Valorization and characterization of the physicomechanical properties of textile waste for polymer composites
Автор: Melesse E.Y., Filinskaya Y.A., Kirsh I.A., Alhkair A.Y.
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Химическая технология
Статья в выпуске: 1 (99) т.86, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The environmental crisis of textile waste in the globe has increased due to the growth of fashion show, industrialization, and demand increment. Despite the Huge amount of textile waste its utilization has not been performed yet except for a little investigation. The present work emphasized the mechanical and permeability character of polymer synthesis of TGGA composites(textile waste, gelatin, glycerol, and acetic acid), fixed at 15% w/w of gelatin, 7 ml glycerol, 6 ml acetic acid through the 2.5% w/w, 5% w/w, and 7%w/w of the amount of cellulose waste. Thereby, the tensile strength of TGGA2 composite showed higher than TGGA1 and TGGA3, due to uniformity distribution of the amount of the textile cellulosic waste. Nonetheless, the elongation at break and water vapor permeability were decreased with the increased amount of the textile waste. Morphological structure of the synthesized composites such as cotton fibers and matrices were visible, rough and non-void area in all the samples. Besides, incorporation of the plasticizing agents confirmed that the TGGA - composites displayed better extensibility and flexibility compared to non-plasticizing composite films currently reported in the literature. Importantly, the produced composites exhibited a functionality equivalent with original packaging materials, which were convectional and natural polymers.
Textile waste, gelatin, composites, glycerin, physico-mechanical properties, valorization
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140305675
IDR: 140305675 | УДК: 640 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2024-1-242-248
Текст научной статьи Valorization and characterization of the physicomechanical properties of textile waste for polymer composites
Currently, the effect of solid waste on the environment has been escalating around the globe due to the high growth of fashion shows, industrialization, and demand increments. Parallel to this, Environmental concerns about the impact of petrochemical plastics, such as their non-biodegradability, non-recyclability, and finding well disposal methods are current art of research [1]. What’s more, solid management, the resource Valorization, are crucial for making the environment green and safe, particularly for textile wastes. Coherently, methane gas is released during the decay of textile wastes in the environment in addition to multiple dyes and chemicals in the textile waste contaminated with soil, which decrease soil fertility and cause greenhouse gasses [2]. Jointly, green composites are the current and future alternative to traditional plastics, because they could be used in food packaging applications and act as eco-friendly.
Organic fabric materials are the vital ingredients in polymer and composite synthesis, which serve as reinforcement and can cause high mechanical strength and low barrier properties. The textile wastes (T-shirts), which are highly cellulosic can be utilized for composites extensions. Despite the huge availability of cellulosic textile wastes, their utilization is not well developed yet. Likewise, there
is a dearth of scientific data regarding the incorporation of plasticizing materials (s) with textile wastes. As a reinforcement, other textile wastes like denim wastes are examined with polypropylene (PP) [3, 4], polypropylene, and polyethylene (PP/PE) [5] in packaging applications through hot press process and in structural application utilized with bio-resins [6] by compression molding, used in furniture materials through the non-woven needle-punching process [7]. Furthermore, the application of denim waste used as adsorbent in water defluorination [8], in composite films[9], and in food packaging application with corn starch has been investigated [10].
The Gist-purpose of this research is that Textile (T-shirt) waste fabric was utilized into polymer composites made using the blending polymerization technique, which combined with gelatin, glycerin, and acetic acid. These could be used instead of some selective convectional-based products in food packaging applications, as well as reduce the amount of textile (T-shirt) wastes that have a high environmental crisis.
Material and methods
Textile (T-shirt) waste (100% cotton), gelatin (100%), glycerin (100%), and acetic acid (9% v/v) were used for the development of the polymer composite solutions.
