8952520. DOI: 10.1155/2016/8952520
- Beloborodova NV, Grechko AV, Olenin AYu. Metabolomic discovery of microbiota dysfunction as the cause of pathology. Open access peer-reviewed chapter. IntechOpen. 2019.
- DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.87176
- Keszthelyi D, Troost FJ, Masclee AA. Understanding the role of tryptophan and serotonin metabolism in gastrointestinal function. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;21(12):1239-1249.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01370.x
- Humane Metabolom Data Base. Showing metabocard for L-tryptophan (HMDB0000929). The Metabolomics Innovation Centre; 2019 [cited 2005 Nov 16]. Available at: http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000929.
- Psychogios N, Hau DD, Peng J, et al. The human serum metabolome. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16957.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016957
- Fukushima T, Iizuka H, Yokota A, et al. Quantitative analyses of schizophrenia-associated metabolites in serum: serum D-lactate levels are negatively correlated with gamma-glutamylcysteine in medicated schizophrenia patients. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101652.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101652
- Rainesalo S, Keränen T, Palmio J, et al. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in epileptic patients. Neurochem Res. 2004;29(1):319-324. doi: 10.1023/b:nere.0000010461.34920.0c.
- Fujigaki S, Saito K, Takemura M, et al. Species differences in L-tryptophan-kynurenine pathway metabolism: quantification of anthranilic acid and its related enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;358(2):329-335.
- DOI: 10.1006/abbi.1998.0861
- Duranton F, Cohen G, De Smet R, et al. Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1-13.
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011121175
- Carling RS, Oegg TJ, Allen KR, et al. Evaluation of whole blood serotonin and plasma and urine 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid in diagnosis of carcinoid disease. Ann Clin Biochem. 2002;39(6):577-582.
- DOI: 10.1177/000456320203900605
- Danaceau JP, Anderson GM, McMahon WM, Crouch DJ. A liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric method for the analysis of serotonin and related indoles in human whole blood. J Anal Toxicol. 2003;27(7):440-444.
- DOI: 10.1093/jat/27.7.440
- Alfredsson G, Wiesel FA. Monoamine metabolites and amino acids in serum from schizophrenic patients before and during sulpiride treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1989;99(3):322-327.
- DOI: 10.1007/bf00445551
- Козлов В.А., Демина Д.В. Триптофан и indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) в патогенезе иммунокомпрометированных заболеваний // Медицинская иммунология. - 2017. - Т.19. - №3. - С. 225-240.
- DOI: 10.15789/1563-0625-2017-3-225-240
- Grohmann U, Fallarino F, Bianchi R, et al. A defect in tryptophan catabolism impairs tolerance in nonobese diabetic mice. J Exp Med. 2003;198(1):153-160.
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030633
- Grohmann U, Puccetti P. The coevolution of IDO1 and AhR in the emergence of regulatory T-cells in mammals. Front Immunol. 2015;6:58.
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00058
- Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology. 2017;112(Pt B):399-412.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.07.002
- Козлов И.А., Клыпа Т.В., Рыбаков В.Ю., Матвеев Ю.Г. Первый опыт назначения серотонина адипината для коррекции сосудистой недостаточности у кардиохирургических больных // Вестник интенсивной терапии. - 2006. - №1. - С. 7-9.
- Kaumann AJ, Levy FO. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors in the human cardiovascular system. Pharmacol Therapeut. 2006;111:674-706.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.12.004
- Dahan D, Hien ТT, Tannenberg P, et al. MicroRNA-dependent control of serotonin-induced pulmonary arterial contraction. J Vasc Res. 2017;54(4):246-256.
- DOI: 10.1159/000478013
- Haynes RL, Frelinger AL, Giles EK, et al. High serum serotonin in sudden infant death syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(29):7695-7700.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1617374114
- Schefold JC, Fritschi N, Fusch G, et al. Influence of core body temperature on Tryptophan metabolism, kynurenines, and estimated IDO activity in critically ill patientsreceiving target temperature management following cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2016;107:107-114.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2016.07.239
- Cason CA, Dolan KT, Sharma G, et al. Plasma microbiome-modulated indole- and phenyl-derived metabolites associate with advanced atherosclerosis and postoperative outcomes. J Vasc Surg. 2018;68(5):1552-1562.e7.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.09.029
- Ситкин С.И., Ткаченко Е.И., Вахитов Т.Я., и др. Метаболом сыворотки крови по данным газовой хроматографии - масс-спектрометрии (ГХ-МС) у пациентов с язвенным колитом и больных целиакией // Гастроэнтерология. - 2013. - №12. - С. 44-57.
- Ilkhanizadeh B, Owji AA, Tavangar SM, et al. Spot urine 5-hydroxy indole acetic acid and acute appendicitis. Hepatogastroenterol. 2001;48(39):609-613.
