Ванадий в среде обитания как фактор риска негативной модификации клеточной гибели: научный обзор
Автор: Долгих О.В., Дианова Д.Г., Казакова О.А.
Журнал: Анализ риска здоровью @journal-fcrisk
Рубрика: Аналитические обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 4 (32), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Отражены результаты исследований по изучению влияния ванадия и его соединений, загрязняющих среду обитания человека, на нарушения состояния здоровья, ассоциированные с дисрегуляцией процесса клеточной гибели. Актуальность исследований последних десятилетий по раскрытию механизмов апоптоза в условиях воздействия химических веществ техногенной природы обусловлена биологической значимостью этого феномена в системе приспособления организма к действию факторов среды. Рассматриваются особенности механизмов апоптоза в условиях избыточного техногенного химического окружения соединениями ванадия. Проведен и представлен анализ научных материалов с формированием научной гипотезы в рамках данной тематики. Показан иммуномодулирующий эффект соединений ванадия, характеризующийся способностью модифицировать события апоптоза за счет смены режимов клеточной смерти (активация / ингибирование апоптоза), что обеспечивает адаптацию организма к изменяющимся условиям среды. Узкий диапазон концентрации ванадия между его эссенциальностью и токсичностью предопределяет разнонаправленные изменения в запуске и завершении апоптоза. Так, индуцированная активация апоптоза способствует развитию аутоиммунных, иммунопролиферативных процессов, в то же время ингибирование клеточной гибели может вызывать иммунодефицитные состояния, воспалительные реакции, нейродегенеративные заболевания. Показано модифицирующее влияние соединений ванадия на регуляцию функции митохондрий, изменение соотношения фосфорилирования / дефосфорилирования белковых продуктов, дисбаланс свободнорадикальных процессов, что в итоге нарушает баланс про- и антиапоптотических сигналов в клетке. Мониторинг показателей апоптоза, характеризующих особенности клеточной гибели в условиях экспозиции ванадия и его соединений, позволит своевременно выявить риск формирования предболезни и предотвратить нанесение вреда здоровью.
Риск, ванадий, среда обитания, клеточная гибель, механизм апоптоза, модификация митохондриальной активности, свободнорадикальное окисление, вред здоровью
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142226401
IDR: 142226401 | УДК: 616-097 | DOI: 10.21668/health.risk/2020.4.18
Vanadium in the environment as a risk factor causing negative modification of cell death (scientific review)
The review dwells on results obtained via examinations that focused on effects produced by vanadium and its compounds contaminating the environment on health disorders related to cell death deregulation. Research works that have been performed over the last decades and focused on revealing the essence of apoptosis mechanism under exposure to technogenic chemicals are truly vital due to this phenomenon having great biological significance within a system of a body trying to adapt to influences exerted by environmental factors. The present work focuses on apoptosis peculiarities under exposure to excess technogenic concentrations of vanadium compounds. Published research works have been analyzed, analysis results are outlined, and a scientific hypothesis has been formulated within the subject matter. We have described an immune-modulating effect produced by vanadium compounds that is able to modify apoptosis events due to changes in cell death modes (apoptosis activation/inhibition) and it provides body adaptation to changing environmental conditions. A range in vanadium concentrations between essential and toxic ones predetermines multi-directional changes in apoptosis induction and completion. Thus, induced apoptosis activation makes for development of autoimmune and immune-proliferative processes; at the same time, cell death inhibition can result in immune deficiency, inflammatory reactions, and neurodegenerative diseases. It was shown that vanadium compounds produced modifying effects on mitochondrial functions regulation, changes in phosphorilation/dephosphorilation ratio in protein products, and imbalance in free radical processes; all this ultimately disrupts a balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic signals in a cell. Monitoring over apoptosis parameters that characterize cell death under exposure to vanadium and its compounds will allow timely detecting risks of pre-nosology state occurrence and prevent damage to health.
Текст обзорной статьи Ванадий в среде обитания как фактор риска негативной модификации клеточной гибели: научный обзор
клеток – форма гибели клеток, которая возникает в результате активации одного или нескольких каскадов передачи сигнала и модулируется (регулируется) посредством фармакологических или генетических вмешательств. В понятие RCD входит апоптоз, аутофагия, аноикис, пироптоз, партанатоз, некроптоз [2].
Апоптоз, эволюционно консервативный процесс, необходим для поддержания клеточного гомеостаза в организме. Апоптоз регулирует баланс между пролиферацией, дифференцировкой и элиминацией ненужных клеток. Случайная гибель клеток (ACD) – моментальная и неконтролируемая форма клеточной гибели, при которой наблюдается полное разрушение плазматической мембраны, обусловленное экстремальными физическими, химическими или механическими факторами. Традиционно некроз рассматривается как случайное и нерегулируемое клеточное событие.
Химические вещества различной природы в условиях современных социальных, экономических и экологических условиях являются источниками постоянной опасности нарушения здоровья. Ванадий является одним из факторов загрязнения среды обитания. Как гаптен, он негативно влияет на сердечно-сосудистую, дыхательную, репродуктивную системы, оказывая нейротоксический и иммунотоксический эффекты [3]. Достижения в области медицины, такие как создание ванадийсодержащих ортодонтических / ортопедических имплантатов и разработка антипаразитарных, противовирусных, антибактериальных, антитромботиче-ских, антигипертензивных, гиполипидемических, спермицидных, противотуберкулезных, противоопухолевых, противодиабетических препаратов диктуют необходимость решения дискуссионных вопросов о влиянии ванадия на иммунную систему [4–9]. Неблагоприятные последствия влияния на здоровье человека химических факторов среды обитания могут проявляться не только развитием иммуноза-висимых заболеваний, но и срывом адаптационных возможностей организма. Одной из причин дезадаптации в условиях воздействия химических веществ является нарушение процесса запрограммированной гибели клетки. Установлено, что различные металлы и органические соединения модифицируют механизмы клеточной гибели [10–12]. Вместе с тем анализ и обобщение литературных данных выявил ряд противоречий о влиянии факторов различной химической природы на процесс клеточной гибели.
Несмотря на значительное количество опубликованных работ о процессах реализации летальной программы клетки, нет научно обоснованного представления о модифицирующем влиянии ванадия на апоптоз. В представленной работе изучены особенности апоптоза в условиях воздействия ванадия.
Ванадий (гаптен) – биологически значимый элемент, который принимает участие во многих фи- зиологических процессах [13–16]. Ванадий является ультрамикроэлементом и присутствует в следовых количествах во всех органах и тканях человека [9, 17]. В целом обобщенные данные показали, что содержание ванадия в организме составляет менее 10 нг/г массы тела [7]. В организме человека ванадий определяется в сердце, почках, печени, мозге, мышцах, костях, жировой ткани, семенниках, щитовидной железе, молозиве, грудном молоке, волосах [3, 7, 9, 18, 19].
Из окружающей среды в организм ванадий попадает главным образом через желудочно-кишечный тракт или бронхолегочную систему. В условиях производства не исключено попадание в организм ванадия и его соединений через кожу и слизистую оболочку глаз [20]. Показано, что ванадий, попавший в организм человека с пищей, в желудочно-кишечном тракте человека плохо абсорбируется (от 0,2 до 1,0 %). Большая часть ванадия, поступившая пероральным путем, превращается в труднорастворимый оксогидроксид ванадия (IV) VO(OH) 2 и выводится с фекалиями, в связи с чем не представляет потенциальной опасности для человека [21]. Однако снижение общего потребления жиров, углеводов и белков может влиять на всасывание ванадия [7].
Основной путь поступления ванадия в организм – через респираторный тракт. Главной мишенью в условиях ингаляционного поступления в организм ванадия являются органы дыхательной системы. Показано, что после хронического воздействия ванадия 0,28 мг/м3 у мышей и крыс уже через два дня отмечались изменения легочной ткани, характеризующиеся воспалением, фиброзом, гиперплазией клеток бронхиолярного и альвеолярного эпителия [22].
Причиной нарушения здоровья взрослого и детского населения является воздействие на организм высоких концентраций ванадия в атмосферном воздухе, а также в воздухе рабочей зоны работающих [4, 8]. Размер ванадийсодержащих частиц и растворимость соединений ванадия являются важными факторами при определении скорости поглощения ванадия в дыхательных путях.
В ранее выполненных исследованиях показано, что ванадий, поступивший в организм человека, обусловливает изменения иммунологической реактивности и повышает генетическую вариативность в популяции. У работающих на металлургическом предприятии, особенностью которого является наличие полного цикла выпуска феррованадия, при идентификации ванадия в крови на уровне верхней границы референтных значений отмечается повышение до 37 % количества апоптотических клеток и лимфоцитов, экспрессирующих CD25+-рецептор [13]. Гиперпродукция проапоптотических цитокинов и гиперэкспрессия раннего активационного маркёра CD25, а также рост уровня Annexin V-позитивных лимфоцитов вывялены у обследуемых детей, проживающих в условиях хронического аэрогенного воздействия V2O5, поступающего в атмосферный воздух с промышленными выбросами металлургических производств. Изучение полиморфизма генов в условиях экспозиции ванадия позволило выявить полиморфные изменения по гетерозиготному варианту генов цитохрома Р450 (CYP2D6rs38), копро-порфирингеназы (CPOXrs1131857), метилентетра-гидрофолатредуктазы (MTHFRrs1801133), пролиферации пероксисомы (PPARG rs4253778), отвечающих за 1-ю и 2-ю фазу детоксикации металлов. Например, частота мутантного гена CYP2D6rs38 превышала аналогичный показатель в 4,3 раза относительно значений, идентифицированных у не экспонированных ванадием взрослых. У детей, экспонированных ванадием, полиморфные изменения характеризовались гетерозиготным полиморфизмом генов детоксикации и оксигенации (CPOX, сульфтрансаминазы - SULT1rs9282861, глутатионтранс-феразы - GSTA4rs3 756980). Установлено, что у детей в условиях воздействия ванадия частота мутантного аллеля в четыре раза превышала аналогичную у не экспонированных ванадием детей.
