The impact of climate change on the risks of defects in wheat grain processing products: safety issues and prevention strategies
Автор: Potoroko I.Yu., Chemek M., Ruskina A.A.
Рубрика: Актуальные проблемы развития пищевых и биотехнологий
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.12, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Climate change issues currently define a set of problems for producers of food raw materials in the agro-industrial sector. Scientific understanding of the relationship between climate change and foodborne diseases is crucial for the development of new methods of mitigation and adaptation of processors. Tracking the risk in the process flow allows to minimize the portion of food products that determines the impact on the food industry. Low quality of food raw materials, the presence of negative factors leads to the formation of waste, the amount of waste worldwide remains critically high, accounting for a third of all food production. Global warming against the background of rising temperatures reduces the availability of food in regions such as the Mediterranean and Europe, forming the difficulty of ensuring stability in the field of food. The current review takes into account climatic conditions and biosafety of grain raw materials, in particular the risk of bacterial contamination and the occurrence of diseases causing bacterial spoilage of products. The most critical is the development of potato disease of wheat bread, the finished product during storage, darkening and destruction of the crumb is visualized, a pungent odor appears. Bacillus ssp can contaminate grain raw materials during harvesting, storage, flour processing and finally baking. The proposed review attempts to explain that climate change, particularly global warming, may be associated with the occurrence of heat-induced bacterial contamination and the occurrence of diseases causing bacterial spoilage of bread. In addition, the current strategy adopted to prevent this microbiological disease in bakery products was described.
Ropiness disease, bacillus ssp, bread, climate change, global warming, food spoilage
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147244573
IDR: 147244573 | УДК: 664.64.019+632.3.01/.08 | DOI: 10.14529/food240301
Текст научной статьи The impact of climate change on the risks of defects in wheat grain processing products: safety issues and prevention strategies
Impact of climate change on food spoilage
Ecosystems are greatly impacted by climate change, which increases the number of harmful microorganisms that contaminate food, endangering food security and subsequently human health [1]. It affects food systems, quality, and safety, including the prevalence of food-borne pathogens [2]. Evidence suggests that climate change affects not only food yields but also food quality and safety. The majority of research on the effects of climate change focus on how primary food production will be affected, as well as how this would affect food security, safety, and nutrition. Conversely, there is insufficient evidence to support the idea that food spoilage is a result of climate change [1].
The process that makes food unpalatable to the consumer is known as food spoilage. The spoiling process most frequently results from microbiological deterioration [3]. Specific Spoilage microorganism such as bacteria can produce sensory defects that impact a food product's appeal to consumers. These flaws include off-flavours, off-odours, visible microbial growth, and texture alterations. Temperature, humidity, and periods of intense precipitation are examples of climate conditions that are anticipated to impact food spoiling microorganisms and raise the risk of food spoilage [1, 4].
Climate change is thought to be especially vulnerable to the spoiling effects of a wide range of food products and raw materials, including bulk dried foods like cereal grains [5]. This is because changes in temperature, humidity, and precipitation can alter intrinsic or extrinsic factors, which in turn can influence the growth of spoilage bacteria [6].
Food spoilage significantly impacts the food industry and contributes to global food waste, accounting for one-third of all food production [7]. With rising temperatures reducing food availability in regions like the Mediterranean and central Europe, ensuring food security is crucial to maintain food stability.
Ropiness in bread: a spoilage phenomenon induced by potato bacteria ( Bacillus ssp )
A major microbiological quality issue affecting bread is ropiness disease, also known as potato disease or mesenteric disease [8]. Rope formation occurs in high-moisture bread loaf regions as a result of volatile molecules that cause patchy discolouration, stringy crumb, and an unpleasant sweet odour similar to that observed in rotting melons or pineapples.
A comparatively diverse microbial population of bacteria from the genus Bacillus is the source of this quality problem in bead [8, 9]. While Bacillus mesentericus is commonly thought of as the infectious agent, research has shown that other related bacteria, including B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. pumilus, B. cereus, B. megatherium, etc., are also involved [10, 11].
