Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида на ростовые показатели, уровень окислительного стресса и фотосинтетических пигментов ряски малой (Lemna minor L.) после воздействия тяжелых металлов
Автор: Боднарь Ирина Сергеевна, Чебан Евгения Васильевна
Журнал: Принципы экологии @ecopri
Рубрика: Оригинальные исследования
Статья в выпуске: 1 (35), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Одним из механизмов снижения токсического действия при избытке тяжелых металлов является продукция у растений фитогормонов брассиностероидов. Экзогенное применение 24-эпибрассинолида оказывало положительное влияние на рост и развитие различных видов растений при действии абиотических факторов. В данном исследовании изучены возможности 24-эпибрассинолида смягчать фитостресс у ряски малой при избыточном поступлении меди, кадмия, цинка, стронция. Предварительное культивирование лабораторной культуры ряски малой в среде с 24-эпибрассинолидом позволило увеличить скорость роста и снизить долю поврежденных растений в экспериментах с цинком (6.3-79 мкмоль/л), медью (12.6 мкмоль/л) и кадмием (5, 12.6 мкмоль/л). Ряд эффективности при экзогенном поступлении брассиностероида по снижению токсичности тяжелых металлов для ряски малой выглядит следующим образом: Zn > Cd > Cu > Sr. На фоне улучшения ростовых и морфометрических параметров ослабление окислительного стресса произошло только в экспериментах с высокой концентрацией стронция (1580 мкмоль/л). Уровень малонового диальдегида (МДА) у растений при совместном воздействии 24-эпибрассинолида и ионов меди был выше, чем только при добавлении металла (p ≤ 0.05). Произошло изменение содержания каротиноидов и хлорофиллов. Применение брассиностероида позволило уменьшить потери хлорофилла а и каротиноидов при действии 12.6 мкмоль/л кадмия и цинка (р ≤ 0.05). Но при отдельных концентрациях тяжелых металлов (например, 12.6 мкмоль/л меди) у предварительно обработанных 24-эпибрассинолидом растений содержание фотоассимилирующих пигментов и каротиноидов было ниже, чем у необработанных (р ≤ 0.05).
Ряска малая, 24-эпибрассинолид, тяжелые металлы, стронций, кадмий, медь, цинк, окислительный стресс
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147231286
IDR: 147231286 | УДК: 581.1
Текст научной статьи Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида на ростовые показатели, уровень окислительного стресса и фотосинтетических пигментов ряски малой (Lemna minor L.) после воздействия тяжелых металлов
Проблема устойчивости растений к антропогенному загрязнению окружающей среды является одной из приоритетных в современной экспериментальной биологии. Промышленное производство – это основная причина избыточного поступления тяжелых металлов в природные воды. Весомый вклад вносят сельское хозяйство, автотранспорт, бытовой мусор. Например, чрезвычайно токсичный для живых организмов кадмий широко используется в элементах питания, красках, его ежегодное потребление превышает 2500 тонн (Faulkner, Schwartz, 2009$ Yuan et al., 2019). Особенно опасно попадание поллютантов в водотоки, это способствует распространению загрязняющих веществ на большие расстояния. С развитием общества возрастает антропогенная нагрузка, появляются новые источники поступления тяжелых металлов в окружающую среду, например, не так давно возникла проблема с утилизацией использованных электронных устройств. Сейчас их доля составляет 1–3 % от всех бытовых отходов, но в скором времени производство подобного мусора может существенно возрасти (Akram et al., 2019$ Brevik et al., 2016).
Растения являются начальным звеном в цепях питания, эволюционно у них сложилась система ответа на различные абиотические факторы, в том числе и на избыточное поступление тяжелых металлов. Одним из способов снизить токсическое действие является продукция брассиностероидов. Брассиностероиды – группа стероидных соединений, выполняющих функцию эндогенных регуляторов роста растений (Mandava et al., 1988). Они найдены у всех растений от низших до высших, обнаружены во всех их частях (пыльца, цветочные почки, плоды, семена, листья, побеги, корни) (Bajguz, Tretyn, 2003). Наиболее распространен и изучен 24-эпибрассинолид (ЭПБ), полигидроксили-рованное стероидное соединение, которое играет значимую роль в регуляции физиологических процессов (Clouse, Sasse, 1998). Он является основным действующим веществом препарата эпин-экстра, используемого в сельском хозяйстве в качестве адапто-гена. ЭПБ способен снизить содержание металлов в различных органах растений, негативные последствия для клеток (Ефимова и др., 2014; Fariduddin et al., 2014). На сегодняшний день накоплены многочисленные сведения о действии брассиностероидов на различные виды растений (Shahzad et al.,
2018). Подтверждено снижение поглощения тяжелых металлов и уровня токсичности в редисе, ячмене, помидоре, сахарной свекле (Janeczko et al., 2005; Ali et al., 2008; Xia et al., 2009). Брассиностероиды изменяют активность ферментов, мембранный потенциал, активируют синтез белков и нуклеиновых кислот, регулируют экспрессию пластидных генов, метаболизм жирных кислот, влияют на гормональный статус организма, что отражается на уровне целого растения усилением роста и повышением продуктивности (Ефимова и др., 2014; Ефимова, 2018; Choudhary et al., 2012; Efimova et al., 2017; Fridman, Savaldi-Goldstein, 2013; Siddiqui et al., 2018). Механизм действия брассиносте-роидов до конца не изучен. Имеющиеся данные по участию ЭПБ в ответе на фитостресс, вызванный избыточным поступлением тяжелых металлов, недостаточны, чаще всего получены для сельскохозяйственных растений, мало показаны изменения морфометрических и биохимических показателей в градиенте концентраций.
Целью настоящего исследования стало изучение способности брассиностероидов снижать фитостресс от воздействия тяжелых металлов (меди, кадмия, цинка, стронция). Выбранные металлы являются широко распространенными загрязнителями окружающей среды. Медь и цинк необходимы для нормального роста и развития растений, но при избыточном поступлении становятся токсичными. Кадмий и стронций не имеют доказанной функции в метаболизме растений, причем кадмий чрезвычайно токсичен. Изучение стабильных изотопов стронция необходимо для оценки последствий загрязнения радиоактивным стронцием-90 (Zheng et al., 2016).
