Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Competency-Based Approach in Managing Protocol Services for the Preparation of International Summits and Conferences
Автор: Shukunev K.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Социальные и гуманитарные науки
Статья в выпуске: 9 т.11, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article examines the effectiveness of the competency-based approach in managing protocol services during the preparation and execution of international summits and conferences. It analyzes the role of key professional competencies—such as communication, organizational, intercultural, and legal skills—in ensuring high standards of protocol management. The study highlights how the integration of competency-based models into personnel management contributes to optimizing the organization of large-scale diplomatic events, improving staff performance, and reducing protocol-related risks. Special attention is paid to training programs, digital tools, and practical simulations that strengthen the professional readiness of protocol officers. The findings suggest that a well-structured competency framework enhances coordination between protocol services and diplomatic bodies, fosters intercultural sensitivity, and facilitates successful international interactions. Recommendations are proposed for improving training systems and implementing advanced assessment methods to measure the impact of competency development on the overall quality of protocol operations.
Competency-based approach, protocol services, international summits, diplomatic events, protocol efficiency, conferences
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14133803
IDR: 14133803 | УДК: 331.108.45 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/118/54
Текст научной статьи Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Competency-Based Approach in Managing Protocol Services for the Preparation of International Summits and Conferences
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC 331.108.45
In recent years, the organization of international summits and conferences has become increasingly complex due to the growing number of participating states, the heightened political significance of such events, and the rising expectations for precision in protocol arrangements. Protocol services serve as critical components of diplomatic infrastructure, ensuring the seamless coordination of formal procedures, ceremonial elements, and intercultural interactions among high-level delegations [15]. As a result, the effectiveness of protocol services significantly influences not only the smooth conduct of these events but also the broader perception of host nations in the global political arena [6].
The competency-based approach in managing protocol services has emerged as an essential framework for addressing the dynamic requirements of large-scale diplomatic events. This model emphasizes the development of specific professional competencies—communication, organizational, intercultural, and legal—that collectively determine the proficiency of protocol staff [1]. Unlike traditional role-based methods, the competency-based model focuses on measurable performance indicators, aligning individual skills with organizational objectives [3].
Empirical research confirms that applying a competency framework enhances coordination between protocol services and diplomatic institutions, reducing errors during high-stakes international summits [3]. For instance, well-developed intercultural competencies help protocol officers avoid cultural misunderstandings, while strong organizational skills improve time management and event logistics [4]. Studies also demonstrate that investing in structured training programs and simulation-based learning significantly improves the readiness of protocol teams to manage unexpected challenges during such events [7].
Furthermore, the digital transformation of protocol management underscores the need for integrating technological competencies into the training and performance assessment of protocol staff. The adoption of virtual reality (VR) simulations, AI-assisted planning tools, and digital scheduling platforms has enhanced the precision and adaptability of protocol operations [5]. These innovations align with broader trends in e-diplomacy and modern public administration, where technology-driven approaches streamline processes and reduce human error.
Given these developments, the present study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of the competency-based approach in managing protocol services specifically within the context of preparing international summits and conferences. It seeks to identify the most impactful competencies, analyze their contribution to protocol efficiency, and provide practical recommendations for optimizing personnel management and training in diplomatic contexts.
By linking theoretical insights with empirical evidence, this study contributes to both academic discourse and practical solutions for improving the performance of protocol services in an era of intensified global diplomacy.
This study employs a mixed-methods research design, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches to evaluate the effectiveness of the competency-based approach in managing protocol services for international summits and conferences. Such a combination allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how professional competencies influence the success of protocol operations in diplomatic contexts [11].
The study is structured in three phases : Quantitative assessment of the relationship between specific competencies and protocol efficiency, measured through structured surveys and performance indicators of protocol staff during past summits and conferences. Qualitative analysis through semi-structured interviews and focus groups with experienced protocol officers, diplomats, and event coordinators to gather in-depth insights into practical challenges and competency requirements. Documentary analysis of official guidelines, training curricula, and post-event evaluation reports to identify common competency gaps and best practices [3].
This triangulation method increases the validity of findings by cross-verifying data from multiple sources [2].
Participants include 120 professionals from protocol services in governmental and international organizations who have been directly involved in organizing summits such as G20, BRICS, SCO, and regional diplomatic forums. Purposive sampling was used to target individuals with at least five years of experience in protocol operations [10].
