Students’ Attitudes About STEM Teaching Case Study From Brčko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Автор: Edisa Puška, Adis Puška, Ilija Stojanović, Branislav Dudić, Jelena Premović
Журнал: International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education @ijcrsee
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 3 vol.11, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The knowledge that is based on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics is the basis for the development of any country. Less developed countries lack experts in these areas. Therefore, the ENABLE-BIH project (Enhancing and Advancing Basic Learning and Education in Bosnia and Herzegovina) was introduced in Bosnia and Herzegovina, which aims to improve the situation in the education sector. This study included the Public Institution “Ninth Elementary School” in Brcko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina in which this project was implemented. The study included a total of 125 students from this school. The aim of this study is to examine the difference between attitudes about STEM from the point of view of gender differences and the age of students. After the data were collected, the statements were grouped into appropriate factors using factor analysis. The factor analysis showed that five factors stand out in this research. The results of multiple regression analysis showed that there is no difference between students ‘attitudes regarding gender differences, while there is a difference regarding students’ age. The results of this research showed that the ENABLE-BIH project delivered good results and suggests the importance of implementing similar projects in the future.
STEM, Brcko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina, ENABLE-BIH, multiple regression analysis, factor analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170200023
IDR: 170200023 | УДК: 37.091.31(497.6); 330.341(497.6) | DOI: 10.23947/2334-8496-2023-11-3-475-485
Текст научной статьи Students’ Attitudes About STEM Teaching Case Study From Brčko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The country’s economic growth and development should be based on new technologies and innovations ( James, 2021 ). Science and engineering are the basis for economic growth and development ( Sahin-Topalcengiz and Yildirim, 2019 ). Nowadays, more investments are done in educating staff who will apply this new knowledge based on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). The best example of the former is the field of energy efficiency ( Radojević, Nikolić and Skerlić, 2020 ). The best example of the former is the field of energy efficiency ( Pašalić et al., 2020 ). However, many countries have challenges with STEM education ( Beswick and Fraser, 2019 ). Tran (2018) pointed out that innovation is crucial for the development of the United States of America (USA), but it lags behind other developed countries in the production of its own qualified staff with STEM competencies. The situation is similar in other countries where demand for STEM skills is growing ( Marginson, et al., 2013 ). Developing countries are increasingly investing in STEM education ( Kelley and Knowles, 2016 ), and this trend has been present in Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH) in recent years. The biggest challenge in the education of staff for STEM areas is the lack of interest of students to study these areas ( Waite and and McDonald, 2019 ). Therefore, it is necessary to gradually introduce these areas to students in the earliest educational process ( Ghanbari, et al., 2023 ).
Bosnia and Herzegovina has begun the introduction of STEM areas in teaching in secondary and primary schools in recent years. The ENABLE-BiH project (Enhancing and Advancing Basic Learning

-
* Corresponding author: edisapuska@yahoo.com
© 2023 by the authors. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
and Education in Bosnia and Herzegovina) was introduced in 2016 in Bosnia and Herzegovina, with the aim to improve learning about STEM courses. The basic idea of this project is to avoid focusing on special or separate disciplines and connecting these courses through practical application. With this approach, students can acquire the key skills and competencies necessary for further progress in the modern environment. This project was implemented throughout the whole country, and 12 schools and 4 areas in Bosnia and Herzegovina were selected. Two schools from the area of the Brcko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BDBiH) have participated in this project. BDBiH is a unique administrative-territorial unit of local self-government under the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which represents its specificity in relation to other areas in the country. Thus, this is the reason for special research interest in the implementation of this project in BDBiH.
The aim of this study is to examine the attitudes of students towards STEM teaching implemented within the ENABLE-BiH project, which is implemented in the Public Institution “Ninth Elementary School” in BDBiH. The special research attention is focused on differences in attitudes towards STEM teaching within the ENABLE-BiH project in relation to the gender differences of students and students who attend general and specialized classes. The contribution of this research is reflected in the following:
-
- Obtaining significant information from students related to STEM classes;
-
- Determining the existence of differences between students’ attitudes;
-
- Providing guidelines for the improvement of STEM teaching in primary education;
In addition to the introduction, this paper consists of five other sections. The second section provides the theoretical framework for the study. The third section oversees the research methodology. This section explains how the research was conducted, presents a research sample, and set research hypotheses. The fourth section provides the findings of the research. In this section, the collected claims are grouped into factors, and then the hypotheses are tested through multiple regression analysis. In the fifth section, the obtained results are explained in more detail through discussion, and the findings are compared with other similar studies. The sixth section presents the most important research results providing guidelines for future research.
Theoretical framework
The concept of STEM education is not a new concept as some authors claim, but this term appeared in the 19th century at Harvard University as part of the standardization of the agricultural school system ( Ostler, 2012 ). After that process, this term was not used often in education, only to come to attention in the 1990s when the National Science Foundation in the United States identified areas crucial for improving economic work in the United States ( Herro, et al., 2017 ). The acronym STEM stands for the education of students in the fields of natural sciences, computer science, engineering, and mathematics. STEM is a specific educational program, designed with the aim of using knowledge from the STEM fields when solving problems in everyday life ( Rizvanović and Alihodžić, 2019 ).