Материалы
В качестве тест-объекта выбрали ряску малую (Lemna minor L.). Этот вид широко применяется при химическом и радиационном загрязнении природных, сточных вод, в фиторемедиации водоемов. В работе использовали лабораторную культуру ряски малой Института биологии ФИЦ КНЦ УрО РАН. Ряска малая – однодольное покрытосеменное растение семейства рясковые. Вид имеет простое строение, состоит из вегетативного тела – фронда (в литературе также встречается: листец, листоветвь, вайя, щиток, пластинка), а также одиночного корня. Фронды имеют в своем составе в основном губчатый мезофилл с большими воздушны- ми мешками, что позволяет растениям плавать на поверхности воды (Цаценко, Пасха-лиди, 2018). Проксимальная часть фронда ряски расщеплена двумя боковыми кармашками, в них закладываются вегетативные почки, дающие начало дочерним растениям при вегетативном размножении (Тахтаджян, 1982). Ряска малая - неукорененный плей-стофит, плавающий на поверхности пресных водоемов, достаточно широко распространен. Вид используется как тест-объект в экологических экспериментах, мониторинге состояния природных и сточных вод благодаря своей неприхотливости, способности к быстрому росту, преимущественно вегетативному размножению, способности реагировать на небольшие изменения состава среды обитания.
Методы
Для культивирования лабораторной культуры использовали среду Штейнберга (Steinberg, 1946). Растения содержали в климатической камере (KBWF 240, Binder, Германия), при температуре 24 ± 0.1 °С, фотопериодичности 16 ч свет/8 ч темнота, 70 % влажности, интенсивность света 8000 люкс (холодно-белый свет люминесцентных ламп). Предварительно ряску выдерживали 24 часа в среде Штейнберга с добавлением ЭПБ с концентрацией 1.25 нмоль/л. В качестве источника гормона использовали препарат эпин-экстра (Нэст М). После предобработки растения помещали в экспериментальные растворы, содержащие тяжелые металлы в различных концентрациях: 3.15, 6.3, 12.6 мкмоль/л Cu2+; 5, 12.6, 37.8 мкмоль/л Cd2+; 6.3, 12.6, 79 мкмоль/л Zn2+; 632, 1100, 1580 мкмоль/л Sr2+. Среда Штейнберга содержит 0.63 мкмоль/л Zn2+, для эксперимента концентрации подбирали в 5, 8, 10, 20 и т. д. раз выше, чем в среде, для остальных ионов тестировали сходные концентрации. Медь, кадмий, цинк, стронций добавляли к среде в виде стерильных растворов CuCl2∙2H2O, CdCl2, ZnSO4∙7H2O, Sr(NO 3 ) 2 . Перед экспериментом с тяжелыми металлами протестировали препарат эпин-экстра. Результат семидневного теста подтвердил, что он не токсичен для ряски малой, в том числе не вызывает угнетения удельной скорости роста.
Для расчета морфометрических показателей отбирали колонии из 2–4 фрондов и переносили в стерильные стеклянные емкости. В начале эксперимента каждая тестовая емкость содержала по 9-12 растений. В со- ответствии с рекомендациями OCDE (2006) ряску выдерживали на экспериментальной среде 7 суток, затем проводили подсчет растений, число поврежденных фрондов (некрозы, хлорозы), измеряли их площадь, учитывали цвет, а также фиксировали прочие изменения в колониях ряски малой. Эксперимент проводили в трех повторностях.
Средняя удельная скорость роста (темп роста) – логарифметическое увеличение темпа роста (OECD, 2006).
Цн= (In (Nj) - In (N))/t, где μi-j – средняя удельная скорость роста от времени i до времени j,
Nj – переменная теста в опыте во время j,
N - переменная теста в контроле во время i, t – период времени от i до j.
У растений из контрольной группы удвоение числа фрондов должно было происходить менее чем за 60 часов.
Расчет площади фрондов проводили по фотографиям, анализируя изображение до воздействия и через семь дней после с помощью программного обеспечения Image J ( NIH , USA).
Маркером окислительного стресса служил малоновый диальдегид (МДА). МДА образуется в клетках при разрушении по-линасыщенных жирных кислот активными формами кислорода (АФК). Уровень МДА рассчитывали через 4 суток после начала воздействия (Urug et al., 2012). 50 мг растительного материала растирали с кварцевым песком, затем добавляли 1.5 мл 20 % трихлоруксусной кислоты (ТХУ), центрифугировали при 10000 g в течение 15 мин. Далее смешали супернатант (0.3 мл) и 1.2 мл 0.5 % тиобарбитуровой кислоты (ТБК) в 20 % трихлоруксусной кислоте. Смесь инкубировали 30 минут при 95 °С, быстро охлаждали, чтобы остановить реакцию, затем центрифугировали 15 мин при 10000 g. Оптическую плотность определяли при 532 нм и 600 нм. В качестве контроля использовали раствор тиобарбитуровой кислоты в трихлоуксусной кислоте. Содержание МДА определяли по формуле:
Cx= (E532- E600) × Ve/k × ms× Va, где Сх - содержание МДА, нмоль/г сырой массы; E – оптическая плотность раствора; Ve - объем экстракта, взятый для анализа, мл; k – коэффициент молярной экстинкции МДА: 156 мМ-1 х см-1; ms - масса образца для экстракции (Молекулярно-генетические и биохимические методы…, 2012).
Уровень хлорофиллов и каротиноидов определяли через четверо суток после начала воздействия. Навеску растительного материала (50 мг) растирали с добавлением небольшого количества кварцевого песка (для лучшего измельчения растений), карбоната кальция (для нейтрализации эндогенных кислот) и 0.7 мг 96 % водного раствора этанола. Затем выдерживали 30 минут при температуре 4 ºС. Полученный гомогенат центрифугировали 10 мин при 13000 g . Экстракт сливали в чистую пробирку. К осадку добавляли раствор этанола и снова центрифугировали. Добавление новой порции растворителя и центрифугирование повторяли до серой окраски осадка. Оптическую плотность проб определяли на спектрофотометре «КФK-2». Концентрацию пигментов рассчитывали по формуле (Lichtenthaler, 1987).
Статистическую обработку проводили с использованием программного пакета Statistica 6.0. Статистическую значимость отличий между параметрами в опыте и контроле определяли с помощью критерия Стьюдента, Манна – Уитни.
Результаты
Удельная скорость роста
Воздействие тяжелых металлов в отдельных рассматриваемых концентрациях приводило к снижению ростовых параметров ( p ≤ 0.05). Добавление 3.15, 6.3, 12.6 мкмоль/л меди снизило темпы роста на 26, 56, 77 % соответственно относительно интактного контроля ( p ≤ 0.05). Благодаря предварительной обработке растений ЭПБ токсичность в варианте с 12.6 мкмоль/л меди уменьшилась, темпы роста ряски относительно растений без предобработки выше на 23 % ( p ≤ 0.05) (рис. 1).
