Воспаление парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин: проблема с 350-летней историей
Автор: Кислицын П.О., Протощак В.В., Кукушкин А.В., Синельников Л.М., Галюк Д.А., Бабкин П.А., Кушниренко Н.П., Паронников М.В., Игловиков Н.Ю.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Инфекционно-воспалительные заболевания
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Воспаление желез Скина одна из частых причин стойкой дизурии и рецидивирующей инфекции нижних мочевыводящих путей. Недостаточная осведомленность об этой патологии может стать причиной диагностических ошибок и неадекватного лечения. В литературе данная патология освещена недостаточно, что послужило причиной подготовки настоящего лекции.
Парауретральные протоки и железы, железы скина, скинеит, хронический скинеит, гомолог простаты у женщин, женская простата, лечение женского уретрита, рецидивирующий цистоуретрит, женская уретра, уретралгия у женщин, операция ризера
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142240785
IDR: 142240785 | DOI: 10.29188/2222-8543-2023-16-4-143-155
Текст научной статьи Воспаление парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин: проблема с 350-летней историей
экспериментальная и клиническая урология № 4 2023
В 2022 году исполнилось 350 лет с момента первого описания парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин. По мнению многих авторов XIX и ХХ веков воспаление желез Скина (ЖС) является одной из частых причин стойкой дизурии и источником рецидивирующей инфекции нижних мочевыводящих путей (ИНМП). Принимая во внимание тот факт, что ИНМП занимают второе место по частоте в мире после острых респираторных инфекций, также логично предположить и высокую распространенность скинеитов. Недостаточная осведомленность о воспалительных заболеваниях парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин может стать причиной ошибочного диагноза, гипердиагностики рецидивирующих циститов, и, как следствие, неправильного лечения. Несмотря на это, освещенность этой проблемы в современной отечественной и зарубежной литературе, на наш взгляд, недостаточная, что послужило причиной подготовки настоящей лекции.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Эпидемиология
Современная медицина располагает данными об эпидемиологии лишь некоторых заболеваний парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин.Согласно S. Raz и соавт., кисты мочеиспускательного канала встречаются у 1–6 % женщин в возрасте от 20 до 60 лет. Распространенность дивертикулов уретры по исследованию L.J. Burrows и соавт. составляет 0,6-4,7% [1, 2]. В то же время сообщения о частоте воспаления парауретральных протоков и желез единичны. По историческим данным, опубликованным в начале XX века, среди пациенток, страдающих гонококковой инфекцией, воспаление желез вдоль мочеиспускательного канала наблюдалось в 54-96% случаев [1–4]. Также отмечалась высокая частота поражений этих структур при трихо-монадном вульвовагините [5, 6].
В настоящее время, учитывая появление эффективной антибактериальной терапии указанных заболеваний, чаще встречается их неспецифическое воспаление. Согласно исследованию М.Н. Слессаревской и соавт., у 4,6 % женщин, направленных к урологу со стойкими дизурическими явлениями и предварительным диагнозом хронический цистит, было выявлено инфек- ционное поражение придаточных желез мочеиспускательного канала [7]. По мнению А.Г. Глухарева, это патологическое состояние в 50% случаев может являться причиной рецидивирующей ИНМП [8]. Таким образом, представления о распространенности данной патологии по данным различных научных изысканий значимо отличаются. Причиной этого может быть малое количество научных публикаций и отсутствие мультицентровых исследований, что препятствует выработке единой терминологии,критериев диагноза и методов его установки. Однако, оценивая эпидемиологию ИНМП, следует учитывать два важных фактора. Пер-вый:ИНМП занимают второе по частоте место в мире после острых респираторных инфекций, а самыми распространенными среди них являются острый и хронический цистит [9, 10]. Второй: флора в придаточных железах уретры часто соответствует влагалищной, что указывает на возможные пути проникновения патогенных микроорганизмов и значение патологий органов малого таза в воспалении структур, рассматриваемых в данном обзоре [8]. Количество инфекций женских половых органов также высоко – около 350 млн. женщин заболевает ежегодно, в большинстве случаев с последующей хронизацией этого процесса [11–13]. Принимая эти факты во внимание, логично предположить высокую частоту воспалителительных процессов в парауретральных протоках и железах в женской популяции.
Тем не менее, в современной отечественной и зарубежной литературе актуальных работ о воспалении парауретральных желез и протоков практически нет, а имеющиеся изыскания в большинстве своем датированы XIX и ХХ веками. Кроме того, в фундаментальных анатомических учебниках и атласах данные об этом органе либо отсутствуют, либо ограничены короткой и сухой констатацией самого факта его наличия. Подобная картина сохраняется в медицинских изданиях для врачей и в клинических рекомендациях для специали-стов.Не нашли своего отображения воспалительные заболевания ЖС и в номенклатуре МКБ-10. Отсутствие знаний об этих структурах ведет к невозможности диагностировать и лечить их патологию, самая частая из которых – их неспецифическая инфекция с осложнением в виде хронического рецидивирующего цистита и стойких дизурических явлений. Следует также помнить, что катаральное воспаление придаточных желез мочеиспускательного канала является, как правило, первым звеном в цепочке развития парауретральной

кисты, ее абсцедирования и последующего формирования дивертикула уретры. Хирургическое лечение названных состояний заключается в иссечении патологических очагов. Объем и тяжесть данных оперативных пособий, возможные интра- и послеоперационные осложнения несут в себе дополнительные риски,которых можно избежать при своевременной диагностике и лечении первичного заболевания. В связи с этим мы проанализировали и обобщили исследования о парауретральных протоках и железах в целом, и их воспалении в частности.
История описания и терминология
Еще в 1672 году нидерландский анатом и физиолог R. D. Graaf (1641-1673) в своем труде «De mulierum orga-nis generationi inservientibus tractatus novus» описал «лакуны, расположенные в конце мочевыводящих путей», которые, по аналогии с мужскими, он принял за выводные протоки «женской простаты» (рис. 1). Согласно его суждению, эти протоки были источником смазочной жидкости, выделяемой при сексуальном возбуждении, а также одним из очагов гонорейной инфекции.

Рис. 1. A – Портрет R. D. Graaf; B – первая страница его трактата о женских болезнях; С – иллюстрация из книги Fig. 1. A is a portrait of R. D. Graaf; B is the first page of his treatise on women's diseases; C is an illustration from the book
Представление R.D. Graaf о том, что «половая жидкость» выделяется в мочеиспускательный канал через парауретральные протоки, было исправлено C. Bartholin в 1677 году, когда он описал железы, которые теперь носят его имя, и объяснил их функцию [14]. К сожалению, к этому времени R. D. Graaf скончался, и учение о парауретральных протоках быстро кануло во временное забвение.
За следующие 200 лет были лишь единичные сообщения о парауретральных протоках и железах. J. As-truc (1737) в трактате о венерических болезнях описал «предстательную железу», окружающую женскую уретру, а также небольшие лакуны по бокам мочеиспускательного канала [15]. E. Winslow (1775) упомянул меньшие лакуны и один больший проток в женском мочеиспускательном канале. A. Boyer (1797) описал отверстия слизисто-секретирующих желез в наружном отверстии и слизистой оболочке уретры. J. Cruveilhier
-
(1844) утверждал, что у женщин простаты нет, но имеются многочисленные крипты слизистой оболочки уретры или лакуны, открывающиеся в просвет мочеиспускательного канала. В 1853 г. R. Virchow описывая камни, которые он находил в женских уретральных железах, упомянул о них, как о гомологах мужской предстательной железы, и отмечал, что при «женском гермафродитизме» камни были особенно многочисленны. Из этих наблюдений он сделал вывод, что уретральные железы женщин гомологичны предстательной железе у мужчин [16].
Широкую же известность парауретральные протоки и железы получили в 1880 году благодаря именитому американскому гинекологу Alexander Johnston Chalmers Skene (1838-1900), описавшему их в своей работе «Анатомия и патология двух важных желез женской уретры» (рис. 2) [17].
