Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз и атипичный хронический миелолейкоз
Автор: Шуваев В.А., Мартынкевич И.С., Кустова Д.В., Байков В.В., Криволапов Ю.А., Белякова Е.А., Барам Д.В.
Журнал: Вестник гематологии @bulletin-of-hematology
Рубрика: Обзор литературы
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз и атипичный хронический миелоидный лейкоз – редкие ми- елопролиферативные новообразования, встречающиеся преимущественно у лиц пожилого возраста и характеризующиеся постоянным нейтрофильным лейкоцитозом, гиперклеточным костным мозгом и гепатоспленомегалией. Симптомы и клинико-лабораторные проявления хронического нейтрофильного лейкоза и атипичного хронического миелолейкоза практически неотличимы от хронического миелоидного лейкоза, а прогноз также схож в эру до внедрения таргетной терапии. В последние годы достигнуты существенные успехи в расшифровке молекулярно-генетических основ патогенеза этих заболеваний. Внедрены молекулярно-генетические критерии диагностики, разработаны подходы к использованию таргетных препаратов. В статье при- ведены современные представления о диагностике и лечении хронического нейтрофильного лейкоза и атипичного хронического миелолейкоза. Также представлено клиническое наблюдение атипичного хронического миелолейкоза.
Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз, атипичный хронический миелолейкоз, молекулярно-генетическая диагностика, таргетная терапия, руксолитиниб
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170199858
IDR: 170199858
Текст научной статьи Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз и атипичный хронический миелолейкоз
Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз (ХНЛ, код по МКБ10 C92.7) – редкий вариант миелопролиферативного новообразования, встречающийся преимущественно у лиц пожилого возраста, характеризующийся постоянным нейтрофильным лейкоцитозом, гиперклеточным костным мозгом и гепатосплено-мегалией, в большинстве случаев ассоциированный с драйверными мутациями в гене рецептора колониестимулирующего фактора 3 типа (CSF3R) [1,2]. Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз имеет общий молекулярно-генетический патогенез, клиническое течение и прогноз с атипичным хроническим миелолейкозом (аХМЛ, код по МКБ10 C92.2). Симптомы и клинико-лабораторные проявления аХМЛ практически неотличимы от ХМЛ, прогноз также был схож с ХМЛ в эру до внедрения таргетной терапии [3]. В отличие от ХМЛ, при ХНЛ и аХМЛ филадельфийская хромосома или ее вариантные транслокации, равно как и ген BCR::ABL не обнаруживаются. В классификации миелоидных новообразований ВОЗ 2016 года аХМЛ отнесен в смешанную группу Миелодиспла-стические синдромы / Миелопролиферативные новообразования. Однако многие полагают, что более целесообразным было бы указание ХНЛ и аХМЛ в одной группе заболеваний или даже объединение в одну нозологическую форму [4]. ХНЛ и аХМЛ традиционно расценивались как редкие заболевания, однако в настоящее время они стали выявляться гораздо чаще. Во многом это связано с более широким применением в диагностике молекулярно-генетических исследований. В США первичная заболеваемость ХНЛ оценивается приблизительно 0,01, тогда как аХМЛ около 0,03 на 100000 населения в год [5]. В настоящей статье, несмотря на общность патогенеза и клинического течения, данные заболевания будут представлены как отдельные нозологические формы.
Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз . Этиология ХНЛ неизвестна, патогенез до недавнего времени также оставался неясным. Благодаря нескольким исследованиям наследственной хронической нейтропении [6] и наследственной (аутосомно-доминантной) нейтрофилии [7] была выявлена патогенетическая роль мутаций рецептора к гранулоцитарному колониестимулирующему фактору (Г-КСФ) третьего типа (CSF3R).
CSF3R является рецептором Г-КСФ, влияющим на пролиферацию, дифференцировку и апоптоз лейкоцитов, который может быть задействован и в онкогенезе [8,9]. Мутации CSF3R описаны у больных с идиопатической хронической нейтропенией при трансформации в острый миелоидный лейкоз [7,1012]. Эти мутации остановки трансляции приводят к укорочению цитоплазматической части рецептора CSF3R и его взаимодействию с белками SHP-1/2 и семейства SOC. Указанные структурные изменения влияют на способность CSF3R регулировать дифференцировку гранулоцитов и повышают их пролиферацию [13-18]. Сигнал с CSF3R передается в ядро посредством JAK-STAT сигнального пути через нерецепторную тирозинкиназу 2 типа SYK и киназу LYN семейства SRC [19,20].
В 2013 г. J. Maxson et al. впервые установили взаимосвязь между наличием мутаций в гене CSF3R, обладающих феноменом аутоактивации, и наличи-
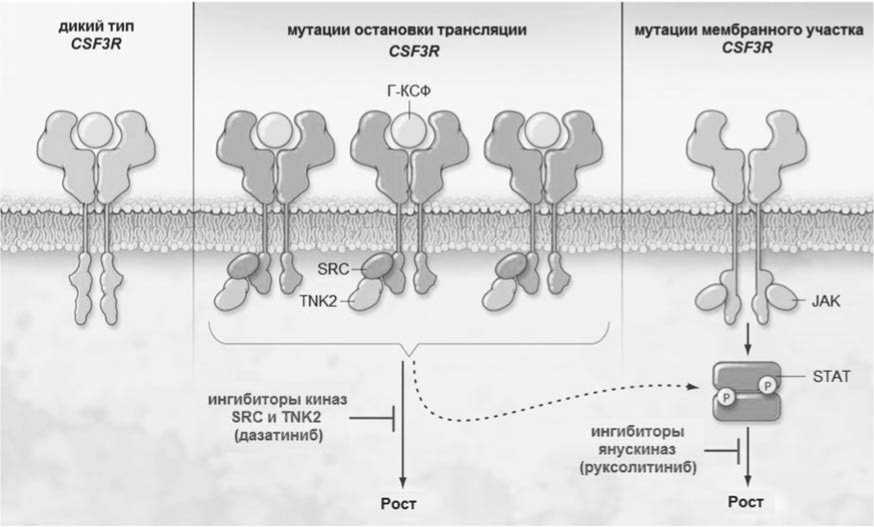
Рис. 1. Молекулярно-генетические основы патогенеза ХНЛ и точки приложения таргетных препаратов [21].
ем ХНЛ [21]. Мутации CSF3R были выявлены у 89% больных ХНЛ. В группе из 16 больных ХНЛ наиболее часто определялись мутации участка рецептора, расположенного проксимально к мембране клетки: T618I у 12 и T615A у 2 больных. Были также выявлены и мутации остановки трансляции, часто в ассоциации с мутациями T618I/T615A. В эксперименте на мышах этими же авторами было показано, что введение клеток с T618I мутацией CSF3R приводит к развитию миелопролиферативного новообразования с летальным исходом [22]. В последующем у больных с ХНЛ были описаны и другие мутации CSF3R (M696T и I598I) [23]. Исходя из молекулярногенетических основ патогенеза ХНЛ были предприняты успешные попытки лечения ХНЛ таргетными препаратами как в эксперименте на мышах, у отдельных пациентов в рамках терапии «off-label», так в ходе клинического исследования фазы II использования руксолитиниба у пациентов с аХМЛ и ХНЛ (рис. IX-1) [21,22,24,25].
Приблизительно 10-20 % пациентов с ХНЛ не имеет мутаций в гене CSF3R и драйвером онкологического процесса в такой ситуации, по аналогии с тринегативными случаями ПМФ и ЭТ, выступают другие генетические аберрации. Как и в случаях с другими Ph-негативными МПН, при ХНЛ нередко обнаруживаются мутации в генах-эпигенетических регуляторах процессов пролиферации, которые могут служить как дополнительными драйверами, так и «катализаторами» прогрессирования заболевания, имеющими прогностическую значимость. Наиболее частыми из них являются мутации в генах ASXL1, SETBP1, SRSF2, TET2, U2AF1 [26].
Клинические проявления ХНЛ неспецифичны и схожи с симптоматикой ХМЛ. Часть больных может не иметь существенных жалоб, они обычно обращаются к гематологу по поводу лейкоцитоза, обнаруженного при профилактическом обследовании. Большинство описанных больных с ХНЛ имели потерю веса, некоторые – слабость. У всех пациентов при обследовании выявлялась спленомегалия, а в клиническом анализе крови наблюдался лейкоцитоз различной степени за счет зрелых нейтрофилов (сегментоядерных и палочкоядерных). Количество молодых форм дифференцировки нейтрофилов до метамиелоцитов не превышает 2 %. Абсолютного увеличения числа моноцитов, эозинофилов, базофилов не отмечается. У около половины больных в момент установления диагноза определяется анемия различной степени тяжести, тромбоцитоз не наблюдался ни у одного пациента, тогда как тромбоцитопения была зарегистрирована у части больных. Уровень активности щелочной фосфатазы нейтрофилов, в отличие от пациентов с ХМЛ был повышен у подавляющего большинства больных ХНЛ. При визуальном исследовании мазка крови при ХНЛ, несмотря на наличие сдвига в лейкоцитарной формуле влево, обнаруживаются лишь единичные бласты. Эритроциты демонстрируют умеренный ани-зопойкилоцитоз. Дакриоциты или эритробласты в периферической крови при ХНЛ не встречаются, в отличие от ПМФ. В миелограмме наблюдается расширение гранулоцитарного ростка до 80 % и более. Большинство гранулоцитов находятся на стадиях созревания. Количество бластов не увеличено. Признаков дисгранулоцитопоэза (гипогрануляция, псевдопельгеризация, тельца Ауэра) не наблюдается. Увеличения процентного содержания эозинофилов, базофилов, моноцитов при ХНЛ в костном мозге не отмечается. Эритроидный росток с нормобласти-ческим типом созревания. Количество мегакариоцитов в пределах нормы, без существенных признаков дисплазии.