- Jangjoo A, Varasteh AR, Mehrabi Bahar M, et al. Is urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid helpful for early diagnosis of acute appendicitis? Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30(4):540-544.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2011.01.027
- Mentes O, Eryilmaz M, Harlak A, et al. The importance of urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels in the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Am J Emerg Med. 2009;27(4):409-412.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2008.03.016
- Oruc MT, Kulah B, Ozozan O, et al. The value of 5-hydroxy indole acetic acid measurement in spot urine in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. East Afr Med J. 2004;81(1):40-41.
- DOI: 10.4314/eamj.v81i1.8793
- Bolandparvaz S, Vasei M, Owji AA, et al. Urinary 5-hydroxy indole acetic acid as a test for early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Clin Biochem. 2004;37(11):985-989.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2004.07.003
- Rao A, Wilson M, Kennedy G, et al. Spot urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid is not an ideal diagnostic test for acute appendicitis. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(9):1750-1753.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.05.059
- Tan B, Qiu Y, Zou X, et al. Metabonomics identifies serum metabolite markers of colorectal cancer. J Proteome Res. 2013;12(6):3000-3009.
- DOI: 10.1021/pr400337b
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, et al. Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(9):2089-2096.
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131
- Ardill JE, Armstrong L, Smye M, et al. Neuroendocrine tumours of the small bowel: interpretation of raised circulating chromogranin A, urinary 5 hydroxy indole acetic acid and neurokinin A. QJM. 2016;109(2):111-115.
- DOI: 10.1093/qjmed/hcv095
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, et al. Fecal microbiota, fecal metabolome, and colorectal cancer interrelations. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0152126.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126
- Uchiyama K, Yagi N, Mizushima K, et al. Serum metabolomics analysis for early detection of colorectal Cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2017;52(6):677-694.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-016-1261-6
- Wei J, Xie G, Zhou Z, et al. Salivary metabolite signatures of oral cancer and leukoplakia. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:2207-2217.
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25881
- Englert JA, Rogers AJ. Metabolism, metabolomics, and nutritional support of patients with sepsis. Clin Chest Med. 2016;37(2):321-331.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccm.2016.01.011
- Meier MA, Ottiger M, Vegeli A, et al. Activation of the tryptophan/serotonin pathway is associated with severity and predicts outcomes in pneumonia: results of a long-term cohort study. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55(7):1060-1069.
- DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0912
- Orešič M, Posti JP, Kamstrup-Nielsen MH, et al. Human serum metabolites associatewith severity and patient outcomes in traumatic brain injury. EBioMedicine. 2016;12:118-126.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.07.015
- Marseglia L, D'Angelo G, Manti S, et al. Melatonin secretion is increased in children with severe traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5). pii: E1053.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18051053
- Lorente L, Martín MM, Abreu-González P, et al. Serum melatonin levels in survivor and non-survivor patients with traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurology. 2017;17:138.
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-017-0922-2
- Lorente L, Martín MM, Abreu-González P, et al. Serum melatonin levels are associated with mortality in severe septic patients. J Crit Care. 2015;30(4):860.e1-6.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.03.023
- Lin C, Chao H, Li Z, et al. Melatonin attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced inflammation: a possible role for mitophagy. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(2):177-186.
- DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12337
- Grima NA, Rajaratnam SM, Mansfield D, et al. Efficacy of melatonin for sleep disturbance following traumatic brain injury: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Med. 2018;16(1):8.
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-017-0995-1
- Mistraletti G, Paroni R, Umbrello M, et al. Melatonin pharmacological blood levels increase total antioxidant capacity in critically ill patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4). pii: E759.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040759
- Сивков А.В., Синюхин В.Н., Арзуманов С.В., и др. Уремические токсины в крови больных с терминальной стадией почечной недостаточности при дисбиозе кишечника // Экспериментальная и клиническая урология. - 2014. - №2. - С. 94-97.
- Лукичёв Б.Г., Подгаецкая О.Ю., Карунная А.В., Румянцев А.Ш. Индоксил сульфат при хронической болезни почек // Нефрология. - 2014. - Т.18. - №1. - С. 25-32.
- Lau WL, Savoj J, Nakata MB, Vaziri ND. Altered microbiome in chronic kidney disease: systemic effects of gut-derived uremic toxins. Clin Sci. 2018;132:509-522.
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20171107
- Huc T, Nowinski A, Drapala A, et al. Indole and indoxyl sulfate, gut bacteria metabolites of tryptophan, change arterial blood pressure via peripheral and central mechanisms in rats. Pharmacological Research. 2018;130:172-179.