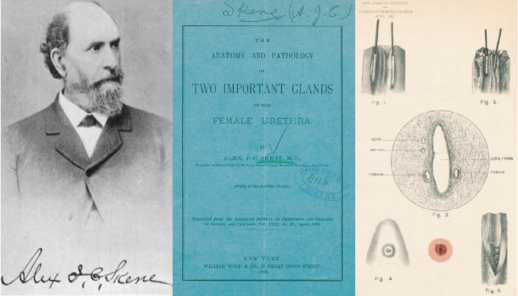
Рис. 2. А – Портрет А. Skene; обложка его книги; иллюстрация из работы [17] Fig. 2. Portrait of A. Skene; the cover of his book; an illustration from the work [17]
-
А. Skene очевидно не знал о наблюдениях анатомов XVII и XVIII веков. Когда он объявил о своем собственном открытии парауретральных протоков в 1880 году, то заявил, что не смог найти никаких упоминаний о них ни в одном из учебников того времени. «Насколько мне известно, – повествовал автор, – анатомия этих желез не была описана, а болезни, которым они подвержены, не упоминались патологоанатомами».
Таким образом, еще в XVII и XIX веках двумя исследователями был сделан важный вывод о связи инфекции в женских половых органах с воспалением парауретральных протоков и желез.
Стоит отметить, что А. Skene являлся одним из основоположников Американского гинекологического общества и его президентом в 1886-1887 гг. Он также руководил основанной им больницей для женщин [18]. Можно предположить,что именно его известность в научных кругах, большое количество публикаций, безусловный авторитет среди коллег как диагноста, так и врача, а также подробно описанная им клиническая картина нового заболевания и методы его лечения послужили причиной, навсегда связавшей его имя с парауретральными протоками и железами. Уже к концу XIX – началу XX веков в зарубежной и отечественной литературе эти структуры стали именоваться

экспериментальная
клиническая урология № 4 2023 железами Скина, а их воспаление – скинеитом. Тем не менее, в перечне международной анатомической терминологии, утвержденной на XV конгрессе в Риме (1999) присутствуют лишь уретральные железы (urethral glands), уретральные лакуны (urethral lacunae) и парауретральные протоки (para-urethral ducts) [19].
Эмбриология, анатомия и гистология
Освещение в профессиональной печати клинических случаев воспаления парауретральных протоков и желез и их успешного лечения побудило в научном сообществе активные исследования их эмбриологии, анатомии, морфологии и роли в организме женщины.
Так, американский эмбриолог F. Jonson в своей работе «The homologue of prostate in the female» подробно изложил результаты сравнительного изучения мужского и женского мочеиспускательного канала на основе серийных срезов эмбриона на разных стадиях развития [20]. Он писал, что одновременно с образованием предстательной железы у мужчины появляются такие же железы и у женщины. Впервые ЖС наблюдаются у эмбрионов размером около 60 мм в длину (рис. 3). Они распределяются по всей уретре на ее передней, задней и латеральной стенках. Одни возникают из проксимального конца урогенитального синуса, другие – из дистального отдела маточно-влагалищного канала. Последние явно дегенерируют, поскольку отсутствуют на более поздних стадиях развития плода и у взрослых
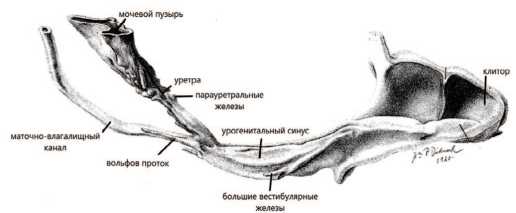
Рис. 3. Иллюстрация из работы F. Jonson (1922). Боковой вид восковой реконструкции уретры и связанных с ней эпителиальных структур эмбриона женского пола 60 мм с зачатками парауретральных желез (33-х кратное увеличение) [20]
Fig. 3. An illustration from the work of F. Jonson (1922). Lateral view of the wax reconstruction of the urethra and associated epithelial structures of a 60 mm female embryo with the rudiments of the paraurethral glands (33-fold magnification) [20]
У эмбриона 275 мм несколько желез находятся сразу за пределами отверстия, относящегося к урогенитальному синусу (рис. 4). Две из них, более крупные,
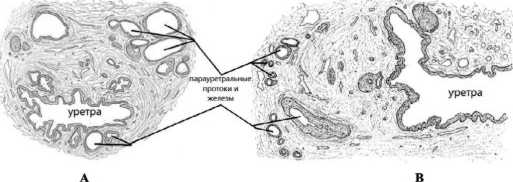
Рис. 4. Поперечный срез уретры: А – Женского эмбриона 275 мм и В – Взрослой женщины (26-ти кратное увеличение [20]
Fig. 4. Transverse section of the urethra: A – Female embryo 275 mm and B –
Adult woman (26x magnification) [20]
чем остальные,расположены по обе стороны от меа-туса. Эти железы соответствуют по положению ЖС, и их происхождение также, как и простатических протоков, принадлежащих урогенитальному синусу, не подлежит сомнению, считал автор.
Сравнивая мужские и женские эмбрионы, F. Jonson подробно описал сходства и различия: в начале развития немногочисленные и мелкие уретральные железы постепенно увеличиваются в количестве, размерах и дают начало разветвлениям. Однако их рост замедлен по сравнению с мужскими, и они никогда не достигают такой высокой степени развития, как в мужской простате. У взрослых их точки сходства с предстательной железой заключаются в их отношении к уретре и ее слизистой оболочке, а также в том, что они представляют собой разветвленные трубчатые железы и направлены проксимально к мочевому пузырю [20].
Резюмируя результаты данного исследования, можно считать эмбриологически доказанной гомологию (др.-греч. ὅμοιος «подобный, похожий» + λογος «слово, закон») парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин с предстательной железой у мужчин. Однако ЖС меньше по количеству,они менее плотно прилегают друг к другу, имеют меньше ветвей и более толстые эпителиальные стенки, небольшие просветы, а в их эпителии менее выражена секреция.
Исследованием протяженности и детальной анатомии этих структур в 1948 году активно занимался американский гинеколог из Чикаго J. Huffman [21]. Чтобы изучить анатомию гомолога предстательной железы у взрослой женщины он исследовал материал одиннадцати аутопсий, три из которых послужили основой для изготовления восковых моделей из серийных срезов (метод,признанный анатомами того времени чрезвычайно точным). В результате этой работы были выявлены некоторые общие для всех образцов характеристики:
-
• самые дистальные парауретральные протоки открываются в мочеиспускательный канал непосредственно в пределах меатуса;
-
• на всех препаратах наибольшее количество парауретральных протоков впадает в дистальную треть мочеиспускательного канала;
-
• имелась определенная тенденция к четырем группам устьев протоков: по две с каждой стороны (вентролатеральная и дорзолатеральная).
В исследованном материале наличие двух крупных латеральных протоков, описанных A. Skene, было скорее исключением, чем правилом, а широкое ветвление терминальных отделов было более выраженным. Только у двух из одиннадцати экземпляров можно было проследить два более крупных канала – по одному с каждой стороны уретры.За исключением большего диаметра и большей длины, они напоминали другие парауретральные протоки, наблюдаемые в том же и дру-

гих исследуемых образцах; выстланы эпителием того же типа и оканчивались трубчатыми железами. Наименьшее количество протоков, обнаруженных в любых из исследованных мочеиспускательных каналов, было шесть, наибольшее – 31 (рис. 5).
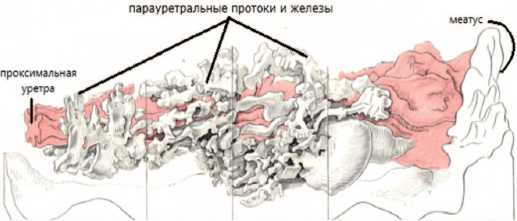
Рис. 5. Трехмерная восковая модель мочеиспускательного канала c парауретральными протоками и железами (I тип) [21]
Fig. 5. Three-dimensional wax model of the urethra with paraurethral ducts and glands (type I) [21]
Исследование показало, что выстланы они большей частью столбчатым эпителием, от низкостолбчатых, приближающихся к кубовидным до умеренно высоких цилиндрических клеток. Внутри этого столбчатого эпителия иногда встречаются структуры, секретирующие слизь, о чем свидетельствует окрашивание муцикармином. Однако не все ветви протоков оканчиваются железами, многие заканчиваются небольшими карманами, крошечными расширенными кистозными пространствами и мелкими ветвящимися канальцами, покрытыми псевдомногослойным столбчатым эпителием. Вблизи их устьев выстилка становится того же типа, что и у уретры на этом уровне, т. е. ближе всего к меатусу они покрыты многослойным плоским эпителием, а в средней трети – переходным эпителием.