Кольцевые сидеробласты при ХНЛ не регистрируются. При гистологическом исследовании костного мозга при ХНЛ наблюдается его гиперклеточ-ность с гранулоцитарной пролиферацией. В отличие от других форм МПН (ИП, ЭТ, ПМФ) мегакариоцитар-ный росток не гиперплазирован и не встречаются мегакариоциты большого размера с признаками атипии, а также их скопления. У большинства больных в гистологических препаратах костного мозга можно выявить начальные признаки ретикулинового фиброза. При цитогенетическом исследовании клеток костного мозга у большинства больных выявлен нормальный кариотип. У некоторых больных определялись трисомии 9 и 21 хромосом, полная или частичная потеря длинного плеча 3, 11, 20 хромосом. При исследовании кариотипа в динамике у некоторых больных с нормальным кариотипом в дебюте заболевания было отмечено возникновение новых генетических аберраций: трисомии 21 хромосомы, транслокация t(2;2), делеции 11, 12, 20 хромосом, моносомия 5 и 7 хромосом (в бластном кризе).
Обобщенная характеристика больных по данным мета-анализа публикаций наблюдения за 40 пациентами ХНЛ представлена в таблице 1 [27].
Таблица 1
Клиническая характеристика больных хроническим нейтрофильным лейкозом [27]
|
Показатель |
Значение |
|
Возраст, медиана (интервал), лет |
66,5 (15-86) |
|
Мужчины/ женщины |
23/17 |
|
Край селезенки ниже реберной дуги, медиана (интервал), см |
4 (1-20) |
|
Гемоглобин, медиана (интервал), г/л |
112 (70-167) |
|
Лейкоциты, медиана (интервал), х 109/л |
39,1 (11,3-125,7) |
|
Нейтрофилы в лейкоцитарной формуле, медиана (интервал), % |
87 (68-98,5) |
|
Незрелые формы (промиелоциты, миелоциты, метамиелоциты) нейтрофилов в лейкоцитарной формуле, медиана (интервал), % |
2 (0-11) |
|
Бласты в лейкоцитарной формуле, медиана, % |
0 |
|
Тромбоциты, медиана (интервал), х 109/л |
136 (7-476) |
|
Частота развития бластного криза %, (к-во больных) |
20 (8) |
|
Медиана наблюдения при развитии бластного криза, медиана (интервал), месяцев |
21 (3-94) |
|
Медиана общей выживаемости, месяцев |
47 |
В классификации ХНЛ выделяют хроническую фазу, фазу акселерации и бластный криз. Критерием бластной трансформации (бластного криза) является повышение количества бластов в костном мозге и/или крови более 20%. Общепринятые диагностические критерии фазы акселерации при ХНЛ отсутствуют. Принято считать, что её признаком является потеря ответа на терапию с нарастанием лейкоцитоза и спленомегалии.
Клиническое течение заболевания у подавляющего большинства больных, несмотря на проведение сдерживающей терапии цитостатиками, характеризуется постепенной потерей эффективности терапии и дальнейшей эволюцией заболевания вплоть до бластного криза. Медиана времени наблюдения за течением ХНЛ до развития бластного криза составляет менее 2 лет. Основной причиной смерти у больных ХНЛ является геморрагический синдром с развитием кровоизлияний в центральную нервную систему. Медиана общей выживаемости составляет менее 4 лет [27,28].
ХНЛ из малоизученного заболевания, диагноз которого устанавливался методом исключения, в настоящее время превращается в нозологическую форму с высокоспецифичными молекулярно-генетическими маркерами [24]. Диагностические критерии ХНЛ в классификации ВОЗ 2016 г. претерпели редакцию, связанную с добавлением критерия наличия специфических генетических изменений. К ним в настоящее время относят следующие [4]:
-
1. Уровень лейкоцитов периферической крови ≥25 х 109/л;
-
• сегментоядерные и палочкоядерные нейтрофилы >80 % в лейкоцитарной формуле;
-
• незрелые (бласты, промиелоциты, миелоциты, метамиелоциты) гранулоциты <10 % в лейкоцитарной формуле;
-
• миелобласты наблюдаются редко
-
• количество моноцитов <1 х 109/л
-
• нет дизгранулоцитопоэза.
-
2. Гиперклеточный костный мозг:
-
• нейтрофильные гранулоциты увеличены в абсолютном и относительном количестве
-
• созревание нейтрофилов не нарушено
-
• миелобласты <5 % ядерных клеток.
-
3. Не соответствует диагностическим критериям ВОЗ для хронического миелолейкоза, истинной полицитемии, эссенциальной тромбоцитемии или первичного миелофиброза.
-
4. Нет перестроек генов PDGFRα, PDGFRß, FGFR1 или PCM::JAK2.
-
5. Наличие CSF3RT618I или других активирующих CSF3R мутаций или (при отсутствии CSF3R мутации) персистирующий не менее 3 месяцев нейтрофилез, спленомегалия при отсутствии явных причин реактивного нейтрофилеза, включая отсутствие плазмоклеточных новообразований или, при наличии, доказательство клональности миелоидных клеток с помощью цитогенетических или молекулярных исследований
Для подтверждения диагноза ХНЛ необходимо наличие всех критериев.
Для диагноза при обследовании больного с подозрением на ХНЛ необходимо проводить ряд исследований, обязательно включающих гистологическое исследование трепанобиоптата костного мозга с оценкой степени фиброза [29] и генетические (цитогенетическое, молекулярно-генетическое) исследования костного мозга и крови. Совокупность результатов исследований в большинстве случаев позволяет провести дифференциальную диагностику с ХМЛ и другими МПН (кариотипирование и FISH для исключения наличия типичной t(9;22) и вариантных транслокаций, образующих слитный ген BCR::ABL, перестроек генов PDGFRα, PDGFRß или FGFR1 или PCM::JAK2, молекулярно-генетическое исследование (качественное) крови на наличие химерного гена BCR::ABL, мутаций в генах JAK2, CALR или MPL). Для подтверждения диагноза ХНЛ необходимо проведение молекулярно-генетического исследования крови методом секвенирования на наличие мутаций в гене CSF3R, при отсутствии данных мутаций основания для подтверждения клонально-сти можно получить с помощью исследования кариотипа и определения мутаций в генах ASXL1, EZH2, TET2, IDH1/2, SRSF2, SF3B1 и других. При возможности планирования алло-ТКМ необходимо проведение HLA-типирования у пациентов и возможных доноров.
До недавнего времени лечение ХНЛ традиционно проводилось с помощью сдерживающей терапии. Наиболее часто использовался гидроксикарбамид (гидроксимочевина) или другие цитостатики в виде монотерапии или в комбинациях. Существует и единичный опыт использования интерферона-альфа [30]. Результаты сдерживающей терапии являются неудовлетворительными: прогрессирование в фазу бластного криза не предотвращается, а общая выживаемость не превышает 4 лет. У небольшого количества (5) молодых больных выполнена аллогенная трансплантация костного мозга (алло-ТКМ) с удовлетворительными результатами: летальный исход в посттрансплантационном периоде лишь у 1 из 5 больных [27].
В последние годы, благодаря расшифровке молекулярно-генетических основ патогенеза ХНЛ, сформулированы показания и получен опыт успешного использования таргетной терапии: ингибиторов янускиназ (руксолитиниб) и SRC-тирозинкиназ (да-затиниб) [24]. Ниже представлена характеристика препаратов, применение которых возможно при ХНЛ:
-
• Цитостатики: гидроксикарбамид; цитарабин; меркаптопурин применяются в качестве монохимиотерапии в низких дозах (гидроксикарбамид 10-30 мг/кг/сут; цитарабин 10-20 мг/м2 /сут 10-14 дней каждый месяц, меркаптопурин 1-2 мг/кг/сут.). Целью применения цитостатиков является сдерживание пролиферации опухоли и контроль показателей крови для профилактики осложнений. Общепринятых стандартных схем применения не существует. Предпочтительным считается постоянный ежедневный или интермитирующий (в случае цитарабина) прием в подобранных с учетом индивидуальной переносимости и возраста больных дозах, позволяющих контролировать показатели крови.
-
• Препараты интерферона-альфа (ИФНα). С учетом вероятных эффектов терапия препаратами интерферона более целесообразна у молодых больных. Оптимальная дозировка препаратов интерферона при ХНЛ не установлена. Принимая во внимание развитие частых побочных эффектов и необходи-
- мость постоянной терапии, лечение проводится в максимально переносимых дозах, обеспечивающих контроль показателей крови. Дозировка может составлять от 3 до 10 млн МЕ/м2 в неделю в дробных дозах. Режим введения также выбирается индивидуально с учетом переносимости (ежедневно, через день, пять дней в неделю и пр.). Сообщений об опыте применения пегилированных форм интерферона при ХНЛ в настоящее время нет.