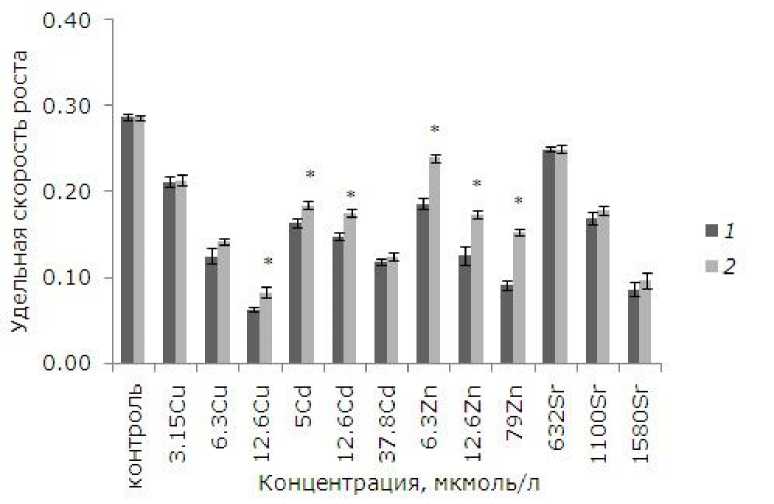
Рис. 1. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на удельную скорость роста ряски малой при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобработанных 24-эпибрассиноли-дом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 1. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the relative growth rate of Lemna minor L. with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. * – the differences are significant in plants pretreated with 24-epi-brassinolide compared to plants without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Student's test
Медь является наиболее токсичным из рассматриваемых металлов. При равной концентрации 12.6 мкмоль/л меди, кадмия, цинка наименьшая удельная скорость роста была у растений после воздействия меди. На последнем месте в ряду токсичности стоит стронций. Ряд токсичности металлов по угнетению удельной скорости роста ряски: Cu > Cd > Zn >Sr.
При воздействии рассматриваемых концентраций кадмия (5, 12.6, 37.8 мкмоль/л) удельная скорость роста снизилась на 43, 52, 58 % относительно интактного контроля. После 5 и 12.6 мкмоль/л кадмия у растений, обработанных ЭПБ, удельная скорость роста выше, чем у необработанных ( р ≤ 0.05). При воздействии 6.3, 12.6, 79 мкмоль/л цинка удельная скорость роста снизилась на 35, 56,
68 % соответственно. У растений, которые предварительно помещали в среду с ЭПБ, снижение удельной скорости было не таким значительным. Удельная скорость роста у них на 22. 28, 40 % выше, чем у растений без предобработки. Однако предварительная обработка ЭПБ не снизила токсический эффект от стронция. В отличие от других металлов стронций менее токсичен, диапазон концентраций, приводящих к угнетению роста, на два порядка выше (632–1580 мкмоль/л).
Таким образом, предобработка ЭПБ позволила увеличить удельную скорость роста после воздействия цинка (во всех концентрациях), меди (12.6 мкмоль/л) и кадмия (5, 12.6 мкмоль/л).
Повреждение фрондов
При действии тяжелых металлов произошли изменения фрондов. При невысоких концентрациях начал разрушаться хлорофилл, появились хлорозы, в дальнейшем при увеличении химической нагрузки листья некротизировались. Доля фрондов с хлорозами и некрозами – важный диагностический признак при биотестировании.
Поврежденность фрондов зависит от концентрации тяжелых металлов. В контроле доля растений с хлорозами и некрозами не превышала 1 %. При воздействии на ряску 3.15 мкмоль/л меди она возросла до 14 %, при 3.15 и 6.3 мкмоль/л составила 100 %. После предобработки ЭПБ уровень повреждений снизился, но не для всех концентраций металла (рис. 2). При высоких концентрациях меди, кадмия и стронция, когда повреждены все фронды, предобработка ЭПБ не оказала положительного эффекта. При воздействии 5, 12.6 мкмоль/л кадмия предобработка ЭПБ позволила снизить долю поврежденных фрондов с 39 до 31 % и с 94 до 67 % соответственно. Растений без видимых изменений стало больше в экспериментах с 3.15, 6.3 мкмоль/л Cu ( р ≤ 0.05). При воздействии низкой и средней концентраций стронция доля поврежденных фрон-дов снизилась благодаря ЭПБ в 2.3 и 1.3 раза соответственно. Из всех рассматриваемых тяжелых металлов лучше всего ЭПБ снизил токсичность цинка: уменьшение доли фрон-дов с некрозами и хлорозами произошло для всех концентраций.
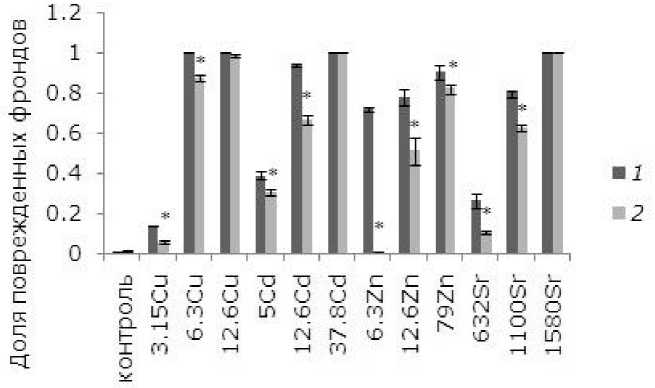
Концентрация, мкмоль/л
Рис. 2. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на долю поврежденных фрондов ряски малой при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобработанных 24-эпибрас-синолидом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Манна – Уитни
Fig. 2. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the proportion of damaged fronds of duckweed with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. * – the differences are significant in plants pretreated with 24-epibrassinolide compared to Lemna minor L. without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Mann – Whitney`s test
Таким образом, предобработка ЭПБ благоприятно отразилась на растениях во всех вариантах эксперимента, кроме высоких концентраций кадмия, стронция и меди.
Площадь фрондов
При воздействии тяжелых металлов на лабораторную культуру ряски малой изменилась площадь фрондов. При воздействии небольших, но «действующих» концентраций удельная скорость роста высокая, появляется достаточно дочерних растений, но с меньшей площадью, чем первоначальные, поэтому средняя площадь растений сокращается линейно в зависимости от концентрации тяжелого металла. При возрастании в среде для культивирования растений содержания токсиканта темпы роста падают. Выживаемость зачатков, т. е. способность развиться в полноценное растение, снижается, новых растений появляется меньше, поэтому средняя площадь теперь близка к первоначальной. Предварительная обработка ЭПБ перед воздействием 632 мкмоль/л стронция способствовала увеличению площади фрондов относительно необработанных растений. Применение фитогормонов привело к повышению удельной скорости роста при воздействии меди, цинка (6.3, 12.6 мкмоль/л), появилось больше дочерних растений, меньших по размерам, но их средняя площадь уменьшилась (рис. 3).