Таким образом, описываемые здесь структуры не являются ни пара-, ни периуретральными. Они лежат не только вдоль и рядом с мочеиспускательным каналом, но также около и вокруг, и впадают в него. Большинство анатомов и докторов до этого исследования считало (а кто-то считает и по-прежнему) гомолог простаты у женщин россыпью незначительных канальцев или выпячиваний с двумя-тремя крупными протоками.
Анатомическое и гистологическое исследование J. Huffman в отличии от клинической работы А. Skene показало обратную тенденцию. Чаще всего ЖС представляют собой выраженное разветвление каналов и желез, окружающих женскую уретру в той или иной степени со всех сторон, особенно латерально и сзади с большим количеством протоков (от 6 до 31). В данном случае мочеиспускательный канал можно сравнить с деревом, вокруг которого от его основания отходят многочисленные низкорослые ветви – парауретральные протоки и железы.
Патогенетические факторы воспаления в ЖС и их гормональная чувствительность
Одним из актуальных вопросов, занимающих внимание исследователей, остается причинная роль ЖС в возникновении и поддержании рецидивирующей ИНМП. Так, R. Deter и соавт. в 1946 году изучили анатомию и морфологию мочеиспускательного канала и периуретральной ткани на материале 100 аутопсий [22]. Железы были обнаружены в 92% наблюдений, однако стоит отметить, что исследование ограничивалось проксимальными 1,5-2 см уретры. Поскольку все образцы имели разное количество железистой ткани, авторы предприняли попытку классифицировать их по степени развития:
-
0 степень – железы отсутствуют;
-
I степень – имеется минимальное количество железистой ткани;
-
II степень – большая часть одного из латеральных краев уретры окружена простыми трубчатыми желе-зами,также имеются три сзади и две на противоположном латеральном крае;
-
III степень – некоторые из желез вокруг этого отдела уретры имеют сложный трубчатый вид; другие относятся к простому трубчатому типу. В просвете одного из ацинусов видна структура, похожая на амиловые тела мужской предстательной железы;
IV степень – группы желез, окруженных концентрическими слоями фиброзной ткани;вне этой группы на разрезе видны еще три железы, просветы которых заполнены гомогенным окрашенным эозином белковым материалом. При большом увеличении видно, что ацинусы этих желез выстланы столбчатым эпителием с базально расположенными ядрами и периферическим участком светлой цитоплазмы (рис. 6).
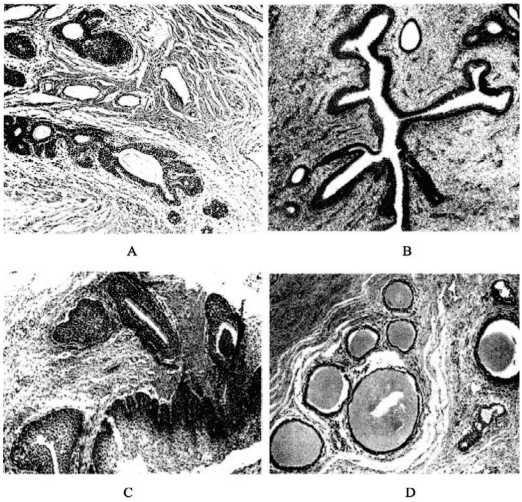
Рис. 6. Поперечные срезы четырех мочеиспускательных каналов и различные степени развития ЖС в них. A – I степень; В – II степень; С – III степень; D – IV степень [22] Fig. 6. Cross sections of the four urethra and various degrees of development of the pancreas in them. A – I degree; B – II degree; C – III degree; D – IV degree[22]
В данной серии было следующее распределение парауретральных протоков и желез: в 8% экземпляров ЖС отсутствовали, 18% образцов имели первую степень развития желез, 29% – вторую, 28% – III и 17% – IV степень соответственно. Количество гистологических препаратов без этих структур (8%), вероятно, можно объяснять исследованием лишь проксимальных 1,5-2 см мочеиспускательных каналов, в то время как анатомическая работа J. Huffman показала большую распространенность ЖС именно в дистальной трети в области меатуса [21].
Также R. Deter и соавт. изучалась локализация желез по окружности уретры. У 100% экземпляров они были обнаружены латерально, дополнительно в 75% случаев – сбоку и сзади, у 16% образцов находились вокруг мочеиспускательного канала.
Второй основной частью данной работы, кроме количественного и пространственного описания ЖС, явилось исследование всех образцов на наличие в них морфологических признаков воспаления с градацией от 0 до 4+. Лейкоцитарная инфильтрация была главным критерием, определяющим выраженность воспалительных изменений. Другими учитываемыми факторами были фиброз, гиперемия, отек и дегенеративные изменения эпителия, выстилающего уретру и ее железы.
Оценочная классификация образцов по выраженности воспалительных изменений:
-
«0» – отсутствие воспалительных изменений;
-
«1+» – едва заметное количество воспалительных изменений;
-
«2+» – выраженная инфильтрация без признаков локализации;
-
«3+» – более выраженная инфильтрация, много лейкоцитов, интактный эпителий;
-
«4+» – выраженная лейкоцитарная инфильтрация с образованием множественных лимфоцитарных узелков и десквамацией эпителия выстилки уретры.
Итоговое распределение было следующим: 61% образцов был отнесен в объединенные группы 0 и 1+ без или с минимальным количеством изменений; 23,3% получили оценку 2+; 6,6% – 3+ и 8,8% – 4+. Следует отметить, что авторами не описаны (или не были выявлены) ни кисты ЖС, ни их абсцедирование как возможный исход катарального воспаления и вызванной им обструкции протоков.
Сопоставив данные из первой (по степени развития) и второй (по выраженности воспаления) классификации, авторы получили следующие результаты:
-
a) в образцах, не имеющих желез (0 степень развития ЖС), в 75% случаев отсутствовало воспаление в мочеиспускательном канале и периуретральных тканях, что является самым высоким показателем интактности среди остальных групп из первой классификации;
-
b) в I и II группах по степени развития желез, выраженность воспалительных изменений ни в одном случае не превышала оценки 1+;
-
c) не было заметной разницы в выраженности воспалительных изменений в II, III и IV группах по степени развития желез [22].
Анализ полученных данных указывает на то, что само наличие желез является важным фактором в адгезии микробной флоры и возникновении воспалительных изменений в мочеиспускательном канале и периуретральных тканях. Однако количество ЖС, присутствующих сверх определенного уровня (II степень развития желез и выше), существенного влияния на выраженность морфологических признаков воспаления в исследуемых образцах не оказывает.
-
С. Lintgen и соавт. также изучили результаты 100 аутопсий. В отличие от предыдущих авторов, исследовалась вся уретра и периуретральные ткани, мочевой пузырь и влагалище. ЖС были обнаружены в каждом случае в дистальной трети уретры и в 65% – в ее проксимальном отделе. Семьдесят шесть из 100 образцов (76%) гистологически показали воспалительную реакцию [23].
Работы R. Deter и С. Lintgen в полной мере доказывают роль парауретральных протоков и желез в развитии воспалительной трансформации тканей как в самой уретре, так и парауретрально. Стоит еще раз подчеркнуть,что указанные научные изыскания являются патоморфологическими. О наличии или отсутствии прижизненных клинических признаков ИНМП у женщин, чьи аутопсийные материалы в последствие изучались известно не было [22, 23].
Кроме того, данные исследования показывают непостоянство ЖС как по расположению, так и по степени развития у разных женщин.Однако причины указанных отличий до сих пор остаются не ясны. Одним из возможных факторов, способствующих их росту, рассматривались эндокринные расстройства.
