Изучение противоопухолевых свойств пептидной конструкции, включающей интернализуемую последовательность и ингибитор RAS-ГТ фазы, в отношении клеток линий рака толстой кишки (НТ29) и рака яичника (OAW-42, OVCAR-3)
Автор: Кулинич Т.М., Шишкин А.М., Иванов А.В., Каминский В.В., Боженко В.К.
Журнал: Вестник Российского научного центра рентгенорадиологии Минздрава России @vestnik-rncrr
Рубрика: Молекулярная медицина
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.21, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель: исследование противоопухолевой активности пептидной конструкции, включающей ингибитор Ras-ГТФазы и интернализуемый вектор, обеспечивающий эффективное внутриклеточное проникновение. Материалы и методы. С помощью методов математического моделирования разработана пептидная конструкция (К26К), являющаяся ингибитором связывания комплекса Ras-Raf ивключающая также последовательность, обеспечивающую эффективную интернализацию пептида в клетки. Исследование проведено в условиях in vitro с использованием в качестве моделей злокачественных заболеваний культуры клеток линий опухолей человека: НТ29 (аденокарцинома толстой кишки человека), OAW-42 (карцинома яичника, человек), OVCAR- 3 (аденокарцинома яичника человека).Исследование проведено путем оценки цитотоксического и цитостатического эффектов последовательности с помощью следующих методов: МТТ-тест; проточная цитофлуориметрия; оценка пролиферации в реальном времени (система iCELLigence).Результаты. Показано, что исследуемая последовательность (К26К) обладает выраженными противоопухолевыми свойствами в отношении клеток колоректального рака и рака яичника, способна индуцировать апоптоз и тормозить процессы пролиферации в культурах клеток опухолей данных локализаций. Заключение. На основании проведенных исследований было показано, что разработанный пептидный ингибитор Ras-ГТФазы обладает выраженными противоопухолевыми свойствами в отношении культур клеток рака толстой кишки и рака яичника человека.
Химерные интернализуемые пептиды, cpps (cell penetrating peptides), апоптоз, рак толстой кишки, рак яичника, ras, ras-гтфаза
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149139201
IDR: 149139201
Текст научной статьи Изучение противоопухолевых свойств пептидной конструкции, включающей интернализуемую последовательность и ингибитор RAS-ГТ фазы, в отношении клеток линий рака толстой кишки (НТ29) и рака яичника (OAW-42, OVCAR-3)
В настоящее время находят все более широкое применение лекарственные средства направленного действия («таргетные» препараты), влияющие на различные этапы процессов внутриклеточной передачи сигнала от лиганд – рецепторных взаимодействий до процессов, протекающих в ядре клеток. Поэтому изучение белков, участвующих во внутриклеточных сигнальных каскадах, безусловно, важно не только для расширения фундаментальных представлений о биологии клеток эукариот, но и для понимания молекулярных механизмов патогенеза различных заболеваний человека и выявления новых молекулярных мишеней для направленного воздействия на них.
Несмотря на то, что Ras самый распространенный онкоген человека, на него не действует ни один из зарегистрированных в настоящее время противоопухолевых препаратов, и до сегодняшнего дня эта мишень была недоступна для фармакотерапии («to be thought of as undruggable») [1]. В ряде работ подчеркивается, что мутации Ras, приводящие к гиперактивации сигнального пути MAPK/ERK, встречаются в 25% всех опухолей человека
[2 – 4]. Однако для новообразований определенных локализаций этот процент существенно выше, например, при раке поджелудочной железы он составляет 90%. Такая же высокая частота мутаций Ras наблюдается для нейробластом и некоторых других новообразований. При одной из наиболее распространенных злокачественных опухолей – колоректальном раке – частота мутаций Ras достигает 50% [5].
