Russian economic journals indexed in web of science: current state and the ways of increasing international visibility
Автор: Tretyakova Olga V.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Discussion platform
Статья в выпуске: 6 (66) т.12, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Determination of strategic directions for development of Russian journals included in the international database Web of Science requires improvement of methods for assessing their level. The article proposes an approach, the essence of which is determined by the use of bibliometric analysis methods for a comprehensive assessment of the state of Russian economic journals, based on the indicators obtained from both international and national citation systems. Our data sources include indices that form the core of Web of Science and the Russian Science Citation Index. We assess the state of 18 Russian economic journals, including the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast issued by Vologda Research Center of RAS. We summarize the experience of this journal in improving its international visibility. We define the factors that impede the integration of Russian journals into the world scientific and information space and outline strategic tasks that should be addressed so that the journals' position in the international space could be improved. The results obtained can be used by scientific organizations and editors to make decisions on the development of periodicals. The conclusions of our study are important for discussing the problem related to choosing approaches and criteria for evaluating scientific journals.
Economic journals, bibliometric indicators, international visibility of the journal, international scientometric databases, web of science, emerging sources citation index
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147224238
IDR: 147224238 | УДК: 001.92 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2019.6.66.17
Текст научной статьи Russian economic journals indexed in web of science: current state and the ways of increasing international visibility
Due to the emergence of new challenges of Russia’s policy in the field of science, the role of scientific journals that present research findings of Russian scientists both nationally and globally has increased. The need to find new ways to integrate into the international space has increased with the launch of the national project “Science” 1 in 2018, which has set tasks for research teams to increase their performance in international scientometric databases (ISDB) and increase the number of journals indexed in them. At the same time, the priorities of the publication policy have been adjusted in favor of qualitative indicators. Thus, the goals of the national project state the number of articles in the first and second quartile journals indexed in the international databases Web of Science and Scopus, and the number of scientists who have published articles in such journals.
Obviously, it is extremely difficult for organizations engaged in socio-economic research to meet such targets. According to expert estimates, highly rated international journals contain a small number of publications by Russian economists, which is due to significant entry barriers associated with the specifics of manuscript review, lack of authors’ affiliation with leading foreign universities and lack of academic degrees obtained in these organizations [1, p. 259]. In this situation, it becomes particularly relevant to develop and promote Russian economic journals included in global citation indexes, to raise their academic level and status in the international space. According to experts, the internationalization of journals provides growth points for the development of science in Russia and prospects for improving its scientific positions in the international arena [2]. Editors need to build a stable system of work to improve the quality characteristics and increase the international visibility of their journals so as to be able to compete with leading foreign publications. In order to determine strategic directions for further development of journals with international certification, it is necessary to work out new approaches to assess their level, which would allow monitoring their quality not only in the national but also in the global segment.
The difficulty of solving this problem lies in the fact that the scientific expert community has not developed clear criteria for evaluating scientific journals. The discussion has unfolded between the supporters of two main approaches – quantitative and qualitative. Despite the lengthy nature of the discussion, experts have not yet reached a consensus on the effectiveness of both scientometric indicators and the expertise of academic journals. The lack of an authoritative scientific citation base in Russia and the low level of scientific ethics [3] are the main obstacles to the establishment of a generally accepted method for evaluating journals. The revealed limitations of bibliometric and expert analysis indicate that the use of any of the approaches, as a rule, does not give a complete picture of the state of scientific periodicals.
In our opinion, we should not underestimate the possibilities of expert evaluation for characterizing small groups of journals. At the same time, quantitative factors may have an advantage for objective analysis of a large sample of publications. In addition, the use of bibliometric indicators is justified for evaluating journals that have already passed the examination and are indexed in ISDB.
Modern research based on the use of bibliometric analysis methods also covers those Russian journals that were included in the Web of Science Core Collection (WoS) relatively recently (in 2015 and later) [4; 5]. Some of the findings are quite applicable to economic journals. However, there is still a need for a separate assessment of their level in order to identify challenges related to improving their quality.
Taking into account the above, we analyzed the bibliometric indicators of Russian economic journals included in WoS in order to conduct a comprehensive assessment of their status and determine possible ways to increase the international visibility of publications. We used the data obtained from the analytical systems Web of Science and Russian Science Citation Index (RSCI) and characterized journals’ positions in the international and national segments of scientific periodicals. Since the reference group also includes the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast published by Vologda Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, we presented a description of its indicators in dynamics and relative to indicators of other journals, and also backed some conclusions with examples from the experience of its development.
The results obtained are relevant not only for identifying strategically important tasks for the development of the selected journal. They can be used by scientific organizations and editorial offices to make decisions on the promotion of periodicals. In addition, the findings of the study are important for developing an approach to the construction of a methodology and selection of criteria for evaluating a scientific journal.
A brief theoretical overview of approaches to evaluating economic journals
To date, there are two main approaches to assessing the level and quality of scientific journals – quantitative, based on the use of bibliometric indicators, and qualitative, which involves expert assessments.
Noting the advantages of quantitative factors, experts emphasize that, although they do not evaluate the content aspects of the journal, but the formal ones, there is a list of formal requirements, compliance with which is considered mandatory in the scientific community for a good journal. Qualitative parameters allow us to objectively assess the scientific level of the journal, but their use is associated with high resource costs, problems of selection of experts, and selection of criteria for analysis [6, pp. 18-19].
If we consider the traditions of evaluating economic journals, we can say that in foreign practice, methods based on the use of different combinations of bibliometric indicators are quite strong. Although one of the earliest ratings of economic journals developed by R. Hawkins, L. Ritter and I. Walter was based on an analysis of the opinions of a wide group of economists who participated in ranking journals from the list formed for the survey [7].
Attempts to evaluate the quality of journals using quantitative methods were mainly related to citation analysis. In early studies, the number of references received by the journal from certain sources [8] or from a pool of “major” journals [9; 10], and the institutional affiliation of the authors of articles [11] were used as criteria for such an assessment. Simple methods of calculating indices were proposed, which measure their contribution to the development of the discipline by analyzing citations of publications from leading economic journals [12].
With the emergence of citation indexes, the methods for evaluating journals based on the study of statistical data from citation systems [13], including the impact factor proposed by E. Garfield [14], have become widely used. Attempts to neutralize the shortcomings of the impact factor led to the emergence of more complex methods based on weighing citations from journals of different levels [15].
Rapid development of the scientometric approach in evaluating economic journals was reflected in the development of their ratings. Efforts to understand the results of rating products have led to the formation of such a method as aggregating the results of various ratings [16]. Despite the existing limitations, such ratings, according to researchers, offer relatively objective information about the scientific quality of publications [17] and are considered a very important tool for evaluating the performance of economic institutions and individual scientists [18].