The term STEM refers to the integration of science (S), technology (T), engineering (E), and mathematics (M) which relates to both workforce and everyday life experiences ( Pimthong and Williams, 2018 ). The STEM term is relevant because every scientific discipline encounters complex and multidimensional problems that need to be solved. To make full use of STEM potential in students, schools need to improve STEM education and improve teaching ( Margot and Kettler, 2019 ). Gomez and Albrecht (2013) advocate the establishment of STEM education and teaching in schools through an interdisciplinary approach. Establishing STEM education in school is an innovative approach to education, it is widely applied in the global environment and is the basis for the development of educational policies and reforms ( Nguyen, Nguyen and Tran, 2020 ). The principle of introducing STEM teaching in schools emphasizes the importance of students’ understanding of science and mathematics but all to be integrated through theology and engineering ( Chesky and Wolfmeyer, 2015 ). The integration and application of STEM concepts and processes are needed by students who should have the opportunity to participate in real multidisciplinary situations ( Pimthong and Williams, 2018 ). The application of STEM teaching with real examples opens up perspectives for students to learn the basics of using STEM disciplines.
The importance of students’ education in STEM areas has gained importance worldwide, and demand for these skills is growing. However, students drop out from these courses, and almost 50% of students do not complete these courses ( Chen, 2013 ). The situation is similar in Germany ( Heublein, et al., 2012 ) and in other countries. In the last twenty years, a decrease in the number of students who choose to continue their education in STEM fields has been observed in many European countries ( Babarović, Pale and Burušić, 2018 ). It has been proven that lower achievements in STEM courses in primary education can influence the choice of continuing education in STEM areas ( Wang and Eccles, 2013 ). To solve this problem, an adequate way to increase students’ interest in STEM subjects is sought ( Sadler, et al.,
-
2012 ). Rosenzweig and Wigfield (2016) point out that STEM educational programs conducted in the upper grades of elementary schools and high schools motivate students for STEM areas and increase their aspirations toward STEM careers. That is the justification why there are more projects in the world that are being introduced in primary and secondary schools in order to increase students’ interest in studying in these areas. The introduction of STEM in education gives high autonomy and independence to students in solving problems in STEM, creates content and activities tailored to the individual needs of students, and there is an interactive approach in teaching aimed at developing student competencies ( Rizvanović and Alihodzić, 2019 ).
Based on the recommendations of the European Commission for Education, which focused on the promotion of key competencies and their inclusion in the education system, the Agency for Preschool, Primary and Secondary Education (APOSO) in 2012 identified key competencies to be developed in Bosnia and Herzegovina. In 2016, following these recommendations, the ENABLE-BiH project was launched in Bosnia and Herzegovina, which aims to strengthen education in STEM areas. The goal of this project has been to contribute to the process of changing the educational paradigm in Bosnia and Herzegovina to enable the development of society and a knowledge-based economy ( Mrdović, 2018 ). This project seeks to set the framework and create a comprehensive basis for the introduction of STEM areas in regular education within existing and / or innovative teaching content. Furthermore, this project aims to integrate different disciplines such as natural science, mathematics, and technology through STEM into a cohesive learning paradigm based on practical applications ( Rizvanović and Alihodzić, 2019 ). Following these interests, a common core curriculum was formed in Bosnia and Herzegovina, composed by the Agency for Preschool, Primary, and Secondary Education (APOSO). In addition, operational curricula for STEM competencies have been designed in order to align the results in mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, geography and informatics, as well as for the courses environment, nature and society, and similar courses with global trends and standards. Therefore, it is important to investigate how students perceive teaching in STEM areas and what their attitudes are towards STEM.
Materials and Method
In this section, an overview of the survey questionnaire, the research and the basic characteristics of students who took part in the survey are presented. Additionally, the research hypotheses based on previously conducted research are introduced. When conducting the research, primary research will be used using questionnaires. The collected questionnaires are coded and prepared for analysis using the SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) 20 software package. The following analyzes will be calculated with this software package: exploratory factor analysis, correlation analysis and regression analysis.
Survey data
The ENABLE-BiH project was implemented in 12 schools in different regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Seven primary schools and five secondary schools were included. A total of 2556 students were included in this project, of which 1636 were students from primary schools, while 920 students were included from secondary schools. The aim of this project was to examine the differences in attitudes towards STEM studying in relation to gender differences of students and in relation to the differences in form of classes looking at general courses and specialized courses, the basic research sample included students of primary schools who took a part in the project. Due to technical and other issues encountered in this study and due to the specifics of Brcko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina, this research was conducted in Public Institution “Ninth Primary School” Maoča. The study included students of the second and third triad who were sent survey questionnaires. A total of 125 students from this school were included, which represents 7.64% of the research population from this school.
For the purposes of this study, the research was conducted in the Public Institution “Ninth Elementary School” located in Brcko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina. This research included students of the second and third triad who were asked to take a part in the survey. The survey questionnaire consisted of two parts. The first part of the questionnaire referred to the characteristics of students in terms of a gender, form of classes and the success of students in the previous period (Figure 1). The second part of the questionnaire consisted of statements related to students ’attitudes about students being required to give their grades ranging from 1 to 5, where 1 was the lowest grade and 5 was the highest grade. A total of 21 questions were used, which are presented in Table 2.
Data was collected from students of the selected school in two ways. Survey questionnaires in paper form were distributed to general class students, while electronic survey questionnaires were sent to students of specialized courses. The justification of this approach one can find in the fact that general class students do not have the informatics course in their curriculum, while specialized class students have this course included, thus these questionnaires were sent as part of the course activity.
