Transformation of machine building of the Republic of Karelia
Автор: Nemkovich Yevgeniy Grigoryevich, Kurilo Anna Yevgenyevna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Branch-wise economy
Статья в выпуске: 1 (25) т.6, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article considers the process of mechanical engineering transformation from the beginning of market reforms up to the present time. The article provides the comprehensive analysis of the republic’s machine-building sector, represented by several types of activities, and presents the dynamics of indicators characterizing its development. Besides, it defines the region’s machine building development prospects.
Region, machine building, economic activities, regional national development
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223441
IDR: 147223441 | УДК: 338.45:
Текст научной статьи Transformation of machine building of the Republic of Karelia
On the modern map of machine building in our country the Republic of Karelia is presented by a small number of enterprises. But all of them have their history, specialization, their problems and strategies, playing a certain role in the economics of the republic.
In the Soviet period, machine building was one of the leading sectors in the economy of the republic. The big enterprises of Petrozavodsk included Onega tractor plant, Petrozavodsk-bummash (the factory of paper-making equipment), the radio manufacturing plant, the factory Onego (microelectronics), the shipbuilding factory Avangard, the machine building plant Stankozavod and a number of smaller enterprises, where dozens of thousands of citizens worked.
Machine-building enterprises produced trail tractors, woodworking machines, papermaking machines, bark-stripping drums, crimping aggregates. The production of Karelian machine builders was exported not only to socialistic countries, but also to Canada, Federal Republic of Germany, Greece. Electronics and instrument engineering accounted for about one third of the output volume. Besides about 10 repair enterprises functioned in the republic.
Machine building of Karelia, which had a wood profile, provided timber processing complex both of the country and of the republic with tree crop harvesters, woodwork machines; and cellulose and paper industry with spare parts, aggregates and even paper-making machines.
In 1985 the share of machine building industry in the whole volume of industrial production of Karelia was 19%, and the share of the employed in this branch was 20% of the number of manufacturing personnel [2, p. 30].
In the late 1980s – early 1990s, at the beginning of economic reforms, price liberalization and external economic relations, the whole industry (and machine building as well) of the country and the republic was built according to branch-wise principle with the high level of specialization and the low level of inter-sectoral and intra-sectoral exchange. After the demolition of the common economic space of USSR and Comecon countries, enterprises found themselves in conditions of shrinkage of outlet areas and absence of competitiveness for many positions in the world market. The enterprises faced a complicated task of finding their place in transitional economy, develop and implement a set of measures aimed at adaptation to the conditions of arising market-driven economy.
Reformation of the enterprises went practically spontaneously and separately, according to branches and territories. The enterprises tried to solve this problem on their own. The situation was escalated by the long delays of payments for already delivered goods. At the same time foreign manufacturers carried out an active policy of penetration into the Russian market. That is why every enterprise developed its own strategy of survival, depending on its abilities and opportunities. New owners and managers often didn’t have experience in running business operations in market conditions.
Machine-building enterprises in the country and in Karelia, confronted with the abrupt drop of purchasing power on their production, had to use the strategies of survival which didn’t correspond with the strategies of dynamic development.
The transformation of enterprises went under unstable conditions of transitional economy under the influence of many contradictory factors of outside environment. Originally a state was the key-subject of reformation. Balancing between market driven approaches and demands on the assurance of people’s survivance, the state moved to the market slowly but without any serious social outbursts [6].
During this period different schemes of enterprises’ disaggregation were used, aimed at removing the disproportions of planned economy. The extrication of main production from non-core kinds of activity was taking place, and auxiliary departments had the opportunity to continue their work as selfcontained subjects of economic activity [8].
The process of restructuring of machinebuilding enterprises in the Republic of Karelia affected departments of social services, auxiliary units, engineer subdivisions and non-core departments of the main production unit. For example, in 1997, 18 associated enterprises were created during the realization of a large-scale project of the disintegration in OJSC Onega tractor plant.