-
• Ингибиторы янускиназ – препараты прицельного (таргетного) действия, блокирующие активность JAK2-киназ, направлены на ключевое звено патогенеза ХНЛ – сигнальный путь JAK-STAT. В Российской Федерации в настоящее время зарегистрирован только один препарат этого класса Руксолитиниб для лечения пациентов с ПМФ и ИП. В экспериментах на клеточных культурах показана высокая активность руксолитиниба в отношении наиболее частых мутаций гена CSF3R (T618I), затрагивающих цитоплазматический участок рецептора CSF3R. В 2013 г. было опубликовано сообщение об успешном опыте применения руксолитиниба у больного ХНЛ с мутацией CSF3RT618I [21]. Теоретические предположения и ограниченный практический опыт послужили основанием для инициации первого клинического исследования использования таргет-ной терапии для лечения аХМЛ и ХНЛ. В клиническом исследовании фазы 2, проводившемся с 2014 по 2020 гг. был включен 51 пациент (22 пациента с ХНЛ и 27 пациентов с аХМЛ, 2 больным при обследовании диагноз ХНЛ или аХМЛ не был подтвержден). Руксолитиниб применялся в дозах, аналогичных таковым для пациентов с ПМФ с коррекцией в зависимости от уровня тромбоцитов. В настоящее время опубликованы результаты анализа лечения 44 пациентов (21 с ХНЛ и 23 с аХМЛ). Общего ответа по критериям протокола достигли 35 % пациентов. Благоприятными факторами для достижения ответа являлись диагноз ХНЛ – 14 пациентов из 21 (67 %), в том числе 4 полных и 10 частичных ответов) и наличие мутаций в гене CSF3R - 13 из 22 больных (59 %) с наличием мутаций достигли ответа, в том числе 3 полного и 10 частичного, тогда как при отсутствии данных мутаций только у 3 из 22 (14%) наблюдался ответ на лечение (2 полных и 1 частичный) [31]. Следует отметить, что пока руксолитиниб не имеет официально зарегистрированных показаний для использования при ХНЛ и его применение у больных ХНЛ в рамках действующих юридических норм возможно только по жизненным показаниям по заключению врачебного консилиума. Рекомендуемая начальная доза руксолитиниба составляет 15 мг 2 раза в день для пациентов с количеством тромбоцитов 100-200х109/л и 20 мг 2 раза в день для пациентов с уровнем тромбоцитов >200х109/л. Максимальная доза составляет 25 мг 2 раза в день внутрь. Наиболее значимыми побочными эффектами рук-солитиниба являются анемия, тромбоцитопения и
- синдром «цитокиновой отдачи», выражающийся в быстром возврате симптомов интоксикации, вплоть до системной воспалительной реакции и спленомегалии [26].
-
• Дазатиниб – многоцелевой препарат, взаимодействующий со многими тирозинкиназными и не-тирозинкиназными белками. Дазатиниб ингибирует тирозинкиназы семейства Src (LYN, SRC, LCK, YES, FYN), и BCR::ABL, KIT, EPHA2, PDGFRβ, PDGFRα. Способен in vitro ингибировать рост клеточных линий, трансдуцированных геном CSF3R с мутацией S783fs, приводящей к остановке трансляции РНК, тогда как клетки с мутацией CSF3RT618I были относительно устойчивы к воздействию дазатиниба [5]. Аналогично руксолитинибу, дазатиниб также не имеет официально зарегистрированных показаний к применению при ХНЛ и может использоваться у этих больных только по жизненным показаниям. Наиболее частыми побочными эффектами использования дазатиниба являются анемия, нейтропения, тромбоцитопения, слабость, периферические отеки и плевральный выпот.
С учетом данных экспериментальных исследований возможными точками приложения таргетных препаратов являются:
-
• ХНЛ с мутациями, затрагивающими цитоплазматический участок рецептора CSF3R. Наиболее эффективным для таких больных может оказаться использование ингибитора янускиназ (руксолити-ниба);
-
• ХНЛ с мутациями остановки трансляции гена CSF3R ожидается большая эффективность применения ингибиторов SRC-киназ (дазатиниб) (рис. 1) [5].
Мониторинг лечения ХНЛ при медикаментозной терапии следует осуществлять с учетом вида лекарственной терапии и индивидуальных проявлений токсичности. В первые три месяца терапии целесообразно проводить оценку клинического анализа крови и биохимических параметров (общий билирубин, АСТ, АЛТ, ЛДГ) не реже 1 раза в месяц. После стабилизации показателей крови и подбора дозы возможно проведение контрольного обследования 1 раз в три месяца. При развитии необъяснимых цитопений, нарастания спленомегалии необходимо проведение исследования костного мозга (стернальная пункция, цитогенетическое исследование) для исключения прогрессирования в фазу акселерации и бластного криза.
Единственным возможным радикальным методом лечения ХНЛ в настоящее время представляется алло-ТКМ, возможность проведения которой следует изучать сразу после установления диагноза у молодых больных ХНЛ без значимой сопутствующей патологии [2].
Атипичный хронический миелолейкоз – миелопролиферативное новообразование с очень схожей с классическим ХМЛ клинической и лабораторной симптоматикой, но без наличия филадель- фийской хромосомы и отсутствием патологического слитного гена BCR::ABL. Как уже упоминалось ранее, аХМЛ в современной классификации ВОЗ отнесен не в группу Миелопролиферативных новообразований, а в смешанный раздел Миелодиспластические синдромы / Миелопролиферативные новообразования [4], хотя общность молекулярно-генетического патогенеза, клиники и подходы к диагностике и лечению аХМЛ имеют много общего с ХНЛ.
В пятой редакции классификации ВОЗ (20222023) название нозологии «Атипичный хронический миелоидный лейкоз» предлагается изменить на «Миелодиспластический синдром / миелопролиферативное новообразование с нейтрофилезом». Мотивом изменения по сообщению авторов является намерение избежать смешения понятий с типичным ХМЛ, BCR::ABL+. К сожалению, такое изменение нельзя признать удачным, так как существующее наименование как раз очень точно отражает клиническую картину и течение заболевания, крайне схожее с ХМЛ [32]. Более логичным было бы, наоборот, объединить аХМЛ с ХНЛ в общую нозологическую форму аХМЛ, имеющую общность патогенеза, течения, диагностики и лечения, и отнести эту форму по несомненным признакам миелопролиферации в группу МПН.
В двух описаниях сериях случаев, наибольших по количеству (55 и 65 пациентов), чаще наблюдались пациенты пожилого возраста с медианой около 60-70 лет, заболевание характеризовалось агрессивным течением, со склонностью к быстрому развитию бластной трансформации (медиана до прогрессирования 11-18 месяцев), общая выживаемость составляла 12-24 месяца [33,34]. Неблагоприятными прогностическими факторами для общей выживаемости считаются гиперлейкоцитоз >40 или >50 х 109/л при первичной диагностике, гепатоспле-номегалия, бластные клетки >5 % в крови, выраженный дизэритрпоэз, трансфузионная зависимость, женский пол, возраст более 65 лет [33-37]. Благодаря молекулярно-генетическим исследованиям выявлены также агрессивные биологические характеристики течения заболевания – наличие мутаций в генах ASXL1, SETBP1 и TET2 [38,39].
Этиология заболевания до настоящего времени остается неизвестной. C развитием молекулярногенетических технологий, в первую очередь секвенирования следующего поколения, было получено много новой информации в исследовании молекулярно-генетического патогенеза аХМЛ. В отличие от классических миелопролиферативных новообразований, при аХМЛ до сих пор не выявлено конкретной драйверной мутации. При обследовании пациентов с аХМЛ выявляются аберрации генов, участвующих в регуляции пролиферации и апоптоза миелоидных предшественников, которые могут наблюдаться и при других миелопролиферативных и миелодиспластических новообразованиях, что подчеркивает общность патогенеза данных заболеваний. Молекулярно-генетическими путями, принимающими участие в патогенезе аХМЛ, с высокой вероятностью могут быть:
-
• эпигенетическая регуляция гистонов с помощью комплекса репрессии транскрипции PRC2 посредством мутаций генов-эпигенетических регуляторов ASXL1 и EZH2;
-
• активация пролиферации с помощью митоген-активирующих протеинкиназ (MAPK) посредством мутаций генов NRAS и PTPN11;
-
• нарушение ингибиции апоптоза онкосупрессором PP2A посредством мутаций гена SETBP1;
-
• стимуляцию пролиферативной активности через JAK-STAT сигнальный путь с помощью мутаций в гене рецептора колониестимулирующего фактора CSF3R;
-
• регуляцию синтеза фосфадитилиэтаноламина с помощью мутаций в гене ETNK1.
Часто (>20 %) при аХМЛ выявляются мутации в генах SETBP1, ASXL1, N/K-RAS, SRSF2, TET2, реже (<10%) в генах CBL, CSF3R, JAK2, ETNK1.3 [36,38,4044].
Наиболее частой (до 25 %) молекулярно-генетической аберрацией при аХМЛ являются мутации в гене SETBP1, имеющем сложный механизм влияния на регуляцию апоптоза. [43]. Ген SETBP1 локализован на 18 хромосоме (18q21.1) и кодирует белок из 1596 оснований с молекулярной массой 170 кДа. Биологической ролью продуцируемого данным геном белка SETBP1 является его связывание с белком SET, который регулирует фосфатазную активность комплекса PP2A, одного из основных онкосупрессоров в клетке. Мутации гена SETBP1 впервые описаны при врожденном нейродегенеративном син- дроме Schinzel–Giedion, проявляющемся задержкой психического развития, роста, часто также имеют место гидронефроз, припадки, поражения органа зрения, большинство детей с данным синдромом не доживают до 2 лет [45]. Приобретенные мутации гена SETBP1 обнаруживаются при хроническом мие-ломоноцитарном лейкозе, других миелоидных новообразованиях, острых лейкозах. При аХМЛ большинство мутаций в гене SETBP1 определяется между 858 и 871 кодонами. Результатом наличия мутаций является замедление деградации кодируемого им белка, что защищает белок SET от действия протеазы. Это приводит к увеличению количества белка, снижению активности PP2A и ускорению пролиферации клеток. Наличие мутаций в гене SETBP1 при аХМЛ чаще сочетается с цитогенетическими аберрациями -7 и i(17)(q10), мутациями генов ASXL1 и CBL, но не с мутациями генов TET2 и JAK2 и ассоциировано с более высоким лейкоцитозом, низкими концентрациями гемоглобина и количества тромбоцитов, ухудшением общей выживаемости [43,46].