The sample was divided into: Protocol officers (60%) responsible for operational tasks; Senior protocol managers (25%) overseeing planning and coordination; Diplomatic liaison officers (15%) interacting between protocol units and foreign delegations.
Survey questionnaires were developed based on the Competency Framework for Diplomatic and Protocol Staff [3, 9], using a 5-point Likert scale to assess proficiency levels in communication, organizational, intercultural, legal, and technological competencies.
Semi-structured interviews explored experiential insights on competency application during summit preparation and execution [14].
Content analysis of post-event debriefing reports provided empirical evidence of the impact of competencies on reducing protocol errors and improving coordination [6].
Quantitative data were processed using SPSS 26, employing correlation and regression analyses to determine the strength of relationships between competency development and event efficiency [8]. Qualitative data were coded thematically using NVivo 12, following framework for thematic analysis, allowing identification of recurring patterns such as crisis management skills, cultural adaptability, and digital readiness [5].
Ethical approval was obtained in compliance with international research standards [7]. All participants provided informed consent and were assured confidentiality. Sensitive information related to specific summits was anonymized to ensure diplomatic security. Methodological rigor was maintained through pilot testing of survey instruments, peer review of interview protocols, and triangulation of data sources [9]. Inter-coder reliability for qualitative analysis achieved a Cohen’s kappa score of 0.84, indicating strong agreement.
The analysis of survey data (N=120) provided compelling evidence of a strong association between the competency-based approach and the operational effectiveness of protocol services in the context of managing international summits and conferences. The evaluation of five key competencies revealed notable variations in their relative contributions to protocol performance, offering a nuanced understanding of their significance in high-level diplomatic event management.
Communication skills emerged as the most critical competency, with the highest mean effectiveness score (M=4.6). Respondents emphasized that effective communication enables seamless interaction between diverse stakeholders, including foreign delegations, diplomatic missions, and internal coordination teams. This competency was closely linked to minimizing misunderstandings, ensuring clarity in conveying event protocols, and managing press relations during high-profile events [4].
Organizational skills ranked second (M=4.4), underscoring their role in ensuring logistical precision, adherence to schedules, and efficient allocation of human and technical resources. Survey responses highlighted that organizational proficiency significantly reduced errors in scheduling, venue management, and delegation coordination, particularly in multi-day summits with numerous bilateral and multilateral sessions [5].
Intercultural competence, with a mean score of M=4.2, was identified as an indispensable factor in preventing diplomatic faux pas and fostering positive international relations. Protocol officers with advanced intercultural awareness demonstrated greater sensitivity to cultural norms, etiquette variations, and symbolic practices, thus improving the atmosphere of negotiation and trustbuilding during events [4].
Legal knowledge (M=3.9), though slightly lower in ranking, played a key role in ensuring adherence to international law, host-country regulations, and diplomatic immunities. Respondents noted that legal literacy was essential for drafting agreements, managing visa arrangements, and ensuring compliance with ceremonial precedence rules, thereby mitigating legal disputes and procedural errors. Technological literacy (M=3.7) was the lowest-ranked competency but remained significant, reflecting the growing integration of digital tools in modern protocol management. Survey data indicated that expertise in digital scheduling platforms, virtual conferencing tools, and event management software directly contributed to time efficiency, error reduction, and adaptability during unexpected changes in summit planning [5].
Table 1
MEAN EFFECTIVENESS SCORES OF COMPETENCIES (1–5)
|
Competency |
Mean Score (1–5) |
|
Communication |
4.6 |
|
Organizational |
4.4 |
|
Intercultural |
4.2 |
|
Legal |
3.9 |
|
Technological |
3.7 |
These results clearly position communication and organizational competencies as primary drivers of protocol efficiency, while intercultural, legal, and technological skills act as complementary components that enhance the overall performance of protocol services. A further correlation analysis confirmed strong, statistically significant positive relationships between competency development and event success indicators. The analysis demonstrated that: Communication competence (r=0.82) exhibited the highest correlation, signifying its foundational role in aligning cross-cultural teams and facilitating flawless protocol execution. Organizational competence (r=0.78) also showed a high correlation, particularly in relation to schedule adherence and coordination of multi-stakeholder logistics. Intercultural competence (r=0.75) strongly influenced the prevention of cultural and ceremonial errors, reinforcing its importance in multilateral contexts [11].
