The analysis of features of measurement of outflow of a current in view of air backlashes at definition of safety of electric toys
Автор: Khromtsov S.V., Rashidova B.R.
Журнал: Вестник Алматинского технологического университета @vestnik-atu
Рубрика: Техника и технологии
Статья в выпуске: 5 (95), 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Scientific novelty of work is presented in the form of definition of the main options of measurement of ways of leakage of current and air gaps at research of safety of electric toys. Practical value is represented by the offered optimum scheme of measurement. Safety requirements belong to electric characteristics of toys with a rated voltage of food up to 24B. Results of work can be usedwhen carrying out standardization and certification of electric toys.
An electric toy, safety of toys, outflow of a current, an air backlash
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140204972
IDR: 140204972 | УДК: 677.614
Текст научной статьи The analysis of features of measurement of outflow of a current in view of air backlashes at definition of safety of electric toys
In recent years in Kazakhstan safety of toys seriously took up the issue, namely sharply there is a question of quality and safety of children's toys as they bear direct threat to health of children. Especially this question is actual for electric toys. It is more than a half taken on check by competent authorities of toys didn't conform to requirements and the norms established by standards.
Objects and research methods
The purpose of this test of electric toys on safety is decrease in danger at game with the toys, especially those risks which aren't obvious to users. Considered safety requirements belong to electric characteristics of toys with rated voltage of a food to 24В and don't cover requirement for placement of batteries which contain the substances dangerous to environment.
Thus we use the following definitions [1]:
-
- A leak way - the shortest way between two current-carrying parts or between a currentcarrying part and an available surface of the
device, measured on a surface of an izolyaktsionny material.
-
- An air gap - the shortest distance between two current-carrying parts or between a current-carrying part and an available surface of the device, measured by air.
The minimum ways of leakage of a current and air gaps between parts of opposite polarity are given in table 1.
Table 1
|
If between parts of different polarity |
Ways of leak, mm |
Air gap, mm |
|
There is a protection against dirt sedimentation |
1,0 |
1,0 |
|
There is no protection against dirt sedimentation |
2,0 |
1,5 |
|
Windings are executed by the varnished or enameled wire |
1,0 |
1,0 |
If between a point in which the winding and the condenser are connected, and resonant tension arises the metal parts separated from current carrying parts by only main isolation, ways of leakage of a current and air gaps should be not less values corresponding to resonant tension. In case of the strengthened isolation these values can be increased.
Results and their discussion
At carrying out measurements we accept the following assumptions:
-
- the groove can have parallel, meeting or dispersing walls;
-
- any groove with the dispersing walls, more than 0,25 mm having the minimum width, depth more than 1,5 mm and width at a bottom of 1 mm or more, we consider as an air gap along which there is no leak way (fig. 8);
-
- any corner with an internal corner less than 800 we consider shunted by a detail from an insulating material in width of 1 mm (0,25 mm in the places protected from sedimentation of dirt), placed in the most adverse situation (fig. 3);
-
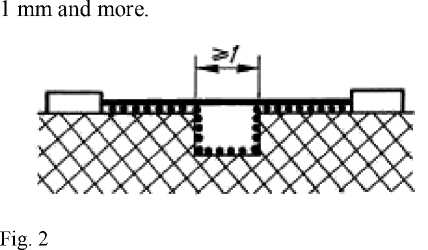
- if the distance between the top edges of a groove equally 1мм (in the places protected from sedimentation of dirt, 0,25 mm) or is more, distance by air between these edges we do not consider as a way leak (fig. 2);
-
- ways of leak and the air gaps which are subject to measurement between parts, moving from each other, we measure when these parts are in the most adverse stationary situation;
-
- at calculation of a total air gap any air gap in width less than 1 mm (0,25 mm for the places protected from sedimentation of dirt) don't consider.
Let's consider the following options of measurement of ways of leakage of a current and air gaps:
The considered way includes a groove with parallel or meeting lateral walls of any depth, width less than 1 mm.
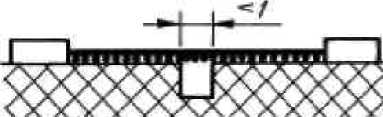
Fig. 1
In this case the way of leakage of a current and an air gap measure directly through a groove as it is specified in drawing 1.
The considered way includes a groove with parallel lateral walls of any depth, width of
In this case an air gap we consider length as "an aim straight line». The way of leak passes on a groove contour.
The considered way includes a V-shaped groove with an internal corner less than the 800th width more than 1 mm.