Клиническая картина аХМЛ очень схожа с ХМЛ и складывается из неспецифической клинической симптоматики в виде общей слабости, чувства тяжести в подреберьях, обусловленных гепатосплено-мегалией и клинико-лабораторной картиной в виде выраженного лейкоцитоза со сдвигом в миелоидном ряду до незрелых предшественников более 10 % с признаками дисплазии. Абсолютное количество моноцитов в крови, вследствие лейкоцитоза может составлять более 1,0 х 109/л, но относительное их количество в лейкоцитарной формуле менее 10 %, базофилия не выражена (<2 %).
Диагностика аХМЛ также, как и в случае с ХНЛ, в первую очередь предполагает исключение клас-
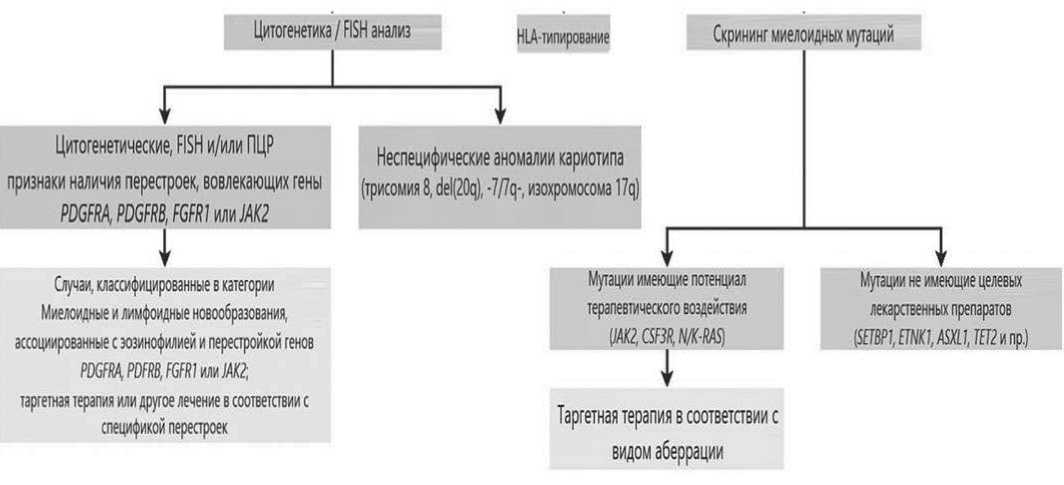
Рис. 2. Алгоритм диагностики аХМЛ [47].
сического ХМЛ и других МПН: цитогенетическое и FISH исследования клеток костного мозга на t(9;22) и вариантные транслокации, образующие слитный ген BCR::ABL, перестроек генов PDGFRα, PDGFRß или FGFR1 или PCM::JAK2, молекулярно-генетическое исследование (качественное) крови на наличие химерного гена BCR::ABL, мутаций в генах JAK2, CALR или MPL). Для подтверждения диагноза аХМЛ необходимо проведение молекулярно-генетического исследования крови методом секвенирования на наличие мутаций в генах SETBP1, ASXL1, N/K-RAS, SRSF2, TET2, CBL, CSF3R, JAK2, ETNK1.3. Обязательным является гистологическое исследование костного мозга с оценкой степени фиброза [29]. Для диагностики аХМЛ возможно использование алгоритма, приведенного на рис. 2 [47].
При исключении других МПН и наличии подозрений на наличие аХМЛ проводится анализ полученной при обследовании информации на соответствие диагностическим критериям аХМЛ ВОЗ 2016 г.:
-
• персистирующий лейкоцитоз более 13х109/л вследствие повышенного количества нейтрофилов и их предшественников с выраженным дисгрануло-поэзом;
-
• незрелые миелоидные предшественники (промиелоциты, миелоциты, метамиелоциты) >10% лейкоцитов крови;
-
• отсутствие либо минимальный моноцитоз (обычно <10 % от числа лейкоцитов);
-
• отсутствие либо минимальная базофилия (<2 %);
-
• отсутствие филадельфийской хромосомы или слитного гена BCR::ABL, несоответствие диагности-
- ческим критериям ВОЗ для истинной полицитемии, эссенциальной тромбоцитемии или первичного миелофиброза;
-
• нет перестроек генов PDGFRα, PDGFRß или FGFR1 или PCM::JAK2;
-
• гиперклеточный костный мозг с гранулоцитарной пролиферацией и дисплазией.
Для верификации диагноза аХМЛ необходимо соответствие всем диагностическим критериям [4]. Основное внимание при подтверждении диагноза аХМЛ необходимо уделить поиску генетических аберраций, например CSF3R, JAK2 и RAS, которые могут быть мишенями при использовании таргетных препаратов. Важно проведение HLA-типирования с целью поиска донора и решения вопроса о выполнении алло-ТКМ.
В настоящее время нет стандартных средств лечения аХМЛ, традиционно для коррекции гиперлейкоцитоза используют циторедуктивную терапию гидроксикарбамидом, но её результаты не могут считаться удовлетворительными с учетом общей и беспрогрессивной выживаемости продолжительностью 12-24 месяцев. Альтернативой или второй линией терапии после гидроксикарбамида являются препараты ИНФ-α, в том числе его пегилиро-ванные формы. В качестве терапии поддержки для коррекции анемии могут применяться препараты эритропоэтина. Характеристика препаратов и их дозировки аналогичны таковым и приведены выше при описании ХНЛ. Единственным возможным радикальным методом лечения аХМЛ является проведение алло-ТКМ, однако проведение данной процедуры возможно у небольшого числа пациентов и
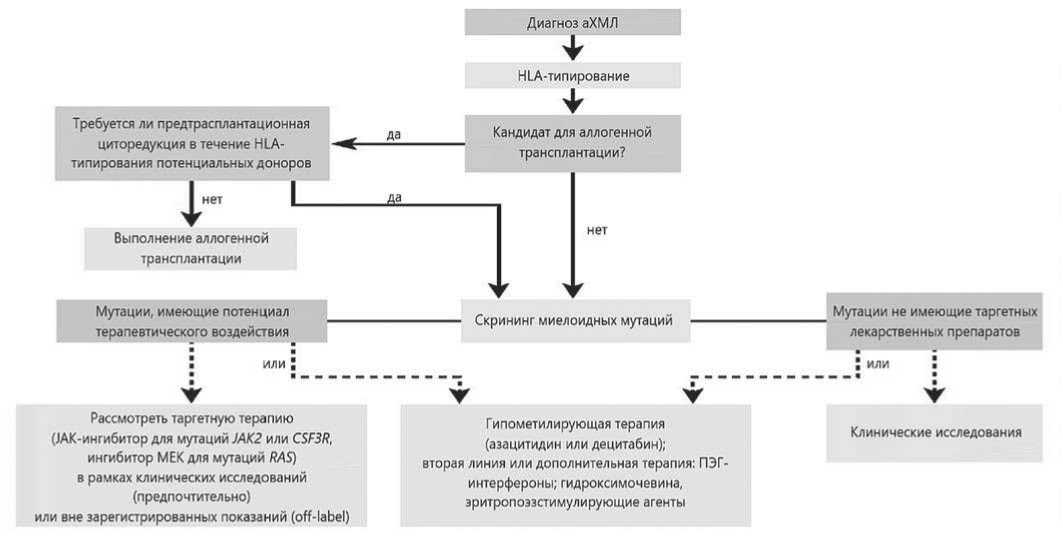
Рис. 3. Перспективный алгоритм лечения аХМЛ [47].
сопряжено с рисками летальности, общая и беспро-грессивная длительная выживаемость при проведении алло-ТКМ в группе МДС/МПН составляет не более 40-50% [48,49]. Наибольшая группа описанных случаев алло-ТКМ при аХМЛ включала 21 пациента. Через 5 лет после алло-ТКМ 17 из 21 пациента были живы, медиана выживаемости составила 46,8 месяцев [50].
С учетом информации, полученной при исследовании молекулярно-генетических аберраций и возможного участия сигнальных путей в патогенезе аХМЛ, основные надежды на улучшение результатов лечения связаны с применением таргетных препаратов и гипометилирующих агентов. Перспективный алгоритм терапии аХМЛ приведен на рис. 3 [47].
Использование большинства таргетных препаратов при аХМЛ пока проводится только в рамках «off-label». В настоящее время проведено только одно клиническое исследование с использованием ингибитора янускиназ руксолитиниба при лечении аХМЛ и ХНЛ. В данное исследование было включено 27 пациентов с аХМЛ, использовались дозировки руксолитиниба, такие же как при лечении ПМФ. Ответ на лечение был оценен у 23 больных. Частичный ответ был получен у 2 пациентов (8,7 %), один из этих пациентов имел мутацию T615A в гене CSF3R [31].