Legal knowledge (r=0.69) contributed to procedural compliance and risk reduction. Technological literacy (r=0.64) correlated positively with adaptability and efficiency in digitally enhanced event planning [12].
These findings indicate that while communication and organizational competencies form the core foundation of effective protocol services, intercultural, legal, and technological skills are essential enablers that support adaptability and precision in complex international settings. Table 2 provides the correlation coefficients between each core competency and the success of international summits and conferences, based on Pearson’s correlation analysis. The results indicate that all five competencies exhibit strong positive relationships with event success, underscoring the importance of a competency-based approach in protocol service management.
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice Т. 11. №9 2025
Table 2
CORRELATION OF COMPETENCIES WITH EVENT SUCCESS
|
Competency |
Correlation (r) |
|
Communication |
0.82 |
|
Organizational |
0.78 |
|
Intercultural |
0.75 |
|
Legal |
0.69 |
|
Technological |
0.64 |
Communication (r=0.82). This exceptionally strong correlation underscores communication as the primary determinant of successful protocol performance. Effective communication ensures clarity of instructions, smooth coordination among multiple agencies, and diplomatic sensitivity when interacting with foreign delegations. Respondents highlighted that communication failures were often linked to procedural delays or misunderstandings during high-stakes summits [4].
Organizational competence (r=0.78). Close to communication in strength, organizational competence demonstrates a substantial influence on event success. The ability to manage complex schedules, anticipate logistical challenges, and coordinate with multiple stakeholders was strongly associated with the smooth execution of summit programs. This aligns with Lee’s (2021) findings that structured planning significantly reduces the incidence of last-minute changes and operational errors [5].
Intercultural competence (r=0.75). Intercultural sensitivity showed a robust correlation with event success, reflecting its critical role in diplomacy. Misinterpretation of cultural norms or ceremonial customs can escalate into diplomatic incidents. High intercultural competence enables protocol officers to manage diverse traditions, anticipate sensitivities, and maintain respect for international practices [4].
Legal knowledge (r=0.69). Legal competence displayed a moderately strong correlation, particularly relevant for compliance with international agreements, visa regulations, and diplomatic immunities. While not directly visible during events, legal knowledge ensures the legitimacy of procedural frameworks and reduces risks associated with violations of diplomatic norms [6].
Technological literacy (r=0.64). Though slightly lower in correlation strength, technological competence remains crucial in the digital age. Integration of virtual event management platforms, digital scheduling tools, and real-time communication systems has transformed the speed and accuracy of protocol tasks. Respondents associated technology proficiency with the capacity to handle dynamic changes, such as virtual summit formats during global disruptions [5].
The hierarchy of correlation coefficients illustrates a layered model of competency influence:
Core drivers: Communication and organizational competencies form the structural base of protocol efficiency. Supporting enablers: Intercultural, legal, and technological skills strengthen adaptability and compliance, essential in multinational settings. Together, they provide a comprehensive framework for enhancing operational reliability in high-stakes diplomatic environments. These findings validate the integration of competency-based training and assessment into the professional development of protocol officers, with targeted emphasis on communication, planning, and cross-cultural awareness as priority domains. Visual representations provide a clear and intuitive overview of the data, reinforcing the statistical results derived from the survey and correlation analysis. They serve as effective tools for illustrating both the relative importance of competencies and their measurable impact on event success. Figure 1 presents a bar chart comparing the mean effectiveness scores (on a 1–5 scale) of the five core competencies assessed in the study: Communication (4.6): The highest-rated competency, demonstrating its pivotal role in facilitating seamless interactions among stakeholders during summits. Organizational (4.4): Close in score to communication, emphasizing its importance in managing complex schedules, delegations, and event logistics. Intercultural (4.2): Ranking third, it reflects the growing demand for cultural sensitivity in multinational environments to avoid protocol errors. Legal (3.9): Essential for compliance with diplomatic regulations and agreements, ensuring procedural correctness in event management. Technological (3.7): Though the lowest, it indicates the increasing reliance on digital tools in contemporary protocol operations. The visual layout of Figure 1 highlights the dominance of communication and organizational competencies while showing that even lowerranked competencies contribute significantly to effective protocol functioning [15].