Гипотезу о том, что гормоны могут являться одним из этиологических факторов в цепочке событий, приводящих к воспалению ЖС исследовал наш соотечественник В. Коренчевский и его коллеги из Института Листера в 1936 году. Он вводил диоландростерон стерилизованным самкам крыс (двусторонняя оварэктомия) в течение 3 недель в дозах от 175 до 700 единиц в день. При вскрытии этих особей у основания и перед мочевым пузырем были обнаружены железы, не встречающиеся в норме. Микроскопически данные структуры имели вид вентральной доли мужской предстательной железы. Такая же железистая ткань была обнаружена у некоторых здоровых особей, но только при гистологическом исследовании – в зачаточном состоянии и с атрофическими клетками [24]. Следовательно, введение диоланд-ростерона провоцировало у лабораторных животных развитие и рост рудиментарного органа.
-
С. Moore и D. Price в 1932 году также указывали, что гормоны гонад стимулируют гомологичные репродуктивные органы, но не действуют на гетерологичные. Например, мужские гормоны не влияют на женскую по-

ловую систему после оварэктомии, но могут стимулировать рудиментарные структуры у женщин, которые гомологичны мужским, как например парауретральные железы [25]. Таким образом, можно сделать вывод о том, что ЖС являются гормонозависимым органом.
Возможна ситуация, когда нормальный баланс мужских и женских половых гормонов по какой-то причине изменен – например, в менопаузе, в период полового созревания, после замужества или при некоторых гинекологических и других заболеваниях. В этих случаях рудиментарные ЖС могли бы подвергнуться гипертрофии. Если экстраполировать результаты работы В. Коренчевского на человека и сопоставить их с исследованием R. Deter, то становятся понятны причины различных степеней развития ЖС в исследуемых образцах. Это может являться рациональным объяснением избирательной заболеваемости скинеитом в популяции. Следовательно, перспективным представляется изучение возможной роли половых гормонов как этиологических факторов риска возникновения воспаления в этом органе.
Иммуногистохимические характеристики ЖС
В конце XX и начале XXI веков с развитием науки ряд исследователей изучал иммуногистохимические характеристики ЖС. M. Wernert и соавт. в 22 случаях из 33 (66,7 %) выявили железы с положительной реакцией на простатическую кислую фосфатазу и простат-специфический антиген (ПСА) [26]. J. Pollen и соавт. и S. Tepper и соавт. описали схожие результаты экспрессии ПСА в 70% и 83% случаев соответственно [27, 28].
M. Zaviačič и соавт. при анализе 130 посмертных гистологических препаратов мочеиспускательного канала у женщин с последующими биохимическими и иммуногистохимическими исследованиями продемонстрировали экспрессию ПСА и простатспецифической кислой фосфатазы в ЖС в 100% наблюдениях [29]. Следует отметить, что M. Zaviačič активно выступал против устоявшегося названия этих структур. В 1999 году он опубликовал монографию под названием «Женская простата. От рудиментарных парауретральных желез и протоков Скина до функциональной простаты женщины» [30]. Он считал, что с исторической точки зрения правильно называть их железами Де Граафа, а учитывая все исследования 20 века, подтверждающие гомологию этих структур с предстательной железой у мужчин – «женской простатой». Однако, еще в 1948 году H. Everett в обсуждении статьи своего коллеги J. Huffman предостерегал того от использования данного термина, считая, что это может привести к избыточной хирургической агрессии [21].
Учитывая приведенные выше работы, можно считать доказанной гомологию парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин с предстательной железой у мужчин и с точки зрения иммуногистохимии.
Исследовалась роль ПСА и в диагностике злокачественных поражений желез Скина [31–34]. T. Korytko и соавт. заявили, что аденокарцинома ЖС может гистологически напоминать рак предстательной железы и проявляться повышенным значением ПСА в сыворотке крови. Как было показано в этом случае, онкомаркер снизился после лучевой терапии. Авторы предположили, что уровень ПСА в крови может быть полезен в качестве лабораторного критерия рецидива заболевания [35].
Ряд авторов оценивал изменения парауретральных желез у женщин с врожденной гиперплазией надпочечников. P. Doherty и соавт. обследовали 11 пациенток с данной нозологией. Периуретральное утолщение при пальцевом вагинальном исследовании было отмечено у одной респондентки с повышенным уровнем 17-гидроксипрогестерона, в остальных 10-и случаях эта ткань не определялась. У другой наблюдаемой с заметно повышенным уровнем тестостерона, андростендиона, дигидротестостерона и 17-гидрокси-прогестерона ПСА составил 0,2 нг/мл, у остальных – менее 0,1 нг/мл. Магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ) выявила отсутствие дефинитивной ткани «женской предстательной железы» у всех обследуемых, несмотря на признаки маскулинизации мочеполовой системы [36]. В работе M. Paulino и соавт. у пяти из 32х женщин (16%) с врожденной гиперплазией надпочечников была выявлена небольшая «простата» с концентрацией ПСА в сыворотке выше 0,1 нг/мл [37]. A. Faradji и соавт. сообщили о 15-летней больной с указанной патологией и недостаточным соблюдением заместительной гормональной терапии.На МРТ было выявлено периуретральное тканевое образование, напоминающего предстательную железу, вес которой оценивался в 4,5 г. Авторы также отметили наличие гипертрофии кавернозных тел клитора, и повышение ПСА в сыворотке крови до 0,24 нг/мл [38].
Таким образом, роль ПСА в диагностике заболеваний ЖС представляет клинический интерес, однако учитывая малую выборку пациентов, безусловно требует дальнейших исследований.
Функция ЖС
Среди современных работ нет единого представления о функционально-физиологическом предназначении парауретральных протоков и желез. Существует множество разногласий по поводу роли ЖС в сексуальной функции и ее связи с «точкой G» [39-41]. В 1950 году E. Gräfenberg на передней стенке влагалища определил область, стимуляция которой вызывает оргазм, отличный от оргазма при стимуляции клитора [42]. В последующем исследовании F. Addiego и соавт. с участием одной пациентки был введен термин
«точка G» [43]. В работе С. Darling и соавт. анонимный опросник был распространен среди 2350 женщин в США и Канаде и 55% из них ответили на него; 82% исследуемых, заявили о наличии чувствительной области на передней стенке влагалища. Кроме того, 40% опрошенных информировали о выделении жидкости в момент оргазма [44]. Ее источником ряд авторов считали именно ЖС [29, 39, 40, 43].
-
F. Wimpissinger обследовал двух пациенток 44 и 45 лет, которые также утверждали об «эякуляции» во время оргазма. По своему биохимическому составу эти выделения имели некоторые параметры (ПСА, простатоспецифическая кислая фосфатаза, глюкоза, К, Na, Cl), обнаруживаемые в секрете предстательной железы у мужчин. Кроме того, при трансвагинальном ультразвуковом исследовании у обеих респонденток была идентифицирована структура, соответствующая ткани ЖС, окружающая женскую уретру по всей длине [45].
В систематическом обзоре Z. Pastor сделал вывод о том,что выделение жидкости обычно не является частью женского оргазма. Однако при анализе 61 работы он выделил два вида «женской эякуляции». Первый – секреция небольшого количества белесоватой жидкости из «женской простаты». Несмотря на то, что по литературным данным его распространенность составляет 10-54%, объективно подтверждены только десятки случаев, остальные сообщения основаны главным образом на субъективных анкетных исследованиях. Второй – выделение значимого количества мочи при пенетрации или оргазме, связанного со стрессовой или ургентной формой недержания мочи соответственно. Кроме того, оба этих явления могут происходить одновременно [46].
В анатомических работах T. Hines и R. Pauls и соавт., касающихся изучения этой области, c проведением 110 вагинальных биопсий, был сделан следующий вывод: «имеющиеся поведенческие, анатомические и биологические исследования слишком слабы, и не доказывают наличие точки G». Авторы считали, что если эта область и существует, ее нельзя связывать с ЖС [47, 48].