Приводим собственное клиническое наблюдение таргетной терапии аХМЛ. Пациентка 1966 г. рождения, обратилась к гематологу по месту жительства в ноябре 2017 г. с жалобами на выраженную слабость, боли, тяжесть в левом подреберье. Клинический анализ крови от 09.11.2017 г.: гемоглобин – 104 г/л, эритроциты – 3,17 х 1012/л, тромбоциты – 223 х 109/л, лейкоциты – 133,9 х 109/л, бластные клетки – 1 %, промиелоциты – 6 %, миелоциты – 14 %, метамиелоциты – 16 %, палочкоядерные – 14 %, сегментоядерные – 45 %, лимфоциты – 2 %, моноциты – 0 %.
УЗИ органов брюшной полости от 03.10.2017 г.: гепатомегалия (печень размерами 157 х 67 мм, воротная вена расширена до 17 мм), диффузные изменения паренхимы печени; спленомегалия (селезенка размерами 200х100 мм). Компьютерная томография от 20.10.2017 г.: печень не увеличена, спленомегалия (селезенка занимает практически всю левую половину брюшной полости, размеры 200 х 130 х 248 мм, вызывает дислокацию прилежащих органов кзади и вправо – левая почка, поджелудочная железа, петли кишечника; корень брыжейки смещен в центрально-правые отделы).
Был заподозрен хронический миелолейкоз, однако этот диагноз не был подтвержден результатами генетического исследования.
Молекулярно-генетическое исследование крови на количественную экспрессию BCR::ABL (белок p210) от 05.10.2017 г.: отрицательно. Цитогенетическое исследование костного мозга от 30.10.2011 г.:
кариотип 46,ХХ [20].
Молекулярно-генетическое исследование крови от 02.11.2017 г.: мутация JAK2V617F – отрицательно. BCR::ABL (белок p210), BCR::ABL (белок p190), BCR::ABL (белок p230) – не обнаружено, MPL (мутации 515 кодона), CALR (мутации 9 экзона) – не обнаружены.
С 14.11.2017 г. начата терапия гидроксикарбамидом в дозе до 2000 мг в сутки.
Гистологическое исследование костного мозга от 30.11.2017 г. (НМИЦ гематологии МЗ РФ, проф. Ковригина А.М.): костные балки с признаками очаговой резорбции. Сохранные костномозговые полости единичные, в них гиперклеточный костный мозг (относительно возрастной нормы), липоциты единичны. Гранулоцитарный росток резко расширен, представлен клетками на всех этапах дифференцировки примерно с равным соотношением элементов промежуточного и зрелого пулов. Эритроидный росток в умеренном количестве, представлен скоплениями эритрокариоцитов разной степени зрелости с наличием отдельных мегалобластоидных форм. Мегакариоциты в немного сниженном количестве, представлены клетками небольших и средних размеров с гиполобулярными и гипохромными ядрами, часть – с диспластическими изменениями. Интер-стициально рассеяны мелкие лимфоидные клетки, зрелые плазматические клетки. Строма полнокровна. Степень ретикулинового фиброза стромы при окраске по Gomori MF – 1. Заключение: при исключении BCR::ABL+ хронического миелолейкоза в костном мозге морфологическая картина в наибольшей степени характеризует заболевание из группы МДС/МПЗ (атипичный ХМЛ?).
В декабре 2017 г. проведено обследование в Рос-НИИГТ ФМБА России.
Клинический анализ крови от 05.12.2017 г.: эритроциты – 3,76 х 1012/л, гемоглобин – 113 г/л, тромбоциты – 361 х 109/л, лейкоциты – 25,8 х 109/л, бластные клетки – 0 %, промиелоциты – 2,0 %, миелоциты – 13,0 %, метамиелоциты – 7,0 %, палочкоядерные – 8 %, сегментоядерные – 53 %, эозинофилы – 0 %, базофилы – 3 %, пролимфоциты – 0 %, лимфоциты – 13 %, моноциты – 1 %, СОЭ – 15 мм/ч.
Биохимические показатели крови от 05.12.2017 г.: билирубин общий – 12,6 мкмоль/л, билирубин связанный – 4,8 мкмоль/л, билирубин свободный – 7,8 мкмоль/л, АСТ – 0,47 мккат/л, АЛТ – 0,43 мккат/л, креатинин – 0,099 мкмоль/л, мочевина – 7,3 ммоль/л, мочевая кислота – 0,265 мкмоль/л, общий белок – 66,2 г/л, альбумин – 46,3 г/л, глюкоза – 3,8 ммоль/л, ЛДГ – 8,8 мккат/л, ЩФ – 3,23 мккат/л, холестерин – 5,1 ммоль/л, общий кальций – 2,26 ммоль/л, фосфор – 1,73 ммоль/л, магний – 1,04 ммоль/л, натрий – 142 ммоль/л, калий – 4,6 ммоль/л, кальций ионизированный – 1,27 ммоль/л, сывороточное железо – 16,96 мкм/л, ОЖСС – 78,33 мкм/л, коэффициент насыщения трансферрина – 21,7%.
Рис. 4. Трепанобиоптат костного мозга. Окраска Азур-Эозин, увеличение х200 (микрофотографии предоставлены проф. Ю.А. Криволаповым и Е.А. Беляковой).
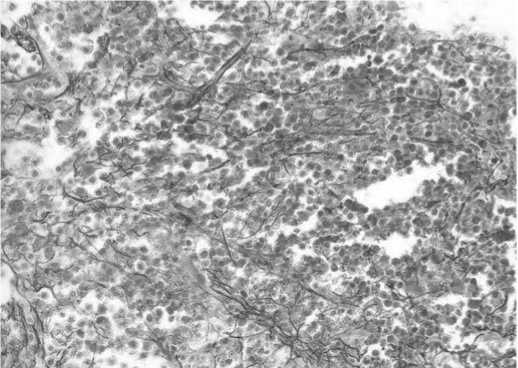
Рис. 5. Трепанобиоптат костного мозга. Ретикулиновый фиброз MF-1. Окраска по методу Гордона-Свита, увеличение х200 (микрофотографии предоставлены проф. Ю.А. Криволаповым и Е.А. Беляковой).
Миелограмма от 05.12.2017 г.: миелокариоциты – 54,0 х 109/л; мегакариоциты – 0 х 109/л, миелобла-сты – 0,6 %, промиелоциты – 5,8 %; миелоциты – 19,4 %; метамиелоциты – 15,0 %; палочкоядерные – 18 %; сегментоядерные – 16,4 %; всего клеток нейтрофильного ряда – 79,8 %; миелоциты эозинофильные – 0,2 %; метамиелоциты эозинофильные – 0,2 %, эозинофилы – 0,6 %, всего клеток эозинофильного ряда – 1,0 %; миелоциты базофильные – 0,4 %; базофилы – 0,4 %; всего клеток базофильного ряда – 0,8 %; лимфоциты – 6,2 %; всего клеток лимфоидного ряда – 6,2 %; моноциты – 1,6 %; всего клеток моноцитарного ряда – 1,6 %, плазмоциты – 0 %; всего клеток плазматического ряда – 0 %; эритробласты – 0,2 %, нормобласты базофильные – 0,4 %; нормо-бласты полихроматофильные – 6,4 %; нормобласты оксифильные – 0,4 %; мегалобласты – 3,2 %; всего клеток эритроидного ряда – 10,6 %; клетки стромы – 0 %; мегакариоциты – 0 %. Пунктат костного мозга нормоклеточный. Нейтрофильный росток расширен, преимущественно за счет миелоцитов и промиелоцитов. Некоторые клетки нейтрофильного ряда склонны к гипогрануляции. Мегакариоциты 2-3 в препарате, отделение пластинок активное. Мегакариоциты диспластичны (гипоплоидные микро-, мезоформы).
-
• Молекулярно-генетическое исследование крови от 05.12.2017 г.: JAK2 (мутации 12 экзона) – не обнаружены.
-
• Цитогенетическое исследование костного мозга от 05.12.2017 г.: 46,XХ [20].
-
• FISH исследование костного мозга от 05.12.2017 г.: химерный ген BCR::ABL не обнаружен в проанализированных интерфазных ядрах.
Гистологическое исследование костного мозга от 05.12.2017 г. (ФГБОУ ВО СЗГМУ им. И.И. Мечнико- ва Минздрава России, к.м.н Е.Е. Леенман): костный мозг гиперклеточный. Миелоидная ткань занимает в среднем 90-100 % объема межбалочных пространств. Лейкоэритробластическое соотношение примерно 5:1. Гранулоцитарный росток расширен, созревание сохранено. Созревающие и незрелые формы образуют небольшие скопления в просвете костномозговых ячеек и вокруг костных балок. Эритроидный росток образован мелкими группами нормобластов и малочисленными мегалобла-стоидными формами. Количество мегакариоцитов несколько увеличено, выражен полиморфизм ядер. Среди мегакариоцитов преобладают клетки небольших размеров с гиполобулярными и дисморфными ядрами, встречаются голоядерные формы. Обнаруживаются гистиоциты с фагоцитированными эритроцитами. Степень выраженности ретикулинового фиброза – 1. Степень выраженности коллагенового фиброза – 0. Степень выраженности остеосклероза – 0. Заключение: гистологические изменения костного мозга соответствуют хроническому миелолейкозу (Ph – негативному), с признаками терапевтического патоморфоза (рис. 4 и 5).
По результатам обследования 14.12.2017 г. установлен диагноз: Атипичный хронический миелоидный лейкоз, BCR::ABL1-. Хроническая фаза от 30.11.2017 г.