As for the Russian experience in identifying the level of economic journals, it has been developing in accordance with the international tradition. We gave a detailed overview of such studies earlier [19]. Here we note only that to date several methodological approaches have been developed in this area. The expert approach is based on the sociological assessments of the opinions of the academic community. The results are presented in the ratings of economic journals, the most famous of which are the NRU HSE project [20] and the rating compiled under the guidance of A.Ya. Rubinshtein [21]. The bibliometric approach based on the analysis of scientometric indicators is reflected in the journal ranking techniques developed by A.A. Murav’ev [22], O.V. Tret’yakova [19, 23]. The cross-citation analysis is related to the network analysis technique based on the identification of systemically significant scientific journals in networks [24]. The Rating of Leading Russian Economic Journals (LREJ Rating) developed by E.V. Balatsky and N.A. Ekimova, is based on the intersection of bibliometric and expert approaches. To date, the results of the fifth wave of LREJ Rating have been published [25]. Like other countries, Russia uses an approach related to the aggregation of existing rating products (Subochev rating [26]; Balatsky– Ekimova consensus rating [27]).
According to the expert community, both quantitative and qualitative approaches used today to evaluate academic journals have both strengths and limitations. The relatively arbitrary choice of bibliometric indicators and their weak correlation with the scientific authority of journals, as well as the insufficient validity of the procedure for aggregating the indicators used, are indicated as vulnerable points in the ratings [28]. The disadvantages of the examination are seen in the problems of selection of experts, in the subjectivity of the assessment, in the impossibility of covering large volumes of publications.
In our opinion, it is almost impossible to do without taking into account quantitative indicators in the process of analyzing fairly large volumes of publications. Moreover, we have always paid attention to the fact that quantitative assessment is not prevailing and in most cases requires the imposition of expert opinion on the results obtained. However, when it comes to journals indexed in international scientometric databases, it is necessary to take into account the fact that these journals have already passed expert evaluation and confirmed their compliance with international quality standards. The analysis of their bibliometric indicators will thus be useful for obtaining objective characteristics that reflect the dynamics of their development and position relative to each other. In addition, when conducting a comprehensive assessment of the status of the small number of journals that are indexed in ISDB, it is important to take into account their indicators obtained from both international and national citation systems in order to clarify some of the conclusions.
Results of assessment of the state of Russian economic journals according to indicators in the international scientometric database Web of Science
At the moment, more than a thousand economic journals are published in Russia. Of these, about 500 publications are indexed in the RSCI. As of December 2019, 18 economic journals are included in the international scientometric database Web of Science. All these publications are included in the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI), which was added to the Web of Science Core Collection at the end of 2015 in order to cover important regional journals and give the academic community the opportunity to discover new areas of research, identify trends in the development of science with additional high-quality data. At the launch of the index, about 1.5 thousand journals were selected, and new publications were added weekly until 2016. As of April 2016, the index included about 3,500 journals [29].
It should be noted that before the introduction of the ESCI index, Russian economic journals were not represented in the Web of Science Core Collection. The first Russian economic journal that was included in the ESCI was the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast published by Vologda Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Its English-language version was among 16 Russian journals that were included in this index at the first stage of selection2.
It is obvious that editors have a lot of work to do to promote their publications in the international environment. In order to develop strategies for their development and identify certain target indicators, it is necessary to organize regular monitoring of bibliometric indicators of publications in Web of Science in order to compare them with indicators of other Russian journals on similar topics, which are also included in Web of Science, and with the data on foreign journals. The complexity of such a monitoring due to the fact that the impact factor is not calculated for publications included in the ESCI [30]. Therefore, other indicators that are automatically generated in Web of Science can be selected for their evaluation, or journal impact factors can be calculated using the methodology adopted in this database.
Table 1. Data on Russian economic journals indexed in Web of Science (ESCI) for the period 2015–2019
|
Journal |
h-index |
Total number of publications, units |
Total number of citations, units |
Number of citations without selfcitation, units |
Average number of citations per article, units |
Selfcitation coefficient, % |
Proportion of links from articles whose authors are affiliated with Russian organizations, % |
Proportion of links from articles whose authors are affiliated with foreign organizations, % |
|
Voprosy Ekonomiki |
9 |
443 |
656 |
418 |
1.48 |
36.3 |
95.8 |
4.2 |
|
Economy of Region |
7 |
499 |
557 |
395 |
1.12 |
29.1 |
87.4 |
12.6 |
|
Foresight and STI Governance |
7 |
130 |
281 |
271 |
2.16 |
3.6 |
72.2 |
27.8 |
|
Terra Economicus |
6 |
192 |
172 |
121 |
0.9 |
29.7 |
77.7 |
22.3 |
|
Economic Policy |
5 |
283 |
187 |
139 |
0.66 |
25.7 |
84.8 |
15.2 |
|
The Journal of the New Economic Association |
5 |
216 |
175 |
158 |
0.81 |
9.7 |
93.7 |
6.3 |
|
Journal of Institutional Studies |
5 |
165 |
159 |
86 |
0.96 |
45.9 |
93.6 |
6.4 |
|
Journal of Mining Institute |
5 |
484 |
232 |
212 |
0.48 |
8.6 |
95.7 |
4.3 |
|
Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast |
4 |
457 |
163 |
105 |
0.36 |
35.6 |
89.8 |
10.2 |
|
World Economy and International Relations |
4 |
764 |
283 |
183 |
0.37 |
35.3 |
96.1 |
3.9 |
|
International Organisations Research Journal |
4 |
186 |
112 |
70 |
0.60 |
37.5 |
58.1 |
41.9 |
|
Journal of Tax Reform |
4 |
69 |
54 |
31 |
0.78 |
42.6 |
82.5 |
17.5 |
|
The Manager |
3 |
285 |
77 |
54 |
0.27 |
31.1 |
51.8 |
48.2 |
|
Business Informatics |
3 |
130 |
53 |
36 |
0.41 |
32.1 |
72.3 |
27.7 |
|
Economics and the Mathematical Methods (archive for 2017–2019) |
2 |
123 |
14 |
9 |
0.11 |
35.7 |
92.3 |
7.7 |
|
Russian Management Journal (archive for 2018–2019) |
1 |
31 |
2 |
3 |
0.06 |
50.0 |
100 |
0 |
|
Contemporary Europe (archive for 2016–2019) |
2 |
433 |
45 |
33 |
0.10 |
26.7 |
78.4 |
21.6 |
|
The St Petersburg University Journal of Economic Studies (archive for 2017–2019) |
1 |
72 |
15 |
8 |
0.21 |
46.7 |
93.3 |
6.7 |
|
Source: own elaboration using Web of Science data as of December 1, 2019. |
||||||||
Journals are ranked by the value of the Hirsch index. Their evaluation is carried out with the help of citation indicators. According to the total number of citations in WoS, the journal Voprosy ekonomiki is the leader. However, it is necessary to say that the value of this indicator is influenced not only by the importance, authority and popularity of the journal, but also by its volume. Since publications differ significantly from each other in volume, it is advisable to estimate the average citation. The selected indicator reflects the average impact of one article. A five-year publication window and a matching citation window are usually used to analyze the average citation. The average number of citations received over the past five years by articles published during the same five years (per article) is determined [31].