Ванадий в организме в большей степени абсорбируется в форме ванадат-аниона, чем в форме ванадил-катиона. При ряде физиологических состояний ванадий в организме находится в виде ванадатов (степень окисления 5+), метаванадата (VО3-), и, вероятно, ортованадата (VО 4 3-). Ванадий обладает способностью изменять степень окисления при переходе из одной среды в другую, что приводит к спонтанному переходу ванадила в ванадат и обратно. Скорость, с которой соединения ванадия трансформируются в организме, и виды, в которые он трансформируется, значительно влияют на процент поглощенного ванадия. Важной характеристикой ванадия является его способность к видообразованию, которое зависит от наличия в организме биологических или синтетических хелаторов, биогенных лигандов [23].
Попав в системный кровоток, ванадий связывается с белками плазмы, в частности с трансферрином и альбумином, низкомолекулярными лигандами, такими как цитрат, оксалат, лактат, фосфат, глицин, гистидин, а также с гемоглобином, и при высоких концентрациях – с иммуноглобулином G [6, 8, 24, 25]. В течение первых 24 ч после проникновения в организм содержание ванадия в крови снижается примерно на 30 % [26]. Между тем способность ванадатов заменять фосфаты в костной ткани приводит к накоплению и длительному сохранению ванадия в костях – более месяца [27].
Проникновение ванадия внутрь клетки происходит за счет транспортных структур мембраны (транспортеров, фосфатных или сульфат-ионных каналов) или рецепторопосредованного эндоцито-за [3]. Поскольку ванадий обладает высокой способностью изменять состояние окисления или обмениваться лигандами (H2O, CO, H+, OH–, Cl–, PO43– и др.) в зависимости от микроокружения, находя- щиеся рядом молекулы могут оказывать значительное влияние на транспорт ванадия через клеточные мембраны. Внутриклеточное распределение ванадия зависит от соединения ванадия, попавшего в организм. В клетке при взаимодействии ванадия с глутатионом, аскорбиновой кислотой или никотина-мидадениндинуклеотидом (NADH) происходит его восстановление от V5+ до V4+ [8, 9, 28]. При этом внутри клетки преобладает ванадил (четырехвалентное состояние). Внутриклеточные окислители, такие как NAD+, O2 и O22-, могут окислять ванадил обратно в ванадат [3]. Взаимопревращение между видами ванадия в клетке (в основном V+4/V+5 и в меньшей степени в V+3) происходит постоянно. Различные компартменты клетки имеют различный рН, в связи с чем обладают неодинаковой способностью поглощать и накапливать ванадий [7]. Внутри клетки соединения ванадия могут либо оказывать прямое влияние на различные органеллы и изменять их функциональную активность, либо могут взаимодействовать с широким спектром белковых молекул и модифицировать внутриклеточные сигнальные каскады.
У мышей в условиях аэрогенного поступления ванадия (V) через 6 ч отмечался воспалительный процесс в легких, через 72 ч – значительное повышение апоптотических клеток. Абсорбируемый ванадий вызывал NADH-оксидазную активность митохондрий, отвечающих за реализацию апоптоза [28]. В экспериментальных моделях in vitro и in vivo установлен дозозависимый эффект ортованадата натрия (Na3VO4) на анапластическую карциному щитовидной железы, который характеризовался остановкой клеточного цикла в фазе G2/M и снижением мембранного потенциала митохондрий (Ψ) [29]. Доказано, что декаванадат, накапливаясь в митохондриях, изменяет активность антиоксидантных ферментов, а также вызывает деполяризацию митохондриальных мембран [30]. На клеточной линии человеческой холангиокарциномы (РС-1) показано, что V5+ вызывает ингибирование цепи переноса электронов и индукцию апоптоза, а также коллапс митохондриального потенциала (ΔΨ) [4]. Обработка изолированных митохондрий печени крыс пятивалентным ванадием (диапазон концентраций 25–200 мкМ) вызывала высвобождение цитохрома из митохондрий [31]. Снижение мембранного потенциала митохондрий на 50 % происходило при инкубации клеток линии гепатоцеллюлярной карциномы человека (HepG2) в течение 72 ч с VO (250 мкг/мл) [32]. Кроме того, ванадий может напрямую влиять на внутреннюю мембрану митохондрий, что впоследствии может нарушать перенос электронов между дыхательными комплексами, вызывая избыточное образование активных форм кислорода (ROS) в митохондриях [33]. К значительной генерации ROS приводит активация р53. Следует отметить, что возможен переход части молекул самого р53 в митохондрию, что сопровождается выхо- дом из митохондрии цитохрома (bcl-2 предотвращал эти эффекты) [34]. Показано взаимодействие между р53 и МАРК-каскадом в регуляции клеточного цикла. Установлена роль р53 в инициации некроза при непосредственном взаимодействии с белком митохондриального матрикса циклофилином D (CYPD), одного из компонентов митохондриальной поры [1]. Ванадий способен вызывать высвобождения Cа2+ из внутриклеточных депо, концентрации которого являются важным регулятором открытия митохондриальной поры [7]. Митохондрии и эндоплазматический ретикулум рассматриваются как емкостные кальциевые депо. Изменение уровня кальция в клетке приводит к активации / ингибированию различных клеточных механизмов, в том числе реализации механизмов клеточной гибели. Накапливаясь в лизосомах митохондрий, оксид ванадия (V) V2O5 стимулировал запуск процесса аутофагии в клетках рака молочной железы (MCF-7) [14]. Экспериментально показано, что в зависимости от времени воздействия оксид ванадия в клетках культуры MCF-7 вызывал как прооксидантные эффекты, так и антиоксидантные свойства. Митохондриям принадлежит ключевая роль в контроле клеточного гомеостаза кальция и генерации ROS, что указывает на участие митохондрий в регуляции различных форм клеточной гибели. Именно на уровне митохондрии происходит «выбор» клеткой механизма реализации летальной программы (апоптоз, некроз). Инициация апоптоза происходит при умеренном повреждении мембран митохондрии, в то время как при значительных повреждениях митохондрии клетка гибнет по пути некроза.
Ванадий является элементом, который находится в различных состояниях окисления и участвует в реакциях, приводящих к образованию свободных радикалов. Независимо от источников происхождения и причин, вызвавших генерацию свободных радикалов, эти молекулярные частицы могут взаимодействовать с нуклеиновыми кислотами, белками, липидами и углеводами. Дисфункция клетки, вызванная окислительным стрессом, часто ассоциирована с повреждениями ДНК, что может обусловливать гибель клетки. Международное агентство по изучению рака (МАИР) причисляет пятиокись ванадия к категории 2В – «вероятно канцерогенные для человека». Показано, что в системе in vivo ванадий вызывает разрыв отдельных нитей ДНК, хромосомные аберрации (структурные и численные) и окисление азотистых оснований [35]. В норме генетически дефектные клетки должны устраняться посредством апоптоза. Существует предположение о том, что недостаточность апоптоза приводит к злокачественной трансформации пораженных клеток и метастазированию опухолей. На клеточной линии гепатоцеллюлярной карциномы человека показано, что ванадий вызывает повреждение ядерной и митохондриальной ДНК и снижает жизнеспособность клеток [36]. Опосредованное негативное влияние ванадия на ДНК в результате генерации активных форм кислорода характеризуется окислением дезоксирибозы, модификацией азотистых оснований, сшиванием и разрывами цепей. Однако другие исследователи отрицают канцерогенные свойства у ванадия [22, 37]. В зависимости от предлагаемой экспериментальной модели, концентрации ванадия и другие ванадийсодержащие химические соединения проявляют противоопухолевые или канцерогенные свойства [21, 38]. Очевидно, невосприимчивость клеток к апоптозу или угнетение данного процесса играют ключевую роль в развитии канцерогенеза.
Соединения ванадия и ванадий ингибируют активность Н+,K+-АТФазы, Na+,K+-АТФазы и Са2+,Mg2+-АТФазы. В зависимости от типа АТФаз наблюдается широкий диапазон их сродства к ванадату [39]. Показано, что относительно других ванадатов, наиболее мощным ингибитором Са2+-АТФазы является декаванадат [V 10 O 28 ]6 [40]. АТФазы являются важнейшими регуляторами множества клеточных функций, в том числе клеточной гибели [41]. В частности неапоптотическая форма клеточной гибели аутосис (autosis) является критически зависимым от активности Na+,K+-АТФазы [1]. Доказано наличие у аденозинтрифосфатаз сигнальной функции. Например, непосредственное взаимодействие между натрий-калиевой аденозинтрифосфатазой (Na+,K+-АТФазой) и киназой Src-семейства инициирует фосфорилирование ряда сигнальных каскадов, контролирующих клеточную гибель. Установлено ингибирующее действие метаванадата и ортованадата на Na+,K+-АТФазу в нейрональных клетках, полученных из гиппокампа крыс [38].