Продолжена терапия гидроксикарбамидом 10001500 мг ежедневно в зависимости от количества лейкоцитов в крови.
При контрольном обследовании в январе-феврале 2018 г. отмечается уменьшение размеров селезенки до 3 см из-под края реберной дуги (первоначально селезенка занимала всю левую половину брюшной полости), сохраняются жалобы на слабость (3 балла по ВАШ), утомляемость, обильную потливость со сменой нательного белья.
Клинический анализ крови от 11.01.2018 г.: эритроциты – 3,43 х 1012/л, гемоглобин – 126 г/л, тромбоциты – 200 х 109/л, лейкоциты – 10,0 х109/л, миелоциты – 2 %, палочкоядерные – 3%, сегментоядерные – 73 %, эозинофилы – 0%, базофилы – 2 %, лимфоциты – 16 %, моноциты – 4%, СОЭ – 3 мм/ч.
Молекулярно-генетическое исследование крови от 02.11.2017 г. (заключение от 17.01.2018 г.): обнаружена мутация в гене ASXL1 (мутации 12 экзона (кодоны 574-1082)), мутации в гене EZH2 (мутации 8,10,15,17,18,19 экзонов) – не обнаружены.
Гистологическое исследование костного мозга от 06.02.2018 г. (ФГБОУ ВО СЗГМУ им. И.И. Мечникова Минздрава России, Е.А. Белякова): трепанобиоптат взят тангенциально. Костные балки неравномерно утолщены, поверхность балок неровная. Костный мозг гиперклеточный. Миелоидная ткань занимает от 60 до 90 % объема межбалочных пространств. Лейкоэритробластическое соотношение примерно 4-5:1. Гранулоцитарный росток омоложен, увеличена доля созревающих – незрелых форм. Эритроидный росток образован мелкими группами нормобла-стов и мегалобластоидными формами. Количество мегакариоцитов несколько увеличено. Среди мегакариоцитов преобладают клетки небольших размеров с гиполобулярными и дисморфными ядрами, встречаются голоядерные клетки с гиперхромными ядрами. Обнаруживаются гистиоциты с фагоцитированными эритроцитами. Степень выраженности ретикулинового фиброза: MF-0. Степень выраженности коллагенового фиброза: Coll-0. Заключение:
гистологические изменения костного мозга наиболее соответствуют хроническому миелолейкозу (Ph – негативному), с признаками терапевтического патоморфоза (рис. 6 и 7).
Получены результаты HLA-типирования от 08.12.2017 г. Получен результат: фенотип – А*02,*25; В*18,*51; С*12,*15; DRB1*04,*13; DQB1*03,*06. Найден 1 потенциально совместимый донор и 27 с 1 mismatch (РФ) и 13 совместимых доноров в международном регистре.
С 05.02.2018 г. начата терапия руксолитинибом в дозе 30 мг в сутки, отмена терапии гидроксикарбамидом. На фоне терапии отмечена выраженная положительная динамика в виде улучшения общего самочувствия, отсутствия спленомегалии.
При контрольном обследовании в мае 2018 г.: жалоб не предъявляет, симптомов опухолевой интоксикации нет, отмечает набор 6-8 кг веса, спленомегалии не определяется.
Клинический анализ крови от 28.05.2018 г.: эритроциты – 3,85 х 1012/л, гемоглобин – 124 г/л, гематокрит – 0,353, тромбоциты – 358 х 109/л, лейкоциты – 8,5 х 109/л, бластные клетки – 0 %, промиелоциты – 0 %, миелоциты – 0 %, метамиелоциты – 0 %, палочкоядерные – 0 %, сегментоядерные – 69 %, эозинофилы – 1 %, базофилы – 0 %, лимфоциты – 29 %, моноциты – 1 %.
Цитогенетическое исследование клеток костного мозга от 21.05.2018 г.: 46XX [30], в одной клетке выявлена i(17q), клональность изменений не подтверждена данными FISH.
Гистологическое исследование костного мозга
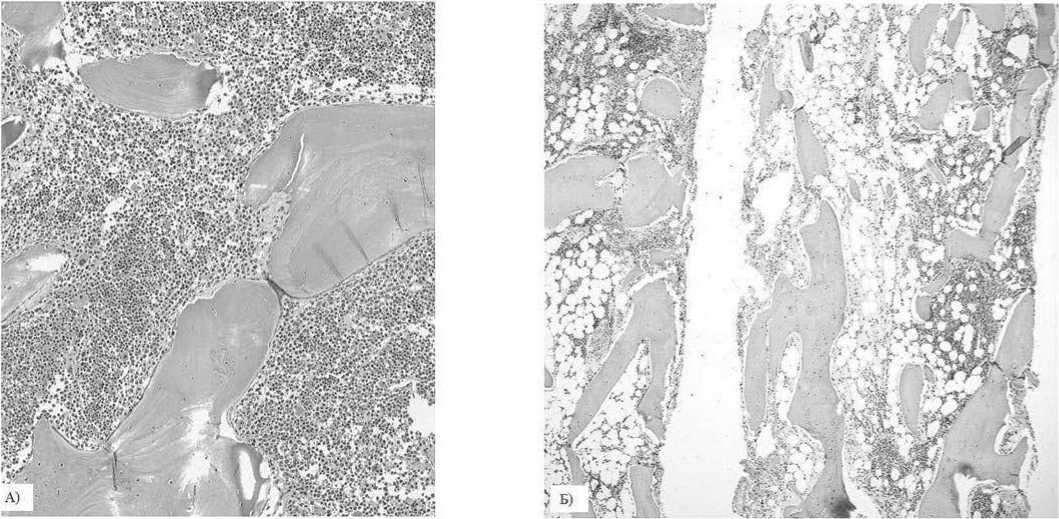
Рис. 6. Трепанобиоптат костного мозга. А) До терапии руксолитинибом, 06.02.2018 г., окраска азуром и эозином, увеличение х50. Б) После 3 месяцев терапии руксолитинибом, 21.05.2018 г., окраска гематоксилином и эозином, увеличение х50 (микрофотографии предоставлены проф. Ю.А. Криволаповым и Е.А. Беляковой).
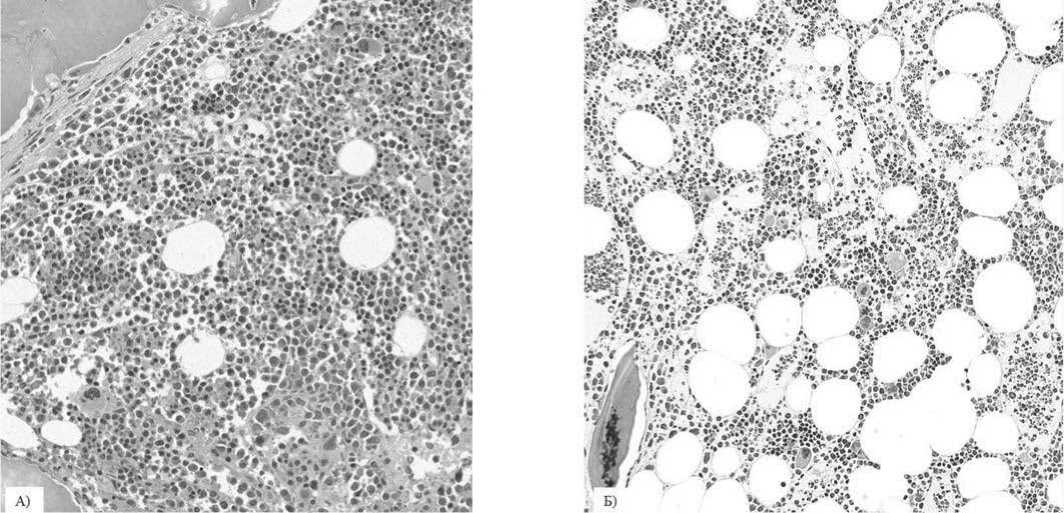
Рис. 7. Трепанобиоптат костного мозга. А) До терапии руксолитинибом, 06.02.2018 г., окраска азуром и эозином, увеличение х200. Б) После 3 месяцев терапии руксолитинибом, 21.05.2018 г.,
окраска гематоксилином и эозином, увеличение Ю.А. Криволаповым и Е.А. Беляковой).
от 21.05.2018 г. (ФГБОУ ВО СЗГМУ им. И.И. Мечникова Минздрава России, Е.А. Белякова): трепанобиоп-тат взят с артефактами механической компрессии. Костные балки неравномерно утолщены, поверхность балок неровная, локально узурированная. Визуализируются расширенные кровеносные синусы, частично заполненные эритроцитами. Миелоидная ткань с признаками отека, распределена в костномозговых ячейках неравномерно и занимает от 5 до 50 % объема межбалочных пространств, в среднем не более 30 %. Лейкоэритробластическое соотношение составляет примерно 3-4:1. Гранулоцитарный росток несколько омоложен, увеличена доля созревающих и незрелых форм. Эритроидный росток образован мелкими группами нормобла-стов и мегалобластоидными формами. Количество мегакариоцитов несколько снижено, они распределены неравномерно среди клеток миелоидной ткани. Среди мегакариоцитов встречаются клетки небольших размеров с гиполобулярными ядрами. Обнаруживаются гистиоциты с фаготицированны-ми эритроцитами. Оценить степень выраженности ретикулинового фиброза невозможно в связи с очаговой деформацией трепанобиоптата. Степень выраженности коллагенового фиброза: Coll-0. Степень выраженности остеосклероза: Os-1. Заключение: гистологические изменения костного мозга наиболее соответствуют хроническому миелолейкозу (Ph-негативному), с признаками терапевтического патоморфоза. По сравнению с предыдущим исследованием от 06.02.2018 обнаруживается значительное снижение клеточности костного мозга, вплоть до х200 (микрофотографии предоставлены проф. наличия участков гипоплазии и отёка миелоидной ткани (рис. 6 и 7).