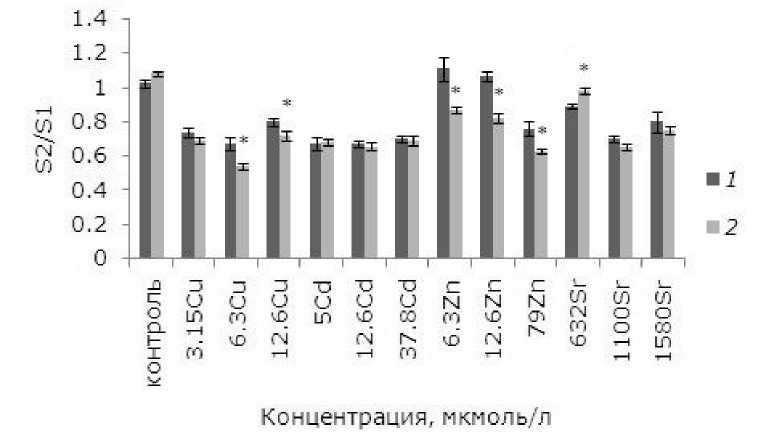
Рис. 3. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на площадь фрондов ряски малой при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. S2/S1 – отношение площадей фрондов; S1 – первоначальная площадь фрон-дов, мм; S2 – площадь фрондов через 7 дней, мм. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобрабо-танных 24-эпибрассинолидом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий
Стьюдента
Fig. 3. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the fronds area of the duckweed with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. S2 / S1 is the area ratio of the fronds; S1 – the original area of fronds, mm; S2 – the area of fronds after 7 days, mm. * - the differences are significant for plants prepared with 24-epibrass-inolide compared with plants without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Student's test
Содержание малонового диальдегида (МДА)
Окислительный стресс является причиной перекисного окисления липидов (ПОЛ), в результате нарушается структура клеточных мембран, снижается их пластичность, изменяется проницаемость. Одним из метаболитов при ПОЛ является малоновый диальдегид (МДА), и его увеличение показывает, что растения находятся в стадии высокого уровня окислительного стресса (Загоскина, Назаренко, 2016).
Брассиностероиды, по данным литературы (Zhao et al., 1990), снижают уровень окислительного стресса за счет стимулирования выработки антиоксидантов. Как пока- зал анализ данных, снижение уровня МДА произошло только в варианте с высокой концентрацией стронция (1058 мкмоль/л). Медь – наиболее редокс-активный металл, поэтому уровень МДА у растений после воздействия меди выше по сравнению с другими металлами (Vidaković-Cifrek et al., 2015) (рис. 4). Избыток меди вызывает окислительный стресс у растений, при этом возрастает содержание высокотоксичных свободных радикалов (De Vos et al., 1991; Gupta et al., 1999; Luna et al., 1994; Shahid et al., 2014; Stohs, Bagchi, 1995). Предобработка ЭПБ привела к увеличению концентрации МДА в клетках после воздействия меди во всех вариантах эксперимента.
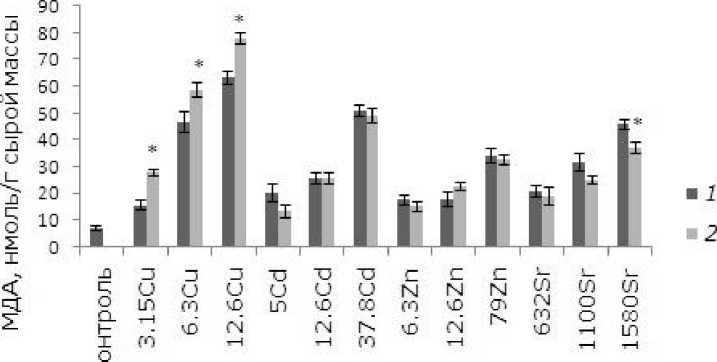
Концентрация, мкмоль/л
Рис. 4. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на содержание малонового диальдегида (МДА) при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобработанных 24-эпибрас-синолидом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Манна – Уитни
Fig. 4. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. * – the differences are significant in plants pretreated with 24-epibrassino-lide compared to Lemna minor L. without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Mann – Whitney`s test
Содержание фотосинтетических пигментов
При высоких уровнях тяжелых металлов тормозились рост и развитие, появились хлорозы и некрозы. Как показал анализ данных, воздействие ионов меди, кадмия, цинка в выбранных концентрациях и 1.58 ммоль/л стронция привело к снижению содержания хлорофилла а относительно контрольных растений. У обработанных ЭПБ растений после воздействия 12.6 мкмоль/л кадмия и цинка уровень хлорофилла выше, чем у необработанных, на 14.5 и 31 % соответственно ( p ≤ 0.05). У лабораторной культуры после воздействия ЭПБ и 12.6 мкмоль/л меди содержание хлорофилла a , наоборот, понизилось на 31 % (рис. 5). Разнонаправленные эффекты наблюдаются после ЭПБ и при анализе содержания хлорофилла b . Предобработка перед воздействием 6.3 мкмоль/л меди привела к снижению токсического воздействия, содержание хлорофилла b увеличилось на 18.7 %, а при 3.15 и 12.6 мкмоль/л, наоборот, уменьшилось на 16.1 и 22.5 % соответственно (рис. 6). Снижение уровня хлорофилла b на 11.1 % по сравнению с необработанными растениями произошло и у растений, подвергшихся воздействию 1580 мкмоль/л стронция.
Уровень каротиноидов повысился у пре-дообработанных ЭПБ растений после 12.6 мкмоль/л кадмия, цинка и 6.3 мкмоль/л меди (p ≤ 0.05). После воздействия высоких концентраций меди, цинка, которые вызывают у 100 % растений повреждения фрон-дов, содержание каротиноидов выше у необработанных ЭПБ растений (рис. 7).
Обсуждение
Основатель биогеохимии В. И. Вернадский в начале XX в. писал о значительной роли геохимических особенностей местности в морфологии и жизнедеятельности живых организмов (Вернадский, 1978). Он подчеркивал, что многие эволюционные изменения видов произошли «в связи с определенными свойствами химической среды, в которой они живут». Растения обладают эволюционно сложившейся системой защиты от стрессоров для адаптации к среде обитания, поэтому способны выжить при изменении ее условий. Изучение способности растений справляться с избытком различных химических веществ необходимо в связи с возросшим уровнем загрязнения почвы, воды, воздуха различными поллютантами, в том числе и тяжелыми металлами.