In a varying degree restructing was conducted by practically all the machine-building enterprises of the republic, releasing non-core production units and minor kinds of activity. As a result, the situation in the machine-building industry of the country and the republic changed fundamentally during the years of economic reforms.
OJSC Onega tractor plant, having cut the volumes of production by 1996 in comparison to 1990 by 23 times – from 11800 tractors a year to 500 tractors – lost competition in the Russian market to Finnish companies (PONSSE, TIMBERJACK) because it wasn’t ready for developing competitive products. The production volumes of CJSC Petrozavodskmash were cut considerably, due to its lack of financial resources for buying abroad licenses for producing modern equipment for papermaking industry. JSC Stankozavod actually curtailed production: 250 machines in 1990 against 29 machines in 1995 and 4 machines in 2006. A considerable slum took place in the volumes of mechanical material maintenance in CJSC Repair and engineering works and in Petrozavodsk automotive equipment maintenance plant, that switched over to building and renting out manufacturing and office property. Their functions were taken by new established enterprises in maintenance service of equipment.
Many enterprises got through the procedure of bankruptcy and changed their owners more than once, and some enterprises couldn’t work in new conditions and were eliminated. The Petrozavodsk radio manufacturing plant went out of business, it fulfilled defence orders and was a part of the Leningrad research and manufacturing combine Leninets; the Petrozavodsk plant Onego dissolved as well, it represented the Leningrad association of electronic instrument engineering Svetlana – the biggest organization in developing and output of electronic goods in the USSR. Shipbuilding factory Avangard went through the procedure of bankruptcy, changed several owners and ceased to exist; it specialized in fulfilling defence orders, building of fishing motor cultivators and trawlers. Its equipment has been sold, the territory rented out for offices and a service centre, its boiler-house heats the city’s residential area.
Eventually the output volumes shrank considerably, and a number of staff as well, but the rest of the enterprises adapted to the conditions of market driven economy, releasing competitive products, carrying out modernization and implementing development strategies. All these enterprises moved off from repetitive manufacturing, organized their own marketing system and work customized.
Positive tendencies in the developing of machine-building industry are the most significant in CJSC Holding Company Petrozavodsk factory of paper-making machine building. It is the biggest producer of technological equipment for cellulose and paper, oil and gas industries in the country. In the course of the reforms, the company’s restructuring was conducted, the system of management was changed; the list of outlet products was expanded. Over a number of years the enterprise cooperates with such famous companies as VOITH (Austria), METSO (Finland), and supplies papermaking and cellulose equipment to Finland, Austria, Norway, Sweden, Great Britain and CIS countries. The goods are produced in accordance with domestic and international standards.
The development of new partner relations with Russian and foreign enterprises allowed the plant to keep the volume of production in all kind of outlet goods and integrate the state corporation Rosatom in OJSC Atomenergomash. At present, one of the main tasks of the enterprise is the demonopolization of market of equipment for atomic power stations. At the same time, the state corporation Rosatom set before CJSC Petrozavodskmash a strategic task of keeping and outputting to the world market production of equipment for paper and paperboard and other industries of the country’s timber complex.
Without reducing production volumes, the enterprise conducts updating and modernization of production. New equipment is bought at the cost of about half million euros. Due to that, in 2010 the volume of goods dispatched by CJSC Petrozavodskmash was 2.1 billion rubles (2.3 times more than in 2009), among them, the atomic industry equipment accounts for 1.6 billion [7]. Following the results of 2011, the total value of produced goods was 2.52 billion roubles, which makes 132% to the level of 2010. The main volume of production is achieved by the orders from the state corporation Rosatom [5].