M. Colson в работе «Женский оргазм: мифы, факты и споры» подробно описывает современные концепции сексологии, в частности вопросы традиционной двойственности вагинального и клиторального оргазмов.В своем обзоре автор делает вывод о том, что вся передняя стенка влагалища (а не только какая-то точка) из-за близости к уретре и клитору, а также к фасции Халбана с богатым нервным и кровоснабжением, должна рассматриваться как единая структура, играющая роль активного органа, используемого для передачи возбуждения клитору путем растяжения находящихся внутри него связок во время полового акта. Кроме того, высокая чувствительность этой зоны связана с набуханием и выпячиванием пещеристых тел клитора при сексуальном возбуждении, и их последующим стимулированием при фрикциях. Считается, что эта зона является источником оргазма, который возникает во время внутривагинальных движений, но также затрагивает и клитор [49]. Также подтверждает эту гипотезу наличие псевдокавернозной эректильной ткани внутри слизистой оболочки передней стенки влагалища, обнаруженной у 89% женщин в серии из 14 аутопсий [50].
Учитывая приведенные научные работы, можно сделать заключение о том, что роль ЖС в сексуальной функции, как и ее участие в образовании «женского эякулята» маловероятна.
Ряд авторов проводили изыскания по поиску других возможных предназначений парауретральных протоков и желез, а именно их места в механизме про-тивомикробной защиты. H. Helmholz изобрел устройство, которое позволяло брать культуры микроорганизмов на разной глубине мужской уретры без контаминации при прохождении инструментов через более дистальные отделы. Все мочеиспускательные каналы содержали бактерии в первом дистальном сантиметре, а их количество прогрессивно уменьшается по мере удаления от меатуса проксимально. У большинства урологически здоровых респондентов бактерии присутствовали и в четвертом сантиметре, но отсутствуют проксимальнее 6-го. Так как женская уретра в длину всего 4 см, автор предположил, что в ней могут существовать иные механизмы противомикробной защиты, препятствующие проникновению бактерий в проксимальный отдел мочеиспускательного канала и далее в мочевой пузырь [51].
C. Cox и соавт. изучали уретральую флору у 52 здоровых респонденток (I группа) и 35 больных с рецидивирующей ИНМП (II группа). С целью исключения контаминации при взятии анализов был переконструирован инструмент Гельмгольца для использования в женской уретре.В этом исследовании также, как и в предыдущей работе, образцы бактерий были получены отдельно из 1-го, 2-го, 3-го и 4-го см мочеиспускательного канала (начиная от меатуса и двигаясь проксимально к шейке мочевого пузыря). При исследовании I группы исследуемых, у всех из них (100%) были выявлены бактериальные штаммы в первом дистальном сантиметре уретры, а у 54% – в 4-ом, прилегающем к шейке мочевого пузыря. Кроме того, 27% выявленных культур были патогенными грамот-рицательными микроорганизмами. У всех исследуемых (100%) из II группы также были выделены бактерии в дистальном сантиметре мочеиспускательного канала, а у 77,2% – в 4-ом. Количество микроорганизмов, полученных из самого дистального и самого проксимального сегмента и у I и II группы снижалось, в 36,1 раз и в 8,3 раза соответственно [52]. Достоверность полученных результатов авторами статистически не оценивалась.
Результаты показывают, что микробный пейзаж мочеиспускательного канала у женщин с рецидивирующей ИНМП содержит более высокий процент патогенных культур, чем уретральная флора здоровых женщин. Кроме того, количество бактерий в проксимальном 4-ом сантиметре мочеиспускательного канала у II группы пациенток на 23,2% больше. Таким образом, вероятно, у больных с хронической ИНМП естественные защитные механизмы повреждены и уже не могут адекватно препятствовать проникновению микроорганизмов в этот важный проксимальный сантиметр мочеиспускательного канала.
J. Hutch и соавт. подтвердили тот факт, что ЖС являются слизесекретирующими структурами, демонстрируя наличие слизи в клетках эпителия, в просвете парауретральных желез и уретры. Если слизь в уретре выполняет ту же функцию, что и в других частях тела (нос, бронхиальное дерево), то она может замедлить или предотвратить проникновение бактерий в мочеиспускательный канал и далее в мочевой пузырь извне [53].
S. Moalem и J. S. Reidenberg предположили наличие антимикробных и защитных свойств в секрете ЖС [54].
C. Kunin и соавт. постулировали, что женская уретра может быть благоприятной средой для колонизации микроорганизмами,но предохранена мощным защитным механизмом.Он включает выделение уропатогенов, связанных с отшелушивающимися клетками уретры, захват бактерий слизью, выделяемой парауретральными железами, периодическое вымывание мочой, локальную продукцию иммуноглобулинов, цитокинов, дефенсинов и мобилизацию лейкоцитов [55].
Таким образом, можно сделать вывод, что нормально функционирующие парауретральные железы являются частью защитного механизма мочевого пузыря. «Разрушение» этих желез рецидивирующей ИНМП может создать ситуацию, в которой они больше не смогут предохранять мочевой пузырь от повторяющейся восходящей бактериальной инвазии или сами являться очагом инфекции.
Обследование и лечение
Клинический портрет пациентки со скинеитом весьма разнообразный.
В работе А.Г. Глухарева симптомы у женщин с воспалением ЖС распределились следующим образом: ди-зурические расстройства встречались в 93,6% случаев, болезненность при мочеиспускании – в 85,1%, боли внизу живота – в 70,3%, боли при половом акте – в 76,6%, жжение в уретре вне акта мочеиспускания – в 72,3%, «боль в положении сидя» – в 55,3%, боли при введении инструмента в уретру – у 100% пациенток [8]. Однако указанные симптомы могут быть вызваны и другими урологическими, а также гинекологическими заболеваниями и не являются патогномоничными для скинеита. Отсутствие специфичных жалоб безусловно усложняет постановку правильного диагноза.
Стандартизированной методики обследования пациентки при подозрении на воспалительные заболевания парауретральных протоков и желез до настоящего времени нет, как и рекомендованных методов лечения. Помимо этого,данный диагноз отсутствует в номенклатуре МКБ-10, в российских клинических рекомендациях и национальном руководстве, что бесспорно затрудняет работу врача.
Для выработки единых подходов к обследованию пациенток с воспалением ЖС в 1964 году А.М. Мажби-цом была предложена клиническая классификация рассматриваемого заболевания:
-
1. интрауретральные скинеиты;
-
2. экстрауретральные скинеиты;
-
3. юкстауретральные скинеиты, когда железы располагаются на поверхности слизистой задней губы мочеиспускательного канала [4].
Диагностика эктрауретральных скинеитов обычно не обременительна – устья протоков расположены латеральнее меатуса и доступны обычному визуальному осмотру. Особую сложность по причине их труд-нодоступности составляет выявление интрауретраль-ного воспаления ЖС, так как в этом случае выводные протоки расположены внутри мочеиспускательного канала. Последние встречаются намного чаще [3, 4].
Для диагностики скинеитов А. М. Мажбиц проводил пальпацию передней стенки влагалища в проекции уретры, при которой можно было определить ее болез-ненность,«зернистость» (частый признак гонорейной этиологии уретрита), а также выделение слизистогнойной капли [4]. C. Eberhart предложил использовать стержневой тест (прижимание уретры в ее средней трети со стороны влагалища к лобковому сим-физу)и катетерный тест (надавливание стеклянным катетером 10 Fr на противоположные стенки уретры при его извлечении) [56]. Для осмотра устьев протоков парауретральных желез в различное время использовались согнутые под углом головные шпильки,метал-лические лопаточки Janet, носовое зеркало, пинцет или зажим типа «москит», разведенные внутри уретры. Однако, все эти инструменты не приспособлены для осмотра мочеиспускательного канала и не обеспечивают должной визуализации. Созданный C. Moore в 1918 году на основе эндоскопа Kelly скинеескоп и усовершенствованный в 1926 году H. Walhter (электрический скинеескоп) не оправдал ожиданий авторов и не получил широкого распространения [57, 58].