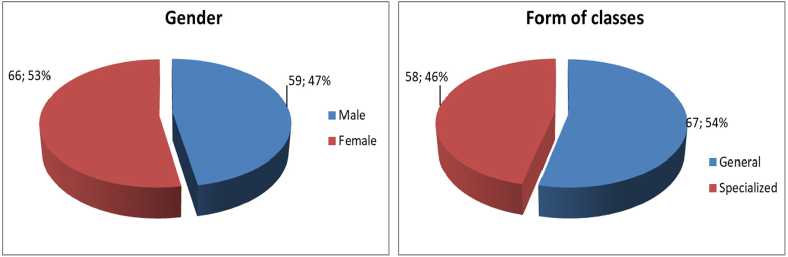
Figure 1. Characteristic of students
A total of 149 questionnaires were collected. However, only 125 questionnaires were included in the analysis because the rate of their completeness rose more than 80%. Survey questionnaires that were completed below 80% were not included in the survey, thus 24 survey questionnaires were excluded from further analysis. All survey questionnaires were coded and included in the statistical package SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences). Using this software, students’ attitudes were first grouped by exploratory factor analysis (EFA), followed by the examination of the reliability of the measurement scale using Cronbach’s alpha (CA) indicators, and then the research hypotheses were examined using multiple regression analysis (VRA).
Research hypotheses
The study of STEM areas is influenced by many factors. Babarović, Pale and Burušić, (2018) in their research highlighted the following factors: gender differences, student age, and student motivation. Reinking and Martin, (2018) pointed out that gender factors are key to accepting STEM study, and at the same time they influence students ’attitudes. In some other studies, it is pointed out that gender differences are decisive factors for acceptance of the STEM areas ( Mavriplis, et al., 2010 ; Robinson and Lubienski, 2011 ; Legewie and DiPrete, 2014 ). Therefore, this research is focused to investigate gender differences and the age of students on their attitudes about STEM study.
By studying gender differences, no unambiguous results were found by Rosenzweig and Wigfield (2016) who concluded that gender does not moderate the systemic effect of motivational interventions. From the above, it can be expected that future STEM interventions will be equally effective for all students. However, the findings by Huppatz and Goodwin (2013) showed that girls lose the most interest in STEM areas between the ages of nine and twelve. Furthermore, Kuschel, et al. (2020) showed that there are a small number of women entrepreneurs in STEM areas, which emphasizes the existing gender biases and systemic shortcomings in social structures. However, the results showed that since the beginning of the 1990s, the number of women who have graduated or obtained their master’s or doctoral degrees in STEM areas has increased ( Reinking and Martin, 2018 ). Still, women are less represented in STEM areas ( Legewie and DiPrete, 2014 ), which is confirmed by research conducted by the authors Wang and Degol (2016) . Based on this, the following hypothesis is set for this study:
H1 – Gender differences in students affect the attitudes toward teaching within the framework ENABLE-BiH project
Although there is not enough evidence to draw firm conclusions that intervention programs are effective for younger students, there is general knowledge that supports this assumption (Babarović, Pale and Burušić, 2018). It has been also shown that motivation and interest in STEM areas decline during the senior years of primary school (Bryan, Glynn and Kittleson, 2011). This is especially present with the female population because they lose interest in the STEM areas during studies, and this is especially present for mathematics courses (Robinson and Lubienski, 2011). Daugherty, Carter and Swagerty, (2014) suggested that in order to increase students’ interest in STEM areas, it is necessary to start encouraging them in a primary school. Opinions about STEM education and engagement are also influenced by transitions within education, from preschool to primary education and from primary to secondary education (Perry and MacDonald, 2015). Archer et al. (2012) in their research showed that the aspirations and attitudes of students aged from 10 to 14 years do not differ significantly. Due to the differences in previous research results, it is necessary to investigate whether differences in age or attendance affect students’ attitudes about STEM studies. Based on this, the following hypothesis is set in the research:
H2 – Age of the students influences the attitudes regarding the teaching within the framework ENABLE-BiH project
Results
Before testing the hypotheses, it is necessary to group the claims via EFA. Within EFA analysis, Varimax factor rotation and Kaiser Normalization were applied ( Zhou and Li, 2023 ). The application of Kaiser Normalization determines the number of factors in the conducted EFA analysis. In order to group a statement into one factor, its value according to Kaiser Normalization must be greater than 1. When performing EFA analysis, it is necessary to meet certain conditions, namely: the correlation matrix is suitable for EFA analysis, which is proved by the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) indicator of sample adequacy and the sphericity of data by Bartlett’s test is satisfied. The values of the KMO indicator should be greater than 0.6, while in Bartlett’s test the significance level should be less than 0.05 (p <0.05) ( Puška, Maksimović and Stojanović, 2018 ). The results obtained by EFA analysis showed that the sample is adequate (KMO = 0.894) and the data are spherical (p <0.000), which confirms this analysis.
The obtained results of EFA analysis showed that the claims were grouped into five factors in which 72.49% of the variance was explained. The obtained factors were used to examine the reliability of the measurement scale of the questionnaire via CA indicators. The value of this indicator should be greater than 0.70 ( Al-Ansi, et al., 2023 ).