Способность ванадата замещать фосфат указывает на их сходство между собой. Многие из полезных или вредных эффектов ванадата, по крайней мере частично, обусловлены схожестью между собой двух анионов. Ванадат и фосфат – это группы с тетраэдрической морфологией и почти сферическим распределением заряда во внешней сфере. Ванадат, таким образом, может легко заменить фосфат в таких ферментах, как фосфатазы и киназы [8]. Однако суммарный ионный заряд основных частиц, присутствующих при pH = 7, различен – два в случае фосфата и один в ванадате, что может привести к различным взаимодействиям с электрофильными группами. Наличие низколежащей d-орбитали и координационного числа больше четырех, обычно пять и шесть, ведет к одноэлектронному восстановлению ванадата. В результате повышается фиксация ванадатов с боковыми цепями аминокислотных остатков белков [42]. В физиологически значимых концентрациях отличительной особенностью ванадата от фосфата является состояние протонирования: при pH = 7 ванадат почти исключительно присутствует в своей дипро-тонированной форме, в то время как фосфат существует в виде смеси моно- и дигидрофосфат [8]. В условиях избыточного содержания ванадия в орга- низме изменение активности ферментативных каскадов в клетке приводит к изменению проводимости апоптотического сигнала.
Протеинкиназы (фосфотрансферазы, киназы) и фосфатазы являются ферментами, катализирующими соответственно фосфорилирование (добавление фосфатной группы) и дефосфорилирование (удаление фосфатной группы) субстрата. В условиях экспозиции ванадием ингибирование или активация ферментов, участвующих в переносе фосфатной группы, достигается в результате антагонизма «ванадат – фосфат». Вследствие более прочного связывания ванадата, чем фосфат, с фосфатсодержащими ферментами, ванадат способен изменять активность ферментов фосфорилирования / дефосфорилирования. Киназы и фосфатазы отвечают за активность сигнальных путей, реализующих каскад физиологических эффектов, вследствие чего данные ферменты отвечают за регуляцию клеточных ответов. Дисбаланс фосфорилирования и дефосфорилирования может негативно влиять на жизненно важные для функционирования клетки процессы – выживание или гибель. Экспериментально установлено, что ванадат ингибирует активность фосфатаз [43]. Между тем ванадий не является специфическим ингибитором всех фосфатаз, механизмы ингибирования ванадийсодержащими химическими комплексами многих ферментов, катализирующих дефосфорилирование субстрата, остаются неясными [7]. Показано, что комплекс оксованадия (IV) (Na2[VO(Glu)2 (CH3OH)] (Glu = glutamate)) в диапазоне концентрации 0,21–0,37 мкМ инактивировал протеинтирозин-фосфатазу 1B (PTP1B) [44]. PTP1B непосредственно взаимодействует с инсулиновым рецептором и де-фосфорилирует тирозиновые остатки, являясь негативным регулятором инсулинового сигнального пути [3]. Сверхэкспрессия данного фермента отмечена при HER2-положительном типе рака. Протеин-тирозинфосфатаза 1B опосредованно потенцирует активность Src (цитозольная тирозинкиназа, не связанная с рецептором). Отдельные соединения ванадия, в частности перванадаты, в низких концентрациях обладают окислительными свойствами и поэтому могут непосредственно активировать Src [45]. Src-киназы способны ингибировать протеазную активность каспазы-8 [46]. При инактивации каспаз FASL способен инициировать гибель клетки по пути некроза. Ванадий, изменяя активность Na+,K+-АТФазы, оказывает опосредованное влияние на Src. Через Src-киназу происходит активация факторов транскрипции, таких как AP-1 и NF-kB, а также ми-тогенактивированных протеинкиназ (МАРК-киназы) и мембраносвязанных белков (Ras), участвующих в передаче сигнала Ras/MAPK-сигнального каскада. Посредством активации Ras/MAP-киназного пути происходит передача сигнала с клеточной мембраны к ядру, тем самым оказывается влияние на экспрессию широкого спектра генов. Результатом такой активации протеинкиназного сигнального каскада является изменение синтеза белковых продуктов, функциональной активности митохондрий и др. [47]. Также Ras является составной частью мультибелко-вого комплекса, регулирующего открытие пор мембраны митохондрии. При формировании данного комплекса молекула Ras поступает из цитоплазмы, тогда как белки семейства BCL-2 – изнутри. Ванадий, изменяя баланс между про- и антиапоптотиче-скими членами семейства BCL-2, нарушая функциональную активность МАР-киназного каскада и факторов транскрипции, а также повышая генерацию активных форм кислорода, модифицирует пути реализации механизмов гибели клетки и, таким образом, играет значимую роль в регуляции жизненного цикла клетки.
Ванадий и соединения ванадия вызывают дисбаланс в системе «окисление – антиокисление» посредством образования ROS. Активные формы кислорода являются ключевым звеном в инициации внутриклеточной сигнальной трансдукции и передачи сигналов на уровне отдельных молекул, вследствие чего значимо изменяют активность МАР-ки-назных каскадов. Модификация фосфорилирования (активация или инактивация) МЕК, ERK1/2, PI3K, p38, JNK ванадием модифицирует запуск и осуществление апоптоза [35]. Доказано влияние внутриклеточного белка р53 на активацию или инактивацию MEK, ERK1/2, PI3K, p38, JNK, TNF-alpha и NF - κB [48]. Молекулярные перестройки в PI3K и МАРК каскадах под воздействием ванадия являются причиной изменения клеточной выживаемости. В результате ингибирования передачи сигнала через PI3K/Akt/mTOR каскад индуцируется FAS-опосредованный апоптоз [49]. Активность фосфатидилинози-тол-3-киназы (PI3K) прямо коррелировала с концентрацией ионов кальция. CD95 не обладает какой-либо ферментативной активностью, однако из-за способности образовывать межбелковые (белок – белок) взаимодействия способен активировать различные сигнальные пути [50]. FAS-индуцированные сигнальные каскады ведут к активации NF-κB, МАРК, инициации апоптоза или некроза [51]. Одним из иммуномодулирующих эффектов ERK1/2, фосфорилирование которой осуществляется рядом с клеточной мембраной, заключается в активации В-лимфо-цитов и Т-лимфоцитов [52]. CD25-рецептор является маркёром ранней активации, CD95-рецептор – маркёром поздней активации Т-лимфоцитов.
В исследованиях, где использовались фармакологические ингибиторы MEK1/2 киназ, доказано участие ERK1/2 в модификации функций митохондрий, участвующих в регуляции и амплификации апоптотического каскада. Чаще всего активация протеинкиназ семейства ERK ассоциирована с клеточным выживанием и стимуляцией пролиферации. ERK протеинкиназы способствуют прохождению клеточного цикла, инактивируя один из его ингибиторов – протеинкиназу MYTI. Сигнальный путь ERK может быть активирован в ответ на сигналы, поступающие от рецепторов, связанных с G-белком, через рецепторную тирозинкиназу, T-клеточный рецептор, N-метил-D-аспартатный рецептор и рецепторы лектина С-типа [52]. Совокупность сигнальных каскадов образует сеть, в которой сигнальный путь ERK сообщается с различными сигнальными путями через множественные разветвления и коллатерали, а его регуляция осуществляется по принципу обратной связи и отношением киназа-субстрат [52].
Ряд исследователей продемонстрировали анти-апоптотический эффект ERK1/2, между тем другие – проапоптотический эффект [7, 53]. В эксперименте на линии клеток меланомного происхождения (А375) показано, что отдельные соединения ванадия (неорганический анион ванадат (V) и оксованадий (IV) комплекс [VO (1.2-диметил-3-гидрокси-4 (1)H) –пири-динонат)2]) в различных концентрациях (4,7 и 2,6 мкМ соответственно) вызывали апоптоз клеток и остановку клеточного цикла. Обработка данными ванадийсодержащими соединениями (четырех- и пятивалентным ванадием) клеток линии А375 ингибировала фосфорилирование ERK примерно на 80 %, вызывая инактивацию киназ МАРК-каскада [54]. В клетках меланомы противоопухолевое действие ванадия обусловлено его способностью индуцировать апоптоз посредством генерации ROS. Экспериментально установлено, что добавление в культуру ванадия (V5+) 100 мкмоль/л-1 снижало жизнеспособность эпителиальных клеток яйцевода. Между тем обработка культивируемых клеток SB203580 (ингибитор р38 МАРК) и U0126 (ингибитор ERK1/2) отменяла апоптоз-индуцирующее влияние ванадия [48]. Инкубация эпителиальных клеток яйцевода с ингибиторами МАРК увеличивала активность каталазы и глутатионпероксидазы (до 89 %), а также предотвращала увеличение концентрации малонового диальдегида. Показано, что окислительный стресс в эпителиальных клетках яйцевода, вызванный ванадием, частично обусловлен активацией p38 MAPK и JNK/Nrf2, что снижает экспрессию детоксицирующих ферментов 2-й фазы. Сигнальный каскад MEK/ERK регулирует экспрессию bcl-2, предотвращающего образования трансмембранных пор в митохондриях [55]. ROS опосредованно через ERK1/2 способны активировать каспазу-3, повышать экспрессию bаk и bax. Будучи активированными, киназы ERK1/2 и JNK способны участвовать в координации работы редокс-чувствительной сигнальной системы Keap1/Nrf2/ARE. Показано, что стимуляция р38 МАК и JNK оказывает в большинстве случаев проапоптотическое воздействие. Установлено, что во многих типах клеток JNK активируется посредством FAS [56]. Между тем только при длительной активации JNK возможна инициация и осуществление апоптоза. В эксперименте показано, что р38 МАРК сигнальный каскад вовлечен в регуляцию факторов транскрипции – р53, NF-κB, Stat1, а также медиаторов апоптоза - bcl-2, Cdc25A [56]. Доказано уча- стие p38 MAPK и JNK в регуляции активности FAS/FASL-системы. p38 MAPK играет важную роль в регуляции ранней экспрессии FASL и FAS-опосредованной активации каспаз. Активированные каспазы стимулируют JNK для дальнейшего усиления экспрессии FASL [57].