In 2012 Petrozavodskmash launched a large-scale project on constructing a shop for producing reactor equipment for atomic power stations. This is the second and the last stage of the investment programme at the total cost of 5 billion rubles which aims at the modernization of the enterprise for the output of large-size equipment for atomic power stations. The construction and repair works are planned to be over in the second half of 2013. The total cost of the project of reactor shop building is over 3 billion rubles. The project of the shop is calculated for annual output of 1.5 sets of reactor block equipment by three-shift work. The contract for purchasing a package type vehicle is already closed; this vehicle will allow transporting a reactor vessel to the port of the enterprise for embarkation.
The management team of CJSC Petrozavodskmash started to work out a strategic development programme and accomplishes business planning for long-term prospects; in the conditions of high uncertainty of Russian business-environment only a few representatives of machine-building industry can afford it.
The oldest enterprise in the country is LLC Onega tractor plant, developing and producing tractors for timber processing complex for more than half a century, was confronted with difficulties in sales of final products because outlet caterpillar models are old-fashioned and are not in such demand as wheeled timber cutting complexes of foreign manufacture. The results of last years testify to instability of manufacturing and financial situation at this enterprise. 663 tractors were produced in 2003 (the volume of output in monetary terms made 516.6 million roubles), in 2005 only 363 tractors of different versions were manufactured. In 2010 the plant managed to sell 76 items.
The factory got through the procedure of bankruptcy, changed several owners. In 2004 it was included in the affiliate group of corporations Tractor Plants and incurred accelerated restructing which was aimed at the elimination of noncompetitive and duplicating other units departments. As a result, the subject-oriented combined machine-building enterprise with enclosed technological cycle transformed into an assembly plant.
The enterprise takes steps on the way of participation in international cooperation and integration into international economic relations. The project involves semi knocked down assembly of modern timber cutting harvesters CHETRA KH-451 made at the Danish plant Silvatec Skovmaskiner A/S which is a part of the concern Tractor Plants.
Long-range engineering projects of constructing and regulating of production of modern complex of machines for Canadian timber cutting technology are conducted at the plant. This complex is composed of felling and milling and delimber-bucker machines, timber loader. This is a new technology of forest harvesting differing from tree-length logs and cut-to-length method used in our and European countries. 175 people worked at the plant in 2012; relocation from the city centre to the second manufacturing area of the enterprise is finished and its development is spreading. Summarizing the results of 2011, about 100 items was assembled and dispatched at the factory. Although it was planned for 2012 to produce 130 tractors, output capacities allow reaching the index of 300 machines a year.
The main enterprise of production of vehicles and equipment in the republic is the Onega shipbuilding factory set up as a successor of shipbuilding-ship repairing capacities OJSC Belomorsko-Onezhskoe parohodstvo. The enterprise is assessed by the Russian Marine Registry of Shipping, Russian River Register and German Lloyd.
Within the framework of presidential programme on the renewal of Russian fleet, a big project on building of “Karelia” type ships was implemented at the factory. This is a selfpropelling, one-screw dry cargo ship, meant for transportation of general and bulk cargoes. Ships like that being of interest for private shipping companies are more effective in marine conditions than familiar to our ship owners crafts of composite class “river-sea”. In 2009 contract liabilities for building of three ships were fulfilled successfully. Despite the world tendency of reducing the purchase orders for constructing of crafts and scarcity of working capital in 2010 CJSC Onega shipbuilding factory reached its maximum efficiency, 4 crafts, and sent them to the customers. In 2011 the factory began to build five oil ships of the type “river-sea” of project RST23 at deadweight capacity 7000 tons.
At present, the capacities of the factory allow building ships at length to 140 m, width to 16.5 m and light-ship to 2.3 thousand tons. The prospects of development of shipbuilding are governed by the “Strategy of development of shipbuilding industry in the Russian Federation for the period till 2020 and the future perspective” and by the federal target programme “The Development of civil marine facilities for 2009 – 2016”. The enterprise has a task of modernization and expansion of production facilities in the short term, which will allow building ships at length to 190 m and light-ship to 3 thousand tons.