Firstly, the Textile (T-shirt) waste was chopped into chunks. 100% cotton fiber used as
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
a source of cellulosic reinforcement and gelatin used as matrix, glycerin for plasticizer and antimicrobial properties, and acetic acid for esterification purposes were collectively introduced and mixed into 120ml DI water solution. With 2.5% w/w, 5% w/w, and 7% w/w of textile cellulose waste and 15% w/w of gelatin at 7 ml of glycerin and 6 ml of acetic acid were investigated respectively. These solutions were polymerized thoroughly in a hotplate at a temperature of 90.2 ± 3 °C and 25 minutes of blending time. The Textile cellulose waste (TC), gelatin (G), glycerin(G), and acetic acid (AA) samples were symbolized by TGGA composites, and TGGA-1, TGGA-2, and TGGA-3, represented for the above composition of the Textile cellulose waste respectively. The gelatinized solutions were cast in rectangular glass plates and dried in the open air for 48 hours for characterization.
Table 1.
Combination of polymer composite disposed in this investigation
|
Sample No |
Textile (T-shirt) waste % (w/w) |
Gelatin % (w/w) |
Glycerin % (v/v) |
Acetic acid % (v/v) |
|
TGGA-1 |
2,5 |
15 |
7 |
6 |
|
TGGA-2 |
5 |
15 |
7 |
6 |
|
TGGA-3 |
7 |
15 |
7 |
6 |
The thickness of the samples was complied with in a micrometer (KM, serial no, 10197–624886, Moscow, Russia) helps to determine the apparent density of the samples by dividing the mass per area and thickness of samples. The average thickness and density of the samples were presented by seven replicated slices that were tried out. The apparent density was determined through the following equation d =---------------- (1)
thickness x area where thickness and area represent, mass, thickness and area of the sample measured by g, µm, and сm2, separately.
The stretching of the samples was tasted through the breaking machine (DM-50, Russia), and three replicated slices were recorded. The maximum load, relative elongation at break, and tensile strength of the samples were determined by calculating the average and standard deviation of the slices.
The water vapor permeability of the composite film was calculated by GOST 25898–2012.
Permeability was carried out every 48 hours for eight days. The WVP was calculated by formula (2):
WVP (10 - 10 g x m -1 x Pa -1 x h -* ) = A m X d (2)
A x t x Ap where Δm (g) is the difference in weight (mass loss) when weighing after two days, and the beginning of the experiment, d is the film thickness (mm), Δt is the residence time of the sample (h), and A is the sample area (Approximately equal to the bottle opening area) (сm2), and p is the partial vapor pressure difference between the two sides of the films at room temperature and it is relatively equal to 4247 Pa and 100% relative humidity.
The morphological structure of the slices was conformed to the scanning microscope (Art. No.52–0100, LCD Microscope, v5.0, Gutenbergstr.2–46414 Rhede, Germany).

(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 1. Photograph of Textile waste, Gelatin, glycerol and acetic acid composites ((a) TGGA-1, (b) TGGA-2, and (c) TGGA-3) samples
Result and discussions
The thickness of the TGGA composites is calculated between the composite film surfaces, it indicates for forecast of the packaging shelf life of the food products. Further, it helps to predict the physio-mechanical properties such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and vapor permeability of the composites[11]. The additives such as glycerol and acetic acid as well as the operating parameters such as temperature, time, and the concentration of the raw materials highly affects the thickness of the films [12].
|
Sample No |
Thickness (mm) |
Density (g/сm3) |
References |
|
TGGA-1 |
0.145 ± 0.119а |
0.269 ± 0.044а |
This study |
|
TGGA-2 |
0.437 ± 0.157b |
0.416 ± 0.096b |
|
|
TGGA-3 |
0.619 ± 0.169с |
0.876 ± 0.141с |
Меlеssе E.Y. et al. Proceedings of VSUET, 2024, vol. 86, no. 1, pp. 242-248
Table 2.
Thickness and density of TGGA composites
The thickness of the TGGA-2 and TGGA-3 composite show thicker than the TGGA-1 composite. This is due to the high amount of dry solids presented in the composites. It enhanced the high loss of strength in the TGGA composites[12]. Not only the strength but also the water vapor permeability of the TGGA composites is affected by the thickness. Besides, the thickness of the composites also identifies their water affinity, compatibility, structure, and free volume between molecules in the synthesized composite samples [13].
Table 3.