As we can see from the data in Table 1, only three journals have more than one citation per article: Foresight and STI Governance , Voprosy ekonomiki , and Economy of Region . At the same time, if accor-ding to the total number of citations the journal Voprosy ekonomiki is the leader, then based on the average number of citations per article, the journal Foresight and STI Governance has the best score – 2.16 citations per article.
Besides, we should point out a high level of self-citation of almost all publications. Global requirements based on Web of Science data determine acceptable values of the selfcitation coefficient up to 20%, since 80% of WoS journals have a self-citation coefficient close to this value3. Of the journals we analyzed, only three (Foresight and STI Governance, The Journal of the New Economic Association, Journal of Mining Institute) have self-citation coefficients within the acceptable value of 20%, while the other journals have them ranging from 25 to 50%.
In addition, according to the findings of our research, articles from domestic economic journals receive citations in WoS mainly from Russian authors. For example, the share of references to the leading Russian journal Voprosy ekonomiki from authors who are affiliated with foreign organizations is less than 5% of its total number of citations. These results largely correlate with the data of the studies on citation of Russian journals included in the ESCI [4].
In our opinion, the current situation is due, first, to the recent inclusion of Russian journals in the international database Web of Science, and second, to a number of factors that prevent their successful integration into the global scientific and information space. The main problem is their low international visibility, which can be increased, on the one hand, by expanding the geography of authors by inviting foreigners and publishing the findings of joint research with foreign scientists, and on the other hand – by expan-ding the range of Russian economic journals in the Web of Science.
The indicators of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast prove that at the moment it is experiencing a number of difficulties similar to the problems of most Russian journals included in WoS. Judging by the relatively low number of links to the journal (on average, 0.36 citations per article), its promotion goals should include significant increase in its international visibi-lity. However, the share of citations from articles the authors of which are affiliated with foreign organizations is more than 10%. This indirectly confirms the fact that the editor has chosen the right direction of work to promote the journal in the international segment.
Table 2. Summary bibliometric indicators of Russian economic journals* indexed in the Web of Science and in the Russian Science Citation Index for 2018 (data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 2018)
|
s |
co |
CM |
CM |
co |
CO |
co |
|
|
^ " " 1 |
co |
ОТ |
co |
co |
s |
co |
|
|
s |
1- |
co |
^ |
co |
CM |
▻- |
co |
|
$ ™ ° ^ c x о CD - |
s |
Q |
co |
co |
|||
|
S |
co |
1- |
CO |
CD |
co |
||
|
■= ^ ° |
«Э |
°? |
co |
CO |
CO |
co |
|
|
1- |
CM |
co |
CD |
co |
co |
||
|
Ш X >. cy Q ® E « |
a |
co |
s |
CO |
CM |
От |
s |
|
1- |
CM |
co |
co |
CO |
|||
|
g E ” |
s |
s |
ОТ |
||||
|
- 2 8 CD C CXI Q 9? X 2 О CD CD ° и M ^ |
s |
co |
co |
a |
co |
s |
UP |
|
о |
g 5 |
g 5 |
g 5 |
g 5 |
g 5 |
||
|
о e | j^ 'ey 5 "= ° g |
co .4 5 2 о E о ® J= g |§±8 |
ъ ° ^ о -У ^ ^ >^ 5 E 2 "55 5 ° ш . ф "^ 8 2 < 1 _E Ш ZD DC ZD |
° 1 ™ i c ° В -— 5 CD ° |
^ CD E E E ^ ” Ъ 8 8 ° S' ° cc ^ io" ^ co CD C 4—< CZ C od C od 3 o 8 ° ° ■5 § о ” 8 5 8 5 ^UJ^QCQCCOQCCO |
о § Ш су ОС <-)
cd
су о £ О) ш ф — c > о |
i ° ” E -S О E E -- ” E й 5 g e S су о о
DC |
|
|
"cy |
§ s -^ CD |
co 1 8 £ <§ |
О = c: U_J DC |
5 । ^ o S P C: -9 23 § Cy Q Lu CD ° сь V) ~cz V) |
S E Lu 9 5 5 § S |
^3 CD - CCS e ^ E ID 1^ CO g § co* 8 § g $ uj <3 S £ |
ex. £ |
|
CM |
co |
^r |
CO |
co |
Indicators of journals included in WoS.
End of Table 2
|
s |
m |
co |
CD |
co |
4- |
CD |
со |
||||
|
^ " " 1 |
CM |
co |
ОТ |
§ |
§ |
CD |
От |
^ |
со |
||
|
s |
CD |
^ |
m |
co |
CD |
CM |
CO |
СО |
со |
||
|
$ та ° ^ c x о CD - |
co |
от |
OP |
co |
co |
co |
CM |
со |
Q |
||
|
S |
CD |
CM |
co |
co |
CM |
CO |
со |
со |
|||
|
■= ^ |
CO |
co |
-7 |
4 |
co |
см |
|||||
|
CD |
co |
CO |
LO |
Ю |
co |
CM |
со |
||||
|
Ш >. ey g ® E « |
ОТ |
от |
co |
co |
о |
CD |
со |
||||
|
CD |
CM |
co |
CD |
co |
co |
CO |
со |
||||
|
g E ” |
от |
S |
CD |
co |
§ |
C° |
co |
СО |
от |
||
|
- 2 2 CD C CXI Q 9? X 2 О CD CD _g c/d CO "O |
co |
от |
8 |
Q |
s |
co |
OP |
со |
|||
|
о |
'ey CD CO D_ |
S о |
g 5 |
'ey |
'ey о CO D_ |
S о |
g 5 |
g 5 |
g 5 |
'ey о СО О- |
та ст |
|
S CO CO |
E 5 O CD О co
CD О Cl |
co -E 5 a ® § о g j= ° ^±8 ^ ZD - LU |
5 CD E S ° co g re UJ ZD ‘o |
5 co co |
ш Ё co 5 |
CD g ^ S ti OZ UJ < |
co -E 5 a ® § ^ ZD - Ш |
co >. о < E о . - 8 § co < Я о < О ё Ш CD ЕЕ ™ ® «5 О § у й "§ о ос о -Е |
"ёу ~ СО ^ |
2 ^ ^ >^ ш Ё со "^ u- CD 05 CD Е С ^ с ZD ZD CO ZD |
|
|
'ey |
^ ’ey CD ^> E Г7 co c: c^ CO cd § 5a a i— la о co |
° § § a ■$ § « a ° a co |
_ g 5 § 5 a * a с C <4 t CQ CD a s> $ Sot |
СЛ <У |
Cl CD ~~ .СУ CD) 5 £ 1 3 1 |
V) g 5 О 5 |
C S' О D3 CD U_j |
g V) CO CQ S a |
g g 5 g 5 5 а § |
О) § tD |
>< £ |
|
co |
op |
CD |
CM |
co |
^r |
CO |
со |
со |
The results of evaluation of scientific economic journals according to the indicators that determine their status at the national level
In order to assess the current status of journals at the national level, we analyzed their bibliometric indicators in the Russian Science Citation Index for 2018 4 . Comparing the data obtained with the results of the analysis of journal indicators in WoS helps clarify some conclusions and adjust the development objectives for an individual publication, and for scientific journals published in Russia in general.