The first factor covered seven claims and explained 22.781% of the variance (table 1). This factor seeks to explain the experience of students in STEM teaching and it provides answers to whether STEM teaching is better than traditional and whether students would still have STEM teaching. The highest grade for this factor was given to the statement “STEM teaching is useful for students” (average = 4.55), while the lowest grades were given to the statements: “I am proud to be part of STEM teaching” and “I would like to continue to have STEM teaching” (average = 4.14). The value of standard deviations (SD) showed that the highest variance in grades for the statement “I wish I still had STEM teaching” (SD = 1,183), while the lowest variance in grades for the statement “STEM teaching is useful for students” (SD = 0.844). The obtained value of the CA indicator (CA = 0.897) showed that the measurement scales of the collected data are reliable for this factor.
The second factor included six claims. This factor seeks to explain whether STEM teaching is interesting and fun for students and whether it allows them to better understand teaching material. The statement “I like examples in STEM teaching” received the highest grade for this factor (Average = 4.50), while the statement “STEM teaching interests me” received the lowest grade (Average = 4.31). The highest variance of grades is found in the statement “STEM teaching is more interesting than traditional” (SD = 1,083), while the lowest variance is in the statement “I like examples in STEM teaching” (SD = 0,783). Measuring scales (CA = 0.835) were also found to be reliable for this factor.
The third factor included three statements where the average values are between 4.33 and 4.42. This factor seeks to explain the usefulness of STEM teaching for students. Of these three statements, the greatest dispersion was in the grades of the statement “STEM teaching helps me master the material” (SD = 1,028), while the smallest dispersion in grades for the statement “STEM teaching makes learning easier” (SD = 0,898). The value of the CA indicator (CA = 0.82) confirmed the measurement scales.
The fourth factor included the fewest claims of all factors, namely two claims in which the average score is uniform. This factor explains the experience of students with STEM teaching. The statement “My experience with STEM teaching is very good” (SD = 1,285) had a greater dispersion of grades. The performed CA analysis (CA = 0.838) confirmed the measurement scale for this factor. The fifth factor included three claims. This factor explains whether STEM teaching aids learning by better understanding the material. The statement “STEM teaching improves my understanding of the material” received the highest average grade (Average = 4.41), with the lowest variance in grades (SD = 0,920). The lowest average grade was given to the statement “STEM teaching helps me learn” (Average = 4.24), which had the highest dispersion (SD = 0,920). For this factor, the measurement scale for the questionnaire was confirmed (CA = 0.745).
Table 1.
Factor and descriptive analysis of claims
|
Claims |
Factor correlation |
Mean |
SD |
Cron bach's Alpha |
|
Factor 1 - Explained variance = 22.781 |
||||
|
I am proud to have been a part of STEM classes |
0.832 |
4.14 |
1.119 |
0.897 |
|
I would recommend STEM classes to everyone |
0.830 |
4.30 |
0.975 |
|
|
STEM teaching is better than traditional teaching |
0.748 |
4.27 |
0.971 |
|
|
I wish I still had STEM classes |
0.725 |
4.14 |
1.183 |
|
|
I wish there were more STEM classes |
0.646 |
4.34 |
1.088 |
|
|
STEM teaching is useful for students |
0.603 |
4.55 |
0.844 |
|
|
I enjoy STEM classes |
0.597 |
4.20 |
1.052 |
|
|
Factor 2 - Explained variance = 15.670 |
||||
|
STEM teaching allows connecting teaching material |
0.702 |
4.46 |
0.822 |
0.835 |
|
STEM teaching interests me |
0.688 |
4.31 |
1.033 |
|
|
The quality of STEM teaching is excellent |
0.663 |
4.32 |
0.926 |
|
|
STEM classes are more interesting than traditional ones |
0.605 |
4.35 |
1.083 |
|
|
I like examples in STEM classes |
0.590 |
4.50 |
0.783 |
|
|
STEM classes are fun |
0.496 |
4.42 |
0.917 |
|
|
Factor 3 - Explained variance = 12.547 |
||||
|
STEM classes help me master the teaching material |
0.738 |
4.33 |
1.028 |
0.828 |
|
In STEM teaching I understand the material better |
0.691 |
4.34 |
0.906 |
|
|
STEM teaching facilitates learning |
0.658 |
4.42 |
0.898 |
|
|
Factor 4 - Explained variance = 10.948 |
||||
|
I have a pleasant experience with STEM teaching |
0.880 |
3.94 |
1.169 |
0.838 |
|
My experience with STEM teaching is very good |
0.791 |
3.95 |
1.285 |
|
|
Factor 5 - Explained variance = 10.544 |
||||
|
STEM teaching helps me to learn |
0.839 |
4.24 |
1.133 |
0.745 |
|
I look forward to STEM continuing in the future |
0.619 |
4.33 |
1.030 |
|
|
STEM teaching improves my understanding of the material |
0.607 |
4.41 |
0.920 |
|
|
KMO = 0.894; Bartlett test = 1818.709; p < 0.000; Total explained variance = 72.490 |
||||
The study of the relationship between the factors was performed using the Pearson correlation coefficient. The results obtained by this analysis showed that for all factors there is a significant positive correlation at a significance level of less than 0.01 (Table 3). Factors 1 and 2 were the most closely related (r = 0.784; p <0.01), while factors 3 and 4 were the least related (r = 0.495; p <0.01)
Table 2.