Тяжелые металлы оказывают значительное воздействие на растительный организм. Они способны связываться с ионами сульфгидрильных групп в белках, ингибировать активность или разрушать ферментные структуры (Hall, 2002). Поступление тяжелых металлов в клетку вызывает окислитель-
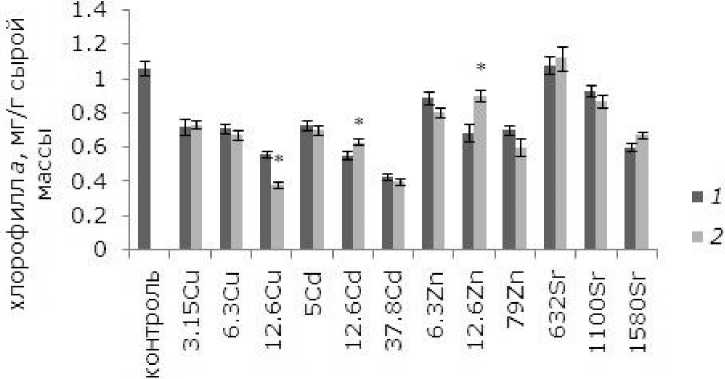
Концентрация, мкмоль/л
Рис. 5. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на содержание хлорофилла а при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобработанных 24-эпибрассинолидом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 5. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the content of chlorophyll a with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. * – the differences are significant in Lemna minor L. pretreated with 24-epibrassinolide compared to plants without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Student's test
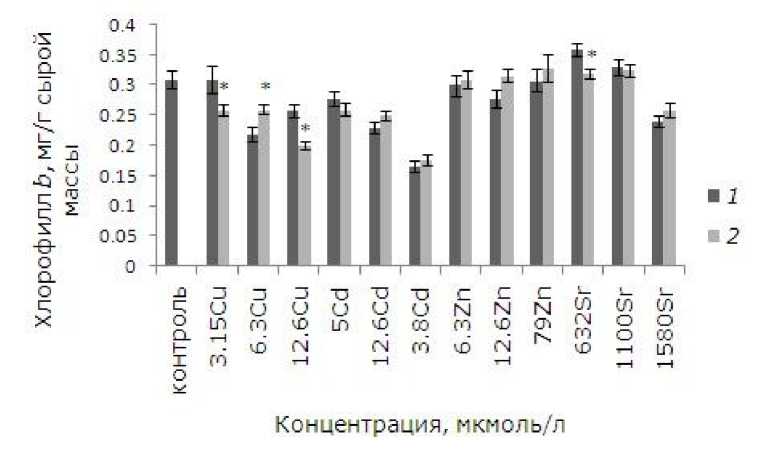
Рис. 6. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на содержание хлорофилла b при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобработанных 24-эпибрассинолидом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 6. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the content of chlorophyll b with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. * – the differences are significant in Lemna minor L. pretreated with 24-epibrassinolide compared to plants without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Student's test
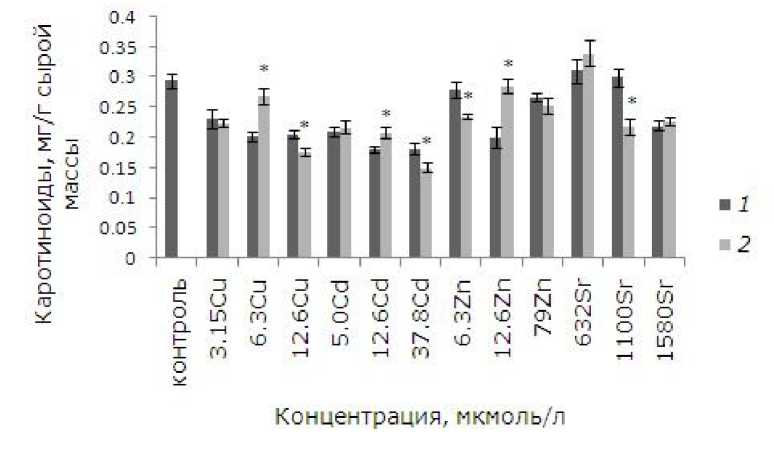
Рис. 7. Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида (эпб) на содержание каротиноидов при избытке меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция. * – отличия достоверны у растений, предобработанных 24-эпибрассинолидом, по сравнению с растениями без предобработки ( p ≤ 0.05), критерий Стьюдента
Fig. 7. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide (EPB) on the content of carotenoids with an excess of copper, cadmium, zinc and strontium. * – the differences are significant in Lemna minor L. pretreated with 24-epibrassino-lide compared to plants without pretreatment ( p ≤ 0.05), Student's test
ный стресс, что провоцирует образование активных форм кислорода (АФК), таких как радикалы супероксида, пероксида, гидроксильного иона (Marschner, 1995). АФК разрушают мембраны за счет перекисного окисления липидов. Однако растения оснащены системой антиоксидантов для удаления АФК и могут адаптироваться к воздействию тяжелых металлов (Salin, 1988). Растительные фитогормоны регулируют производство антиоксидантов при действии тяжелых металлов, а также блокируют их поступление (Ashraf, Foolad, 2007). По литературным данным, брассиностероиды снижают уровень окислительного стресса. Применение ЭПБ уменьшало окислительную деградацию в клеточных органеллах и содержание МДА путем модуляции продукции антиоксидантов (Zhao et al., 1990). Есть сведения, что ЭПБ присоединяется к мембранным белкам и АФК, исключая вероятность ПОЛ (Сао et al., 2005). Экзогенное применение брасси-ностероиодов модифицировало антиоксидантные ферменты (супероксиддисмутазу, каталазу, глутатионпероксидазу, аскорбатпероксидазу), неферментативные антиоксиданты (аскорбиновую кислоту, токоферолы, каротиноиды, глутатион). При связывании с мембранными участками ЭПБ усиливал ферментную и метаболическую активность и снижал токсичность тяжелых металлов (Хрипач и др., 1995). Брассиностероиды спо- собны оказывать влияние на другие гормоны. Внесение экзогенного ЭПБ приводило к сдвигам в гормональном статусе (Bajguz, Hayat, 2009; Saini et al., 2013). Механизмы протекторного действия брассиностерои-дов до конца еще не изучены.