To compare the indicators of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast and other Russian economic journals included in WoS, we have summarized a number of bibliometric indicators that allow us to perform a comprehensive analysis of their citation (Tab. 2) . In the general list, journals are ranked according to an integral indicator 5 in the Science Index-2018 rating. For each journal, the values of five indicators are given: the two-year and five-year impact factors, the five-year self-citation coefficient, the five-year Herfindahl index for citing journals 6 , and the Herfindahl index for organizations of authors 7 .
All indicators are ranked. As a result, the so-called summary rating of journals is obtained; it is a systematized set of absolute and relative indicators of journals for the year and it is a necessary tool to make vertical and horizontal comparisons.
Indicators of the two impact factors – two-year and five-year – are selected as ranking criteria. As we explained earlier in our research, this is due to the desire to identify the journals that publish the papers that receive most citations since their publication, and at the same time to smooth out the outliers from the influence of individual articles with abnormal citation by using a wider publication window [19]. To assess the authority that the journals indexed in ISDB have in the Russian academic community, we compared the values of the two-year and five-year RSCI impact factor with their median values in the group of journals in the category “Economy. Economic science” (data of the Russian Science Citation Index as of August 2018). We have found out that all the journals had two-year and five-year impact factors higher than the median value for the discipline (the median distribution of the two-year impact factor values of the journals in 2018 was 0.371; the median distribution of the five-year impact factor values was 0.289). Twelve editions had the value of the two-year impact factor more than 1. Thus, the share of highly cited journals is 67%. They can be described as having a high level of impact in the academic environment.
Evaluating the level of journals’ self-citation by WoS indicators, we conclude that it is high. At the same time, almost all journals (except for the Journal of Tax Reform ) have low selfcitation coefficients in the RSCI. They prove that the journals have chosen the right policy in this aspect. According to the data obtained, we can say that the high percentage of self-citation in Russian economic journals in WoS is due to
Figure 1. Dynamics of indicators of the number of articles and citations of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast in the RSCI (data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019)
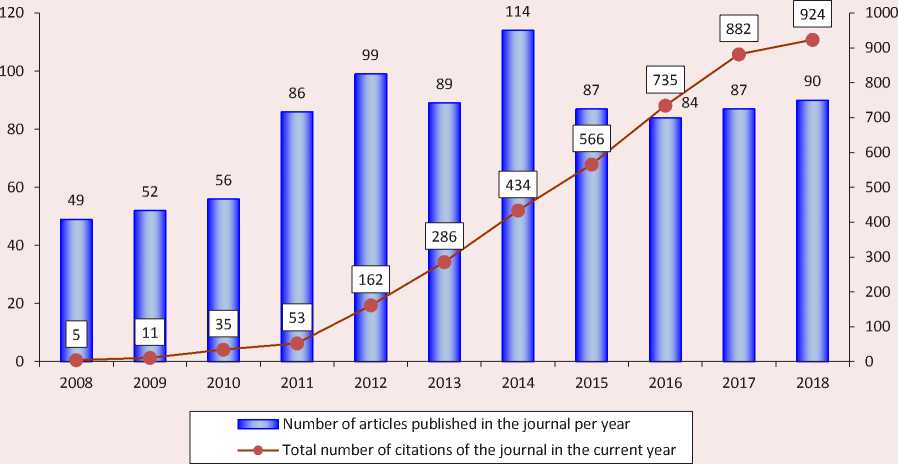
Figure 2. Dynamics of the impact factor of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast in the RSCI (data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019)
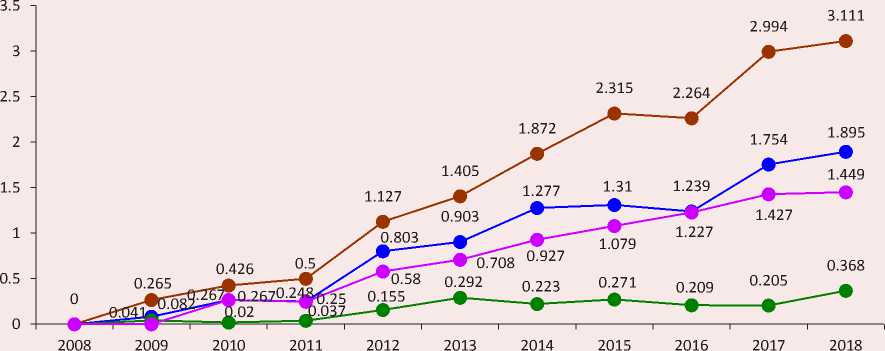
—•— Two-year RSCI impact factor
—•— Two-year RSCI impact factor including citations from all sources
—•— RSCI core impact factor
—•— Five-year RSCI impact factor
Figure 3. Dynamics of self-citation coefficients of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast in the RSCI (data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019)
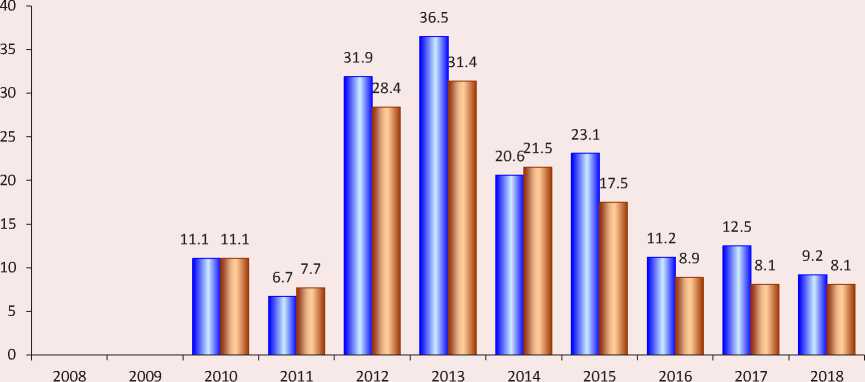
□ Two-year self-citation coefficient, %
□ Five-year self-citation coefficient, %
Figure 4. Dynamics of the five-year Herfindahl index for citing journals and the Herfindal index for organizations of authors of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast in the RSCI (data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019)
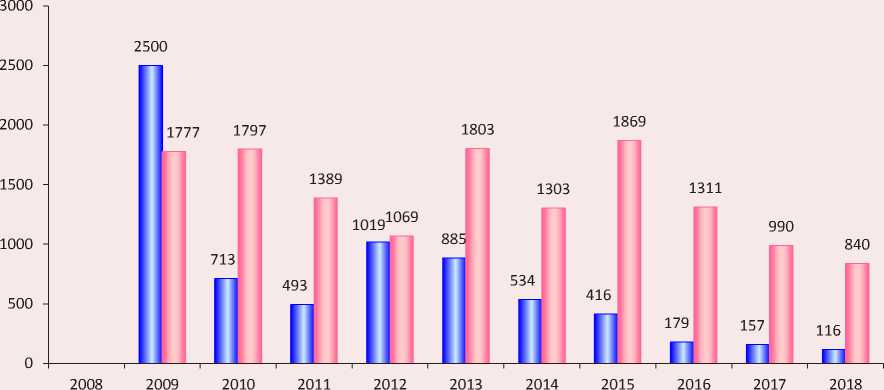
п Five-year Herfindahl index for citing journals
□ Five-year Herfindahl index for authors' organizations objective reasons. All of the above confirms that today the small number of Russian economic journals indexed in WoS is a limiting factor for them. This fact, which somewhat distorts the situation concerning citation, has a negative impact on the self-citation indicators in ISDB.