Correlation between research factors
|
Factor 1 |
Factor 2 |
Factor 3 |
Factor 4 |
Factor 5 |
|
|
Factor 1 |
1.000* |
||||
|
Factor 2 |
0.784* |
1.000* |
|||
|
Factor 3 |
0.588* |
0.749* |
1.000* |
||
|
Factor 4 |
0.590* |
0.594* |
0.495* |
1.000* |
|
|
Factor 5 |
0.697* |
0.659* |
0.650* |
0.576* |
1.000* |
Note: *. Correlation at a significance level of 0.01
The research hypotheses were tested using the VRA ( Oliinyk, 2023 ). The task of the VRA is to include several factors in the analysis to assess the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable ( Famo and Machate, 2023 ; Štilić, et al., 2023 ). The examination of the hypotheses was carried out by applying indifferent statistics at the significance level of 0.05 ( Abdeldayem, Aldulaimi and Baqi, 2022 ). Since two hypotheses have been set, two VRAs were applied.
During the examination of the first research hypothesis, we started from the assumption that there is a significant difference in students’ attitudes in relation to the gender difference, and for that purpose, a VRA model was created. The results of this analysis showed that there is no significant statistical difference in these attitudes (F-test = 1,779; p = 0.122), which provided a basis for rejection of the first hypothesis of the research. This VRA model explained 7% of the baseline (R2 = 0.070). Observing the individual influence of the factors, it was noticed that only with factor 5 there is a significant statistical difference (t-test = 2.128; p = 0.035), and this factor had the greatest influence on the direction of the regression function (Beta = 0.295). With two factors there is a negative influence on the direction of the regression function, namely with factor 1 (Beta = -0.192) and factor 3 (Beta = - 0.112).
While we examined the second hypothesis, the research started from the assumption that the age of students influences attitudes about STEM teaching. For this purpose, two groups of students were formed. One group of students attends general classes and the other specialized classes. The results of the conducted VRA showed that there is a significant statistical difference between the observed groups of students (F-test = 11,088; p = 0,000), and thus the second research hypothesis was accepted. This VRA model explained 31.8% of the baseline (R2 = 0.318). Observing the partial influence of individual factors on the regression function, there is a significant statistical difference between three factors: factor 1 (t-test = 2,869; p = 0.005), factor 3 (t-test = -5,204; p = 0.000) and factor 4. (t-test = 2,780; p = 0.006). It should be mentioned that with factor 2 (Beta = -0.161) and factor 3 (Beta = -0.633) there is a negative influence on the direction of the regression function. The same results would be obtained by applying ANOVA analysis because hypotheses are tested in MRA in SPSS using ANOVA analysis ( Puška, Maksimomvić and Stojanović, 2018 ).
Table 3.
Hypothesis testing using regression analysis
|
Independent variable: Gender difference |
Beta |
t-value |
P |
|
Factor 1 |
-0.192 |
-1.217 |
0.226 |
|
Factor 2 |
0.071 |
0.404 |
0.687 |
|
Factor 3 |
-0.112 |
-0.789 |
0.431 |
|
Factor 4 |
0.136 |
1.162 |
0.248 |
|
Factor 5 |
0.295 |
2.128 |
0.035 |
|
Model summary: R = 0.264; R2 = 0.070; F-test = 1.779; significance = 0.122 |
|||
|
Independent variable: Age |
Beta |
t-value |
P |
|
Factor 1 |
0,387 |
2.869 |
0.005 |
|
Factor 2 |
-0,161 |
-1.068 |
0.288 |
|
Factor 3 |
-0,633 |
-5.204 |
0.000 |
|
Factor 4 |
0,278 |
2.780 |
0.006 |
|
Factor 5 |
0,012 |
0.102 |
0.919 |
Model summary: R = 0.564; R2 = 0.318; F-test = 11.088; significance = 0.000
Discussions
In order to determine the existence of differences between students’ attitudes regarding STEM teaching which was implemented within the ENABLE-BiH project, which was assessed in the Public Institution “Ninth Elementary School” Brcko District, data were first collected by students through a questionnaire. The questionnaire was distributed in two ways, physically and electronically, with paper and electronic questionnaires. It was observed during the data collection that a smaller number of blank questionnaires were for questionnaires distributed in paper form compared to questionnaires distributed in electronic form. The reason should be sought in the fact that students who received an electronic version of the questionnaire could open it on various media (Petrović, 2014). Some students opened the survey, started filling it out, and dropped out. Another disadvantage of the electronic survey is that one student can fill in the survey several times. However, in this research, access to the surveys was limited with the IP address disabling that one student completes the survey more than once. In this way, this shortcoming was solved.
Factor analysis grouped the data collected from students and the claims related to STEM teaching from the ENABLE-BiH project were grouped into five factors. These factors cover 72.49% of the variance that is common for social research ( Puška, et al., 2021 ). Looking at the claims placed in the corresponding factors one can see there is a connection between these claims. In factor 1, all the claims are related to the intention to further use STEM teaching, that STEM teaching is useful and that students enjoy it. Factor 2 grouped the claims concerning the interestingness, quality, and fun of STEM teaching. Factor 3 grouped the claims concerning understanding, mastery, and learning assistance by STEM teaching. Factor 4 grouped the claims related to STEM teaching experience. Factor 5 included the claims regarding learning assistance, rejoicing in the continued use of STEM teaching, and the claim related to understanding the material.