Textile waste and gelatin (TGGA) composites
|
Samples |
Tensile strength (МРа) |
Maximum load (N) |
Elongation at break (%) |
references |
|
TGGA-1 |
5.11 ± 0.6 |
21.98 ± 1.9 |
12.63 ± 3.3 |
Present study |
|
TGGA-2 |
26.42 ± 4.6 |
76.1 ± 9.3 |
12.48 ± 1.8 |
|
|
TGGA-3 |
11.81 ± 0.5 |
54.95 ± 2.6 |
16.73 ± 1.8 |
The mechanical performance of the composite samples is measured in terms of the tensile strength (TS) and elongation at break (EB). The maximum strength of the composite at break nominates the TS, whereas the deformation of the film until it breaks is measured by elongation. To be more resistance and more selective of the film, the response variable (TS and EB) must be higher in values [14]. The physical and mechanical properties of the produced composite are represented in Table 2. The three composites (TGGA-1, TGGA-2, and TGGA-3) rеvеаеdl an excellent tensile property as different references reported in the literature. However, the tensile strength (TS) of the TGGA-composites varies with the amount of cellulose. The TGGA-2 composite (26.42 ± 4.6 МРа) shows higher TS of the TGGA-1 (5.11 ± 0.6МРа) and TGGA-3(11.81 ± 0.5МРа) composites, this may be due to the uniformity of fiber distribution of the cellulose particle with the gelatin and glycerol and acetic acid during the development of the polymer composite. All in one, the TS of TGGA composites mended equivalent to gelatin/chitosan (7.44–11.28МРа) [15], gelatin/MMT nano-particles (3.9–10.9МРа [16], and gelatin/chitosan nano-particles/ oregano essential oil (3.28–10.57МРа) [17]. Even if the TGGA composites (specifically the TGGA-2) shows to a comparable to conventional plastics such as polypropylene and textile waste (22–32 МРа) [3] and resin (15–55 МРа) [18]. However, it is lower
Further, elongation of the TGGA composites exabits higher than the starch-cellulose-based composites (4.0 ± 0.6%)[10], this is due to the plasticizer components (such as glycerol and acetic acid) that added during the development of the composite. The effect of the acetic acid and glycerol could enhance the elongation at the break of the composites [22, 23]. Particularly, the addition of acetic acid and glycerol in the polymerization of the cellulose-based materials causes lowering rigorousness, glass transition temperature, and increasing their elongation at break and augmenting the longevity, and compatibility of the composites [22, 24].But, elongation at break of the pure form of the Bovine gelatin from Bone (70.50%) [25], Chicken feet (33.97%)[26], and Chicken skin (265. 67%) [27] comparably, higher than the TGGA composites.
The water vapor permeability (WVP) of the TGGA composites is presented in Figure 2. The WVP can be affected by the concentration of plasticizing agents and the structure of the materials. The WVP of the TGGA composites highly relayed in the amount of the cellulose amount. It enhances the mechanical properties, lowers the water uptake ratio, moisture content, water vapor permeability, and tensile strength, and increases the elongation at break [24]. Additionally, adding of glycerol in development of cellulose based films can increase the EA from 6.9 to 25.4% as reported in literature [28]. Instead, it (glycerol) decreases the barrier properties by intercepting the hydrogen bond between the nano cellulose chains, facilitating the permeability of the gas molecules [29]. Therefore, a new trend should be set about the addition of glycerol between good plasticizing efficiency and weak gas barrier nature.
The shelf-life and quality of produced composite samples highly fluctuated with the thickness and the WVP. The WVP must be lowered to obtain excellent films. Side reactions (oxidation) and high microbial growth are amended due to the exalt of the WVP of the produced composites [30]. The WVP of the TGGA composites elaborated according to the current reports from the literature of Bovine gelatin from Bone (1.5×10–7)[25], Chicken feet (1.17×10– 10) [26], and Chicken skin (2.7×10–10) [27] composites. Overall, the WVP of TGGA composites afforded with the amount of the cellulose inversely relation. In all of the TGGA composite samples showed that when the residence time increased, the WVP of the samples decreased. In comparison, the WVP of TGGA-1 sample in 48, 96, 144 and 192 hrs is 7.66, 22, 63.48, and 96.5%, which showed higher than of the TGGA-2 (4.13%, 17.13%,
18.85% and 17.95%) and TGGA-3 (4.54%, 18.56%, 16.45%, and 15.95%) composite samples respectively. This is due to the thickness matter of the synthesized composites. The thicker material can block or restrict the vapor permeability compared to the thinner[10]. Therefore, the greater amount of cellulose and thickness in the film can decrease the WVP of the TGGA composites.