Методы, обычно применяемые для обследования пациенток с рецидивирующими ИНМП, в диагностике больных со скинеитом в литературе не описаны Имеющееся в настоящее время эндоскопическое
оборудование больше предназначено для осмотра мужского мочеиспускательного канала. Визуализация же женской уретры с его помощью выражено ограничена в проксимальном отделе, и практически невозможна в дистальном.
Стоит отметить, что отсутствие специализированного приспособления для полноценного осмотра дистальной трети женской уретры, где и расположены устья протоков ЖС, является и на сегодняшний день одной из главных проблем в обследовании пациенток и, как следствие, в постановке правильного диагноза.
Современные клинические работы, описывающие методику консервативного лечения скинеита с доказанной или предполагаемой эффективностью,в литературе отсутствуют. Исторически использовалось местное туширование выводных протоков ЖС, инстилляции в них различных растворов, антибактериальная, физио- и бальнеотерапия [3, 17].
В первой половине XX века ряд авторов предлагали гальванокаустику протоков ЖС, что представляло из себя разрушение тканей с помощью платиновой проволоки, накаленной электрическим током [3]. В 1918 году C. Moore при хроническом воспалении ЖС первым предложил выполнять их электрокоагуляцию [57]. В последующем R. Le Fur и H. Walther также описали результаты применения этого метода [59, 60]. Позднее наши соотечественники В.А. Гораш (1929), М.А. Гельман (1931) и А.М. Мажбиц (1936) использовали данный вариант оперативного пособия для лечения гонорейных скинеитов, отмечая частую необходимость выполнения повторных операций из-за пропущенных при первом хирургическом вмешательстве протоков [3]. В 1959 году C. Eberhart сравнивал результаты двух вариантов хирургического лечения скинеита. Первый способ заключался в механическом отрыве протока ЖС с помощью специального зонда и последующим удалением его вместе с частью слизистой уретры. Второй вариант лечения был дополнен предварительной коагуляцией железы.Эффективность методик составила 100% и 60% соответственно [61]. Стоит отметить выраженную травматичность и, вероятно, болезненность указанной методики хирургического лечения. Однако автор не описал в своей работе ни осложнений, ни наличия послеоперационного болевого синдрома у своих пациенток.
В свою очередь еще А. Skene в своей статье писал «…в следующем случае, который попадет в мои руки и не поддастся лечению, я вскрою проток, разрезав его изнутри наружу». Его задумку с появлением современного электрохирургического инструментария реализовал L. Riba в 1956 г. Он описал электрорезекцию ЖС у 35 больных при резистентном трихомониазе, расценив инфекцию в парауретральных железах как источник рецидива и причину низкой результативности проводимой консервативной терапии. Общая эффективность составила 86%, однако 23% пациенткам потребовались две и более операции [5].
-
C. Riеser в 1968 году опубликовал результаты электрорезекции ЖС у 206 пациенток при их неспецифическом хроническом воспалении и рецидивирующей ИНМП. Методика операции заключалась в следующем: электрод электрохирургического аппарата вводился на всю глубину инфицированных протоков парауретральных желез, и с помощью тока вскрывался по всей длине по направлению к просвету уретры (рис. 7). Дополнительно при наличии воспалительных изменений в области треугольника Льето, как он считал вторично вызванных инфекцией в парауретральных протоках и железах, выполнялась его фульгурация. Автор также указывал что, некоторым пациенткам (количество в статье не указывается) потребовалась повторная операция, направленная на разрушение инфицированного протока, пропущенного во время первоначальной процедуры [62].
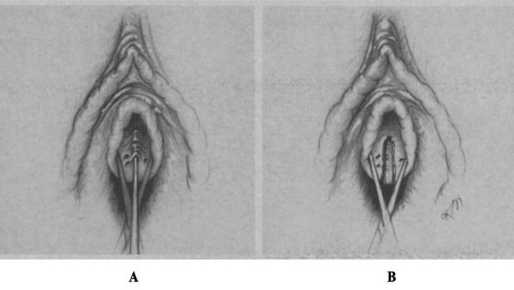
Рис. 7. Этапы операции. A – Введение электрода в инфицированный проток
ЖС; B – послеоперационный вид коагулированного протока ЖС [62]
Fig. 7. Stages of the surgery. A – Insertion of the electrode into the infected duct of the Skene glands; B – postoperative view of the coagulated duct of the Skene glands [62]
-
E. Lewis и соавт. в 1973 году выполнили операцию по методике C. Riеser 70 пациенткам: 62 из них (88%) почувствовали значимое улучшение состояния после первого хирургического пособия, 8 женщинам (12%) потребовалась повторное вмешательство по удалению остаточных инфицированных протоков. Общий результат авторы оценили в 100%. Также они особо отмечали что, «метод заслуживает более широкого применения и может быть успешно использован всякий раз, когда заболевание парауретрального протока выявляется у больной с рецидивирующим цистоуретритом при отсутствии другой патологии мочевыводящих путей» [63].
-
E. Leiter с соавт. и A. Rouxel с соавт. получили схожие показатели в 93% и 85% при выборке 16 и 21 пациенток соответственно [64, 65].
Позже работы A. Lachand и G. Karam с соавт. характеризовались менее впечатляющими показателями, а именно 65% и 70% при выборке 34 и 61 больная соответственно. Однако оба автора отмечали, что для этой группы респонденток, страдающих хронической рецидивирующей ИНМП с многолетним анамнезом заболевания, даже
такой уровень удовлетворенности можно считать значимым достижением [66, 67].
Самые скромные результаты описаны в публикации P. Hedlund – 44% из 41 женщины. Однако при анализе статьи такой низкий показатель эффективности может быть связан с широкой и разнообразной выборкой пациенток. Среди них были больные с дивертикулом уретры (14,5%), сакроилеитом (12%) и интерстициальным циститом (4%) [68].
В настоящее время, эру расцвета антибактериальных препаратов, повсеместное их назначение при любых жалобах на дизурию привело к тому, что клиническая картина пациентки с хроническим воспалением ЖС стала иной – более сглаженной. Этот факт безусловно затрудняет диагностику, увеличивает длительность заболевания, чаще приводит к хронизации инфекционного процесса, а также может негативно влиять на результаты как консервативного, так и хирургического лечения пациенток.
Нами систематизирован мировой опыт выполнения операции, предложенной C. Riеser. Материал был отобран из доступных литературных источников в период с 1968 года по настоящее время с использованием ключевых слов: «операция Ризера»; «метод Ризера»; «хирургическое лечение уретрита»; «хирургическое лечение скинеита»; «лечение воспалительных поражений уретры»; «рецидивирующий цистоуретрит». («Rieser's surgery»; «Rieser method»; « surgical treatment of urethri-tis»; «surgical treatment of skineitis»; «treatment of inflammatory lesions of the urethra»; «recurrent cystourethritis») Обобщенные данные представлены в таблице 1.
Таким образом, операция Ризера является эффективным методом лечения женщин с хроническим воспалением ЖС. Безусловно, строгий отбор пациенток является важным критерием успеха хирургического пособия. Основными факторами, приводящими к повторным вмешательствам, являются не обнаруженные при первом пособии протоки. Связано это с недостаточной визуализацией искомых структур, прежде всего по причине отсутствия специализированного инструмента для осмотра женского мочеиспускательного канала в целом и устьев протоков ЖС в частности.
ВЫВОДЫ
История исследования парауретральных протоков и желез насчитывает более трех с половиной столетий. Рассвет их изучения пришелся на конец XIX – начало XX веков. За это время различными учеными подробно описана анатомия, эмбриология, гистология и морфология этого органа.На основе этих основополагающих работ вместе с иммуногистохимическими изысканиями доказана гомология придаточных желез мочеиспускательного канала у женщин с предстательной железой у мужчин. Вопросы, связанные с их функцией, до сих пор остаются предметом научных и клинических дискуссий. Тем не менее представляется разумным предположения о роли ЖС в механизме противомикробной защиты мочевых путей. Связь воспаления в описываемых анатомических структурах с рецидивирующей ИНМП к настоящему моменту можно считать доказанной.