Показано, что применение известных ингибиторов Braf при наличии Ras мутаций приводит к парадоксальной активации Craf и MAPK сигнального пути и вызывает активацию роста опухоли вместо ее торможения. Ингибиторы Braf (такие как Zelboraf и похожие на него) вызывают образование стабильных комплексов-димеров Braf-Craf и Craf-Craf. Образование этих комплексов селективно усиливает образование мембранных нанокластеров онкогенных K-Ras и N-Ras, которые, в свою очередь, приводят к активации MAPK каскада. Таким образом, применение Braf ингибиторов ограничено для пациентов с Ras мутациями [6, 7] Большая частота мутаций Ras при злокачественных заболеваниях делает его привлекательной мишенью для противоопухолевой терапии. Способы достижения этой цели могут быть основаны на ингибировании ферментов посттрансляционной модификации Ras-белка, таких как фарнезилтрансфераза (FTI) и геранилтрансфераза I, которые участвуют в присоединении прениловой группы к аминокислотным остаткам Ras белка. Описанный ранее ингибитор FTI показал себя как потенциальный кандидат в качестве противоопухолевого агента при Ras-активированных вариантах опухолей [8 – 10]. Несмотря на то, что FTI проявил активность в отношении вариантов рака с мутациями H-RAS и N-RAS он оказался не активным в отношении опухолей с мутантными вариантами K-RAS. Таким образом, несмотря на то, что ряд ингибиторов фарнезилтрансферазы показали обнадеживающую противоопухолевую активность, необходимо продолжить поиски средств ингибирования мутантных форм K-RAS. Другие подходы поиска ингибиторов мутантных вариантов Ras основаны на исследовании молекулярного механизма передачи сигнала с участием белков семейства Ras. Ключевая реакция активации Ras и дальнейшей передачи им сигнала заключается в связывании GTP (ГТФ). Поэтому активно исследовались подходы для воздействия именно на G-домен Ras. Эти подходы были основаны на попытках увеличения скорости гидролиза мутантной формы Ras [11, 12], ингибировании обмена GDP-GTP [13, 14] или разработке методов конкурентного связывания с эффектором или его активацией [15, 16].
Превращение Ras-GDP в активную форму Ras-GTP происходит с участием нуклеотид-обменного фактора (guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF)), такого как, например, SOS1. Анализ трехмерных структур связывания этих ингибиторов Ras показал, что они локализуются, как правило, в домене switch II, в результате их связи с молекулой происходит ингибирование перехода GDP в GTP, активируемого молекулой GEF [17, 18]. Было высказано предположение, что ингибиторы, реализующие такой механизм, могут быть активными и в отношении опухолей с диким типом Ras [19]. Здесь следует отметить семейство ковалентных ингибиторов для KRAS G12C – преимущественного варианта мутаций при аденокарциноме легкого, этот тип селективности трудно достижим для других типов мутаций из-за особенностей трехмерной структуры Ras. Один из двух известных ковалентных ингибиторов Ras представляет собой аналог нуклеотида, который связывается в участке связывания GDP [20], а другой ингибитор связывается в районе структуры Ras, описываемой как «a pocket between switch II and helix 3» [21]. Еще одна стратегия создания ингибиторов основана на поиске веществ, стабилизирующих структуру Ras, а именно области, получившей название switch I [22, 23]. Стабилизация этой части молекулы Ras в «открытой» конформации приводит к невозможности взаимодействия Ras с эффекторными белками.
В последнее время был произведен экспериментальный скрининговый анализ большой группы библиотек для идентификации ингибиторов Ras, были использованы методы компьютерного анализа локализации участков связывания и поиска «горячих» точек [24, 25]. Эти исследования привели к открытию группы малых молекул, связывающихся с G- карманом Ras, которые продолжают активно изучаться. Однако полученные знания в этой области на данный момент не позволяют ингибировать белок-белковое взаимодействие в комплексах Ras [26, 27]. Таким образом, имеющиеся в настоящее время ингибиторы Ras, несмотря на их активные поиски, остаются мало эффективными. Поэтому ряд авторов предлагает использовать их комбинацию нескольких ингибиторов для увеличения суммарного эффекта [28].
В научной литературе встречаются единичные работы, в которых описывается использование пептидов для ингибирования Ras-GTP [29 – 31]. Так, Upadhyaya с соавторами провели компьютерный анализ пептидной библиотеки и выявили несколько циклических пептидов, обладающих свойствами ингибирования Ras и внутриклеточной интернализации, что приводило к активации апотоза в клетках.