Аналитический обзор российских и зарубежных научных источников показал, что в настоящее время накоплен значительный материал о модифицирующем влиянии ванадия на активацию программы апоптоза. Между тем многие вопросы, касающиеся, возможно, новых механизмов запуска и изменения клеточной гибели ванадием, остаются дискуссионными. Ряд исследователей продемонстрировали апоптоз-индуцирующие свойства у ванадия и способность инициировать некроз [54, 58–60]. Однако другие ученые доказали способность ванадия ингибировать реализацию апоптоза [61]. Вместе с тем на современном этапе медико-биологических наук большинство авторов придерживается мнения, что в условиях воздействия ванадия апоптоз - это основной путь клеточной гибели [35]. При этом необходимо уточнить, что большая часть выполненных исследований, посвященных изучению модифицирующего влияния ванадия на механизмы апоптоза, выполнена на клеточных линиях опухолевых клеток.
В системе in vivo оксованадий в диапазоне концентраций от 1,0 до 5,0 мг/кг массы тела снижал уровень FAS-зависимого апоптоза [61]. Обработка SOV (ортованадат натрия), который относится к ингибиторам тирозиновых фосфопротеинфосфатаз, зависимо от дозы тормозила развитие апоптоза клеток оральной сквамозной клеточной (плоскоклеточной) карциномы (Cal27) [60]. Обработка V 2 O 5 естественных киллеров (NK-92MI) вызывала гиперэкспрессию FAS, FASL и CD25. Инициированный ванадием процесс перекисного окисления липидов мембраны способствует изменению экспрессии мембранных рецепторов. Повышения уровня FAS-лиганда зарегистрировано при концентрации пентокид ванадия на уровне 50 мМ, максимальные значения экспрессии CD95-антигена зафиксированы при концентрации 100 мМ, а CD25-антигена – 400 мМ [49]. Продемонстрировано ингибирование FAS-опосредованного апоптоза, обусловленного фосфорилированием про-теинкиназы B (PKB), в условиях экспозиции комплексных соединений ванадия (IV) [48]. Дисбаланс антиапоптотических и проапоптотических членов семейства белков BCL-2, активация онкопротеина c-fos, расщепление Поли(АДФ-рибоза)PARP и дозозависимая активация апоптоза наблюдались при обработке ванадил сульфатом человеческих эпидермальных кератиноцитов (HaCaT) [62]. На клеточных линиях показана способность ванадия инициировать рецепторзависимый и р53-регулируемый апоптоти-ческий сигнал в клетке. Повышение активности инициаторной каспазы-8 в клеточной линии фибросаркомы мыши (L929) и уровня экспрессии р53
в клеточной линии гепатоцеллюлярной карциномы человека (HepG2) вызывало добавление в культуры ванадия (IV) [59]. Ванадий, вызывая образование активных форм кислорода, запускал механизмы аутофагии, некроптоза и митотической катастрофы в клеточной линии метастатической аденокарциномы поджелудочной железы (AsPC-1) [63]. В системе in vitro (суспензия лейкоцитов, полученная из периферической крови практически здоровых детей, экспонированных ванадием) ванадий при экспозиционной дозе 0,0005 мкг/см3 вызывал клеточную гибель по механизму некроза. Наночастицы пентоксида ванадия (30–60 нм) ингибировали пролиферацию клеток меланомы (B16F10), карциномы легкого (A549), поджелудочной железы (PANC1). Интернализация V2O5, внутриклеточно генерируя ROS и вызывая активацию белка p53 и подавление белка сурвивина в раковых клетках, приводила к процессу апоптоза. Однако не отмечено выраженного цитотоксического эффекта ванадия по отношению к нормальным клеткам (культура фибробластических почечных клеток NRK-49F, клеточная линия, полученная из эмбриональных почек человека HEK 293, культура клеток яичников китайского хомячка CHO-K1) [64]. Очевидно, модифицирующее влияние ванадия на клеточную гибель зависит от многих составляющих: степени окисления ванадия, экспозиционной дозы, времени воздействия, видовой и органной принадлежности клеток, стадии дифференцировки, стадии зрелости и функционального состояния клетки, что требует соответствующей интерпретации полученных результатов [13, 21, 27, 36, 44, 54, 58, 60].
Для полного понимания модифицирующего влияния ванадия на апоптоз необходимо дальнейшее углубленное изучение механизмов клеточной гибели с учетом фундаментальных закономерностей процесса, а также, принимая во внимание особенности реализации апоптоза, обусловленные влиянием гаптена. С целью экстраполяции воздействия ванадия на здоровый организм в перспективе существует необходимость экспериментального моделирования апоптоза не только на клетках опухолевых культур, но и более широкого использования в системе in vitro клеток или линий клеток здорового человека. Возможно, узкий диапазон концентрации ванадия между его эссенциальностью и токсичностью предопределяет разнонаправленные изменения в запуске и завершении апоптоза [16, 38]. В свою очередь, следует учитывать и особенности объекта (организма: возраст, пол, генетические особенности метаболизма ксенобиотиков и т.д.; клетки: тканевая принадлежность, функциональная активность и т.д.), на который оказывает воздействие ванадий [3, 4, 7, 8, 31–33, 37, 48, 62, 63]. Гипотетический механизм клеточной гибели, модифицированный соединениями ванадия техногенной природы, представлен на рисунке.
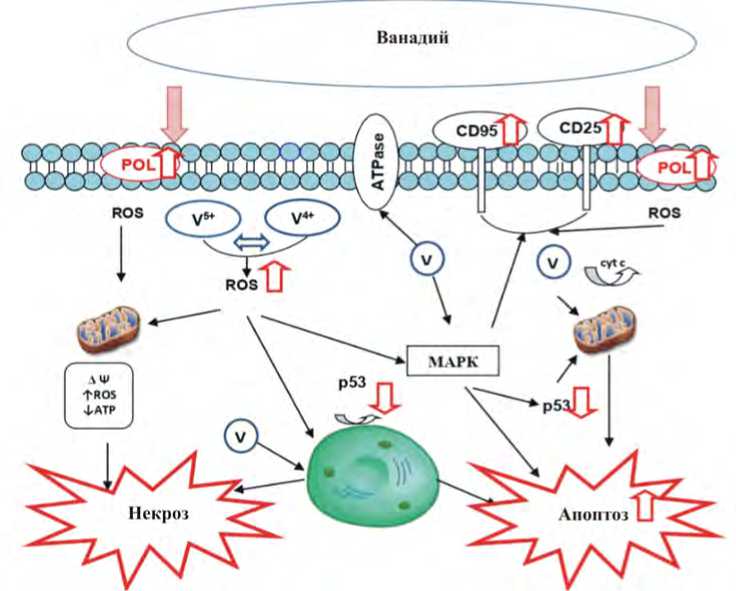
Рис. Гипотетический механизма клеточной гибели, модифицированный соединениями ванадия техногенной природы: POL – перекисное окисление липидов, МАРК– митогенактивируемые протеинкиназные каскады; ROS – активные формы кислорода; cyt c – цитохром с ; ΔΨ – коллапс митохондриального потенциала
Контроль клеточной популяции в многоклеточном организме – это важный биологический процесс, который дает возможность организму избавиться от потенциально опасных клеток. Активация апоптоза способствует развитию аутоиммунных, иммунопро-лиферативных процессов, ингибирование клеточной гибели может вызывать иммунодефицитные состояния, воспалительные реакции, нейродегенеративные заболевания. При воздействии химических веществ, загрязняющих окружающую среду, увеличивается вероятность нарушения клеточной гибели. Особую озабоченность вызывает опасность для здоровья, которой подвергаются многие взрослые и дети по причине загрязнения среды обитания ванадием и его соединениями вследствие техногенной деятельности человека. Опасность ванадия определяется тем, что он обладает способностью модифицировать механизмы реализации апоптоза. Так, вызванное ванадием перекисное окисление липидов, имеющее цепной характер, приводит к изменениям биофизических свойств мембран (повышение проницаемости и изменение текучести), накоплению свободных радикалов и изменению мембранной рецепции. Внутри клеток соединения ванадия и ванадий при развитии метаболических реакций в различных клеточных компар-тментах также могут вызывать образование активных форм кислорода. ROS на уровне отдельных белковых молекул, действуя на них как ингибитор или актива- тор, влияют на биохимические и физиологические механизмы внутриклеточной сигнализации. Иммуномодифицирующий эффект ванадия связан с блокированием / активированием активности ферментов путем создания комплексов с их субстратами и конкуренцией с фосфатом в фосфатсвязывающих сайтах ферментов, что в итоге формирует изменения звеньев внутриклеточных каскадов передач [9]. Очевидно, ванадий имеет значительный иммунотерапевтический потенциал, так как способен модифицировать процессы, приводящие к жизни или смерти клетки, что обусловливает актуальность дальнейшего изучения и анализа молекулярных механизмов и сигнальных каскадов в условиях воздействия гаптена (ванадия). Мониторирование биологических показателей, определяющих клеточную гибель в условиях экспозиции ванадия и его соединений, дает возможность своевременно идентифицировать риск формирования предболезни и предотвратить нанесение вреда здоровью. Проведенный анализ научной литературы позволил выявить особенности и определить вероятные механизмы реализации сценария клеточной гибели в условиях окружения ванадием техногенного происхождения.