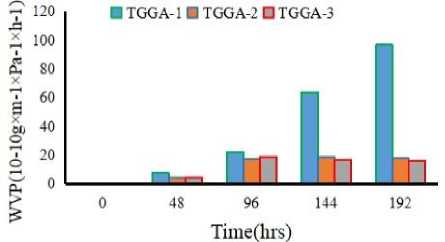
Figure 2. Water vapor permeability of the TCGA composites
The morphological image of the TGGA composites is presented in Figure 3. The magnification level of the microscope is 4х and 10х. The surface of the produced composites is highly and directly affected by the concentration, structure and particle size of the chunk cellulosic waste materials. The cotton fibers and matrices are visible in all the samples; however, more fiber and thick matrices are shown in the highest amount of the cellulose (7% w/w) in both 4х and 10х levels of magnification. More fibrous and matrix structure of the highest concentration is shown in the higher resolution of the microscope (10х). Further, all the samples displayed roughness, but there was no visible void area showed. The surface of the composites showed two color types such as black and white. The black image of the TGGA composites elaborated the cotton fiber of the cellulose textile waste, nevertheless, the white color shows the gelatin material. Besides, the morphological image of the composite samples is not uniform, this is due to the non-uniform particle size of the chunk cellulosic textile waste used during the raw material preparation. In addition to that, the low viscosity and unequal size of particle size are the main causes for the fibrous and non-uniform structure of the produced composite samples. The dense (edge of the samples) of the composite samples concentrated on one side of the sample, particularly at the bottom this happened during the casting because of the low viscosity.
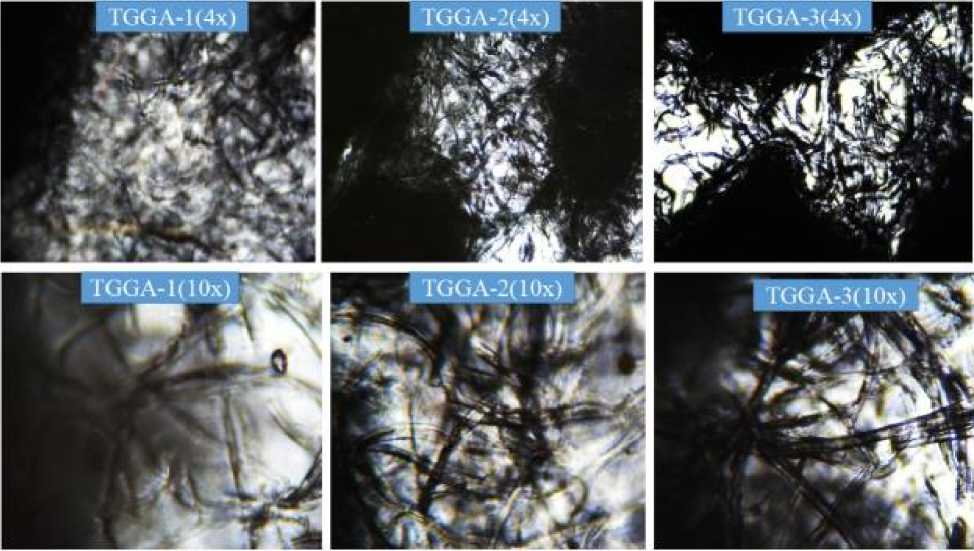
Figure 3. The morphological image of TGGA composites
Conclusions
A polymer composites (cellulosic textile waste, gelatin, glycerol, and acetic acid) were produced in this investigation. The study was fixed at 15% w/w of gelatin, 7 ml glycerol, and 6 ml acetic acid through the 2.5% w/w, 5% w/w, and 7%w/w of the textile cellulose waste. The Valorization of the textile waste for gelatin composite is still underdeveloped. The thickness, morphological structure, tensile strength, and water vapor permeability of the textile waste / gelatin/glycerol / acetic acid were examined. The morphological surface of the composites was highly concerned by the concentration of the textile waste. More fibrous and matrix
Меlеssе E.Y. et al. Proceedings of VSUET, 2024, vol. 86, no. 1, pp. structure of TGGA-2 and TGGA-3 composite shows in the higher resolution of the microscope (10х). Further, all the samples are displayed roughness, but there is no visible void area showed. The synthesized composites have shown good tensile strength, elongation rate, and water vapor preamble. The higher concentration of cellulose in the composite material enhanced lower tensile strength and elongation at break and it can be balanced by addition of the glycerol and acetic acid. All in one, the tensile strength, elongation at break, and water vapor permeability of the TGGA composites pointed out the feasible of the TGGA composites in the food packaging industry. At the last, this way of investigation is also a good trend for green economy policy, because it tries to emphasize waste recycling and minimization of solid environmental pollution.