One of the effective examples of successful cooperation between republican bodies and manufacturers can be found in the establishment of two subsidiary enterprises of Finnish concern PKC Group – LLC AEK and LLC Electrokos in the city of Kostomuksha. In 2003 – 2005 a group of companies of this concern completed the construction of a production base for outlet of electric wiring for automotive industry and electronic components. The sum of investments made up more than 1063 million rubles. It enabled to create 193 new workplaces.
LLC Electrokos offers services in engineering and producing electronics. LLC AEK, having become one of the essential branch offices of the foreign owner in manufacturing electric wiring for heavy-duty Volvo and Scania vehicles, employs more than 800 people, mainly women. Half of all products manufactured in the republic according to the type of economic activity “Production of electric, electronic and optical equipment” fall on these enterprises.
In this field of economic activity a newly developed research and production enterprise Proriv (the city of Petrozavodsk) works successfully; in Russia it is a leading developer and producer of testing facilities and measuring equipment in the field of electromagnetic compatibility.
On the whole, the production index in the type of economic activity “Production of electric, electronic and optical equipment” in 2011 was 111.3% [5].
In the process of transformation of Karelian machine building LLC Research and Production Company Microprofil which produces mechanical equipment for manufacturing of corrugated fibreboard.
Innovative enterprise CJSC SPA Engineering centre of fire robotics “EFER” specializes in developing and producing firefighter hydraulic and hand fire nozzles, fire-fighting robots, robotize firefighter complexes.
CJSC Petrozavodsky opitno-mehaniches-ky zavod manufactures machines for woodworking enterprises, equipment and instruments for plants of forest and wood-working industry branches.
During the restructurization of the mining and beneficiation complex in Kostomuksha an enterprise of wide-line profile LLC ZRGOO was created (repair mining and concentrating equipment factory). It implements machine processing of large-size parts (to 28 t), manufactures forge pieces (to 100 kg), spare parts for heavy dumpers and executes other works.
Following the results of 2011 products at total 518.1 million roubles or 125% to the level of 2010 were manufactured in LLC ZRGOO. It was possible due to the increasing in production volumes of the main customer of the enterprise (LLC Karelsky Okatysh).
Modern conditions of economic management and the transition of plants to a new technological mode caused the emergence of servicing enterprises. For example, in 2011 a factory of unit repair LLC Zeppelin Russland (Petrozavodsk) started working in the Republic of Karelia. The company, being a dealer of the world famous company Caterpillar, which produces different heavy equipment, works successfully on the territory of the European part of our country for more than 10 years and it already has its branch office in the town of Kostomuksha.
All these examples show the level of development of machine building in the republic. In manufacturing works it is represented by the following types of economic activity: producing of machine and equipment
(136 enterprises), manufacturing of end metal goods (106), producing of electric, electronic and optical equipment (68), manufacturing of vehicles and devices (23 plants). Meanwhile, the main potential of machine-building goods production in the republic (95%) is concentrated in 9 enterprises.
About one third of the production volume, dispatched according to the type of economic activity “Manufacturing works” (fig. 1) falls on the share of machine-building profile enterprises. Since 2005 to 2008 this share increased from 24.4% to 30%. In 2009 (due to the crisis) indexes dropped, after that in 2010 the summary rate of machine-building products figured up to 27.3% from the volume of goods dispatched on the type of economic activity “Manufacturing works”.
In the enterprises of machine-building profile 19.4 thousand people work, or 5.6% of those employed in the republic’s economy. the products are manufactured to the amount of 13.5 billion roubles. Cost effectiveness of production is an average of 5.3%.