Молекулярно-генетическое исследование крови от 02.11.2017 г. (результат получен 28.05.2018 г.): секвенирование гена CSF3R (мутации 14 экзона) – обнаружена мутация (T618I).
Установлен окончательный диагноз: Атипичный хронический миелоидный лейкоз, CSFR3RT618I+, ASXL (12 экзон)+. Хроническая фаза от 30.11.2017 г.
Следует отметить, что это первый известный нам диагноз аХМЛ в отечественной практике, который был верифицирован с помощью молекулярно-генетических методов исследования (секвенированием гена CSF3R).
Пациентка впоследствии получала руксолити-ниб в дозе 30 мг в сутки с удовлетворительной переносимостью. Приблизительно через полтора года приема руксолитиниба начал отмечаться умеренный тромбоцитоз, который потребовал добавления гидроксикарбамида в дозе 500 мг в сутки.
В апреле 2021 г. пациентка перенесла новую коронавирусную инфекцию с пневмонией, в сентябре 2021 г. проведена операция эндопротезирования левого тазобедренного сустава без осложнений. Выполнена контрольная трепанобиопсия костного мозга (рис. 8 и 9).
Гистологическое исследование трепанобиоптата В 21-10722 (ПСПбГМУ им.ак. И.П. Павлова, проф. В.В. Байков): трепанобиоптат костного мозга, размером – 1,2 х 0,15 см. Костные балки умеренной толщины. Лакуны широкие. MF0 (окраска солями серебра). Костный мозг с неравномерным распределением
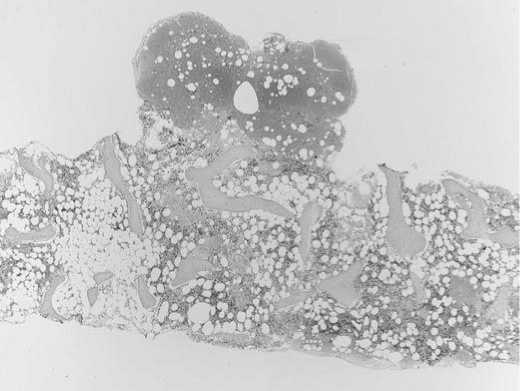
Рис. 8. Трепанобиоптат костного мозга. Неравномерно гипоклеточный костный мозг. В части лакун гемопоэз отсутствует. Окраска гематоксилин-эозин x28 (микрофотографии предоставлены проф. В.В. Байковым.
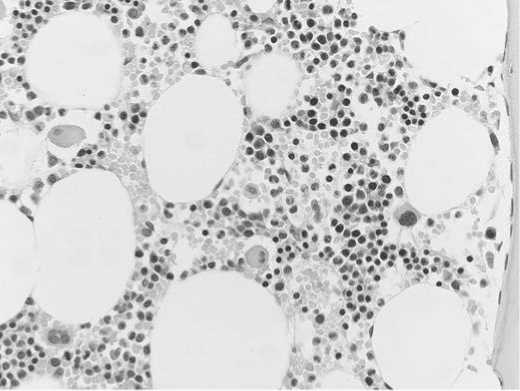
Рис. 9. Трепанобиоптат костного мозга. Резко выраженное сужение гранулоцитарного ростка. Окраска гематоксилин-эозин x400 (микрофотографии предоставлены проф. В.В. Байковым).
очагов гемопоэза. В 2-3 лакунах – жировой костный мозг >80 % площади лакун, в остальных – гемопоэтические островки занимают около 30 % площади лакун. Лейко-эритробластическое отношение – около 2:1. Гранулоцитарный росток сужен, встречаются промежуточные и зрелые формы. Клетки с бластной морфологией немногочисленные. Эритропоэз нормобластического типа, омоложен. Эри-трокариоциты располагаются интерстициально и в виде островков. Группы клеток – вблизи трабекул. Умеренно выраженный избыток мегакариоцитов в части лакун. Клетки полимфорфны. В значительном количестве клетки среднего размера с гипо-/би-/ монолобулярными ядрами. Лимфоидные клетки – в умеренном количестве, клетки лежат интерстици-ально. Плазматические клетки – в небольшом количестве. Заключение: неравномерно гипоклеточный костный мозг с умеренно выраженным избытком мегакариоцитов в части лакун, диспластическими чертами в мегакариоцитах. С учетом ранее диагностированного аХМЛ, описанные изменения можно рассматривать в русле указанного диагноза (с учётом терапии).
Молекулярно-генетическое исследование крови от 28.10.2021 г.: обнаружена мутации в G646fsX12) в гене ASXL1 (также обнаружены полиморфизмы G652S, G643A), мутации в гене CSF3R (в 14 экзоне) – не обнаружены.
Пациентка продолжает прием руксолитиниба 30 мг в сутки и гидроксикарбамида 500 мг в сутки с удовлетворительной переносимостью и контролем показателей крови.
Клинический анализ крови от 30.01.2023 г.: эритроциты – 3,85 х 1012/л, гемоглобин – 130 г/л, гематокрит – 0,37, тромбоциты – 531 х 109/л, лейкоциты
– 14,67 х 109/л, бластные клетки – 0 %, промиелоциты – 0 %, миелоциты – 1 %, метамиелоциты – 0 %, палочкоядерные – 2 %, сегментоядерные – 85 %, эозинофилы – 0 %, базофилы – 0 %, лимфоциты – 11%, моноциты – 1%.
В настоящее время проводится обследование с целью подготовки к проведению алло-ТКМ.
Заключение . Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз и хронический атипичный миелолейкоз – редкие варианты опухолей миелоидной ткани. Этиология заболеваний остается до сих пор неизвестной. В результате исследований расшифрованы молекулярно-генетические основы патогенеза в виде мутаций гена рецептора к Г-КСФ (CSF3R), приняты новые критерии диагноза, включающие молекулярно-генетические методы. Лечение обычно проводится с помощью сдерживающей монохимиотерапии и оказывает незначительное влияние на общую выживаемость больных. Применение аллогенной трансплантации костного мозга, единственного радикального метода лечения, может быть использовано только у небольшой части пациентов молодого возраста без существенной сопутствующей патологии. Начато проведение клинических исследований по использованию таргетной терапии при хроническом нейтрофильном лейкозе и атипичном хроническом миелолейкозе, для оценки возможного позитивного влияния этого вида лечения не течение и исходы у пациентов с этими заболеваниями.
Конфликты интересов
Шуваев В.А. ООО "Новартис фарма" лекторские гонорары.
Байков В.В. ООО "Новартис фарма" лекторские гонорары.
Источники финансирования авторы.
Исследование не имело спонсорской поддержки. Анализ и интерпретация данных: В.А. Шуваев.
Вклад авторов Подготовка рукописи: В.А. Шуваев.
Сбор и обработка данных: В.А. Шуваев. Окончательное одобрение рукописи: все авторы.
Предоставление материалов исследования: все
Список литературы Хронический нейтрофильный лейкоз и атипичный хронический миелолейкоз
- Szuber, N., Elliott, M., Tefferi, A. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, molecular genetics, prognosis, and management // Am J Hematol. – 2020. – Vol. 95, №2. – P. 212-224.
- Szuber, N., Elliott, M., Tefferi, A. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia: 2022 update on diagnosis, genomic landscape, prognosis, and management // Am J Hematol. – 2022. – Vol. 97, №4. – P. 491-505.
- Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Where Are We Now? / E. Crisà, M. Nicolosi, V. Ferri et al. // International Journal of Molecular Sciences. – 2020. – Vol. 21, №18. – P. 6862.
- The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia / D.A. Arber, A. Orazi, R. Hasserjian et al. // Blood. – 2016. – Vol. 127, №20. – P. 2391-2405.
- Epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myeloproliferative disorders in the United States, 2001-2004, using data from the NAACCR and SEER programs / D.E. Rollison, N. Howlader, M.T. Smith et al. // Blood. – 2008. – Vol. 112, №1. – P. 45-52.
- Germeshausen, M., Ballmaier, M., Welte, K. Incidence of CSF3R mutations in severe congenital neutropenia and relevance for leukemogenesis: results of a long-term survey // Blood. – 2006. – Vol. 109, №1. – P. 93-99.
- An activating mutation in the CSF3R gene induces a hereditary chronic neutrophilia / I. Plo, Y. Zhang, J.-P. Le Couédic et al. // The Journal of Experimental Medicine. – 2009. – Vol. 206, №8. – P. 1701-1707.
- Beekman, R., Touw, I.P. G-CSF and its receptor in myeloid malignancy / R. Beekman, I.P. Touw // Blood. – 2010. – Vol. 115, №25. – P. 5131-5136.
- Impaired Production and Increased Apoptosis of Neutrophils in Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor–Deficient Mice / F. Liu, H.Y. Wu, R. Wesselschmidt et al. // Immunity. – 1996. – Vol. 5, №5. – P. 491-501.
- Mutations in the Gene for the Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating–Factor Receptor in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Preceded by Severe Congenital Neutropenia / F. Dong, R.K. Brynes, N. Tidow et al. // New England Journal of Medicine. – 1995. – Vol. 333, №8. – P. 487-493.