Значимую проблему для диагностики скинеита в настоящее время представляет отсутствие или крайне низкая чувствительность и специфичность имеющихся лабораторных, инструментальных и лучевых методов. Помимо этого, существующие способы объективного обследования пациенток с данным заболеванием устарели и не стандартизированы.Постановка правильного диагноза также затруднена из-за отсутствия специализированного инструмента для осмотра женской уретры и устьев протоков ЖС. Этот же фактор влияет на значимое количество повторных оперативных вмешательств в связи с пропущенными при первом пособии инфицированными протоками.
Таким образом, улучшение результатов лечения пациенток с рецидивирующей ИНМП, обусловленной хроническим воспалением парауретральных протоков и желез,путем разработки инструмента для осмотра женского мочеиспускательного канала, стандартизации имеющихся и поиском новых методов диагностики, улучшением результатов хирургического лечения является важной клинической и социальноэкономической задачей современного здравоохранения.
Таблица 1. Результаты выполнения операции Ризера различными исследователями
Table 1. Results of the Riеzer operation performed by various researchers
|
Авторы, дата публикации Authors, publication date |
Количествово пациентов Number of patients |
Улучшение после первой операции Success after first operation |
Улучшение после повторной операции Success after reoperation |
Результат Result |
|
Rieser C. (1968) [62] |
206 |
НД |
НД |
100% |
|
Lewis E.L. и соавт. (1973) [76] |
70 |
88% |
12% |
100% |
|
Leiter E. (1973) [63] |
16 |
81% |
12% |
93% |
|
Rouxel A. (1979) [65] |
21 |
НД |
НД |
85% |
|
Hedlund P.O. (1979) [68] |
41 |
39% |
5% |
44% |
|
Lachand A.T. (1989) [66] |
34 |
55% |
10% |
65% |
|
Karam G. и соавт (1990) [61] |
61 |
НД |
НД |
70% |
*НД – нет данных, no data
ИШАТШШРЕЕЕШЕ
Список литературы Воспаление парауретральных протоков и желез у женщин: проблема с 350-летней историей
- Raz S, Rodriguez L. Female Urology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company; 2008. 1056 р. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4160-2339-5.X5002-2.
- Burrows LJ, Howden NL, Meyn L, Weber AM. Surgical procedures for urethral diverticula in women in the United States, 1979-1997. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2005;16(2):158-61. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-004-1145-9.
- Мажбиц А.М. Заболевания скеневых желез. В кн: Акушерско-гинекологическая урология с атласом Л.,1936:116-24. [Mazhbits A.M. Diseases of the skeletal glands. In Obstetric and gynecological urology with atlas. Leningrad, 1936:116-124. (In Russian)].
- Мажбиц А. М. Оперативная урогинекология. M.: Медицина, 1964. 416 c. [Mazhbits A.M. Operative urogynecology. Moscow: Medicine, 1964. 416 p. (In Russian)].
- Riba LW. Chronic trichomonas skeneitis. J Urol 1949;62(4):503-6. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)68964-X.
- Прилепская В.Н., Мирзабалаева А.К., Кира Е.Ф., Гомберг М.А., Аполихина И.А., Байрамова Г.Р. и др. Федеральные клинические рекомендации. Диагностика и лечение заболеваний, сопровождающихся патологическими выделениями из половых путей женщин. М. 2013; 50 с. [Prilepskaya V.N., Mirzabalaeva A.K., Kira E.F., Gomberg M.A., Apolikhina I.A., Bayramova G.R., et al. Federal Clinical guidelines. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases accompanied by pathological secretions from the genital tract of women. Moscow 2013; 50 p. (In Russian)].
- Слесаревская М.Н., Игнашов Ю.А., Кузьмин И.В., Аль-Шукри С.Х. Стойкая дизурия у женщин: этиологическая диагностика и лечение. Урологические ведомости 2021;11(3):195-204. [Slesarevskaya M.N., Ignashov Y.A., Kuzmin I.V., Al-Shukri S.K. Persistent dysuria in women: etiological diagnostics and treatment. Urologicheskie vedomosti = Urology reports 2021;11(3):195-204. (In Russian)]. http://doi.org/10.17816/uroved81948.
- Глухарев А.Г. Воспаление парауретральных желез у женщин – скинеит. Журнал акушерства и женских болезней 1999;48(2):79-81. [Gluharev A.G. Inflammation of parauretral glanduli in women – scineitis. Zhurnal akusherstva i zhenskix boleznej = Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases 1999;48(2):79-81. (In Russian)]. http://doi.org/10.17816/JOWD88155.
- Яковлев С.В., Суворова М.П. Обоснование выбора антибиотика для лечения цистита: рекомендации клинических фармакологов. Обзор литературы. Терапевтический архив 2022;94(8):1006–13. [Yakovlev SV, Suvorova MP. Rationale for choosing an antibiotic for the treatment of cystitis: recommendationsw of clinical pharmacologists: areview. Terapevticheskii Arkhiv = Therapeutic Archive 2022;94(8):1006–13. (In Russian)]. http://doi.org/10.26442/00403660.2022.08.201775.
- Taich L, Zhao H, Cordero C, Anger JT. New paradigms in the management of recurrent urinary tract infections. Curr Opin Urol 2020;30(6):833-7. http://doi.org/10.1097/MOU.0000000000000823.
- Cates W Jr, Rolfs RT Jr, Aral SO. Sexually transmitted diseases, pelvic inflammatory disease, and infertility: an epidemiologic update. Epidemiol Rev 1990;12:199-220. http://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036054.
- Привалова М.А. Изменение местного иммунитета при воспалительных заболеваниях женских половых органов. Вестник новых медицинских технологий 2008;15(2):55-6. [Privalova M.A. Changes in local immunity in inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. Vestnik novykh meditsinskikh tekhnologii = Bulletin of New Medical Technologies 2008;15(2):55-6. (In Russian)].
- Centres for disease control and prevention sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2010;(59):63-7.
- Бартолиновы железы. Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона: в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). СПб., 1890-1907. [Bartholin glands. Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 supplements). St. Petersburg, 1890-1907. (In Russian)].
- Astruc J. A treatise of the venereal disease, trans. London W. Barrowby. 1737. Vol. 2. 16 p.
- Virchow R. Prostata-concretionen beim Weib. Archiv für pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für klinische Medicin 1853;5(3):403-.
- Skene AJC. Anatomy and pathology of two important glands of the female urethra. Am J Obs Dis Women & Child 1880;13:265-70.
- Speert H. Obstetrical-gynaecological eponyms: Alexander Skene and the paraurethral ducts. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp 1956;63(6):908-10. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1956.tb05588.x.
- Международная анатомическая терминология. Под ред. Л.Л. Колесникова. М.: Медицина, 2003. 424 с. [International anatomical terminology. Edited by N. L.L. Kolesnikov. M. Medicine, 2003. 424 p. (In Russian)]. URL: https://vk.com/doc137257920_480135654?hash=xzVUvlScQ19k7eQMvlaAvjdbHRKKs8r0WgFVP3t4cQs.
- Johnson FP. The homologue of the prostate in the female. J Urol 1922;8(1):13. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)73790-1.
- Huffman JW. The detailed anatomy of the para-urethral ducts in the adult human female. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1948;55(1):86-101. http://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(48)90157-4.
- Deter RL, Caldwell GT., Folsom AI. A clinical and pathological study of the posterior female urethra. J Urol 1946;55:651-62. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)69961-0.
- Lintgen C., Herbut PA. A clinico-pathological study of 100 female urethras. J Urol 1946;55:298-305. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)69915-4. PMID: 21015578.
- Korenchevsky V, Dennison M. The histology of the sex organs of ovariectomised rats treated with male or female sex hormone alone or with both simultaneously. J Pathol Bacteriol 1936;42(1):91-104. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1700420113.
- Moore CR, Price D. Gonad hormone function and the reciprocal influence between gonads and hypophysis with its bearing on the problem of sex. Am J Anat 1932;50(1):13-61. https://doi.org/10.1002/aja.1000500103. URL:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/aja.1000500103.
- Wernert N, Albrech M, Sesterhenn I, Goebbels R, Bonkhoff H, Seitz G, et al. The 'female prostate': location, morphology, immunohistochemical characteristics and significance. Eur Urol 1992;22(1):64-9. http://doi.org/10.1159/000474724.