В данной работе изучено воздействие различных концентраций меди, кадмия, цинка и стронция на растения, предварительно на сутки помещенные в среду с добавлением ЭПБ. В результате эксперимента были получены противоречивые данные. Положительный эффект от применения ЭПБ наблюдался в увеличении удельной скорости роста, снижении доли растений с хлорозами и некрозами после воздействия отдельных тяжелых металлов в определенных концентрациях. Но после совместного использования ЭПБ и меди увеличилась продукция МДА. Произошло изменение содержания каротиноидов и хлорофиллов.
Медь – необходимый для жизнедеятельности растений элемент, но его избыток вызывает хлорозы и некрозы, задержку и ингибирование роста корней, побегов, листьев. В условиях избытка металла центральный ион молекулы хлорофилла Mg2+ замещается медью, что приводит к ухудшению функции хлорофильных комплексов, потому что металлозамещенный хлорофилл не подходит для фотосинтеза (Küpper, Kroneck, 2005). Снижение содержания хлорофилла и из- менение структуры хлоропластов и состава тиллакоидных мембран были найдены в листьях шпината, риса, пшеницы, фасоли, орегано (Baszynski et al., 1988; Lidon, Henriques, 1991, 1993; Ciscato et al., 1997; Pätsikkä et al., 1998). На клеточном уровне избыток меди может инактивировать и нарушить структуру белка в результате неизбежного связывания с сульфгидрильными группами, тем самым ингибируя активность фермента. Токсичность может возникнуть вследствие индукции дефицита других эссенциальных ионов, нарушения процессов клеточного транспорта и окислительного стресса (Yruela, 2009). У ряски начиная с 0.3 мкмоль/л меди происходило снижение удельной скорости роста, увеличение доли поврежденных растений, концентрации МДА. Предварительная обработка ЭПБ способна смягчить токсическое действие меди. Темпы роста выше у обработанных растений по сравнению с необработанными при воздействии 12.6 мкмоль/л меди, доля растений с хлорозами и некрозами снижалась после 3.15 и 6.3 мкмоль/л меди. Уровень хлорофилла b, каротиноидов у растений после ЭПБ увеличился в экспериментах с 6.3 мкмоль/л меди (р ≤ 0.05). У ряски наиболее чувствительны зачатки новых растений, поэтому стимулирование роста ЭПБ привело к появлению растений с более низкой площадью фрондов. По литературным данным, ЭПБ способен снижать окислительный стресс. Но, по результатам данного эксперимента, уровень МДА выше у растений после ЭПБ по сравнению с необработанными (р ≤ 0.05). Уровень хлорофилла а и каротиноидов выше у необработанных растений после воздействия 12.6 мкмоль/л меди.
Кадмий является переходным элементом с атомным весом 112.4 г, имеет 2 валентности, поэтому высоко реактивен по своей природе. Это необязательный элемент для живых организмов, хорошо усваивается растениями и влияет на морфологию, структурные, биохимические и физиологические функции (Ekmekci et al., 2008). Кадмий провоцирует развитие окислительного стресса, регулируя ферментативные и неферментативные антиоксиданты, которые обезвреживают АФК и обеспечивают выживаемость растений (Shahzad et al., 2018). Применение брассиностероидов снижало токсическое воздействие кадмия в Raphanus sativus L. за счет повышения уровня свободного пролина, повышения активности антиоксидантных ферментов, таких как каталаза, супероксид- дисмутаза, аскорбатпероксидаза (Anuradha, Rao, 2007). В данном исследовании положительный эффект по снижению токсического действия ЭПБ наблюдали после воздействия 5, 12.6 мкмоль/л кадмия: увеличилась удельная скорость роста ряски малой и снизился уровень повреждений фрондов. Применение фитогормона привело к повышению содержания хлорофилла b, каротиноидов у растений после 12.6 мкмоль/л. Но после ЭПБ у растений ниже по сравнению с необработанными концентрация каротиноидов при 37.8 мкмоль/л кадмия.
Цинк – эссенциальный микроэлемент, участвует в белковом, углеводном и фосфорном обмене, в биосинтезе витаминов и ауксинов, выступает в качестве кофактора или компонента нескольких ферментов, связанных с синтезом белков, а также нуклеиновых кислот и липидов, играет важную роль в поддержании целостности плазматических мембран, тем самым снижая окислительный стресс от присутствия токсикантов. Избыток цинка ингибирует рост и развитие растений (Елькина, 2009; Rout, Das, 2003). Применение ЭПБ при избытке цинка уменьшило его токсичность (Ramakrishna, Rao, 2012) благодаря смягчению окислительного стресса. Эффективность брассиностероидов и их накопление для хлореллы располагаются в следующем порядке: Zn > Cd > Pb > Cu (Bajguz, 2000, 2002). Как для хлореллы, лучше всего ЭПБ снизил токсическое действие на ряску от избытка цинка. Во всех вариантах эксперимента у предобработанных гормоном растений увеличилась удельная скорость роста, при этом средняя площадь растений снизилась, стало меньше фрондов с хлорозами и некрозами. Положительный эффект был и в увеличении содержания хлорофилла а , каротиноидов после воздействия 12.6 мкмоль/л цинка. Уровень каротиноидов у ряски после применения ЭПБ ниже, чем у необработанных растений после 6.3 мкмоль/л цинка.
Стронций – щелочноземельный металл II группы, имеет стабильные (Sr-84, 86, 87, 88) и радиоактивные (Sr-85, 89, 90) изотопы. Химическое и биохимическое поведение стронция и радиостронция схожи в почве и воде. Стронций для растений несущественен, но способен замещать кальций и вызывать его недостаток в организме (Miller et al., 1993). Находясь в избытке, он вызывает окислительный стресс, что было показано на примере редьки посевной (Wang et al., 2012), ряски малой (Боднарь и др., 2018).
Данных по механизму действия брассино-стероидов при избытке стронция в литературе нет. Как показали результаты настоящего исследования, благодаря ЭПБ снизился уровень поврежденных растений (при 632, 1100 ммоль/л), увеличилась площадь фрондов (при 632 мкмоль/л). Показано смягчение окислительного стресса, концентрация МДА (при 1580 мкмоль/л) ниже, чем у растений без предварительного культивирования в среде с ЭПБ. При этом уровень хлорофилла b и каротиноидов после воздействия 632 мкмоль/л стронция оказался выше у растений, выращенных без применения ЭПБ.