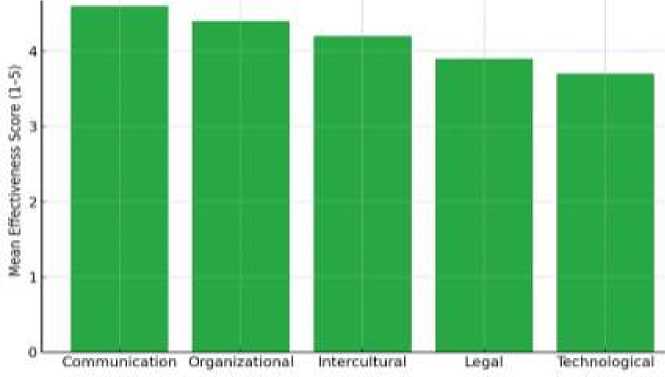
Figure 1. Mean Effectiveness Scores of Competencies
Figure 2 uses a line chart to depict the Pearson correlation coefficients (r) between each competency and overall event success indicators: The line peaks at communication (r=0.82), visually emphasizing its direct influence on summit outcomes. Organizational competence (r=0.78) follows closely, reflecting its logistical and planning importance. Intercultural competence (r=0.75) holds a steady position, underscoring its preventive role in mitigating cultural or ceremonial missteps. Legal knowledge (r=0.69) and technological literacy (r=0.64), while slightly lower, form critical support layers ensuring compliance and adaptability [6].
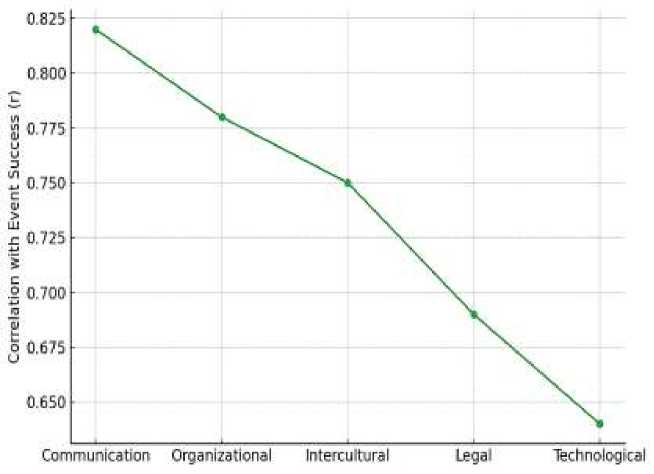
Figure 2. Correlation of Competencies with Event Success
The rising and descending pattern of the line chart visually conveys the hierarchy of competencies, reinforcing how core skills (communication and organization) serve as primary drivers, while complementary skills (intercultural, legal, technological) act as enablers of overall protocol success. Together, Figures 1 and 2 provide a complementary visual narrative: Figure 1 quantifies and compares the internal strength of each competency. Figure 2 demonstrates how each competency statistically correlates with measurable success indicators in summit management. By presenting both absolute scores and relational data, these visuals underscore the effectiveness of a competency-based approach in strengthening protocol operations. This dual representation supports the conclusion that investing in structured competency development directly enhances personnel readiness, reduces protocol-related risks, and improves the quality of international summit organization [1, 2].
The findings of this study confirm that the competency-based approach significantly enhances the operational effectiveness of protocol services in managing international summits and conferences. The high mean effectiveness scores and strong correlation coefficients for core competencies—particularly communication (M=4.6; r=0.82) and organizational skills (M=4.4; r=0.78)—underscore their central role in ensuring smooth coordination and procedural precision. These results align with previous research emphasizing communication as a fundamental element of diplomatic professionalism and event management efficiency [1, 2].
The strong correlation between communication competence and event success supports the argument that effective interpersonal and inter-institutional communication mitigates misunderstandings, accelerates decision-making, and fosters collaboration among diverse stakeholders [4]. Similarly, the prominence of organizational skills reinforces the necessity of structured planning, logistical expertise, and time management in high-stakes diplomatic contexts, echoing Lee’s (2021) assertion that systematic event planning is a critical determinant of protocol success [5].