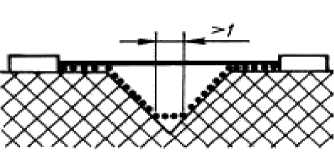
Fig. 3
In this case also air gap consider length as "an aim straight line». The way of leak passes on a groove contour, however we shunt a groove bottom an element the in length 1 ми (0,25 mm in the places protected from sedimentation of dirt).
The considered way includes an edge.
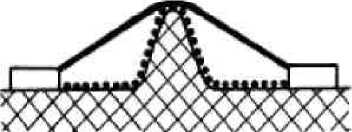
Fig. 4
As air gap it is considered the shortest distance by air through an edge. The way of leak passes on an edge contour.
The considered way includes, not stuck together connection with grooves in width less than 1 mm (0,25 mm in the places protected from sedimentation of dirt) from each party.
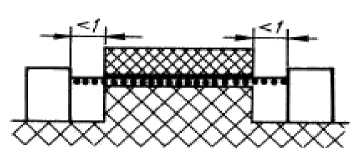
Fig. 5
By leakage of a current and an air gap we consider length as "an aim straight line» as it is specified in drawing 5.
The considered way includes, not stuck together connection with grooves in width of 1 mm or more on each party.
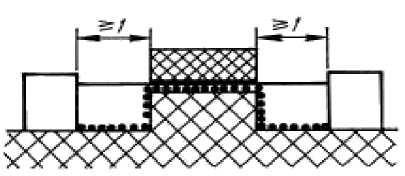
Fig. 6
Air gap we consider length as "an aim straight line». The way of leak passes on contours of grooves.
The considered way includes, not stuck together connection with a groove on one party, which already 1 mm, and with a groove on other party of 1 mm and more.
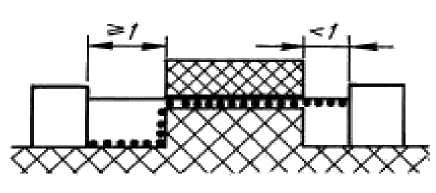
Fig. 7
The air gap and way of leakage of a current measure, as is specified in drawing 7.
The considered way includes a groove with dispersing lateral walls depth of 1,5 mm or more, width in the bottleneck more than 0,25 mm and width at a bottom of 1 mm or more.
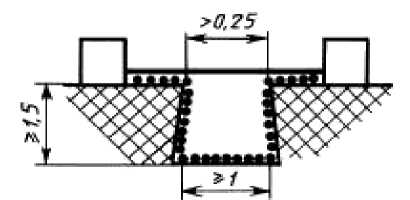
Fig. 8
Air gap consider length as "an aim straight line». The way of leak passes on a groove contour.
The gap between a screw head and a hollow wall dostaktochno is great and (fig. 9) is taken into consideration.
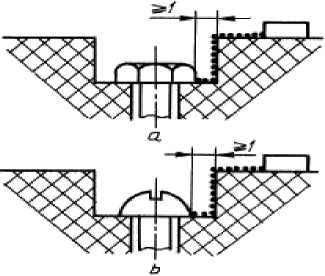
Fig. 9
he current of leak is measured, applying the scheme provided on drawing 10.
Thus:
R 1 = 1500 Ohm ± 0,1 %; R 2 = 500 Ohm ±0,1 %; R3 = 10 кOhm ±0,1 %;
С 1 = С 2 = 0,22 мкФ ±0,1 %.
The current of leak is counted according to the voltmeter indication, delenny on 500 Ohm.
The voltmeter should provide measurement of exact average quadratic value from 0 to 1 MHz.
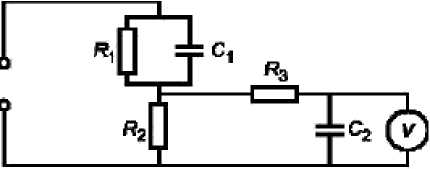
Fig. 10
Conclusions, conclusion
Thus, results of the conducted researches allowed to define the minimum ways of leakage of current and air gaps between parts of the opposite polarity, ensuring safety of electric toys. Thus electric toys conditionally share on working from the transformer and from the battery. Tension in the power supply shouldn't exceed 24 volts. The transformer has to be made of strong fire-resistant materials. Special demands are made as well to batteries: they have to be explosion-proof, and risk to receive blow by current has to be minimized. All contacting and capable to contact to a source of electricity of a detail have to be isolated. Electric toys shouldn't serve as a hindrance to other electrical equipment. Heating most up parts shouldn't cause burns.
Список литературы The analysis of features of measurement of outflow of a current in view of air backlashes at definition of safety of electric toys
- ГОСТ 51557-99 «Игрушки электрические. Требования безопасности».