Финансирование. Исследование не имело спонсорской поддержки
Список литературы Ванадий в среде обитания как фактор риска негативной модификации клеточной гибели: научный обзор
- Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018 / L. Galluzzi, I. Vitale, S.A. Aaronson, J.M. Abrams, D. Adam, P. Agostinis, E.S. Alnemri, L. Altucci [et al.] // Cell Death & Differentiation. - 2018. - Vol. 25, № 3. - Р. 486-541. DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
- Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015 / L. Galluzzi, J.M. Bravo-San Pedro, I. Vitale, S.A. Aaronson, J.M. Abrams, D. Adam, E.S. Alnemri, L. Altucci [et al.] // Cell Death & Differentiation. - 2015. - Vol. 22, № 1. - Р. 58-73. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.137
- Zwolak I. Protective effects of dietary antioxidants against vanadium-induced toxicity: A Review // Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. - 2020. - Vol. 7, № 2020. - P. 1490316. DOI: 10.1155/2020/1490316
- Vanadium dioxide nanocoating induces tumor cell death through mitochondrial electron transport chain interruption / J. Li, M. Jiang, H. Zhou, P. Jin, K.M.C. Cheung, P.K. Chu, K.W.K. Yeung // Global Challenges. - 2019. - Vol. 3, № 3. - P. 1800058. DOI: 0.1002/gch2.201800058
- Exploring oxidovanadium (IV) homoleptic complexes with 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as prospective antitrypanosomal agents / G. Scalese, I. Machado, I. Correia, J.C. Pessoa, L. Bilbao, L. Perez-Diaz, D. Gambino // NJC. - 2019. - № 45. - Р. 17756-17773. DOI: 10.1039/c9nj02589h
- Rehder D. Vanadium. Its role for humans // Met. Ions Life Sci. - 2013. - № 13. - Р. 139-169.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-7500-8_5
- Vanadium in biological action: chemical, pharmacological aspects, and metabolic implications in diabetes mellitus / S. Treviño, A. Díaz, E. Sánchez-Lara, B.L. Sanchez-Gaitan, J.M. Perez-Aguilar, E. González-Vergara // Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. - 2019. - № 188. - P. 68-98.
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-018-1540-6
- Rehder D. The role of vanadium in biology // Metallomics. - 2015. - № 7. - Р. 730-742.
- DOI: 10.1039/C4MT00304G
- Воробьева Н.М., Федорова Е.В., Баранова Н.И. Ванадий: биологическая роль, токсикология и фармакологическое применение // Биосфера. - 2013. - Т. 5, № 1. - С. 77-96.https://elibrary.ru/pic/1pix.gif
- Dolgikh O.V., Zaitseva N.V., Dianova D.G. Regulation of apoptotic signal by strontium in immunocytes // Biochemistry (Moscow) Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology. - 2016. - Vol. 10, № 2. - Р. 158-161.
- DOI: 10.1134/S1990747816010049
- Heavy metals contaminating the environment of a progressive supranuclear palsy cluster induce tau accumulation and cell death in cultured neurons / C. Alquezar, J.B. Felix, E. McCandlish, B.T. Buckley, D. Caparros-Lefebvre, C.M. Karch, L.I. Golbe, A.W. Kao // Scientific Reports. - 2020. - Vol. 10, № 569. - P. 12.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-56930-w
- Anti-cancer effect of gallic acid in presence of low level laser irradiation: ROS production and induction of apoptosis and ferroptosis / K. Khorsandi, Z. Kianmehr, Z. Hosseinmardi, R. Hosseinzadeh // Cancer Cell. Int. - 2020. - Vol. 20, № 18. - P. 18.
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-1100-y
- Дианова Д.Г., Долгих О.В. Экспозиция ванадием как фактор негативной активации лимфоцитов // Уральский медицинский журнал. - 2012. - Т. 102, № 10. - С. 78-80.
- Paradigm of Vanadium pentoxide nanoparticle-induced autophagy and apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells / P.R.P. Suma, R.A. Padmanabhan, S.R. Telukutla, R. Ravindran, A.K.G. Velikkakath, C.D. Dekiwadia, W. Paul, S.J. Shenoy [et al.] // BioRxiv. - 2019. - № 18. - P. 33.
- DOI: 10.1101/810200
- MacGregor J.A., White D.J., Williams A.L. The limitations of using the NTP chronic bioassay on vanadium pentoxide in risk assessments // Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. - 2020. - № 113. - P. 104650.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104650
- Adam M.S.S., Elsawy H. Biological potential of oxo-vanadium salicylediene amino-acid complexes as cytotoxic, antimicrobial, antioxidant and DNA interaction // J. Photoch. Photobio. B. - 2018. - № 184. - P. 34-43.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.05.002
- Ванадийсодержащие соединения: химия, синтез, инсулиномиметические свойства / Е.В. Федорова, А.В. Бурякина, Н.М. Воробьёва, Н.И. Баранова // Биомедицинская химия. - 2014. - Т. 60, № 4. - С. 416-429.
- Estimation of the daily soil/dust (SD) ingestion rate of children from Gansu Province, China via hand-to-mouth contact using tracer elements / J. Ma, L.B. Pan, Q. Wang, C.Y. Lin, X.L. Duan, H. Hou // Environ. Geochem. Health. - 2018. - Vol. 40, № 1. - Р. 295-301.
- DOI: 10.1007/s10653-016-9906-1
- Occurrence of selected elements (Ti, Sr, Ba, V, Ga, Sn, Tl, and Sb) in deposited dust and human hair samples: implications for human health in Pakistan / S.A.M.A.S. Eqani, Z.I. Tanveer, C. Qiaoqiao, A. Cincinelli, Z. Saqib, S.I. Mulla, N. Ali, I.A. Katsoyiannis [et al.] // ESPR. - 2018. - Vol. 25, № 13. - Р. 12234-12245.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-017-0346-y
- Пятиконнова А.М., Поздняков А.М., Саркитов Ш.С. Токсическое действие ванадия и его соединений // Успехи современного естествознания. - 2013. - № 9. - С. 120.
- Biochemical and medical importance of vanadium compounds / J. Korbecki, I. Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Gutowska, D. Chlubek // Acta. Biochim. Pol. - 2012. - Vol. 59, № 2. - P. 195-200.
- Toxicological review of vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) (CAS No. 1314-62-1). In Support of Summary Information on the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). - Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2011. - Р. 210.
- Why antidiabetic vanadium complexes are not in the pipeline of "big pharma" drug research? A Critical Review / T. Scior, J.A. Guevara-Garcia, Q.T. Do, P. Bernard, S. Lauferd // Сurr Med. Chem. - 2016. - Vol. 23, № 25. - Р. 2874-2891.
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867323666160321121138
- On the transport of vanadium in blood serum / D. Sanna, M. Serra, G. Micera, E. Garribba // Inorg. Chem. - 2009. - Vol. 48, № 13. - Р. 5747-5757.
- DOI: 10.1021/ic802287s
- Speciation of potential anti-diabetic vanadium complexes in real serum samples / D. Sanna, M. Serra, G. Micera, E. Garribba // J. Inorg. Biochem. - 2017. - № 173. - Р. 2-65.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.04.023
- Vivo complexes with antibacterial quinolone ligands and their interaction with serum proteins / D. Sanna, V. Ugone, G. Sciortino, P. Buglyó, Z. Bihari, P.L. Parajdi Losonczi, E. Garribba // Dalton Trans. - 2018. - Vol. 47, № 7. - Р. 2164-2182.
- DOI: 10.1039/c7dt04216g
- Rehder D. The (Biological) Speciation of Vanadate (V) as Revealed by 51V NMR - A Tribute on Lage Pettersson and His Work // J. Inorg. Biochem. - 2015. - Vol. 147. - Р. 25-31.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.12.014
- Vanadium-induced apoptosis and pulmonary inflammation in mice: role of reactive oxygen species / L. Wang, D. Medan, R. Mercer, D. Overmiller, S. Leornard, V. Castranova, X. Shi, M. Ding [et al.] // J. Cell. Physiol. - 2003. - Vol. 195, № 1. - Р. 99-107.
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.10232
- Sodium orthovanadate inhibits growth and triggers apoptosis of human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo / Q.Y.W. Jiang, D. Li, M. Gu, K. Liu, L. Dong, C. Wang, H. Jiang, W. Dai // Oncol. Lett. - 2019. - Vol. 17, № 5. - Р. 4255-4262. 10.1016/S0168-8278 (00) 80101-4
- DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(00)80101-4
- Irving E., Stoker A.W. Vanadium compounds as PTP inhibitors // Molecules. - 2017. - Vol. 22, № 12. - P. 2269.