In order to take into account not only the volume but also the scale of citation, i.e. to distinguish the publications that have a small number of sources that refer to them from the journals that are well known in the academic community, we used the Herfindahl index for citing journals. Low values (less than 1000) of this indicator for all the journals except for the Journal of Tax Reform , allow us to conclude that they are in demand among a wide range of publications.
At the same time, the analysis of the Herfindahl index values for authors’ organizations revealed a high proportion of local publications among Russian economic journals with international certification, i.e. those with a narrow circle of authors who are usually affiliated with the parent organization. According to the index values for 2018, the total share of publications with a high level of locality (Herfindahl index value above 1000) was 72% (13 journals).
Having analyzed the indicators of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast we see that it occupies a fairly high position among other publications of similar remit. In 2008–2019, about 900 scientific articles were published in its issues; the subject of the articles corresponds to the priority areas of fundamental and applied research in the field of economics. Since 2015, the annual volume of articles has stabilized, while the rate of growth in the number of citations has continued to increase. In 2018, the annual number of citations received by the journal increased by 1.6 times compared to the level of 2015, the year in which the journal was included in the Web of Science database (Fig. 1).
On the whole, positive dynamics of the journal’s impact factors (Fig. 2) allows us to draw a conclusion that its scientific authority is increasing. According to the values of the two-year and five-year impact factors of the RSCI for 2018, the journal ranks sixth among 18 other journals from the reference group (Tab. 2) . Judging by the value of the two-year impact factor (1.895) the journal is highly cited, has a certain impact on the development of its scientific field and is perceived by the scientific community of economists as authoritative. It should be emphasized that the increase in the impact factor is due to an increase in the number of links from external sources, which is indicated by a decrease in the self-citation coefficients of the journal (Fig. 3) .
The growing popularity of the journal in the scientific community is indirectly evidenced by the dynamics of the five-year Herfindahl index for citing journals (Fig. 4). The data presented in the diagram clearly show that, after the journal was included in the WoS, the range of publications that cite it has significantly expanded. This is confirmed by a decrease in the index value by 3.5 times in 2018 compared to the value of 2015. Another significant achievement in the development of the journal is related to overcoming its nature as a local publication. The decrease in the Herfindahl index for authors’ organizations in 2017 and 2018 indicates the effectiveness of the editor’s work to expand the geography of the journal’s authors.
It is important to note that in general, according to the results of a comprehensive bibliometric analysis, which is conducted in the RSCI for periodicals, the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast ranked 7th in the Science Index rating for 2018 on the subject “Economy. Economic sciences” (from 386 journals; data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019), improving its rank by two positions compared to the 2017 rating.
Dynamics of the journal’s positions in the Science Index rating (Tab. 4) clearly shows that over the past five years, the journal’s position has improved significantly: if in 2014 it ranked 52nd in the thematic rating among 347 economic journals, being at the same time on the 565 place in the overall rating, then in 2018 it reached 53rd place in the overall rating (among 3,542 journals), improving its position 10-fold, and it reached 7th place in the thematic rating among economic publications.
In 2018, the journal was included in the core of top ten scientific publications on economics, affiliated with organizations of the academic sector (Tab. 5) . Since 2016, it has been included in the Diamond List of Russia’s leading economic journals (Balatsky–Ekimova rating) [25; 32], compiled on the basis of an analysis of bibliometric parameters and expert assessments (Tab. 6) . Thus, at present, we can state that the journal is among Russia’s leading economic journals.