The obtained values showed that there is a positive significant correlation between all factors. The correlation for all claims ranges between 0.495 and 0.784, which is a very good correlation, especially when it comes to social research ( Puška, Maksimović and Stojanović, 2018 ). However, this association does not mean that the gender difference and the age of students influence the observed factors. The results of the VRA showed that the age of students affects the observed factors while the gender difference does not. These results indicate that boys and girls equally accept STEM teaching and their attitudes are similar, thus confirming the results provided by Rosenzweig and Wigfield (2016) . The attitudes they used are most similar in factor 2 because the significant value in VRA is the highest which shows that there is the smallest difference in attitudes in this particular case. With factors 1 and 3, there is a negative influence on the direction of regression analysis, which indicates that girls have better attitudes than boys regarding these two factors. This indicates that interest by girls has not decreased in STEM teaching, which does not confirm the results provided by Huppatz and Goodwin (2013) . This finding is very positive, as it reduces gender discrimination in STEM teaching. If girls maintain their interest in STEM teaching, it is expected that there will be a larger number of women who will work in STEM areas in Bosnia and Herzegovina in the future. In this way, the justification of the ENABLE-BIH project in Bosnia and Herzegovina was confirmed, because this project delivered a positive effect on students in their early years and reduces gender discrimination in STEM areas.
Observing the difference between the ages of students, the results of the VRA showed that there is a significant difference between the attitudes. However, by analyzing individual factors, one can see that in factors 2 and 3 there is a negative impact on the direction of regression analysis, which shows that students from specialized classes have better attitudes towards these factors than students from general class. Furthermore, the results for factor 5 indicate that there is no difference between the attitudes of these students. In this way, it was proven that students’ attitudes do not decrease with the age of students, and the observed students accept STEM classes from the ENABLE-BiH project equally well, thus denying the results from Bryan, Glynn and Kittleson, (2011) .
The findings from this study show that there is no gender discrimination in terms of acceptance of STEM classes’ from the ENABLE-BiH project. In addition, the results show that the interest is higher in certain segments of STEM teaching among students in specialized classes in relation to students in general classes. All mentioned point to the fact that the ENABLE-BIH project provided good results and it is necessary to implement more similar projects in order to improve the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina in the STEM area. With the improvement of the STEM area, it is possible to achieve the growth and development of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Conclusions
Education in STEM areas is key for the development of any country. Influencing the acceptance of STEM studies by students provides a good basis for continuing studies in these areas, which creates a favorable climate for development. This research was conducted in the Brcko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina and included students of the Public Institution “Ninth Elementary School”. The aim of this study was to examine the existence of differences in the gender and age structure of students. The results show that there is no gender difference in students’ attitudes towards STEM teaching implemented within the ENABLE-BiH project, thus rejecting the first hypothesis of this research. Furthermore, the results show that there is a difference in terms of student age, thus accepting the second hypothesis of this study. Further insight into the results of the VRA indicates that there is a difference between the attitudes of students, but there is no uniform difference. Some claims are better assessed by students from specialized classes in relation to students from general classes and vice versa. In this way, it has been proven that students are equally interested in STEM teaching.
The study findings show that the ENABLE-BIH project implemented in Bosnia and Herzegovina delivered good results, which was fully confirmed by this research. Therefore, in the future, more similar projects should be implemented in Bosnia and Herzegovina in order to influence students to continue their studies in these areas. Furthermore, the implementation of this project has shown that students need to get closer to the STEM area, by making a connection between these areas in teaching that is also enriched with practical exercises. In this way, students can understand these areas and have better attitudes regarding these STEM. This should affect the strengthening of STEM areas in Bosnia and Herzegovina and contribute to the development of the country. In the future, it is necessary to include more schools and students with similar projects in order to have a greater impact on the acceptance of STEM areas by students.