The potato is one of the most common vectors of this bacteria, which is why it was given one of the names listed above. Most writers believe that meteorological circumstances during harvesting (drought, dust, wind) and wheat storage conditions contribute to increased B. mesentericus infection.
The importance of climate conditions in the contamination of bread primary material (cereals grain) by Bacillus ssp
Contamination of cereals grain by bacillus ssp from the soil during harvesting process:
Gram-positive, rod-shaped, aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, motile, endosporeforming bacteria are known as Bacillus species. These bacteria cannot grow on the surface of cereal plants because they are not a component of their epiphytic microbiota. The genus Bacillus contains very little bacteria (approximately 5 cfu/g) on the surface of cereal plants, but these bacteria are present in the soil (Fig. 1), where their concentration can reach 105 cfu/g [12]. The primary means by which these bacteria enter the grain mass is through dust particles that adhere to the grains during wheat harvesting and primary processing (Fig. 1).
Research studies indicated that wheat from hotter, wetter regions has higher microbial loads, while wheat grown in warm, dry conditions has lower bacterial counts [13]. Temperatures between 13.7 °C and 31.5 °C and low humidity levels (bellow 55 %) reduce microbial loads [13].
Contamination of cereals grain by bacillus ssp during storage:
A wheat grain storage system is an artificial ecosystem where deterioration occurs due to abiotic physical, chemical, and biotic factors, including temperature, moisture, storage structure, microorganisms, insects, and birds [14].
The higher ambient temperature brought on by climate change would directly affect the storage temperature in conventional wheat storage systems, where temperature regulation may only be accomplished by aeration [15]. The amount of Bacillus spores increased during storage due to an increase in ambient temperature (Fig. 1).
Dry grains are often kept in environments that inhibit the growth of microorganisms. As a result, bacterial spores cannot germinate until the temperature and moisture content of the grain rise [8]. In fact, wheat postharvest losses and grain storage length are significantly influenced by grain moisture, which has to be less than 14.5 % (w/w). As a result, during cereal storage, the excessive moisture and temperature rise within the grain may cause bacterial spore germination [6].
Then, when the grains are ground, these bacteria – which now form a component of the cereal
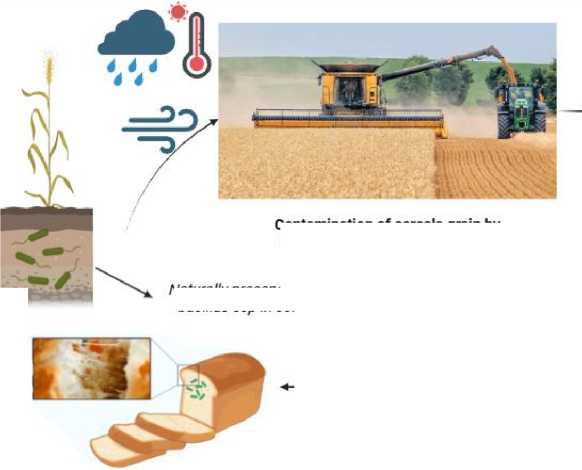
Naturally presence of bacillus ssp in soil
Bacillus ssp germination and rope spoilage of the bread
Contamination of cereals grain by bacillus ssp from the soil during harvesting process
Resistance of bacillus ssp during baking process

Contamination of cereals grain by bacillus ssp during storage

Contamination of cereals grain by bacillus ssp during grinding process
microbiota – find their way into the flour [8]. Flour with a high level of microbial contamination is obtained by inadequate cleaning of the grain surface prior to the grinding process [16].
Contamination during grinding process of the cereals grain by bacillus ssp:
During the grinding process, flour can be contaminated by bacteria due to equipment, with high microbial counts in tempering bins [17]. Therefore, in some cases, flour may be more contaminated with spore-forming bacteria than the original grain [18]. Second-grade flour often contains more spore-forming bacteria than higher-grade flours [13].
This contamination increases the risk of potato pathogens in bread. Flour, does not support bacterial growth and is considered as microbio-logically safe. However, the high bacterial dormant spore concentrations in the obtained floor after grain grinding, can endanger bread quality and shelf life [8, 19].