Table 3. Top 10 journals from the Science Index rating for 2018 on the subject “Economy. Economic sciences” (data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019)
|
Journal |
SI value |
Rating position 2017 |
Rating position 2018 |
|
Voprosy ekonomiki |
22.669 |
1 |
1 |
|
Foresight and STI Governance |
13.928 |
2 |
2 |
|
Economy of Region |
11.334 |
3 |
3 |
|
The Journal of the New Economic Association |
6.908 |
7 |
4 |
|
Spatial Economics |
6.604 |
5 |
5 |
|
World Economy and International Relations |
6.400 |
4 |
6 |
|
Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast |
5.193 |
9 |
7 |
|
Economic Policy |
4.545 |
13 |
8 |
|
The St Petersburg University Journal of Economic Studies |
4.002 |
24 |
9 |
|
Tomsk State University Journal of Economics |
3.947 |
11 |
10 |
Table 4. Dynamics of values of the integral indicator and positions of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast in the Science Index rating
(data of the Scientific Electronic Library as of August 17, 2019)
|
Indicator |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
|
The journal’s score in the SCIENCE INDEX rating |
0.014 |
0.156 |
0.210 |
0.237 |
0.333 |
0.723 |
1.080 |
2.852 |
3.792 |
5.193 |
|
Place in the Science Index ranking on the subject “Economics. Economic sciences” |
117 |
58 |
67 |
68 |
70 |
52 |
45 |
13 |
9 |
7 |
|
Number of journals in the Science Index rating on the subject “Economics. Economic sciences” |
201 |
228 |
252 |
291 |
322 |
347 |
369 |
386 |
388 |
388 |
|
The journal’s place in the overall Science Index rating |
1632 |
781 |
842 |
914 |
897 |
565 |
420 |
111 |
74 |
53 |
Table 5. Top 10 journals from the Impact Rating of economic journals of the academic sector – 2018
|
Journal |
Indicators in the RSCI for 2016 (RSCI data as of April 2018) |
Integral indicator |
Position |
|||
|
IF2 |
IF5 |
HIJ |
HP |
|||
|
Voprosy ekonomiki |
7.288 |
4.650 |
81 |
33 |
2.000 |
1 |
|
Economy of Region |
2.500 |
1.484 |
146 |
7 |
0.757 |
2 |
|
The Journal of the New Economic Association |
1.118 |
0.828 |
117 |
0 |
0.731 |
3 |
|
Studies on Russian Economic Development |
2.538 |
2.104 |
206 |
3 |
0.699 |
4 |
|
Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast |
1.363 |
1.149 |
176 |
4 |
0.568 |
5 |
|
The Bulletin of the Institute of Economics of the Russian Academy of Sciences |
0.788 |
0.499 |
155 |
3 |
0.552 |
6 |
|
ECO |
0.910 |
0.628 |
161 |
3 |
0.543 |
7 |
|
Spatial Economics |
2.000 |
1.357 |
304 |
2 |
0.485 |
8 |
|
Applied Econometrics |
0.981 |
0.799 |
230 |
0 |
0.414 |
9 |
|
Economics of Contemporary Russia |
0.607 |
0.829 |
224 |
0 |
0.412 |
10 |
|
Notes: IF2 – two-year RSCI impact factor without self-citation (including the translated version); IF5 – five-year RSCI impact factor without self-citation; HIJ – Herfindahl five-year index for citing journals; HP – number of highly cited (hot) papers. Source: The impact rating of academic journals in economics: ranking criteria and methodology. Compiled by O.V. Tret’yakova [19]. |
||||||
Table 6. Diamond List of Russian economic journals, 2019
|
Journal |
Founder/publisher (city) |
Position in the 2016 rating |
Position in the 2019 rating |
|
Voprosy ekonomiki |
Editorial Board of the journal Voprosy ekonomiki (Moscow) |
1 |
1 |
|
Foresight and STI Governance |
National Research University “Higher School of Economics” (Moscow) |
2 |
2 |
|
Economy of Region |
Institute of Economics of the Ural Branch of RAS; Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B.N. Yeltsin (Yekaterinburg) |
3 |
3 |
|
World Economy and International Relations |
Russian Academy of Sciences, Institute of World Economy and International Relations of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Moscow) |
7 |
4 |
|
Studies on Russian Economic Development |
Institute of Economic Forecasting of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Moscow) |
6 |
5 |
|
International Organisations Research Journal |
National Research University “Higher School of Economics” (Moscow) |
15 |
6 |
|
Terra Economicus |
Southern Federal University (Rostov-on-Don) |
8 |
7 |
|
The Journal of the New Economic Association |
“Journal of the New Economic Association” (Moscow) |
5 |
8 |
|
Economic Policy |
Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration; Gaidar Institute for Economic Policy (Moscow) |
4 |
9 |
|
Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast |
Vologda Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Vologda) |
10 |
10 |
|
Russian Journal of Money and Finance |
Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Moscow) |
11 |
|
|
Business Informatics |
National Research University “Higher School of Economics” (Moscow) |
14 |
12 |
|
Russian Management Journal |
Saint Petersburg State University. Higher School of Management (Saint Petersburg) |
17 |
13 |
|
Source: Leading Russian Economic Journals Rating – 2019. Compiled by E.V. Balatsky and N.A. Ekimova [25; 32]. |
|||
Ways to increase the international visibility of a scientific journal
The analysis has revealed a number of problems that are mostly typical of all Russian economic journals included in the Web of Science. In our opinion, with the expansion of the range of Russian journals in this database, the problem of high self-citation will gradually be leveled by increasing the share of links from external sources. At the same time, each of the journals will have to improve the accessibility of published materials for the international scientific community. This can be done by expanding the number of foreign authors, improving the quality of published materials by strengthening peer review and inviting leading foreign experts to evaluate the articles.
The availability of a full-text English version of the journal is an important condition for increasing its international visibility. According to O.V. Kirillova, “English-language journals are much more likely to achieve high results than the journals issued in the language of the country in which they are published” [2]. In our opinion, the best way is to issue the journal in two identical versions in Russian and English, in which the output data of the articles completely coincide. The journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast is published in this very format. According to experts, publishing Russian journals in two languages seems to be the most appropriate solution, because when making the journal available to foreign readership, it is also important to preserve the Russian scientific language and scientific communication in the Russianspeaking environment [2].
Editors use various methods to ensure that the journal is in demand by the international academic community. For this purpose, journals are sent to foreign libraries and placed in foreign repositories; they are placed in open access [33]. The search for articles by Russian authors in the international information space is improved by assigning digital object identifiers to publications, which provide crosslinking of articles from world journals on the portals of foreign publishers and contribute to their correct citation [33; 34]. Editors develop programs for the participation of journals in public events, develop networks of so-called “ambassadors” of publications, i.e. persons who work to find new authors, including foreign ones [34].
The experience of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast in implementing the above goals was presented at the international conference “World-Class Scientific Publication” [35]. Summarizing the main conclusions of the report, we note that long-term research projects that are being worked on jointly with foreign scientific organizations, as well as the direct participation of the journal in international projects, contribute a lot to improving the quality of foreign content.
SI-DRIVE (Social Innovation: Driving Force of Social Change) is one of the most successful projects in which the journal participated. It was implemented for four years by a scientific consortium that comprised 26 countries. Russia was represented solely by a group of researchers from Vologda Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The journal issued by VolRC RAS was presented at international seminars and conferences held within the framework of the project: in Leiden (Netherlands, February 2017), Dusseldorf (Germany, April 2017), and Brussels (Belgium, October 2017). In January 2018 the journal was presented in Brussels at the first meeting of the European School of Social Innovation (ESSI), which was formed after the completion of the SI-DRIVE project. In the same year, the journal became an official partner of ESSI.
The work of the journal in this project helped solve several important tasks related to the expansion of the geography of its foreign authors and strengthening the composition of the Editorial Board by inviting foreign participants 8 of the project to join it. Based on the results of joint research, the project published a series of articles prepared by authors from different countries: The Netherlands, UK, Spain, Portugal, Germany, Lithuania, Turkey, and Brazil (see EaSC : 2016, no. 5, pp. 195-218; 2017, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 242-258). Two joint publications were published by scientists from Vologda Research Center in collaboration with SI DRIVE project manager from Germany (see EaSC : 2017, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 21-36), as well as with researchers from Spain and China (see EaSC : 2018, vol.11, no. 2, pp. 52-68.). It should be emphasized that the published materials cover issues that are actively discussed in the European academic community, so the potential for citing them is estimated to be quite high.