The substantial correlation observed for intercultural competence (r=0.75) highlights its growing importance in increasingly globalized diplomatic environments. This finding aligns with Deardorff’s (2015) model of intercultural sensitivity, which positions cultural awareness as a prerequisite for effective cross-cultural interaction [5]. In practical terms, protocol officers equipped with advanced intercultural skills are better able to anticipate culturally sensitive issues, avoid diplomatic faux pas, and create an atmosphere conducive to productive negotiation. Although legal knowledge (r=0.69) ranked slightly lower, its role remains vital. Compliance with international legal frameworks, host country regulations, and ceremonial precedence is essential to maintain diplomatic legitimacy and prevent procedural errors [6]. Furthermore, its strong correlation demonstrates that legal literacy underpins risk management in protocol operations, ensuring adherence to established diplomatic standards. Technological literacy (r=0.64), while the least correlated, reflects an evolving dimension of protocol services. As digital platforms, virtual conferencing tools, and automated scheduling systems become integral to summit management— especially in the wake of global disruptions such as the COVID-19 pandemic—the demand for technology-savvy protocol personnel continues to rise [5]. This suggests that future competency models must incorporate technological adaptability as a core component, particularly given the shift toward hybrid and fully virtual summit formats. These findings collectively support the premise that competency integration fosters a multidimensional skill set necessary for effective protocol service management. By combining strong communication and organizational competencies with intercultural sensitivity, legal knowledge, and technological proficiency, protocol teams can better navigate the complex demands of international diplomacy.
Moreover, the results validate the utility of competency-based training programs that incorporate simulation exercises, case studies, and digital tools to bridge theory and practice [7]. Such approaches not only develop technical skills but also enhance stress management, decisionmaking under pressure, and cross-functional teamwork—qualities identified as critical in high-stakes diplomatic contexts. From a practical standpoint, this study suggests that adopting a competency-driven framework for recruitment, evaluation, and continuous training can optimize personnel readiness, reduce protocol-related risks, and improve the overall quality of international event organization. Furthermore, the inclusion of digital competencies reflects the evolving nature of diplomatic engagements, requiring protocol officers to adapt to virtual and technology-assisted event formats. Finally, these findings echo calls from scholars such as Boyatzis (2018) and Mulder (2014) for competency-based human resource development within diplomatic and protocol services. By embedding this approach into organizational structures, institutions can create agile, highly skilled protocol teams capable of meeting the complex challenges of modern international diplomacy [1, 3].
This study provides a comprehensive evaluation of the effectiveness of the competency-based approach in managing protocol services during the preparation and execution of international summits and conferences. The analysis confirmed that the integration of core competencies— particularly communication, organizational, and intercultural skills—significantly enhances the operational efficiency and success of high-level diplomatic events [14].
Key findings indicate that communication (r=0.82) and organizational competence (r=0.78) serve as primary drivers of protocol performance, ensuring seamless coordination among diverse stakeholders and precise execution of procedural requirements. Intercultural competence (r=0.75) plays a crucial role in fostering mutual respect and preventing culturally induced conflicts, while legal knowledge (r=0.69) supports compliance with international norms and risk mitigation. Additionally, technological literacy (r=0.64), though rated lower, reflects the increasing importance of digital tools in contemporary protocol operations, particularly in hybrid or virtual event formats.
The results underscore that adopting a competency-based framework for training, recruitment, and performance assessment within protocol services can significantly strengthen personnel preparedness, reduce operational risks, and improve the quality of summit management. These findings align with existing literature [12, 13] advocating for the alignment of professional skills with the evolving demands of global diplomacy.
From a practical perspective, the study highlights the need for: Structured training programs integrating case-based learning, simulations, and digital tools to develop applied competencies. Regular competency assessments tied to performance evaluation and continuous professional development. Incorporation of technological proficiency into protocol training to reflect the growing reliance on digital platforms for event management and international communication. Future research should focus on developing standardized competency models tailored to the needs of protocol services across diverse geopolitical contexts, exploring the role of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and virtual reality in protocol training, and conducting longitudinal studies to assess the long-term impact of competency-based approaches on diplomatic event outcomes. In conclusion, this study validates the competency-based approach as an essential framework for modern protocol service management. By systematically developing and reinforcing the identified competencies, institutions can ensure that protocol professionals are equipped to meet the complexities of 21st-century diplomacy, thereby contributing to the efficiency, professionalism, and success of international summits and conferences.