Germination of bacillus spore during baking process:
Bacillus endospores are thermally stable, capable of withstanding baking in the midst of bread crumb [20]. In such suitable conditions (temperatures over 25 °C combined with an aw ≥ 0.95 and pH > 5) bacterial species that form ropes begin to proliferate and create proteolytic and amylolytic enzymes, which cause the bread's crumb to break down and cause ropiness or potato diseases [8, 20] (Fig. 1).
Food Safety Concerns due to ropiness spoilage of the wheat bread
Bread with high levels of Bacillus species, such as B. cereus, can be dangerous for patients in hospitals, persons with pre-existing diseases, and people of all ages [21]. Elevations of B. subtilis or B. licheniformis have been associated with foodborne outbreaks and have been known to induce vomiting or diarrhoea [22, 23]. Toxins such lichenysin A, amylisin, and pumilacidin are produced, for instance, by B. licheniformis, B. subitilis, B. mojavenis, and B. pumilus. Moreover, amylosin production by B. amylo-liquefaciens has been reported [22]. While isolates of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens kept their cytotoxic action and nearly all survived heat treatment, de Bellis et al. [22] observed that 30 % of the strains belonged to other Bacillus species.
Prevention against ropiness spoilage of the bread
Bread frequently suffers from ropiness spoiling, thus it's critical to properly preserve the goods. There are several ways to increase the shelf life of bread, such as the use of active pack- aging systems, modified environment packaging, natural antimicrobials, and preservatives [24].
Disinfection of the primary material (cereal grains) using novel technology:
In order to maintain food grains clean and uncontaminated, and ultimately to maintain the food products' safety, freshness and nutritional value, a number of food processing techniques have been researched and put to use. Due to their capacity to drastically cut processing times overall while consuming very little energy, nonthermal techniques like cold plasma, irradiation, ozonation, microwave, radiofrequency, infrared, ohmic heating, and nanotechnology have drawn a lot of attention among these technologies [25, 26].
Maintaining a low PH medium using organic preservatives:
In rope formers, ropiness can be avoided by using preservatives such as organic acid (calcium propionate, acetic acid…). This finding was explored in vitro on Bacillus strains from ropy bread by Pattison et al. [27] who discovered that the above-mentioned organic acids halted the bacterial growth. The efficiency of a preservative dropped when the pH was changed to that of baked brown bread, however calcium propionate remained effective [11].
Maintaining a low PH medium using lactic acid bacteria of the sourdough:
Baker's sourdough, a flour and water mixture, is commonly used to give bread its sour flavour. Antimicrobial compounds released by Lactobacillus bacteria (LAB) and yeasts, which dominate the sourdough microbiota, prevent Bacillus development [28, 29]. Elsanhoty et al. [30] reported that Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifi- dobacterium lactis reduced Bacillus ssp. development in bread dough. The pH of the bread decreases substantially as a result of LAB's production of lactic and acetic acids, which largely inhibits the development of Bacillus species.
Surprisingly, breads made with 20 % sourdough and the same lactic acid concentrations did not inhibit Bacillus growth and subsequent rope production [31].
This finding demonstrates that the combination of low-molecular-mass compounds produced by LAB and a low pH inhibits rope formation [8]. It is hypothesised that the organic acids and antibacterial chemicals produced by LAB work in synergetic way to inhibit Bacillus development in bread [32].
Conclusion
Overall, growing conditions, such as crop growth sites, and climatic parameters, such as relative humidity, temperature, and precipitation levels, have an impact on the cereal microbiota. The degree of contamination of cereal grains and their byproducts by Bacillus ssp ., the main bacterial agent for ropiness in bread, can also vary. All these factors can have an effect on the quality of cereal grain by-products, such as wheat bread. For better preservation and to reduce the safety risk related to the contamination of rope formation in bread due to Bacillus ssp., novel nonthermal technology such as cold plasma, as well as the use of LAB and organic acid preservatives to maintain a low pH medium, could be effective in preventing bread from the rope spoilage.
However, future research should focus on other eco-friendly and bio-preservation methods that ensure more safety for the food product and, subsequently, human health.