- DOI: 10.3390/Molecules22122269
- Toxicity of vanadium on isolated rat liver mitochondria: A new mechanistic approach / M.-J. Hosseini, F. Shaki, M. Ghazi-Khansari, J. Pourahmad // Metallomics. - 2013. - Vol. 5, № 2. - Р. 152-156.
- DOI: 10.1039/c2mt20198d
- Toxicity of native and oxovanadium (IV/V) galactomannan complexes on HepG2 cells is related to impairment of mitochondrial functions / M.M. Cunha-de Padua, S.M.S.C. Cadena, C.L.O. Petkowicz, G.R. Martinez, M. Merlin-Rocha, A.L. Merce, G.R. Noleto // Carbohydrate Polymers. - 2017. - Vol. 1, № 173. - Р. 665-675.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.027
- Vanadium compounds induced mitochondria permeability transition pore (PTP) opening related to oxidative stress / Y. Zhao, L. Ye, H. Liu, Q. Xia, Y. Zhang, X. Yang, K. Wang // J. Inorg. Biochem. - 2010. - Vol. 104, № 4. - Р. 371-378.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio
- Молекулярные маркеры каспаза-зависимого и митохондриального апоптоза: роль в развитии патологии и в процессах клеточного старения / А.С. Дятлова, А.В. Дудков, Н.С. Линькова, В.Х. Хавинсон // Успехи современной биологии. - 2018. - Т. 138, № 2. - С. 126-137.
- Oxidative stress and vanadium [Электронный ресурс] / M. Rojas-Lemus, P. Bizarro-Nevares, N. López-Valdez, A. González-Villalva, G. Guerrero-Palomo, M.E. Cervantes-Valencia, O. Tavera-Cabrera, N. Rivera-Fernández [et al.] // IntechOpen. - 2020. - URL: https: //www.intechopen.com/online-first/oxidative-stress-and-vanadium (дата обращения: 29.09.2020).
- In vitro study of the protective effect of manganese against vanadium-mediated nuclear and mitochondrial DNA damage / L. Rivas-García, J.L. Quiles, L.A. Varela, M. Arredondo, P. Lopez, A.R. Dieguez, P. Aranda, J. Llopis [et al.] // Food and Chemical Toxicology. - 2019. - № 135. - P. 110900.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.110900
- Vanadium pentoxide: Use of relevant historical control data shows no evidence for carcinogenic response in F344/N rats / T.B. Starr, J.A. Macgregor, K.D. Ehman, A.I. Kikiforov // Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. - 2012. - Vol. 64, № 1. - Р. 155-160.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2012.06.017
- Essentiality and toxicity of vanadium supplements in health and pathology / K. Gruzewska, A. Michno, T. Pawelczyk, H. Bielarczyk // J. Physiol. Pharmacol. - 2014. - Vol. 65, № 5. - Р. 603-611.
- An EXAFS Approach to the Study of Polyoxometalate-Protein Interactions: The Case of Decavanadate-Actin / M.P.M. Marques, D. Gianolio, S. Ramos, L.A.E. Batista de Carvalho, M. Aureliano // Inorg Chem. - 2017. - Vol. 56, № 18. - Р. 10893-10903.
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01018
- Rb (+) occlusion stabilized by vanadate in gastric H(+)/K(+)-ATPase at 25 °C / M.R. Montes, A.J. Spiaggi, J.L. Monti, F. Cornelius, C. Olesen, P.J. Garrahan, R.C. Rossi // Biochim. Biophys. Acta. - 2011. - Vol. 1808, № 1. - Р. 316-322.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.08.022
- Silencing of proteasome 26S subunit ATPase 2 regulates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration / J. He, J. Xing, X. Yang, C. Zhang, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, X. Xu, H. Wang [et al.] // Chemotherapy. - 2019. - Vol. 64, № 3. - Р. 146-154.
- DOI: 10.1159/000502224
- Inhibitory effects of decavanadate on several enzymes and Leishmania tarentolae in vitro / T.L. Turner, V.H. Nguyen, C.C. McLauchlan, Z. Dymon, B.M. Dorsey, J.D. Hooker, M.A. Jones // J. Inorg. Biochem. - 2011. - № 108. - Р. 96-104.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.09.009
- Vanadium-phosphatase complexes: Phosphatase inhibitors favor the trigonal bipyramidal transition state geometries / C.C. McLauchlan, B.J. Peters, G.R. Willsky, D.C. Crans // Coord. Chem. Rev. - 2015. - Vol. 301-302, № 15. - Р. 163-199.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.12.012
- Inhibition protein tyrosine phosphatases by an oxovanadium glutamate complex, Na2[VO (Glu)2(CH3OH)] (Glu = glutamate) / L. Lu, S. Wang, M. Zhu, Z. Liu, M. Guo, S. Xing, X. Fu // Biometals. - 2010. - Vol. 23, № 6. - Р. 1139-1147.
- DOI: 10.1007/s10534-010-9363-8
- Vanadium compounds as pro-inflammatory agents: effects on cyclooxygenases / J. Korbecki, I. Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Gutowska, D. Chlubek // Int. J. Mol. Sci. - 2015. - Vol. 16, № 6. - Р. 12648-12668.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160612648
- CD95/FAS, Non-apoptotic signaling pathways, and kinases / M.L. Gallo, A. Poissonnier, P. Blanco, P. Legembre // Front. Immunol. - 2017. - Vol. 27, № 8. - P. 1216.
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01216
- Lingrel J.B. The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabainbinding site of the Na, K-ATPase // Annu. Rev. Physiol. - 2010. - Vol. 17, № 72. - Р. 395-412.
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135725
- Vanadate oxidative and apoptotic effects are mediated by the MAPK-Nrf2 pathway in layer oviduct magnum epithelial cells / J. Wang, X. Huang, K. Zhang, X. Mao, X. Ding, Q. Zeng, S. Bai, Y. Xuan [et al.] // Metallomics. - 2017. - Vol. 9, № 11. - Р. 1562-1575.
- DOI: 10.1039/c7mt00191f
- Vanadium pentoxide prevents NK-92MI cell proliferation and IFNγ secretion through sustained JAK3 phosphorylation / F. Gallardo-Vera, D. Diaz, M. Tapia-Rodriguez, G.T. Fortoul, F. Masso, E. Rendon-Huerta, L.F. Montaño // J. of Immunotoxicol. - 2016. - Vol. 13, № 1. - Р. 27-37.
- DOI: 10.3109/1547691X.2014.996681
- Guegan J.-P., Legembre P. Nonapoptotic functions of FAS/CD95 in the immuneresponse // FEBS. - 2018. - Vol. 285, № 5. - Р. 809-827.
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14292
- Activation of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways contributes to the inflammatory responses, but not cell injury, in IPEC-1 cells challenged with hydrogen peroxide / K. Xiao, C. Liu, Z. Tu, Q. Xu, S. Chen, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Zhang [et al.] // Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. - 2020. - № 2020. - P. 5803639.
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5803639
- Comprehensive analysis of ERK1/2 substrates for potential combination immunotherapies / L. Yang, L. Zheng, W.J. Chng, J.L. Ding // Trends Pharmacol. Sci. - 2019. - Vol. 40, № 11. - Р. 897-910.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.09.005
- Wortzel I., Seger R. The ERK cascade: distinct functions within various subcellular organelles // Genes Cancer. - 2011. - Vol. 2, № 3. - Р. 195-209.
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601911407328
- Antiproliferative activity of vanadium compounds: effects on the major malignant melanoma molecular pathways / M. Pisano, C. Arru, M. Serra, G. Galleri, D. Sanna, E. Garribba, G. Palmieri, C. Rozzo // Metallomics. - 2019. - Vol. 11, № 10. - Р. 1687-1699.
- DOI: 10.1039/C9MT00174C
- MAP kinases and prostate cancer / G. Rodrıguez-Berriguete, B. Fraile, P. Martınez-Onsurbe, G. Olmedilla, R. Paniagua, M. Royuela // J. Signal. Transduction. - 2012. - № 2012. - P. 169170.
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/169170
- Мисюрин В.А. Структура и свойства основных рецепторов и лигандов внешнего пути апоптоза // Российский биотерапевтический журнал. - 2015. - Т. 14, № 2. - С. 23-30.
- Regulation of FAS Ligand expression during activationinduced cell death in T cells by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase / B.J. Zhang, J.-X. Gao, K. Salojin, Q. Shao, M. Grattan, C. Meagher, D.W. Laird, T.L. Delovitch // J. Exp. Med. - 2000. - Vol. 191, № 6. - Р. 1017-1030.
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.6.1017
- Sodium orthovanadate inhibits growth and triggers apoptosis of human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo / Q.Y.W. Jiang, D. Li, M. Gu, K. Liu, L. Dong, C. Wang, H. Jiang, W. Dai // Oncol. Lett. - 2019. - Vol. 17, № 5. - Р. 4255-4262.
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10090
- Vanadium complex induced apoptosis in hepg2 cells by the up-regulation of p53, p21, and caspase-8 / H.B. Aliabad, S.K. Falahati-Pour, H. Ahmadirad, M. Mohamadi, M.R. Hajizadeh, G. Bakhshi, M. Mahmoodi // WCRJ. - 2019. - № 6. - P. e1293.