Participation in major international conferences as a so-called “supporting journal” has become another point of growth for the development of foreign content of the journal. In particular, it has been an information partner of the Management International Conference for three years. Presentations of the journal were held in the framework of the Editorial Panel in Italy (2017), Slovenia (2018), and Croatia (2019). As a result, several articles were published by authors from European countries: Romania, Poland, Croatia, and Hungary (see EaSC : 2017, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 234-247; 2018, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 185-201; 2018, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 182-197; 2019, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 220-233).
Another event that is significant for the development of the journal is its presentation at the international seminar on trust issues held in Tokyo (Rikkyo University, October 2018). The results of the seminar showed that a number of Japanese and Russian studies on social problems, despite the presence of specific features for each country, are based on similar methods. That is why it was decided to present the research findings of Japanese colleagues on the pages of the journal. Its previous issue contained three articles by scientists from Japan on the formation and development of sociological knowledge in their country (see EaSC : 2019, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 158-174.).
All of the above makes it possible to state that the measures listed above help expand the range of foreign contributors and improve the quality of foreign-language content by publishing articles with a higher citation potential in international indexes. An indicator of effectiveness of these activities is the presence of links from foreign authors in the journal. Promising areas of work to improve the journal’s international visibility may be related to improving the quality of the metadata of papers and creating content that meets the needs of a global audience, expanding the program of participation in international scientific events, and increasing its distribution channels.
Conclusion
The results of the analysis of bibliometric indicators of Russian economic journals included in the Web of Science allowed us to identify factors that will negatively affect their position in the international space; in our opinion, the major factor is their small number. Since Russian economic journals have been included in WoS relatively recently, their international visibility is still low and the number of references from foreign publications is small. The bulk of citation is obtained from
Russian sources. Thus, the issue of increasing the citation level of Russian journals in international scientometric databases can be solved, on the one hand, by increasing the number of indexed Russian journals, and on the other hand, by improving their international visibility, expanding the foreign authors’ audience, and publishing materials with high citation potential on issues relevant to the global academic community.
The dynamics of the main indicators of the journal Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast indicates the effec-tiveness of the system approach that is used to solve key tasks to achieve compliance with all the requirements for a modern academic journal. The high values of the journal’s impact factor in the RSCI allow us to conclude that it has become a well-known publication in the scientific community and that it has an impact on the development of economic science in Russia. Its wide popularity is confirmed by a significant number of citing scientific journals and the expanding geography of the composition of its authors, as evidenced by the low values of the Herfindahl indices. All this makes it possible to classify the journal as one of the leading Russian economic publications and determine its status as a national journal. The fact that it has been included in the main scientometric database proves that the high level of the journal is recognized not only among Russian economists, but also in the international academic community.
At the same time, the analysis of the journals’ indicators in WoS has revealed a number of problems that should be addressed in order to strengthen its international position. The journal faces significant challenges in gaining a readership abroad and increasing its citation rate. Therefore, new tools and mechanisms will be needed to ensure the worldclass quality of the publication, increase its accessibility and visibility in the international information space.
We believe that to improve the position of Russian economic journals in international scientometric databases, it is necessary to consolidate efforts on the part of the academic and editorial community. Certain conditions for this were created by the Association of Science Editors and Publishers (ASEP), chaired by O.V. Kirillova. Thanks to her efforts, the Section of Economic Journals was founded, which organizes specialized round tables in the framework of the annual conference “World-Class Scientific Publication”. We can say that a platform has been created for conducting a professional conversation between representatives of the world’s largest publishers, information and analytical resources, editors of economic journals, and economists. Although a number of issues in the field of improving the quality of economic journals are being successfully resolved, the presence of barriers that prevent their integration into the international space requires expanding the format of such events. One of the ways to address the issues may be to organize quarterly seminars that bring together (possibly online) leading experts in the field of editorial publishing, editors, reviewers, and authors. In addition, closer cooperation between the academic community and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation is required to develop system-wide measures to support domestic scientific periodicals, develop national bibliographic databases, and provide comprehensive incentives to leading journals included in international citation indexes.
Список литературы Russian economic journals indexed in web of science: current state and the ways of increasing international visibility
- Murav'ev A.A. About Russian economic science through the prism of publications of Russian scientists in domestic and foreign journals for 2000-2009. Ekonomicheskii zhurnal Vysshei shkoly ekonomiki=Economic Journal of the Higher School of Economics, 2011, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 237-264. (In Russian).
- Kirillova O.V. About the influence of the language of articles on the indicators of scientific journals in international scientometric databases. Nauchnyi redaktor i izdatel'=Science Editor and Publisher, 2019, vol. 4, no. 1-2, pp. 21-33. 10.24069/2542-0267-2019-1-2-21-33. (In Russian). DOI: 10.24069/2542-0267-2019-1-2-21-33.(InRussian)
- Balatsky E.V., Ekimova N.A. Opportunities for the consolidation of rating products in the internet environment. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 2018, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 37-51. 10.15838/esc.2018.2.56.3. (In Russian). DOI: 10.15838/esc.2018.2.56.3.(InRussian)
- Moskaleva O.V., Pislyakov V.V. Russian scholarly journals in Emerging Sources Citation Index. In: Nauchnoe izdanie mezhdunarodnogo urovnya - 2017: mirovaya praktika podgotovki i prodvizheniya publikatsii: materialy 6-i Mezhdunarodnoi nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii, g. Moskva, 18-21 aprelya 2017 g. [World-Class Scientific Publication - 2017: Best Practices in Preparation and Promotion of Publications: Proceedings of the 6th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Moscow, April 18-21, 2017]. Yekaterinburg: Izd-vo Ural. un-ta, 2017. Pp. 78-81. 10.24069/2017.978-5-7996-2227-5.13. (In Russian). DOI: 10.24069/2017.978-5-7996-2227-5.13.(InRussian)
- Moskaleva O.V. Russian journals in Web of Science Core Collection. Nauchnyi redaktor i izdatel'=Science Editor and Publisher, 2018, vol. 3, no. 1-2, pp. 26-32. 10.24069/2542-0267-2018-1-2-26-32. (In Russian). DOI: 10.24069/2542-0267-2018-1-2-26-32.(InRussian)
- Kotlyarov I.D. Principles of assessing the quality of scholarly journals. Obrazovanie i nauka=Education and Science, 2010, no. 8 (76), pp. 4-19. (In Russian).
- Hawkins R.G., Ritter L.S., Walter I. What economists think of their journals. The Journal of Political Economy, 1973, vol. 81, no. 4, pp. 1017-1032.