- Etinger A, Kumar, Ackley W, et al. The effect of isohydric hemodialysis on the binding and removal of uremic retention solutes. Plos One. 2018;13(2):e0192770.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192770
- Chen JJ, Zhou CJ, Zheng P, et al. Differential urinary metabolites related with the severity of major depressive disorder. Behav Brain Res. 2017;332:280-287.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.06.012
- Шилов Ю.Е., Безруков М.В. Кинуренины в патогенезе эндогенных психических заболеваний. Актуальные вопросы неврологии и психиатрии // Вестник РАМН. - 2013. - Т.68. - №1. - С. 35-41.
- DOI: 10.15690/vramn.v68i1.535
- Tomasi CD, Salluh J, Soares M, et al. Baseline acetylcholinesterase activity and serotonin plasma levels are not associated with delirium in critically ill patients. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(2):170-177.
- DOI: 10.5935/0103-507X.20150029
- Peitl V, Vidrih B, Karlović Z, et al. Platelet serotonin concentration and depressive symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2016;239:105-110.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.03.006
- Rihua X, Haiyan X, Krewski D., Guoping H. Plasma concentrations of neurotran smitters and postpartum depression. J Cent South Univ (Med Sci). 2018;43(3):274-281.
- DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.03.007
- Rothhammer V, Mascanfroni ID, Bunse L, et al. Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nat Med. 2016;22(6):586-597.
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4106
- Dodd D, Spitzer MH, van Treuren W, et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature. 2017;551(7682):648-652.
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24661
- Keszthelyi D, Troost FJ, Jonkers DM, et al. Does acute tryptophan depletion affect peripheral serotonin metabolism in the intestine? Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(3):603-608.
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.111.028589
- Dinan TG, Stanton C, Cryan JF. Psychobiotics: a novel class of psychotropic. Biol Psych. 2013;74(10):720-726.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.001
- Roman P, Carrillo-Trabalón F, Sánchez-Labraca N, et al. Are probiotic treatments useful on fibromyalgia syndrome or chronic fatigue syndrome patients? Systematic review. Ben Microb. 2018;9(4):603-611.
- DOI: 10.3920/BM2017.0125
- Hubbard TD, Liu Q, Murray IA, et al. Microbiota metabolism promotes synthesis of the human Ah receptor agonist 2,8-dihydroxyquinoline. J Proteome Res. 2019;18(4):1715-1724.
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00946
- Aoki R, Aoki-Yoshida A, Suzuki Ch, Takayama Y. Indole-3-pyruvic acid, an aryl hydrocarbon receptor activator, suppresses experimental colitis in mice. J Immunol. 2018;201(12):3683-3693.
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701734
- Brito JS, Borges NA, Anjos JS, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and uremic toxins from gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease patients: is there a relationship? Biochemistry. 2019;58(15):2054-2060.
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01305
- Addi T, Poitevin S, McKay N, et al. Mechanisms of tissue factor induction by the uremic toxin indole-3 acetic acid through aryl hydrocarbon receptor/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93(1):121-136.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-018-2328-3
- de Loor H, Poesen R, De Leger W, et al. A liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry method to measure a selected panel of uremic retention solutes derived from endogenous and colonic microbial metabolism. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;936:149-156.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.06.057
- Danaceau JP, Anderson GM, McMahon WM, Crouch DJ. A liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric method for the analysis of serotonin and related indoles in human whole blood. J Anal Toxicol. 2003;27(7):440-444.
- DOI: 10.1093/jat/27.7.440
- Шевченко В.Е. Современные масс-спектрометрические методы в ранней диагностике рака // Масс-спектрометрия. - 2004. - №1. - С. 103-126.
- Паутова А.К., Бедова А.Ю., Саршор Ю.Н., Белобородова Н.В. Определение ароматических микробных метаболитов в сыворотке крови методом газовой хромато-масс-спектрометрии // Журнал аналитической химии. - 2018. - Т.73. - №2. - С. 121-128.
- DOI: 10.7868/S0044450218020044
- Wu H, Xue R, Dong L, et al. Metabolomic profiling of human urine in hepatocellular carcinoma patients using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;648(1):98-104.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.06.033
- Jiang G, Shen X, Kang H, et al. Serum metabolite profiling of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma based on a multiplatform approach. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018;1077-1078.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.01.034
- Struck-Lewicka W, Kordalewska M, Bujak R, et al. Urine metabolic fingerprinting using LC-MS and GC-MS reveals metabolite changes in prostate cancer: a pilot study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015;111:351-361.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.12.026
- Pavlenko D, Giasafaki D, Charalambopoulou G, et al. Carbon adsorbents with dual porosity for efficient removal of uremic toxins and cytokines from human plasma. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14914.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15116-y
- Phonchaia A, Wilairatb P, Chantiwasa R. Development of a solid-phase extraction method with simple MEKC-UV analysis for simultaneous detection of indole metabolites in human urine after administration of indole dietary supplement. Talanta. 2017;174:314-319.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.06.019