Figure 1. Scheme of volume of products dispatched on the type of economic activity “Manufacturing works” in the Republic of Karelia in 2005 – 2010
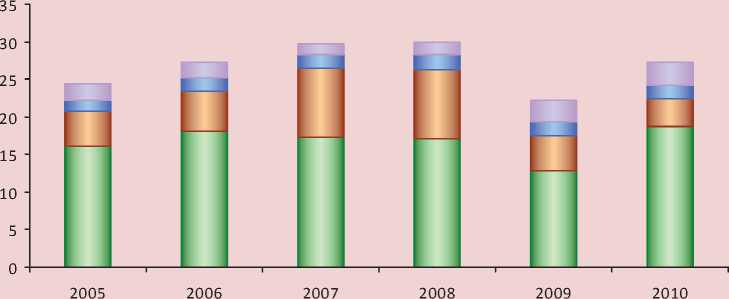
□ Production ofvehicles and equipment, share, %
□ Production of electrical, electronic and optical equipment, share, % о Production of machines and equipment, share, %
□ Metallurgical production and manufacturing of end metal goods, share, %
Average monthly salary is progressively increasing. If in 2005 it was 10% lower than the average in the republic, then in 2010 it was 12% higher.
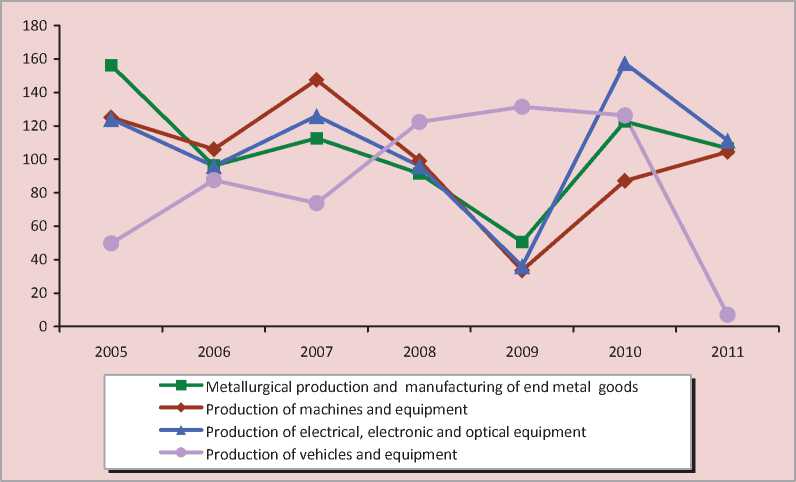
The analysis of machine-building enterprises’ work shows some stabilization of manufacturing situation approximately by 2005, first of all in big plants. In the period of 2005 – 2007 the factory output was increasing, which is confirmed by industrial production indexes (fig. 2) . From the beginning of the crisis in 2008 the development slowed down, and in 2009 the indexes in three types of economic activity of machine-building industry dropped considerably. Then the situation began to improve. While the type of economic activity “Manufacturing of vehicles and devices” is in the opposite phase of main tendency, which is connected with the technology of ship producing. In 2011 we see the dropping of this type of activity index to 7%.
Steps taken by the government of the country, republic and enterprises, allowed in 2011 to increase production volumes on the following types of economic activity: manufac- turing of machines and equipment (104.4%), metallurgical production and production of end metal goods (106.7%), manufacturing of electric, electronic and optical equipment (111.3%). At the same time, in the enterprise of vehicle production befell a sudden drop of industrial production index – to 7.1%. Because of the change of the owner who unsuccessfully tried to convert the manufacturing to producing ships of a different class, the enterprise turned out to be in a situation of bankruptcy.
Enterprises producing competitive goods demonstrate a positive dynamics of development, because they possess modern technologies and a modern system of management. Here a computer monitoring of the whole life circle of products is provided – from formation to running.
In the medium term, steps in enterprises’ development will be directed towards their further reconstructing and modernization on the basis of implementation of modern, high efficiency equipment, mastering of new product kinds, more effective usage of manufacturing facilities.