This study has shown that innovations in education, in this case, the convergence of STEM areas through the connection of different areas, have a significant impact on the students’ acceptance of STEM studies. In future projects and research, it is necessary to use innovations in teaching in a similar way to improve students’ curiosity for STEM studies, which creates a precondition for strengthening these areas in certain countries. The scientific validity of the conducted research was to understand how elementary school students accept STEM subjects because it is very important to prepare students for these subjects. The social justification of this research is based on the preparation of students in elementary school for these subjects, so that they can continue their careers in them and so that there will be no shortage of occupations in the future.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the respondents who participated in the research and the reviewers who made a valuable contribution to the quality of the work by giving constructive suggestions.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P., and A.P.; methodology, E.P.; software, A.P.; formal analysis, E.P and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P. and I.S.; writing—review and editing, A.P. and I.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Список литературы Students’ Attitudes About STEM Teaching Case Study From Brčko District of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Abdeldayem, M. M., Aldulaimi, S. H., & Baqi, A. (2022). Corporate Sustainability Strategies Are Often Easier Said Than Done. Opportunities and Challenges in Sustainability, 1(1), 76-85. https://doi.org/10.56578/ocs010108 DOI: https://doi.org/10.56578/ocs010108
- Al-Ansi, A. M., Jaboob, M., & Awain, A. M. S. B. (2023). Examining the Mediating Role of Job Satisfac-tion between Motivation, Organizational Culture, and Employee Performance in Higher Education: A Case Study in the Arab Region. Education Science and Management, 1(1), 30-42. https://doi.org/10.56578/esm010104 DOI: https://doi.org/10.56578/esm010104
- Archer, L., DeWitt, J., Osborne, J., Dillon, J., Willis, B., & Wong, B. (2012). “Balancing acts’’: Elementary school girls’ negotiations of femininity, achievement, and science. Science Education, 96(6), 967-989. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21031 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21031
- Babarović, T., Pale, P., & Burušić, J. (2018). The Effects of the Elementary School STEM Intervention Program on Students’ Attitudes and Interests: The Application of Propensity Score Matching Technique. Društvena istraživanja, 27(4), 583-604. https://doi.org/10.5559/di.27.4.01 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5559/di.27.4.01
- Beswick, K., & Fraser, S. (2019). Developing mathematics teachers’ 21st century competence for teaching in STEM contexts. ZDM Mathematics Education, 51, 955–965 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-019-01084-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-019-01084-2
- Bryan, R. R., Glynn, S. M., & Kittleson, J. M. (2011). Motivation, achievement, and advanced placement intent of high school students learning science. Science Education, 95(6), 1049-1065. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.20462 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.20462
- Chen, X. (2013). STEM attrition: college students’ paths into and out of STEM fields (NCES 2014-001), Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
- Chesky, N.Z., & Wolfmeyer, M.R. (2015). Philosophy of STEM Education. Palgrave Macmillan: New York. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137535467
- Daugherty, M. K., Carter, V., & Swagerty, L. (2014). Elementary STEM Education: The Future for Technology and Engineering Education? Journal of STEM Teacher Education, 49(1), 45-55. https://doi.org/10.30707/JSTE49.1Daugherty DOI: https://doi.org/10.30707/JSTE49.1Daugherty
- Famo, M. & Machate, M. (2023). Demographic Influences on Indigenous Knowledge Practices in Chief Albert Luthuli Municipality. Acadlore Transactions on Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 1(2), 77-86. https://doi.org/10.56578/atams010203 DOI: https://doi.org/10.56578/atams010203
- Ghanbari, M., Zolfaghari, D., & Yadegari, Z. (2023). Mitigating Construction Delays in Iran: An Empirical Evaluation of Building Information Modeling and Integrated Project Delivery. Journal of Engineering Management and Systems Engineering, 2(3), 170-179. https://doi.org/10.56578/jemse020304 DOI: https://doi.org/10.56578/jemse020304
- Gomez, A., & Albrecht, B. (2013). True STEM education. Technology and Engineering Teacher, 73(4), 8-16.
- Herro, D., Quigley, C., Andrews, J., & Delacruz, G. (2017). Co-Measure: developing an assessment for student collaboration in STEAM activities, International Journal of STEM Education, 4(1), 26, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-017-0094-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-017-0094-z
- Heublein, U., Richter, J., Schmelzer, R., & Sommer, D. (2012). Die entwicklung der schwund- und studienabbruchquoten an den deutschen hochschulen: statistische berechnungen auf der basis des absolventenjahrgangs 2010 [The development of attrition and dropout rates at German universities: statistical calculations based on the 2010 graduate class]. Forum hochschule, 2012, 3. Hannover: HIS
- Huppatz, K., & Goodwin, S. (2013). Masculinised jobs, feminised jobs and men’s “gender capital” ex-periences: Understanding occupational segregation in Australia. Journal of Sociology, 49(2-3), 291-308. https://doi.org/10.1177/1440783313481743 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1440783313481743
- James, J. (2021). Confronting the scarcity of digital skills among the poor in developing countries. Development Policy Review: The Journal of the Overseas Development Institute, 39(2), 324–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/dpr.12479 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/dpr.12479
- Kelley, T. R., & Knowles, J.G. (2016). A conceptual framework for integrated STEM education. International Journal of STEM Education, 3(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-016-0046-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-016-0046-z
- Kuschel, K., Ettl, K., Díaz-García, C. & Agnete Alsos, G. (2020). Stemming the gender gap in STEM entrepreneurship – insights into women’s entrepreneurship in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 16, 1-15 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-020-00642-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-020-00642-5
- Legewie, J., & DiPrete, T. A. (2014). The high school environment and the gender gap in science and engineering. Sociology of Education, 87(4), 259–280. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038040714547770 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0038040714547770
- Marginson, S., Tytler, R., Freeman, B., & Roberts, K. (2013). STEM: Country comparisons. Melbourne: Australian Council of Learned Academies
- Margot, K. C., & Kettler, T. (2019). Teachers’ perception of STEM integration and education: a system-atic literature review. International Journal of STEM Education, 6(1) Article number: 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-018-0151-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-018-0151-2
- Mavriplis, C., Heller, R., Beil, C., Dam, K., Yassinskaya, N., Shaw, M., & Sorensen, C. (2010). Mind the Gap: Women in STEM Career Breaks. Journal of Technology Management & Innovation, 5(1). 140-151. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-27242010000100011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-27242010000100011
- Mrdović, S. (2018). Nacrt Operativnog nastavnog plana i programa (ONPP) za STEM kompetencije zasnovanog na ZJNPP definiranoj na ishodima učenja – IT [Draft of the Operational Curriculum and Program (ONPP) for STEM competencies based on the ZJNPP defined on learning outcomes - IT], Sarajevo: Save the Children za sjeverozapadni Balkan
- Nguyen, T.P.L., Nguyen, T.H., Tran, T.K. (2020). STEM Education in Secondary Schools: Teachers’ Perspective towards Sustainable Development. Sustainability. 12(21), 8865. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218865 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218865
- Oliinyk, A. (2023). The Impact of Countries’ Participation in the ICT Services Market on Economic Growth, CPI, and Exchange Rates. Economics - innovative and economics research journal, 11(1), 269–287. https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2023-0009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2023-0009
- Ostler, E. (2012). 21st century STEM education: A tactical model for long-range success, International Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 2(1), 28-33.