Список литературы The impact of climate change on the risks of defects in wheat grain processing products: safety issues and prevention strategies
- Misiou, O.; Koutsoumanis, K. Climate Change and Its Implications for Food Safety and Spoilage. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 142–152. DOI: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.03.031.
- Awad, D.A.; Masoud, H.A.; Hamad, A. Climate Changes and Food-Borne Pathogens: The Impact on Human Health and Mitigation Strategy. Clim. Change 2024, 177, 92. DOI: 10.1007/s10584-024-03748-9.
- Onyeaka, H.N.; Nwabor, O.F. Chapter 2 - Food Ecology and Microbial Food Spoilage. In; Onyeaka, H.N., Nwabor, O.F.B.T.-F.P. and S. of N.P., Eds.; Academic Press, 2022; pp. 3–18. ISBN 978-0-323-85700-0.
- Koutsoumanis, K.P.; Misiou, O.D.; Kakagianni, M.N. Climate Change Threatens the Microbiological Stability of Non-Refrigerated Foods. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111990. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111990.
- Naumenko, N.; Potoroko, I.; Kalinina, I.; Naumenko, E.; Ivanisova, E. The Effect of Ultrasonic Water Treatment on the Change in the Microstructure of Wheat Grain, Dough, and Wheat Flour Bread. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 1986438. DOI: 10.1155/2022/1986438.
- Moses, J.; Jayas, D.; Alagusundaram, K. Climate Change and Its Implications on Stored Food Grains. Agric. Res. 2015, 4. DOI: 10.1007/s40003-015-0152-z.
- Duchenne-Moutien, R.A.; Neetoo, H. Climate Change and Emerging Food Safety Issues: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1884–1897. DOI: 10.4315/JFP-21-141.
- Pacher, N.; Burtscher, J.; Johler, S.; Etter, D.; Bender, D.; Fieseler, L.; Domig, K.J. Ropiness in Bread-A Re-Emerging Spoilage Phenomenon. Foods (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 11. DOI: 10.3390/foods11193021.
- Pepe, O.; Blaiotta, G.; Moschetti, G.; Greco, T.; Villani, F. Rope-Producing Strains of Bacillus Spp. from Wheat Bread and Strategy for Their Control by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2321–2329. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.2321-2329.2003.
- Iurie, R. Bread Rope Spoilage Development. J. Eng. Sci. 2023, 30. DOI: 10.52326/jes.utm.2023.30(2).16.
- Pereira, A.P.M.; Stradiotto, G.C.; Freire, L.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Crucello, A.; Morassi, L.L.P.; Silva, F.P.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Occurrence and Enumeration of Rope-Producing Spore Forming Bacteria in Flour and Their Spoilage Potential in Different Bread Formulations. LWT 2020, 133, 110108, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110108.
- Borriss, R. Chapter 7 - Bacillus. In; Amaresan, N., Senthil Kumar, M., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A.B.T.-B.M. in A.-E., Eds.; Academic Press, 2020; pp. 107–132. ISBN 978-0-12-823414-3.
- Sabillón Galeas, L.; Bianchini, A. From Field to Table: A Review on the Microbiological Quality and Safety of Wheat-Based Products. Cereal Chem. J. 2015, 93. DOI: 10.1094/CCHEM-06-15-0126-RW.
- Christopoulos, M. V; Ouzounidou, G. Chapter 17 - Climate Change Leading to Postharvest Losses in Bread Wheat. In; Ozturk, M., Gul, A.B.T.-C.C. and F.S. with E. on W., Eds.; Academic Press, 2020; pp. 257–264. ISBN 978-0-12-819527-7.
- Jian, F.; Jayas, D.S. The Ecosystem Approach to Grain Storage. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 148–156. DOI: 10.1007/s40003-012-0017-7.
- Osman Erkmen, T.F.B. Spoilage of Cereals and Cereal Products. In Food Microbiology: Principles into Practice; 2016; pp. 364–375 ISBN 9781119237860.