Заключение
Применение ЭПБ повысило стрессоустой-чивость ряски малой к действию тяжелых металлов, но эффективность зависела от концентрации металла. Окончательно неизвестно, модулируют ли брассиностероиды прямую или косвенную реакцию растений на окислительный стресс. Уровень МДА снизился в варианте 1580 мкмоль/л стронция. Предварительное применение экзогенного ЭПБ в условиях медного стресса привело к увеличению темпов роста, снижению доли растений с хлорозами и некрозами, но при этом повысилось содержание МДА, снизился уровень фотоассимилирующих пигментов при отдельных концентрациях меди. Наиболее эффективен ЭПБ при цинковом стрессе: во всех концентрациях увеличились темпы роста, снизилась доля поврежденных фрондов.
Список литературы Влияние 24-эпибрассинолида на ростовые показатели, уровень окислительного стресса и фотосинтетических пигментов ряски малой (Lemna minor L.) после воздействия тяжелых металлов
- Боднарь И. С., Чебан Е. В., Зайнуллин В. Г. Особенности воздействия ионов меди и стронция на ряску малую (Lemna minor L.) // Принципы экологии. 2018. № 2. С. 3-21.
- Вернадский В. И. Живое вещество . М.: Наука, 1978. 363 с.
- Елькина Г. Я. Поведение цинка в системе почва-растение в условиях европейского Северо-Востока // Агрохимия. 2009. № 11. С. 57-64.
- Ефимова М. В. Физиологические механизмы повышения солеустойчивости растений Solanum tuberosum L. брассиностероидами в зависимости от способа воздействия // Механизмы устойчивости растений и микроорганизмов к неблагоприятным условиям среды: Сборник материалов Годичного собрания Общества физиологов растений России, Всероссийской научной конференции с международным участием и школы молодых ученых, Иркутск, 10-15 июля 2018 г. Иркутск: Изд-во Института географии им. В. Б. Сочавы Со РАН, 2018. Ч. I. С. 316-318.
- Ефимова М. В., Савчук А. Л., Хасан Дж. А. К., Литвиновская Р. П., Хрипач В. А., Холодова В. П., Кузнецов Вл. В. Физиологические механизмы повышения солеустойчивости растений рапса брас-синостероидами // Физиология растений. 2014. Т. 61. № 6. С. 778-789.
- Загоскина Н. В., Назаренко Л. В. Активные формы кислорода и антиоксидантная система растений // Вестник МГПУ. Сер.: Естественные науки. 2016. № 2. С. 9-23.
- Молекулярно-генетические и биохимические методы в современной биологии растений / Под ред. Вл. В. Кузнецова, В. В. Кузнецова, Г. А. Романова. М.: БИНОМ, 2012. С. 348-349.
- Тахтаджян А. Л. Жизнь растений . Т. 6. М.: Просвещение, 1982. С. 493-500.
- Хрипач В. А., Жабинский В. Н., Лахвич Ф. А. Перспективы практического применения брассиносте-роидов - нового класса фитогормонов: Обзор // Сельскохозяйственная биология. Сер.: Биология растений. 1995. № 1. С. 3-11.
- Цаценко Л. В., Пасхалиди В. Г. Рясковые как модельный объект в биотестировании водной и почвенной среды // Масличные культуры. Научно-технический бюллетень Всероссийского научно-исследовательского института масличных культур. 2018. Вып. 4 (176). С. 146-151.
- Ashraf M., Foolad M. R. Roles of glycinebetaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance // Environmental and Experimental Botany. 2007. Vol. 59. P. 206-216.
- Akram R., Natasha, Fahad S., Hashmi M. Z., Wahid A., Adnan M., Mubeen M., Khan N., Rehmani M., Awais M., Abbas M., Shahzad K., Ahmad S., Hammad H. M., Nasim W. Trends of electronic waste pollution and its impact on the global environment and ecosystem // Environmental Science and Pollution Research Serves the International. 2019. № 17. P. 16923-16938. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-04998-2
- Ali B., Hasan S. A., Hayat S., Hayat Q., Yadav S., Fariduddin Q., Ahmad A. A. Role for brassinosteroids in the amelioration of aluminium stress through antioxidant system in mung bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) // Environmental and Experimental Botany. 2008. Vol. 62. № 2. P. 153-159.
- Anuradha S., Rao S. S. R. Effect of brassinosteroids on radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings growing under cadmium stress // Plant, Soil and Environmental. 2007. Vol. 53. P. 465-472.
- Bajguz A. Blockade of heavy metals accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris cells by 24-epibrassinolide // Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 2000. Vol. 38. P. 797-801.
- Bajguz A. Brassinosteroids and lead as stimulators of phytochelatins synthesis in Chlorella vulgaris // Journal of Plant Physiology. 2002. Vol. 159. P. 321-324.
- Bajguz A., Hayat S. Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses // Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. 2009. Vol. 47. № 6. P. 1-8.
- Bajguz A., Tretyn A. The chemical characteristic and distribution of brassinosteroids in plants // Phyto-chemistry. 2003. Vol. 62. № 7. P. 1027-1046.
- Baszynski T., Tukendorf A., Ruszkowska M., Skórzynska E., Maksymiec W. Characteristics of the photosynthetic apparatus of copper nontolerant spinach exposed to excess copper // Journal of Plant Physiology. 1988. Vol. 132. P. 708-713.
- Breivik K., Armitage J. M., Wania F., Sweetman A. J., Jones K. C. Tracking the global distribution of persistent organic pollutants accounting for E-waste exports to developing regions // Environmental Science and Technology. 2016. Vol. 50. P. 798-805.
- Cao S., Xu Q., Cao Y., Qian K., An K., Zhu Y., Binzeng H., Zhao H., Kuai B. Loss of function mutations in DET2 gene lead to an enhanced resistance to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis // Physiologia Plantarum. 2005. Vol. 123. P. 57-66.
- Choudhary S. P., Yu J. Q., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K., Tran L. S. Benefits of brassinosteroid crosstalk // Trends in Plant Science. 2012. Vol. 17. P. 594-605.
- Ciscato M., Valcke R., van Loven K., Clijsters H., Navari-Izzo F. Effects of in vivo copper treatment on the photosynthetic apparatus of two Triticum durum cultivars with different stress sensitivity // Physiologia Plantarum. 1997. Vol. 100. P. 901-908.
- Clouse S. D., Sasse J. M. Brassinosteroids: Essential Regulators of Plant Growth and Development // Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology. 1998. Vol. 49. P. 427-451.
- De Vos C. H. R., Schat H., De Waal M. A. M., Voojis R., Ernst W. H. O. Increased resistance to copper-induced damage of the root cell plasmalemma in copper tolerant Silene cucubalus // Physiologia Plantarum. 1991. Vol. 82. P. 523-528.
- Ekmekci Y., Tanyolag D., Ayhan B. Effects of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme and photosynthetic activities in leaves of two maiz cultivars // Journal of Plant Physiology. 2008. Vol. 165. P. 600-611.