- DOI: 10.32113/wcrj_20195_1293
- Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway by a vanadyl compound mediates its neuroprotective effect in mouse brain ischemia / N. Shioda, T. Ishigami, F. Han, S. Moriguchi, M. Shibuya, Y. Iwabuchi, K. Fukunaga // Neuroscience. - 2007. - Vol. 148, № 1. - Р. 221-229.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.040
- Vanadium-induced apoptosis of HaCaT cells is mediated by c-fos and involves nuclear accumulation of clusterin / S. Markopoulou, E. Kontargiris, C. Batsi, T. Tzavaras, I. Trougakos, D.A. Boothman, E.S. Gonos, E. Kolettas // FEBS J. - 2009. - Vol. 276, № 14. - Р. 3784-3799.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07093.x
- Халил А., Джемесон М. Ортованадат натрия ингибирует пролиферацию и запускает апоптоз в клетках оральной сквамозной клеточной карциномы in vitro // Биохимия. - 2017. - Т. 82, № 2. - С. 258-265.
- New oxidovanadium (IV) coordination complex containing 2-methylnitrilotriacetate ligands induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines / S. Kowalski, D. Wyrzykowski, S. Hac, M. Rychlowski, M.W. Radomski, I. Inkielewicz-Stepniak // IJMS. - 2019. - Vol. 20, № 2. - P. 261.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020261
- Anti-angiogenic vanadium pentoxide nanoparticles for the treatment of melanoma and their in vivo toxicity study / S. Das, A. Roy, A.K. Barui, M.M.A. Alabbasi, M. Kuncha, R. Sistla, B. Sreedhar, C.R. Patra // Nanoscale. - 2020. - Vol. 12, № 14. - Р. 7604-7621.
- DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00631a
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L. [et al.]. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell. Death & Differentiation, 2018, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 486-541.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
- Galluzzi L., Bravo-San Pedro J.M., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L. [et al.]. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell. Death & Differentiation, 2015, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 58-73.
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.137
- Zwolak I. Protective effects of dietary antioxidants against vanadium-induced toxicity: A Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev, 2020, vol. 7, no. 2020, pp. 1490316.
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1490316
- Li J., Jiang M., Zhou H., Jin P., Cheung K.M.C., Chu P.K., Yeung K.W.K. Vanadium dioxide nanocoating induces tumor cell death through mitochondrial electron transport chain interruption. Global Challenges, 2019, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 1800058. DOI: 0.1002/gch2.201800058
- Scalese G., Machado I., Correia I., Pessoa J.C., Bilbao L., Perez-Diaz L., Gambino D. Exploring oxidovanadium (IV) homoleptic complexes with 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as prospective antitrypanosomal agents. NJC, 2019, no. 45, pp. 17756-17773.
- DOI: 10.1039/c9nj02589h
- Rehder D. Vanadium. Its role for humans. Met. Ions Life Sci, 2013, no. 13, pp. 139-169.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-7500-8_5
- Treviño S., Díaz A., Sánchez-Lara E., Sanchez-Gaitan B.L., Perez-Aguilar J.M., González-Vergara E. Vanadium in biological action: chemical, pharmacological aspects, and metabolic implications in diabetes mellitus. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res, 2019, no. 188, pp. 68-98.
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-018-1540-6
- Rehder D. The role of vanadium in biology. Metallomics, 2015, no. 7, pp. 730-742.
- DOI: 10.1039/C4MT00304G
- Vorob'eva N.M., Fedorova E.V., Baranova N.I. Vanadium: Its biological role, toxicology, and pharmacological applications. Biosfera, 2013, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 77-96 (in Russian).https://elibrary.ru/pic/1pix.gif
- Dolgikh O.V., Zaitseva N.V., Dianova D.G. Regulation of apoptotic signal by strontium in immunocytes. Biochemistry (Moscow) Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology, 2016, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 158-161.
- DOI: 10.1134/S1990747816010049
- Alquezar C., Felix J.B., McCandlish E., Buckley B.T., Caparros-Lefebvre D., Karch C.M., Golbe L.I., Kao A.W. Heavy metals contaminating the environment of a progressive supranuclear palsy cluster induce tau accumulation and cell death in cultured neurons. Scientific Reports, 2020, vol. 10, no. 569, pp. 12.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-56930-w
- Khorsandi K., Kianmehr Z., Hosseinmardi Z., Hosseinzadeh R. Anti-cancer effect of gallic acid in presence of low level laser irradiation: ROS production and induction of apoptosis and ferroptosis. Cancer Cell. Int, 2020, vol. 20, no. 18, pp. 18.
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-1100-y
- Dianova D.G., Dolgikh O.V. Exposure of vanadium as a factor of adverse activation of lymphocytes. Ural'skii meditsinskii zhurnal, 2012, vol. 102, no. 10, pp. 78-80 (in Russian).
- Suma P.R.P., Padmanabhan R.A., Telukutla S.R., Ravindran R., Velikkakath A.K.G., Dekiwadia C.D., Paul W., Shenoy S.J. [et al.]. Paradigm of Vanadium pentoxide nanoparticle-induced autophagy and apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. bioRxiv, 2019, no. 18, pp. 33.
- DOI: 10.1101/810200
- MacGregor J.A., White D.J., Williams A.L. The limitations of using the NTP chronic bioassay on vanadium pentoxide in risk assessments. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2020, no. 113, pp. 104650.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104650
- Adam M.S.S., Elsawy H. Biological potential of oxo-vanadium salicylediene amino-acid complexes as cytotoxic, antimicrobial, antioxidant and DNA interaction. J. Photoch. Photobio. B., 2018, no. 184, pp. 34-43.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.05.002
- Fedorova E.V., Buryakina A.V., Vorob'eva N.M., Baranova N.I. The vanadium compounds: chemistry, synthesys, insulinomimetic properties. Biomeditsinskaya khimiya, 2014, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 416-429 (in Russian).
- Ma J., Pan L.B., Wang Q., Lin C.Y., Duan X.L., Hou H. Estimation of the daily soil/dust (SD) ingestion rate of children from Gansu Province, China via hand-to-mouth contact using tracer elements. Environ. Geochem. Health, 2018, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 295-301.
- DOI: 10.1007/s10653-016-9906-1
- Eqani S.A.M.A.S., Tanveer Z.I., Qiaoqiao C., Cincinelli A., Saqib Z., Mulla S.I., Ali N., Katsoyiannis I.A. [et al.]. Occurrence of selected elements (Ti, Sr, Ba, V, Ga, Sn, Tl, and Sb) in deposited dust and human hair samples: implications for human health in Pakistan. ESPR, 2018, vol. 25, no. 13, pp. 12234-12245.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-017-0346-y
- Pyatikonnova A.M., Pozdnyakov A.M., Sarkitov Sh.S. Toksicheskoe deistvie vanadiya i ego soedinenii [Toxic effects produced by vanadium and its compounds]. Uspekhi sovremennogo estestvoznaniya, 2013, no. 9, pp. 120 (in Russian).
- Korbecki J., Baranowska-Bosiacka I., Gutowska I., Chlubek D. Biochemical and medical importance of vanadium compounds. Acta. Biochim. Pol., 2012, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 195-200.
- Toxicological review of vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) (CAS No. 1314-62-1). In Support of Summary Information on the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). Washington, DC, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Publ., 2011, 210 p.
- Scior T., Guevara-Garcia J.A., Do Q.T., Bernard P., Lauferd S. Why antidiabetic vanadium complexes are not in the pipeline of "big pharma" drug research? A Critical Review. Curr. Med. Chem., 2016, vol. 23, no. 25, pp. 2874-2891.
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867323666160321121138
- Sanna D., Serra M., Micera G., Garribba E. On the transport of vanadium in blood serum. Inorg. Chem, 2009, vol. 48, no. 13, pp. 5747-5757.
- DOI: 10.1021/ic802287s
- Sanna D., Serra M., Micera G., Garribba E. Speciation of potential anti-diabetic vanadium complexes in real serum samples. J. Inorg. Biochem, 2017, no. 173, pp. 2-65.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.04.023
- Sanna D., Ugone V., Sciortino G., Buglyó P., Bihari Z., Parajdi Losonczi P.L., Garribba E. Vivo complexes with antibacterial quinolone ligands and their interaction with serum proteins. Dalton Trans, 2018, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 2164-2182.
- DOI: 10.1039/c7dt04216g
- Rehder D. The (Biological) Speciation of Vanadate (V) as Revealed by 51V NMR - A Tribute on Lage Pettersson and His Work. J. Inorg. Biochem, 2015, vol. 147, pp. 25-31.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.12.014
- Wang L., Medan D., Mercer R., Overmiller D., Leornard S., Castranova V., Shi X., Ding M. [et al.]. Vanadium-induced apoptosis and pulmonary inflammation in mice: role of reactive oxygen species. J. Cell. Physiol, 2003, vol. 195, no. 1, pp. 99-107.
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.10232
- Jiang Q.Y.W., Li D., Gu M., Liu K., Dong L., Wang C., Jiang H., W Dai. Sodium orthovanadate inhibits growth and triggers apoptosis of human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Lett, 2019, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 4255-4262.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(00)80101-4
- Irving E., Stoker A.W. Vanadium compounds as PTP inhibitors. Molecules, 2017, vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 2269.
- DOI: 10.3390/Molecules22122269
- Hosseini M.-J., Shaki F., Ghazi-Khansari M., Pourahmad J. Toxicity of vanadium on isolated rat liver mitochondria: A new mechanistic approach. Metallomics, 2013, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 152-156.