Acknowledgment
All authors appreciate for Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Russian Biotechnological University.
Список литературы Valorization and characterization of the physicomechanical properties of textile waste for polymer composites
- Radhakrishnan S. Denim recycling. Textiles and Clothing Sustainability: Recycled and Upcycled Textiles and Fashion. 2017. pp. 79-125. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-2146-6_3
- Wallander M. Why textile waste should be banned from landfills. Retrieved October. 2012. vol. 5. pp. 2013.
- Gómez Gómez J., González Madariaga F., Rosa Sierra L., León Morán R. et al. Scrap denim-PP composites as a material for new product design. Systems&Design: Beyond Processes and Thinking. 2016. doi: 10.4995/ifdp.2016.3360
- Wang S., Zhang T., Zhang X., Ge S. et al. Development of 3D needled composite from denim waste and polypropylene fibers for structural applications. Construction and Building Materials. 2022. vol. 314. pp. 125583. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125583.
- Sezgin H., Kucukali-Ozturk M., Berkalp O.B., Yalcin-Enis I. Design of composite insulation panels containing 100% recycled cotton fibers and polyethylene/polypropylene packaging wastes. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2021. vol. 304. pp. 127132. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127132
- Temmink R., Baghaei B., Skrifvars M. Development of biocomposites from denim waste and thermoset bio-resins for structural applications. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2018. vol. 106. pp. 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.12.011
- Meng X., Fan W., Wan Mahari W.A., Ge S. et al. Production of three-dimensional fiber needle-punching composites from denim waste for utilization as furniture materials. Journal of cleaner production. 2021. vol. 281. pp. 125321. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125321
- Mendoza-Castillo D.I., Reynel-Ávila H.E., Bonilla-Petriciolet A., Silvestre-Albero J. Synthesis of denim waste-based adsorbents and their application in water defluoridation. Journal of Molecular Liquids. 2016. vol. 221. pp. 469-478. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.06.005
- Zhong T., Dhandapani R., Liang D., Wang J. et al. Nanocellulose from recycled indigo-dyed denim fabric and its application in composite films. Carbohydrate polymers. 2020. vol. 240. pp. 116283. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116283
- Haque A.N.M.A., Naebe M. Sustainable biodegradable denim waste composites for potential single-use packaging. Science of The Total Environment. 2022. vol. 809. pp. 152239. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152239
- Zhang X., Liu Y., Yong H., Qin Y. et al. Development of multifunctional food packaging films based on chitosan, TiO2 nanoparticles and anthocyanin-rich black plum peel extract. Food hydrocolloids. 2019. vol. 94. pp. 80-92. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.03.009
- Alizadeh Sani M., Tavassoli M., Salim S.A., Azizi-lalabadi M. et al. Development of green halochromic smart and active packaging materials: TiO2 nanoparticle-and anthocyanin-loaded gelatin/κ-carrageenan films. Food Hydrocolloids. 2022. vol. 124. pp. 107324. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107324
- Khodaei D., Álvarez C., Mullen A.M. Biodegradable packaging materials from animal processing co-products and wastes: An overview. Polymers. 2021. vol. 13. no. 15. pp. 2561. doi:10.3390/роlуm13152561
- Haghighi H., Biard S., Bigi F., de Leo R. et al. Comprehensive characterization of active chitosan-gelatin blend films enriched with different essential oils. Food Hydrocolloids. 2019. vol. 95. pp. 33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.019
- Hosseini S.F, Rezaei M., Zandi M., Farahmandghavi F. Development of bioactive fish gelatin/chitosan nanoparticles composite films with antimicrobial properties. Food chemistry. 2016. vol. 194. pp. 1266-1274. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.004.