- Identification of a nonsense mutation in the granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor receptor in severe congenital neutropenia / F. Dong, L.H. Hoefsloot, A.M. Schelen et al. // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. – 1994. – Vol. 91, №10. – P. 4480-4484.
- Sequential gain of mutations in severe congenital neutropenia progressing to acute myeloid leukemia / R. Beekman, M.G. Valkhof, M.A. Sanders et al. // Blood. – 2012. – Vol. 119, №22. – P. 5071-5077.
- The Carboxyl Terminus of the Granulocyte Colony- Stimulating Factor Receptor, Truncated in Patients with Severe Congenital Neutropenia/Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Is Required for SH2-Containing Phosphatase-1 Suppression of Stat Activation / F. Dong, Y. Qiu, T. Yi et al. // The Journal of Immunology. – 2001. – Vol. 167, №11. – P. 6447-6452.
- G-CSF receptor truncations found in SCN/AML relieve SOCS3-controlled inhibition of STAT5 but leave suppression of STAT3 intact / G.-J.M. Van De Geijn, J. Gits, L.H.J. Aarts et al. // Blood. – 2004. – Vol. 104, №3. – P. 667-674.
- Defective Internalization and Sustained Activation of Truncated Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor Found in Severe Congenital Neutropenia/Acute Myeloid Leukemia / A.C. Ward, Y.M. Van Aesch, A.M. Schelen, I.P. Touw // Blood. – 1999. – Vol. 93, №2. – P. 447-458.
- Perturbed Granulopoiesis in Mice With a Targeted Mutation in the Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor Gene Associated With Severe Chronic Neutropenia / M.H.A. Hermans, A.C. Ward, C. Antonissen et al. // Blood. – 1998. – Vol. 92, №1. – P. 32-39.
- Hunter, M.G., Avalos, B.R. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor mutations in severe congenital neutropenia transforming to acute myelogenous leukemia confer resistance to apoptosis and enhance cell survival // Blood. – 2000. – Vol. 95, №6. – P. 2132-2137.
- Impaired neutrophil maturation in truncated murine G-CSF receptor–transgenic mice / T. Mitsui, S. Watanabe, Y. Taniguchi et al. // Blood. – 2003. – Vol. 101, №8. – P. 2990-2995.
- Requirement of Src Kinase Lyn for Induction of DNA Synthesis by Granulocyte Colony-stimulating Factor / S.J. Corey, P.M. Dombrosky-Ferlan, S. Zuo et al. // Journal of Biological Chemistry. – 1998. – Vol. 273, №6. – P. 3230-3235.
- Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling involves the formation of a three-component complex with Lyn and Syk protein-tyrosine kinases / S.J. Corey, A.L. Burkhardt, J.B. Bolen et al. // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. – 1994. – Vol. 91, №11. – P. 4683-4687.
- Oncogenic CSF3R Mutations in Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia and Atypical CML / J.E. Maxson, J. Gotlib, D.A. Pollyea et al. // New England Journal of Medicine. – 2013. – Vol. 368, №19. – P. 1781-1790.
- The CSF3R T618I mutation causes a lethal neutrophilic neoplasia in mice that is responsive to therapeutic JAK inhibition / A.G. Fleischman, J.E. Maxson, S.B. Luty et al. // Blood. – 2013. – Vol. 122, №22. – P. 3628-3631.
- CSF3R T618I is a highly prevalent and specific mutation in chronic neutrophilic leukemia / A. Pardanani, T.L. Lasho, R.R. Laborde et al. // Leukemia. – 2013. – Vol. 27, №9. – P. 1870-1873.
- An overview on CALR and CSF3R mutations and a proposal for revision of WHO diagnostic criteria for myeloproliferative neoplasms / A. Tefferi, J. Thiele, A.M. Vannucchi, T. Barbui // Leukemia. – 2014. – Vol. 28, №7. – P. 1407-1413.
- Phase 2 Study of Ruxolitinib in Patients with Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia or Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia / K.-H. Dao, R.H. Collins, J.E. Cortes et al. // Blood. – 2018. – Vol. 132, №Supplement 1. – P. 350-350.
- Maxson, J.E., Tyner, J.W. Genomics of chronic neutrophilic leukemia // Blood. – 2017. – Vol. 129, №6. – P. 715-722.
- WHO-defined chronic neutrophilic leukemia: a long-term analysis of 12 cases and a critical review of the literature / M.A. Elliott, C.A. Hanson, G.W. Dewald et al. // Leukemia. – 2004. – Vol. 19, №2. – P. 313-317.
- Chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL): a clinical, pathologic and cytogenetic study / M.A. Elliott, G.W. Dewald, A. Tefferi, C.A. Hanson // Leukemia. – 2001. – Vol. 15, №1. – P. 35-40.
- European consensus on grading bone marrow fibrosis and assessment of cellularity / J. Thiele, H.M. Kvasnicka, F. Facchetti et al. // Haematologica. – 2005. – Vol. 90, №8. – P. 1128-1132.
- Successful alpha-2b-interferon therapy for chronic neutrophilic leukemia / S. Meyer, W. Feremans, B. Cantiniaux et al. // Am J Hematol. – 1993. – Vol. 43, №4. – P. 307-309.
- Efficacy of Ruxolitinib in Patients With Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia and Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia / K.T. Dao, J. Gotlib, M.M.N. Deininger et al. // Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. – 2020. – Vol. 38, №10. – P. 1006-1018.
- The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms / J.D. Khoury, E. Solary, O. Abla et al. // Leukemia. – 2022. – Vol. 36. – P. 1703–1719.
- Identification of risk factors in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia / M. Breccia, F. Biondo, R. Latagliata et al. // Haematologica. – 2006. – Vol. 91, №11. – P. 1566-8.
- The new genetics of chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML: implications for diagnosis and treatment / J. Gotlib, J.E. Maxson, T.I. George, J.W. Tyner // Blood. – 2013. – Vol. 122, №10. – P. 1707-1711.
- Characteristics and survival of BCR/ABL negative chronic myeloid leukemia: a retrospective analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database / S. Giri, R. Pathak, M.G. Martin, V.R. Bhatt // Ther Adv Hematol. – 2015. – Vol. 6, №6. – P. 308-12.
- Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia is clinically distinct from unclassifiable myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms / S.A. Wang, R.P. Hasserjian, P.S. Fox et al. // Blood. – 2014. – Vol. 123, №17. – P. 2645-51.
- Characteristics and survival of BCR/ABL negative chronic myeloid leukemia: a retrospective analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database / S. Giri, R. Pathak, M.G. Martin, V.R. Bhatt // Therapeutic advances in hematology. – 2015. – Vol. 6, №6. – P. 308-312.
- Targeted next generation sequencing and identification of risk factors in World Health Organization defined atypical chronic myeloid leukemia / M.M. Patnaik, D. Barraco, T.L. Lasho et al. // Am J Hematol. – 2017. – Vol. 92, №6. – P. 542-548.
- Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia: a rare entity with management challenges / P. Dhakal, K. Gundabolu, C. Amador et al. // Future Oncol. – 2018. – Vol. 14, №2. – P. 177-185.
- Recurrent ETNK1 mutations in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia / C.B. Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Donadoni, A. Parmiani et al. // Blood. – 2015. – Vol. 125, №3. – P. 499-503.
- Lasho, T. Atypical CML- the role of morphology and precision genomics // Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. – 2020. – Vol. 33, №2. – P. 101133.
- Specific molecular mutation patterns delineate chronic neutrophilic leukemia, atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia / M. Meggendorfer, T. Haferlach, T. Alpermann et al. // Haematologica. – 2014. – Vol. 99, №12. – P. e244-6.
- Recurrent SETBP1 mutations in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia / R. Piazza, S. Valletta, N. Winkelmann et al. // Nat Genet. – 2013. – Vol. 45, №1. – P. 18-24.
- The JAK2 V617F activating tyrosine kinase mutation is an infrequent event in both "atypical" myeloproliferative disorders and myelodysplastic syndromes / D.P. Steensma, G.W. Dewald, T.L. Lasho et al. // Blood. – 2005. – Vol. 106, №4. – P. 1207-9.
- Overlapping SETBP1 gain-of-function mutations in Schinzel-Giedion syndrome and hematologic malignancies / R. Acuna-Hidalgo, P. Deriziotis, M. Steehouwer et al. // PLOS Genetics. – 2017. – Vol. 13, №3. – P. e1006683.
- SETBP1 mutations occur in 9% of MDS/MPN and in 4% of MPN cases and are strongly associated with atypical CML, monosomy 7, isochromosome i(17)(q10), ASXL1 and CBL mutations / M. Meggendorfer, U. Bacher, T. Alpermann et al. // Leukemia. – 2013. – Vol. 27, №9. – P. 1852-60.
- Gotlib, J. How I treat atypical chronic myeloid leukemia // Blood. – 2017. – Vol. 129, №7. – P. 838-845.
- Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms / S.N. Lim, J.H. Lee, J.H. Lee et al. // Blood Res. – 2013. – Vol. 48, №3. – P. 178-84.
- Postallogeneic monitoring with molecular markers detected by pretransplant next-generation or Sanger sequencing predicts clinical relapse in patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms / Y. Fu, T. Schroeder, T. Zabelina et al. // European Journal of Haematology. – 2014. – Vol. 92, №3. – P. 189-194.
- Clinical course and molecular features in 21 patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia / M. Koldehoff, N.K. Steckel, Y. Hegerfeldt et al. // International Journal of Laboratory Hematology. – 2012. – Vol. 34, №1. – P. e3-e5.