Таким образом, разработка новых, эффективных ингибиторов Ras-киназ, а особенно их мутантных форм, остается одной их актуальнейших и не решенных задач современной онкологии. Подход с использованием технологии химерных пептидов, включающих транспортную часть и функциональную часть, ингибирующую образование белковых комплексов Ras c эффекторными молекулами, является перспективным и новаторским подходом.
Немаловажной проблемой при создании лекарственных препаратов является проблема эффективного внутриклеточного проникновения, доставки активных соединений в клетки. Метод внутриклеточной доставки различных веществ, основанный на технологии пептидных векторов, обладающих способностью проникать в клетки, не повреждая плазматическую мембрану, является весьма перспективным ввиду слабой иммуногенности таких соединений и способности переносить достаточно крупные молекулы. Соединение возможности целевой доставки пептидов в клетку и обнаружение коротких функциональных доменов в белках регуляторах различных клеточных функций создали предпосылки для конструирования молекул имеющих патогенетическую направленность [32, 33].
Относительная простота синтеза таких молекул позволяет говорить о принципиальной возможности создания индивидуальных химиопрепаратов на их основе, т.е. влияющих на патологические изменения свойственные данной конкретной опухоли [34].
В данном исследовании была проведена разработка молекулярной структуры химерной пептидной последовательности, включающей в свой состав активную группу – ингибитор Ras-ГТФазы и интернализуемый вектор (последовательность, обладающая свойствами CPPs, cell penetrating peptides). С помощью метода твердофазного синтеза данная последовательность (Ras-CPP) была синтезирована в достаточном для проведения исследований эффективности количестве. Методом МТТ-теста и проточной цитометрии (окраска AnnexinV/PI) был оценен цитотоксический эффект и проапоптотический эффект, использование метода «пролиферации в реальном времени» RTCA iCELLIgence позволило оценить цитостатический эффект исследуемой последовательности.
Цель: исследование противоопухолевой активности пептидной конструкции, включающей ингибитор Ras-ГТФазы и интернализуемый вектор, обеспечивающий эффективное внутриклеточное проникновение.
Материалы и методы
Исследование эффективности последовательности пептидного ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы (К26К) было проведено в условиях in vitro , в качестве тест-систем были использованы клетки линий опухолей человека НТ29 (аденокарцинома толстой кишки человека), OAW-42 (карцинома яичника, человек), OVCAR-3 (аденокарцинома яичника человека).
Опухолевые клетки культивировали в стандартных условиях с добавлением ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы в различных концентрационных соотношениях и на протяжении различного времени. По окончании культивирования в заданных условиях были оценены такие показатели как количество выживших клеток, уровень апоптоза, пролиферативная активность. Количество выживших клеток определялось при помощи теста на активность митохондриальных ферментов (МТТ-тест). Уровень апоптоза был определен методом проточной цитофлуориметрии с помощью окраски АннексинV/Пропидия йодид и окраски фиксированных образцов Пропидием йодидом. Пролиферативная активность определялась методами проточной цитофлуориметрии (окраска фиксированных образцов Пропидием йодидом и последующее определение количества клеток в различных фазах клеточного цикла) и методом оценки пролиферации в реальном времени. Контрольными образцами являлись клетки линий НТ-29, OAW-42, OVCAR-3, без воздействия исследуемого лекарственного средства. Все эксперименты выполнены не менее чем в трех независимых повторах.
Результаты
Цитотоксический эффект был оценен несколькими методами. В первую очередь были поставлены эксперименты, в которых с помощью МТТ-теста оценивали количество живых клеток, оставшихся в культуре после воздействия последовательности К26К в разных концентрациях. Время инкубации исследуемых клеточных культур с пептидным ингибитором Ras-ГТФазы составляло 24 и 48 часов. Было проведено исследование воздействия на культуры лекарственного средства К26К в различных концентрациях от 2 до 40 мкМ. При исследовании влияния лекарственного средства К26К на культуру клеток НТ-29, было показано, что количество живых клеток уменьшается при увеличении концентрации К26К в диапазоне от 5 до 40 мкМ, через 24 часа инкубации при концентрации 40 мкМ К26К количество живых клеток снижается до 51%.