- DOI: 10.1039/c2mt20198d
- Cunha-de Padua M.M., Cadena S.M.S.C., Petkowicz C.L.O., Martinez G.R., Merlin-Rocha M., Merce A.L., Noleto G.R. Toxicity of native and oxovanadium (IV/V) galactomannan complexes on HepG2 cells is related to impairment of mitochondrial functions. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017, vol. 1, no. 173, pp. 665-675.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.027
- Zhao Y., Ye L., Liu H., Xia Q., Zhang Y., Yang X., Wang K. Vanadium compounds induced mitochondria permeability transition pore (PTP) opening related to oxidative stress. J. Inorg. Biochem, 2010, vol. 104, no. 4, pp. 371-378.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio
- Dyatlova A.S., Dudkov A.V., Lin'kova N.S., Khavinson V.Kh. Molecular markers of caspase-dependent and mitochondrial apoptosis: the role of pathology and cell senescence. Uspekhi sovremennoi biologii, 2018, vol. 138, no. 2, pp. 126-137 (in Russian).
- Rojas-Lemus M., Bizarro-Nevares P., López-Valdez N., González-Villalva A., Guerrero-Palomo G., Cervantes-Valencia M.E., Tavera-Cabrera O., Rivera-Fernández N. [et al.]. Oxidative stress and vanadium. IntechOpen, 2020. Available at: https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/oxidative-stress-and-vanadium (29.09.2020).
- Rivas-García L., Quiles J.L., Varela L.A., Arredondo M., Lopez P., Dieguez A.R., Aranda P., Llopis J. [et al.]. In vitro study of the protective effect of manganese against vanadium-mediated nuclear and mitochondrial DNA damage. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2019, no. 135, pp. 110900.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.110900
- Starr T.B., Macgregor J.A., Ehman K.D., Kikiforov A.I. Vanadium pentoxide: Use of relevant historical control data shows no evidence for carcinogenic response in F344/N rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2012, vol. 64, no. 1, pp. 155-160.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2012.06.017
- Gruzewska K., Michno A., Pawelczyk T., Bielarczyk H. Essentiality and toxicity of vanadium supplements in health and pathology. J. Physiol. Pharmacol, 2014, vol. 65, no. 5, pp. 603-611.
- Marques M.P.M., Gianolio D., Ramos S., Batista de Carvalho L.A.E., Aureliano M. An EXAFS Approach to the Study of Polyoxometalate-Protein Interactions: The Case of Decavanadate-Actin. Inorg. Chem., 2017, vol. 56, no. 18, pp. 10893-10903.
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01018
- Montes M.R., Spiaggi A.J., Monti J.L., Cornelius F., Olesen C., Garrahan P.J., Rossi R.C. Rb(+) occlusion stabilized by vanadate in gastric H(+)/K(+)-ATPase at 25°C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 2011, vol. 1808, no. 1, pp. 316-322.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.08.022
- He J., Xing J., Yang X., Zhang C., Zhang Y., Wang H., Xu X., Wang H. [et al.]. Silencing of proteasome 26S subunit ATPase 2 regulates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration. Chemotherapy, 2019, vol. 64, no. 3, pp. 146-154.
- DOI: 10.1159/000502224
- Turner T.L., Nguyen V.H., McLauchlan C.C., Dymon Z., Dorsey B.M., Hooker J.D., Jones M.A. Inhibitory effects of decavanadate on several enzymes and Leishmania tarentolae in vitro. J. Inorg. Biochem., 2011, no. 108, pp. 96-104.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.09.009
- McLauchlan C.C., Peters B.J., Willsky G.R., Crans D.C. Vanadium-phosphatase complexes: Phosphatase inhibitors favor the trigonal bipyramidal transition state geometries. Coord. Chem. Rev., 2015, vol. 301-302, no. 15, pp. 163-199.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.12.012
- Lu L., Wang S., Zhu M., Liu Z., Guo M., Xing S., Fu X. Inhibition protein tyrosine phosphatases by an oxovanadium glutamate complex, Na2[VO(Glu)2(CH3OH)](Glu = glutamate). Biometals, 2010, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 1139-1147.
- DOI: 10.1007/s10534-010-9363-8
- Korbecki J., Baranowska-Bosiacka I., Gutowska I., Chlubek D. Vanadium compounds as pro-inflammatory agents: effects on cyclooxygenases. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 12648-12668.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160612648
- Gallo M.L., Poissonnier A., Blanco P., Legembre P. CD95/FAS, Non-apoptotic signaling pathways, and kinases. Front. Immunol, 2017, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 1216.
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01216
- Lingrel J.B. The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabainbinding site of the Na, K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 2010, vol. 17, no. 72, pp. 395-412.
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135725
- Wang J., Huang X., Zhang K., Mao X., Ding X., Zeng Q., Bai S., Xuan Y. [et al.]. Vanadate oxidative and apoptotic effects are mediated by the MAPK-Nrf2 pathway in layer oviduct magnum epithelial cells. Metallomics, 2017, vol. 9, no. 11, pp. 1562-1575.
- DOI: 10.1039/c7mt00191f
- Gallardo-Vera F., Diaz D., Tapia-Rodriguez M., Fortoul G.T., Masso F., Rendon-Huerta E., Montaño L.F. Vanadium pentoxide prevents NK-92MI cell proliferation and IFNγ secretion through sustained JAK3 phosphorylation. J. of Immunotoxicol, 2016, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 27-37.
- DOI: 10.3109/1547691X.2014.996681
- Guegan J.-P., Legembre P. Nonapoptotic functions of FAS/CD95 in the immuneresponse. FEBS, 2018, vol. 285, no. 5, pp. 809-827.
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14292
- Xiao K., Liu C., Tu Z., Xu Q., Chen S., Zhang Y., Wang X., Zhang J. [et al.]. Activation of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways contributes to the inflammatory responses, but not cell injury, in IPEC-1 cells challenged with hydrogen peroxide. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev, 2020, no. 2020, pp. 5803639.
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5803639
- Yang L., Zheng L., Chng W.J., Ding J.L. Comprehensive analysis of ERK1/2 substrates for potential combination immunotherapies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci, 2019, vol. 40, no. 11, pp. 897-910.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.09.005
- Wortzel I., Seger R. The ERK cascade: distinct functions within various subcellular organelles. Genes Cancer, 2011, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 195-209.
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601911407328
- Pisano M., Arru C., Serra M., Galleri G., Sanna D., Garribba E., Palmieri G., Rozzo C. Antiproliferative activity of vanadium compounds: effects on the major malignant melanoma molecular pathways. Metallomics, 2019, vol. 11, no. 10, pp. 1687-1699.
- DOI: 10.1039/C9MT00174C
- Rodrıguez-Berriguete G., Fraile B., Martınez-Onsurbe P., Olmedilla G., Paniagua R., Royuela M. MAP kinases and prostate cancer. J. Signal. Transduction, 2012, no. 2012, pp. 169170.
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/169170
- Misyurin V.A. Structure and functions of main apoptosis receptors and ligands. Rossiiskii bioterapevticheskii zhurnal, 2015, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 23-30 (in Russian).
- Zhang B.J., Gao J.-X., Salojin K., Shao Q., Grattan M., Meagher C., Laird D.W., Delovitch T.L. Regulation of FAS Ligand expression during activationinduced cell death in T cells by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J. Exp. Med, 2000, vol. 191, no. 6, pp. 1017-1030.
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.6.1017
- Jiang Q.Y.W., Li D., Gu M., Liu K., Dong L., Wang C., Jiang H., Dai W. Sodium orthovanadate inhibits growth and triggers apoptosis of human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Lett, 2019, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 4255-4262.
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10090
- Aliabad H.B., Falahati-Pour S.K., Ahmadirad H., Mohamadi M., Hajizadeh M.R., Bakhshi G., Mahmoodi M. Vanadium complex induced apoptosis in hepg2 cells by the up-regulation of p53, p21, and caspase-8. WCRJ, 2019, no. 6, pp. e1293.
- DOI: 10.32113/wcrj_20195_1293
- Shioda N., Ishigami T., Han F., Moriguchi S., Shibuya M., Iwabuchi Y., Fukunaga K. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway by a vanadyl compound mediates its neuroprotective effect in mouse brain ischemia. Neuroscience, 2007, vol. 148, no. 1, pp. 221-229.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.040
- Markopoulou S., Kontargiris E., Batsi C., Tzavaras T., Trougakos I., Boothman D.A., Gonos E.S., Kolettas E. Vanadium-induced apoptosis of HaCaT cells is mediated by c-fos and involves nuclear accumulation of clusterin. FEBS J, 2009, vol. 276, no. 14, pp. 3784-3799.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07093.x
- Khalil A., Dzhemeson M. Sodium orthovanadate inhibits proliferation and triggers apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Biokhimiya, 2017, vol. 82, no. 2, pp. 258-265 (in Russian).
- Kowalski S., Wyrzykowski D., Hac S., Rychlowski M., Radomski M.W., Inkielewicz-Stepniak I. New oxidovanadium (IV) coordination complex containing 2-methylnitrilotriacetate ligands induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines. IJMS, 2019, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 261.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020261
- Das S., Roy A., Barui A.K., Alabbasi M.M.A., Kuncha M., Sistla R., Sreedhar B., Patra C.R. Anti-angiogenic vanadium pentoxide nanoparticles for the treatment of melanoma and their in vivo toxicity study. Nanoscale, 2020, vol. 12, no. 14, pp. 7604-7621.
- DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00631a