- Efimova M. V., Vankova R., Kusnetsov V. V., Litvinovskaya R. P., Zlobin I. E., Dobrev P., Vedenicheva N. P., Sauchuk A. L., Karnachuk R. A., Kudryakova N. V., Kuznetsov V. V. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide and green light on plastid gene transcription and cytokinin content of barley leaves // Steroids. 2017. Vol. 120. P. 32-40.
- Fariduddin Q., Yusuf M., Ahmad I., Ahmad A. Brassinosteroids and their role in response of plants to abiotic stresses // Biologia Plantarum. 2014. Vol. 58. P. 9-17.
- Faulkner E. B., Schwartz R. J. High peformance pigments. N. Y.: John Wiley and Sons, 2009. 516 p.
- Fridman Y., Savaldi-Goldstein S. Brassinosteroids in growth control: How, when and where // Plant Science. 2013. Vol. 209. P. 24-31.
- Hall J. L. Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance // Journal of Experimental Botany. 2002. № 53. P. 1-11.
- Gupta M., Cuypers A., Vangronsveld J., Clijsters H. Copper affects the enzymes of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and its related metabolites in the roots of Phaseolus vulgaris // Physiologia Plantarum. 1999. Vol. 106. P. 262-267.
- Janeczko A., Koscielniak J., Pilipowicz M., Szarek-Lukaszewska G., Skoczowski A. Protection of winter rape photosystem 2 by 24-epibrassinolide under cadmium stress // Photosynthetica. 2005. Vol. 43. P. 293-298.
- Küpper H., Kroneck P. M. H. Heavy metal uptake by plants and cyanobacteria // Metal Ions in Biological Systems. 2005. Vol. 44. P. 97-144.
- Lichtenthaler H. K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes // Methods in Enzymology. 1987. № 148. P. 350-382.
- Lidon F. C., Henriques F. S. Limiting step in photosynthesis of rice plants treated with varying copper levels // Journal of Plant Physiology. 1991. Vol. 138. P. 115-118.
- Lidon F. C., Henriques F. S. Changes in the thylakoid membrane polypeptide patterns triggered by excess Cu in rice // Photosynthetica. 1993. Vol. 28. P. 109-117.
- Luna C. M., González C. A., Trippi V. S. Oxidative damage caused by excess of copper in oat leaves // Plant & Cell Physiology. 1994. Vol. 35. P. 11-15.
- Mandava N. B. Plant growth-promoting brassinosteroids // Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology. 1988. Vol. 391. № 1. P. 23-52.
- Marschner H. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, 1995. 889 p.
- Miller E. K., Blum J. D., Friedland A. J. Determination of soil exchangeablecation loss and weathering rates using Sr isotopes // Nature. 1993. Vol. 362. P. 438-441.
- OECD Guidelines for the testing chemicals. Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Paris, 2006.
- Pätsikkä E., Aro E.-M., Tyystjärvi E. Increase in the quantum yield of photoinhibition contributes to copper toxicity in vivo // Plant Physiology. 1998. Vol. 117. P. 619-627.
- Ramakrishna B., Rao S. S. R. 24-Epibrassinolide alleviated zinc-induced oxidative stress in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings by enhancing antioxidative system // Plant Growth Regulators. 2012. Vol. 68. P. 249-259.
- Rout G. R., Das P. Effect of metal toxity on plant growth and metabolism // Agronomie. 2003. Vol. 23. P. 3-11.
- Saini S., Sharma I., Kaur N., Pati P. K. Auxin - a master regulator on plant root development // Plant Cell Reports. 2013. Vol. 32. № 6. P. 741-757.
- Salin M. L. Toxic oxygen species and protective systems of the chloroplast // Physiologia Plantarum. 1988. Vol. 72. P. 681-689.
- Shahid M., Pourrut B., Dumat C., Nadeem M., Aslam M., Pinelli E. Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants // Reviews Environonmental Contamination Toxicology. 2014. Vol. 232. P. 1-44.
- Shahzad B., Tanveer M., Che Z., Rehman A., Alam Cheema S., Sharma A., Song H., Rehman S., Zhaorong D. Role of 24-epibrassinolide (EBL) in mediating heavy metal and pesticide induced oxidative stress in plants: A review // Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2018. Vol. 147. P. 935-944.
- Siddiqui H., Hayat S., Bajguz A. Regulation of photosynthesis by brassinosteroids in plants // Acta Physiologiae Plantarum. 2018. Vol. 40 (3). P. 59.
- Steinberg R. Mineral requirement of Lemna minor L. // Plant Physiol. 1946. Vol. 21. P. 42-48.
- Stohs S. J., Bagchi D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions // Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 1995. Vol. 18. P. 321-336.
- Urug Parlac K., Demirezen Yilmaz D. Response of antioxidant defences to Zn stress in three duckweed species // Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2012. № 85. P. 52-58.
- Vidakovic-Cifrek Z., Tkalec M., Sikic S., Tolic S., Lepedus H., Pevalek-Kozlina B. Growth and photosynthetic responses of Lemna minor L. exposed to cadmium in combination with zinc or copper // Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. 2015. Vol. 66. P. 141-152.
- Wang D., Wen F., Xu C., Tang Y., Luo X. The uptake of Cs and Sr from soil to radish (Raphanus sativus L.) -potential for phytoextraction and remediation of contaminated soils // Journal of Environmental Radioactivity. 2012. Vol. 110. P. 78-83.
- Xia X. J., Zhang Y., Wu J. X., Wang J. T., Zhou Y. H., Shi K., Yu Y. L., Yu J. Q. Brassinosteroids promote metabolism of pesticides in Cumcumber // Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2009. Vol. 57. P. 8406-8413.
- Yuan Z., Luo T., Liu X., Hua H., Zhuang Y., Zhang X., Zhang L., Zhang Y., Xu W., Ren J. Tracing anthropogenic cadmium emissions: From sources to pollution // Science Total Environment. 2019. P. 87-96.
- Yruela I. Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions // Functional Plant Biology. 2009. Vol. 36. P. 409-430.
- Zhao Y. J., Xu R. J., Luo W. H. Inhibitory effects of abscisic acid on epibrassinolide-induced senescence of detached cotyledons in cucumber seedlings // Chinese Science Bulletin. 1990. Vol. 35. P. 928-931.
- Zheng G., Pemberton R., Li P. // Bioindicating potential of strontium contamination with Spanish moss Tilandsia usneoides // Journal of Environmental Radioactivity. 2016. Vol. 152. P. 23-27.