- Pašalić, S., Mastilo, Z., Đurić, A., & Marković, D. (2020). Demographic Trends and the Educational System of the Republic of Srpska. Economics - innovative and economics research journal, 8(1), 93–113. https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2020-0007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2020-0007
- Perry, B., & MacDonald, A. (2015). Educators’ expectations and aspirations around young children’s mathematical knowledge. Professional Development in Education, 41(2), 366-381. https://doi.org/10.1080/19415257.2014.990578 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19415257.2014.990578
- Petrović, M. (2014). Prednosti i nedostaci onlajn-istraživanja. Marketing, 45(1), 63-74. https://doi.org/10.5937/markt1401063P DOI: https://doi.org/10.5937/markt1401063P
- Pimthong, P., & Williams, J. (2018). Preservice teachers’ understanding of STEM education. Kasetsart Journal of Social Sciences, 41(2), 289-295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjss.2018.07.017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjss.2018.07.017
- Puška, A., Maksimović, A., & Stojanović, I. (2018). Improving organizational learning by sharing infor-mation through innovative supply chain in agro-food companies from Bosnia and Herzegovina. Opera-tional Research in Engineering Sciences: Theory and Applications, 1(1), 76-90. https://doi.org/10.31181/oresta19012010175 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31181/oresta19012010175p
- Puška, E., Ejubović, A., Đalić, N., & Puška, A. (2021). Examination of influence of e-learning on aca-demic success on the example of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Education and Information Technologies, 26(2), 1977-1994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10343-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10343-9
- Radojević, A., Nikolić, D., & Skerlić, J. (2020). Review of Energy Consumption and CO2 Emission in School Buildings: Case Study of the City of Kragujevac. Applied Engineering Letters, 5(3), 104-109. https://doi.org/10.18485/aeletters.2020.5.3.5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18485/aeletters.2020.5.3.5
- Reinking, A., & Martin, B. (2018). The Gender Gap in STEM Fields: Theories, Movements, and Ideas to Engage Girls in STEM. Journal of new approaches in educational research, 7(2), 148-153. https://doi.org/10.7821/naer.2018.7.271 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7821/naer.2018.7.271
- Rizvanović, A., & Alihodžić, B. (2019). STEM pristup u podučavanju matematike [A STEM approach to teaching mathematics]. Zbornik radova PROZOR u svijet obrazovanja, nauke i mladih, 97-113.
- Robinson, J. P., & Lubienski, S. T. (2011). The development of gender achievement gaps in mathe-matics and reading during elementary and middle school: examining direct cognitive assessments and teacher ratings. American Educational Research Journal, 48(2), 268-302. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831210372249 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831210372249
- Rosenzweig, E. Q., & Wigfield, A. (2016). STEM Motivation Interventions for Adolescents: A Promising Start, but Further to Go. Educational Psychologist, 51(2), 146-163. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2016.1154792 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2016.1154792
- Sadler, P. M., Sonnert, G., Hazari, Z., & Tai, R. (2012). Stability and volatility of STEM career interest in high school: a gender study. Science Education, 96(3), 411-427. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21007
- Sahin-Topalcengiz, E. & Yildirim, B. (2019). The development and validation of Turkish version of the elementary teachers’ efficacy and attitudes towards STEM (ET-STEM) scale. Journal of Education in Science, Environment and Health, 5(1), 12-35. https://doi.org/10.21891/jeseh.486787 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21891/jeseh.486787
- Štilić, A., Mastilo, A., Vuković, K., & Mastilo, D. (2023). Innovative Solutions for Economic Growth: Ex-ploring the Impact of Economic Freedoms on Foreign Direct Investment Attraction. Economics - inno-vative and economics research journal, 11(1), 29–44. https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2023-0013 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2023-0013
- Tran, Y. (2018). Computer Programming Effects in Elementary: Perceptions and Career Aspirations in STEM. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 23(2), 273-299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-018-9358-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-018-9358-z
- Waite, A. M., & McDonald, K. S. (2019). Exploring challenges and solutions facing STEM careers in the 21st century: A human resource development perspective. Advances in Developing Human Resources, 21(1), 3-15. https://doi.org/10.1177/1523422318814482 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1523422318814482
- Wang, M.-T., & Degol, J. L. (2016). School climate: A review of the construct, measurement, and impact on student outcomes. Educational Psychology Review, 28(2), 315–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-015-9319-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-015-9319-1
- Wang, M.-T., & Eccles, J. S. (2013). School context, achievement motivation, and academic engage-ment: A longitudinal study of school engagement using a multidimensional perspective. Learning and Instruction, 28, 12-23, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2013.04.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2013.04.002
- Zhou, L. & Li, J. J. (2023). The Impact of ChatGPT on Learning Motivation: A Study Based on Self-Determination Theory. Education Science and Management, 1(1), 19-29. https://doi.org/10.56578/esm010103 DOI: https://doi.org/10.56578/esm010103