- Martucci J.F., Ruseckaite R.A. Antibacterial activity of gelatin/copper (II)-exchanged montmorillonite films. Food hydrocolloids. 2017. vol. 64. pp. 70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.10.030
- Hosseini S.F., Rezaei M., Zandi M., Farahmandghavi F. Preparation and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles‐loaded fish gelatin‐based edible films. Journal of Food Process Engineering. 2016. vol. 39. no. 5. pp. 521-530. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.12246
- Temmink R., Baghaei B., Skrifvars M. Development of biocomposites from denim waste and thermoset bio-resins for structural applications. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2018. vol. 106. pp. 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.12.011
- Lee J.T., Kim M.W., Song Y.S., Kang T.J. et al. Mechanical properties of denim fabric reinforced poly (lactic acid). Fibers and Polymers. 2010. vol. 11. pp. 60-66. doi: 10.1007/s12221–010–0060–6
- Shankar S., Wang L.F., Rhim J.W. Effect of melanin nanoparticles on the mechanical, water vapor barrier, and antioxidant properties of gelatin-based films for food packaging application. Food Packaging and Shelf Life. 2019. vol. 21. pp. 100363. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100363
- Echegaray M., Mondragon G., Martin L., González A. et al. Physicochemical and mechanical properties of gelatin reinforced with nanocellulose and montmorillonite. Journal of Renewable Materials. 2016. vol. 4. no. 3. pp. 206-214. doi: 10.7569/JRM.2016.634106
- Ben Z.Y., Samsudin H., Yhaya M.F. Glycerol: Its properties, polymer synthesis, and applications in starch based films. European Polymer Journal. 2022. vol. 175. pp. 111377. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111377
- Li X., Zhang H., He L., Chen Z. et al. Flexible nanofibers-reinforced silk fibroin films plasticized by glycerol. Composites Part B: Engineering. 2018. vol. 152. pp. 305-310. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.08.136
- Ili Balqis A.M., Nor Khaizura M.A.R, Russly A.R., Nur Hanani Z.A. Effects of plasticizers on the physicochemical properties of kappa-carrageenan films extracted from Eucheuma cottonii. International journal of biological macromolecules. 2017. vol. 103. pp. 721-732. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.105
- Kalantarmahdavi M., Salari A., Pasdar Z., Amiryousefi M.R. Edible hyaluronic acid‐rich burger separator discs prepared from slaughterhouse waste. Food Science & Nutrition. 2022. vol. 10. no. 10. pp. 3515-3526. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2740.
- Fatima S., Mir M.I., Khan M.R., Sayyed R.Z. et al. The optimization of gelatin extraction from chicken feet and the development of gelatin based active packaging for the shelf-life extension of fresh grapes. Sustainability. 2022. vol. 14. no. 13. pp. 7881. doi: 10.3390/su14137881
- Said N.S., Sarbon N.M. Response surface methodology (RSM) of chicken skin gelatin based composite films with rice starch and curcumin incorporation. Polymer Testing. 2020. vol. 81. pp. 106161. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.106161
- Xiao C., Zhang Z., Zhang J., Lu Y. et al. Properties of regenerated cellulose films plasticized with α‐monoglycerides. Journal of applied polymer science. 2003. vol. 89. no. 13. pp. 3500-3505. doi: 10.1002/app.12509
- Hubbe M.A., Ferrer A., Tyagi P., Yin Y. et al. Nanocellulose in thin films, coatings, and plies for packaging applications: A review. BioResources. 2017. vol. 12. no. 1. pp. 2143-2233. doi: 10.15376/biores.12.1.2143–2233
- Tyuftin A.A., Kerry J.P. Gelatin films: Study review of barrier properties and implications for future studies employing biopolymer films. Food Packaging and Shelf Life. 2021. vol. 29. pp. 100688. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100688