Figure 2. Industrial production index on the types of economic activity in the Republic of Karelia in 2005 – 2010, in % to the previous year
For example, CJSC Holding company Petrozavodskmash and the State Corporation Rosatom, which is continuing to implement the integration project, by 2015 plan to carry out technical re-equipment of the existing production, prepare facilities for increasing production volumes and for developing the production of Russian nuclear industry equipment. Besides, it is planned to develop the resource efficient production of environmentally safe shipping packaging set for keeping and transporting of spent nuclear fuel. In addition, CJSC Petrozavodskmash will continue its work on the conclusion of longterm contracts for manufacturing goods for its traditional customers – cellulose and paper and oil and gas industries.
Other machine-building enterprises have their development programmes as well. Several factors are needed for their implementation, including the modernization of manufacturing, the expanding of distribution areas and output of new products.
In order to keep their competitiveness in the conditions of Russia’s joining WTO and given the increase of foreign machine-building goods’ import, enterprises have to perform a deep organizational and management modernization and to enter the path of innovation development.
It is necessary to develop a mutually beneficial partnership between business and state through the increase of social responsibility of enterprises and enhancement of state support instruments. Under these circumstances collective and cooperated actions of authorities and employers in the revival of the image of working professions and in steep increase of moral and financial incentive for employees of machine building plants are needed.
In the opinion of several experts the republic can become an area for implementation of the cluster approach to development of innovation timber machine building with high level of competitiveness of output goods, covering the requirements of Russian timber enterprises, in the first place those of the RF North-Western Federal District [4]. Forest-industry and wood machine building clusters of the republic are able to cover requirements of wood enterprises of the region in equipment and to maintain deliveries to other regions of the country and for export.
In general, during the years of political and economic changes machine building in the republic fell under complete transformation. Essentially new enterprises were created, which have adopted the rules of market driven economy and are now shifting to a new organizational and technological mode of production, they are able to compete in the conditions of the world market.
At the present stage of development, machine builders of the republic undertake mission of maintaining and enhancing the achieved level of manufacturing, its technical re-equipment and production of competitive goods which comply with the world standards.
That is why the elaboration of a system strategy of development of machine building in the Republic of Karelia as part of publicprivate partnership appears to be essential [3].
In general, the positive dynamics of production indexes, negotiation of the consequences of the crisis and practical actions of owners and top-managers of machinebuilding enterprises indicate that, despite the existing difficulties and problems, Karelian machine building has good development prospects.
Список литературы Transformation of machine building of the Republic of Karelia
- Volnukhin N.M., Odlis D.B., Kobzev M.V. Breaking up into smaller units by means of creating associated companies (the case of OJSC Onega tractor plant) Petrozavodsk: OTZ-CONSULT, 1999.
- Karelian ASSR in numbers: stat. coll. Petrozavodsk: SU KASSR, 1987.
- Kurilo A.Ye., Nemkovich Ye.G. Formation of the institute of public-private partnership in the Republic of Karelia. Regional economics: theory and practice. 2012. No. 25 (256). P. 12-21.
- Odlis D.B., Shegelman I.R. Prerequisites for the development of the wood machine-building cluster in Karelia. Microeconomics. 2009. No. 8. P. 253-256.
- The report of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Republic of Karelia on the 2011 performance. Official Karelia. Official portal of governmental authorities of the Republic of Karelia. Available at: http://www.gov.karelia.ru/gov/Power/Ministry/Development/economy.html
- Rudakov M.N., Odlis D.B. Ways to overcome the crisis of Russian wood machine building. ECO. 2010. No. 1. P. 76-89.
- Socio-economic condition of the Republic of Karelia according to the results of 2010. Official Karelia. Official portal of governmental authorities of the Republic of Karelia. Available at: http://www.gov.karelia.ru/Power/Ministry/Development/Economy/itog2010.html
- Haynish S. 20th anniversary of the Russian management consulting: some lessons, thoughts, paradoxes, illusions. Problems of the theory and practice of management. 2002. No. 5. P. 106-112.