- Pollen JJ, Dreilinger A. Immunohistochemical identification of prostatic acid phosphatase and prostate specific antigen in female periurethral glands. Urology 1984;23(3):303-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-4295(84)90053-0.
- Tepper SL, Jagirdar J, Heath D, Geller SA. Homology between the female paraurethral (Skene's) glands and the prostate. Immunohistochemical demonstration. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1984;108(5):423-5.
- Zaviacic M, Ablin RJ. The female prostate. J Natl Cancer Inst 1998;90(9):713-4. http://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/90.9.713.
- Zaviačič M. The human female prostate. From vestigial Skene’s paraurethral glands and ducts to woman’s functional prostate. Bratislava, Slovak Academic Press, 1999: 172 p.
- Terzic MM, Stimec BV. A long-term course of a primary urethral/paraurethral adenocarcinoma. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 2000;11(6):392-4. http://doi.org/10.1007/s001920070011.
- Dodson MK, Cliby WA, Keeney GL, Peterson MF, Podritz KC. Skene's gland adenocarcinoma with increased serum level of prostate-specific antigen. Gynecol Оncol 1994;55(2):304-7. http://doi.org/10.1006/gyno.1994.1294.
- Spencer JR, Brodin AG, Ignatoff JM. Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the urethra: evidence for origin within paraurethral ducts. J Urol 1990;143(1):122-5. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39887-7.
- Sloboda J, Zaviacic M, Jakubovský J, Hammar E, Johnsen J. Metastasizing adenocarcinoma of the female prostate (Skene's paraurethral glands). Histological and immunohistochemical prostate markers studies and first ultrastructural observation. Pathol Res Pract 1998;194(2):129-36. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0344-0338(98)80080-0.
- Korytko TP, Lowe GJ, Jimenez RE, Pohar KS, Martin DD. Prostate-specific antigen response after definitive radiotherapy for Skene's gland adenocarcinoma resembling prostate adenocarcinoma. Urol Oncol 2012;30(5):602-6. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.06.015.
- Doherty PJ, Friedman AA, Migeon CJ, Macura KJ, Salmasi AH, Lakshmanan Y. Absence of prostatic growth in large cohort of adult female patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Urol 2012;188(4 Suppl):1588-95. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.02.029.
- Paulino Mda C, Steinmetz L, Menezes Filho HC, Kuperman H, Della Manna T, Vieira JG, et al. Pesquisa de tecido prostático em pacientes 46, XX portadoras da forma clássica de hiperplasia congênita das suprarrenais [Search of prostatic tissue in 46, XX congenital adrenal hyperplasia]. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2009;53(6):716-20. http://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-27302009000600004.
- Faradji A, Lair M, Derinck A, Najdawi M, Chabut M, Feray D, et al. Hyperplasie congénitale des surrénales et hypertrophie des glandes de Skene: à propos d’une «prostate» chez une adolescente. Imagerie de la Femme 2020;30(2):101-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femme.2020.06.004.
- Юцковская Я.А., Мартов А.Г., Лешунов Е.В. Женская предстательная железа. Урология 2014;(3):86-8. [Yutskovskaya Y.A., Martov A.G., Leshunov E.V. Female prostate gland. Urologiia = Urology 2014;(3):86-8. (In Russian)].
- Stifter KF. Die dritte Dimension der Lust. Das Geheimnis der weiblichen Ejakulation. Frankfurt am Main, Berlin: Ullstein 1988:224–8.
- Masters W.H., Johnson V.E. Human Sexual Response. Boston: Little, Brown, & Co; 1966: 366 p.
- Grafenberg E. The role of the urethra in female orgasm. Int J Sexol 1950;3(2):146.
- Addiego F, Belzer EG, Comolli, J, Moger W, Perry JD, Whipple B. Female ejaculation: a case study. J Sex Res 1981;17(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224498109551094.
- Darling CA, Davidson JK Sr, Conway-Welch C. Female ejaculation: perceived origins, the Grafenberg spot/area, and sexual responsiveness. Arch Sex Behav 1990;19(1):29-47. http://doi.org/10.1007/BF01541824.
- Wimpissinger F, Stifter K, Grin W, Stackl W. The female prostate revisited: perineal ultrasound and biochemical studies of female ejaculate. J Sex Med 2007;4(5):1388-93. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00542.x.
- Pastor Z. Female ejaculation orgasm vs. coital incontinence: a systematic review. J Sex Med 2013;10(7):1682-91. http://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12166.
- Hines TM. The G-spot: a modern gynecologic myth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185(2):359-62. http://doi.org/10.1067/mob.2001.115995.
- Pauls R, Mutema G, Segal J, Silva WA, Kleeman S, Dryfhout V, et al. A prospective study examining the anatomic distribution of nerve density in the human vagina. J Sex Med 2006;3(6):979- 87. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00325.x.
- Colson M. H. Female orgasm: myths, facts and controversies. Sexologies 2010;19(1):8-14. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sexol.2009.11.003.
- D'Amati G, di Gioia CR, Bologna M, Giordano D, Giorgi M, Dolci S, et al. Type 5 phosphodiesterase expression in the human vagina. Urology 2002;60(1):191-5. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(02)01663-1.
- Helmholz HF Sr. Determination of the bacterial content of the urethra: a new method, with results of a study of 82 men. J Urol 1950;64(1):158-66. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)68615-4.
- Cox CE, Lacy SS, Hinman F Jr. The urethra and its relationship to urinary tract infection. II. The urethral flora of the female with recurrent urinary infection. J Urol 1968;99(5):632-8. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)62762-9.
- Hutch JA. The role of urethral mucus in the bladder defense mechanism. J Urol 1970;103(2):165-7. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61914-1.
- Moalem S, Reidenberg JS. Does female ejaculation serve an antimicrobial purpose? Med Hypotheses 2009;73(6):1069-71. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2009.07.024.
- Kunin CM, Evans C, Bartholomew D, Bates DG. The antimicrobial defense mechanism of the female urethra: a reassessment. J Urol 2002;168(2):413-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64649-6.
- Eberhart C. The etiology and treatment of urethritis in female patients. J Urol 1958;79(2):293-9. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)66271-2.
- Moore CB. Treatment of chronic gonorrheal skenitis with the electric cautery. J Am Med Assoc 1918;71(25):2056-7. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1918.26020510002009b.
- Walther HWE. An electric skeneoscope. J Am Med Assoc 1927;88(1):27. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1927.92680270002008a.
- Le Fur R.: Diathermy in urology. Bull med 1922;(36):5-9.
- Walther HWE, Peacock CL. Diathermy in urology: preliminary report. JAMA 1924;83(15):1142–7. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1924.02660150026009.
- Eberhart C, Morgan JW. The treatment of urethritis in female patients, II. Obstet Gynecol Surv 1959;14(4):627-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)65980-9.
- Rieser C. A new method of treatment of inflammatory lesions of the female urethra. JAMA 1968;204(5):378-84. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1968.03140180028008.
- Lewis EL, Griffith TH. Recurring cystourethritis in women: is an effective therapy available? J Urol 1973;110(5):544-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)60275-1.
- Leiter E. Management of recurrent cystourethritis in women. Urology 1973;1(2):111-3. http://doi.org/10.1016/0090-4295(73)90594-3.
- Rouxel A, Etienne P, Keribin D, Auvigne J. Treatment of urethro-cystalgies in adult women using Rieser's operation. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1977;83 Suppl 2:655-9.
- Lachand AT. Results of the Rieser intervention in the prevention of recurrent cystitis of the female in 34 cases. Annales D'urologie 1989;23(4):347-8.
- Karam G, Glemain P, Bouchot O, le Normand L, Auvigne J. Electrocoagulation of the paraurethral glands (Reiser's operation) in women with urethro-cystalgia. Annales D'urologie 1990;24(5):367-71.
- Hedlund PO. Experience of the Rieser operation for chronic female urethritis. A follow-up study of 42 cases. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1979;13(3):217-9. http://doi.org/10.3109/00365597909179528.