- Coats A.W. The role of scholarly journals in the history of economics: An essay. Journal of Economic Literature, 1971, no. 9 (1), pp. 29-44.
- Billings B., Viksnins G. The relative quality of economics journals: an alternative rating system. Economic Inquiry, 1972, no. 10 (4), pp. 467-469.
- Lovell M.C. The production of economic literature: An interpretation. Journal of Economic Literature, 1973, no. 11, pp. 27-55.
- Moore W. The relative quality of economics journals: a suggested rating system. Western Economic Journal, 1972, no. 10, pp. 156-169.
- Bush W.C., Hamelman P.W., Staaf R.J. A quality index for economics journals. The Review of Economics and Statistics, 1974, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 123-125.
- Diamond A.M. The core journals of economics. Current Contents, 1989, no. 21(1), pp. 4-11.
- Garfield E. Citation indexes for science. Science, 1955, no. 122, pp. 108-111.
- Liebowitz S.J., Palmer J.C. Assessing the relative impacts of economics journals. Journal of Economic Literature, 1984, no. 22, pp. 77-88.
- Bornmann L., Butz A., Wohlrabe K. What are the top five journals in economics? A new meta-ranking. Applied Economics, 2018, no. 50:6, pp. 659-675.
- Ritzberger K. A ranking of journals in economics and related fields. German Economic Review, 2008, no. 9 (4), pp. 402-430.
- Halkos G.E., Tzeremes N.G. Measuring economic journals' citation efficiency: a data envelopment analysis approach. Scientometrics, 2011, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 979-1001.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11192-011-0421-y
- Tret'yakova O.V. The impact rating of academic journals in economics: ranking criteria and methodology. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 2018, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 179-194. 10.15838/esc.2018.3.57.12. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.15838/esc.2018.3.57.12.(InRussian)
- HSE project on expert ranking of Russian scientific journals. 2015. Available at: http://www.hse.ru/academexpert/journals.
- Rubinshtein A.Ya. Russian economic journals: the table of ranks. Ekonomicheskaya nauka sovremennoi Rossii=Economics of Contemporary Russia, 2018, no. 1, pp. 108-130. (In Russian).
- Murav'ev A.A. On the scientific impact of Russian journals in economics and related disciplines. Voprosy ekonomiki=Economics Issues, 2013, no. 4, pp. 130-151. (In Russian).
- Tret'yakova O.V. Ranking of scholarly journals of economic institutes of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 2015, no. 5 (41), pp. 159-172. 10.15838/esc/2015.5.41.11. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.15838/esc/2015.5.41.11.(InRussian)
- Aleskerov F.T., Badgaeva D.N., Pislyakov V.V., Strerligov I.A., Shvydun S.V. An importance of Russian and international economic journals: a network approach. Zhurnal novoi ekonomicheskoi assotsiatsii=The Journal of the New Economic Association, 2016, no. 2 (30), pp. 193-205. (In Russian).
- Balatsky E.V., Ekimova N.A. Competition of Russian economic journals in the world market. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 2019, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 124-139. 10.15838/esc.2019.3.63.8. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.15838/esc.2019.3.63.8.(InRussian)
- Subochev A.N. How different are the existing ratings of Russian economic journals and how to unify them? Zhurnal novoi ekonomicheskoi assotsiatsii=The Journal of the New Economic Association, 2016, no. 2 (30), pp. 181-192. (In Russian).
- Balatsky E.V., Ekimova N.A. Russian economic journal consensus ranking: ideology and experience of making up. Zhurnal institutsional'nykh issledovanii=Journal of Institutional Studies, 2018, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 93-106. 10.17835/2076-6297.2018.10.1.093-106. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.17835/2076-6297.2018.10.1.093-106.(InRussian)
- Rubinshtein A.Ya. Ranking of Russian economic journals: the scientific method or "numbers game"? Zhurnal novoi ekonomicheskoi assotsiatsii=The Journal of the New Economic Association, 2016, no. 2 (30), pp. 162-175. (In Russian).
- Huang Y., Zhu D., Lv Q. et al. Early insights on the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI): an overlay map-based bibliometric study. Scientometrics, 2017, vol. 111, no. 3, pр. 2041-2057. Available at:
- DOI: 10.1007/s11192-017-2349-3
- Markusova V.A. Bibliometric characteristics of Russian science in the Emerging Sources Citation Index. Informatsionnye protsessy i sistemy=Information Processes and Systems, 2016, no. 11, pp. 24-31. (In Russian).
- Pislyakov V.V. Bibliometric indicators in Tomson Reuters resources. In: Rukovodstvo po naukometrii: indikatory razvitiya nauki i tekhnologii [Guidance on scientometrics: science and technology development indicators]. Yekaterinburg, 2014. Pp. 75-109. (In Russian).
- Balatsky E.V., Ekimova N.A. International landscape of the market of Russian economic journals. Ekonomicheskie i sotsial'nye peremeny: fakty, tendentsii, prognoz=Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 2018, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 110-124. 10.15838/esc.2018.4.58.7. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.15838/esc.2018.4.58.7.(InRussian)
- Kuklin A.A., Balyakina E.A. Active policy - the key to the success of an international economic journal. Ekonomicheskaya politika=Economic Policy, 2017, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 160-177. 10.18288/1994-5124-2017- 6-08. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.18288/1994-5124-2017-6-08.(InRussian)
- Gavrilicheva N.A., Okhon'ko Ya.N. Promotional strategy after the journal's inclusion in Scopus. In: Kirillova O.V. (Ed.). Materialy 4-i Mezhdunarodnoi nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii "Nauchnoe izdanie mezhdunarodnogo urovnya - 2015: sovremennye tendentsii v mirovoi praktike redaktirovaniya, izdaniya i otsenki nauchnykh publikatsii", 26-29 maya 2015 g. [Proceedings of the 4th International scientific and practical conference "World-class scientific publication-2015: current trends in the world practice of editing, publishing and evaluating scientific publications"]. Saint Petersburg, 2015. Pp. 33-38. (In Russian).
- Tret'yakova O.V. Integrating Russian journals into international scientific and information space: growth points for economic publications. In: Nauchnoe izdanie mezhdunarodnogo urovnya - 2018: redaktsionnaya politika, otkrytyi dostup, nauchnye kommunikatsii: materialy 7-i mezhdunarod. nauch.-prakt. konf., Moskva, 24-27 aprelya 2018 g [World-class scientific publication - 2018: Editorial Policy, Open Access, Scientific Communications: Proceedings of the 7th International Scientific and Practical Conference. Moscow, April 24-27, 2018]. Мoscow, 2018. Pp. 139-144. 10.24069/konf-24-27-04-2018.25. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.24069/konf-24-27-04-2018.25.(InRussian)