- Müller, A.; Nunes, M.; Maldaner, V.; Coradi, P.C.; de Moraes, R.; Martens, S.; Leal, A.; Pereira, V.; König, C. Rice Drying, Storage and Processing: Effects of Post-Harvest Operations on Grain Quality. Rice Sci. 2022, 29. DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.12.002.
- Naumenko, N.; Potoroko I.; Kalinina, I.; Fatkullin, R.; Ivanisova, E. The Influence of the Use of Whole Grain Flour from Sprouted Wheat Grain on the Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Dough and Bread. Int. J. food Sci. 2021, 2021, 7548759. DOI: 10.1155/2021/7548759.
- Carlin, F. Origin of Bacterial Spores Contaminating Foods. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 177–182. DOI: 10.1016/j.fm.2010.07.008.
- Farmiloe, F.J.; Cornford, S.J.; Coppock, J.B.M.; Ingram, M. The Survival of Bacillus Subtilis Spores in the Baking of Bread. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1954, 5, 292–304. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740050608.
- Jessberger, N.; Dietrich, R.; Granum, P.E.; Märtlbauer, E. The Bacillus Cereus Food Infection as Multifactorial Process. Toxins (Basel). 2020, 12, DOI: 10.3390/toxins12110701.
- Bellis, P.; Minervini, F.; Di Biase, M.; Valerio, F.; Lavermicocca, P.; Sisto, A. Toxigenic Potential and Heat Survival of Spore-Forming Bacteria Isolated from Bread and Ingredients. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 197C, 30–39, DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.12.017.
- (BIOHAZ), E.P. on B.H. Risks for Public Health Related to the Presence of Bacillus Cereus and Other Bacillus Spp. Including Bacillus Thuringiensis in Foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04524. DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4524.
- Kalinina, I.; Fatkullin, R.; Naumenko, N.; Nataliya, P.; Stepanova, D. The Influence of Flavonoid Dihydroquercetin on the Enzymatic Processes of Dough Ripening and the Antioxidant Properties of Bread. Fermentation 2023, 9, 263. DOI: 10.3390/fermentation9030263.
- Los, A.; Ziuzina, D.; Bourke, P. Current and Future Technologies for Microbiological Decontamination of Cereal Grains. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1484–1493. DOI: 10.1111/1750-3841.14181.
- Sirohi, R.; Tarafdar, A.; Kumar Gaur, V.; Singh, S.; Sindhu, R.; Rajasekharan, R.; Madhavan, A.; Binod, P.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, A. Technologies for Disinfection of Food Grains: Advances and Way Forward. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110396. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110396.
- Pattison, T.L.; Lindsay, D.; von Holy, A. In Vitro Growth Response of Bread-Spoilage Bacillus Strains to Selected Natural Antimicrobials. J. Basic Microbiol. 2003, 43, 341–347. DOI: 10.1002/jobm.200390037.
- Plessas, S.; Mantzourani, I.; Alexopoulos, A.; Alexandri, M.; Kopsahelis, N.; Adamopoulou, V.; Bekatorou, A. Nutritional Improvements of Sourdough Breads Made with Freeze-Dried Functional Adjuncts Based on Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum Subsp. Plantarum and Pomegranate Juice. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 12. DOI: 10.3390/antiox12051113.
- Suo, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Recent Research Advances of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sourdough: Origin, Diversity, and Function. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 66–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.cofs.2020.09.007.
- Elsanhoty, R.; Ghonamy, A.G.; El-Adly, N.A.; Hassanien, M. Impact of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacterium on the Survival of Bacillus Subtilus During Fermentation of Wheat Sourdough: Impact of Lab on Bacillus Subtilus During Fermentation of Wheat Sourdough. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 41. DOI: 10.1111/jfpp.13086.
- Mantzourani, I.; Plessas, S.; Saxami, G.; Alexopoulos, A.; Galanis, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Study of Kefir Grains Application in Sourdough Bread Regarding Rope Spoilage Caused by Bacillus Spp. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 17–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.07.098.
- Siedler, S.; Balti, R.; Neves, A.R. Bioprotective Mechanisms of Lactic Acid Bacteria against Fungal Spoilage of Food. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 138–146. DOI: 10.1016/ j.copbio.2018.11.015.