При исследовании цитотоксического влияния последовательности К26К, на клетки линии OAW-42 также было показано, что снижение количества живых клеток происходит пропорционально увеличению концентрации К26К в диапазоне от 2 до 40 мкМ, однако достоверное снижение количества живых клеток относительно контрольных образцов наблюдается только при увеличении концентрации более 40 мкМ. Так, при концентрации 40 мкМ происходит снижение количества живых клеток на 48%.
Аналогичные результаты изменения количества живых клеток были получены при исследовании воздействия последовательности К26К на культуру клеток OVCAR-3. Значимые снижения количества живых клеток наблюдались при воздействии К26К в концентрациях более 30 мкМ.
На основании проведенных исследований противоопухолевого эффекта потенциального лекарственного средства К26К методом МТТ было показано, что последовательность обладает выраженым цитотоксическим действием относительно исследуемой линии аденокарциномы толстой кишки НТ-29 и, в меньшей степени, воздействует на линии рака яичника (OVCAR-3, OAW-42). Эффект пропорционален концентрации лекарственного средства и увеличивается при более длительном времени воздействия, для НТ-29 различия при инкубации 24 и 48 часов достоверны. На рисунке 1 показано сравнение цитотоксического эффекта последовательности К26К относительно трех исследуемых линий.
Сравнение количества живых клеток для исследуемых линий, 24 часа, МТТ-тест
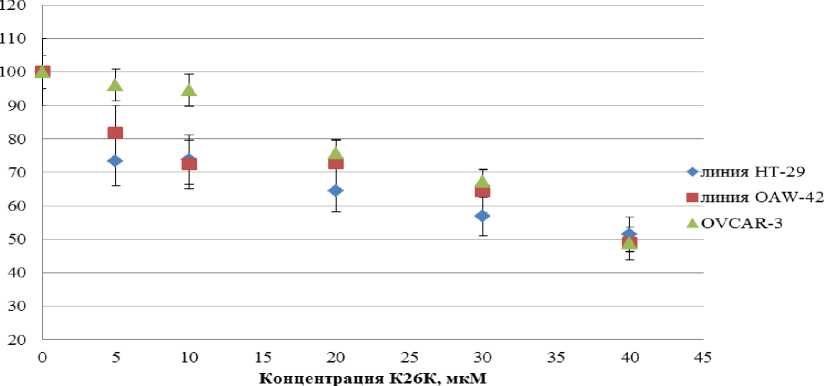
Рис. 1. Воздействие последовательности К26К на культуры клеток НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42, время инкубации 24 часа.
Показано, что при инкубации с пептидным ингибитором К26К 24 часа, достоверные отличия наблюдаются для культуры OVCAR-3, при малых концентрациях К26К (до 20 мкМ), эффект воздействия минимален. При увеличении времени воздействия до 48 часов, наибольший эффект наблюдался при инкубации К26К с клетками НТ-29, данная культура оказалась наиболее чувствительной к воздействию.
Цитометрический анализ был проведен на проточном цитофлуориметре CytomixFC 500 (BeckmanCoulter, США). Накопление производили до 10000 событий. Для настройки режимов компенсации и установки границ квадрантов использовали следующие контроли: неокрашенные клетки; клетки, окрашенные только AnnexinV-FITС (без PI); клетки, окрашенные только PI (без AnnexinV-FITС). В образце оценивали показатели прямого (FSC) и бокового (SSC) светорассеяния клеток, интенсивность флуоресценции AnnexinV-FITС (FL1) и PI (FL3). Оценка цитотоксического и проапоптотического эффектов проводилась для концентраций К26К – 5, 10, 20, 30 и 40 мкМ; время инкубации составило 24 часа. В таблице 1 представлены результаты для клеток культур НТ-29, OVCAR-3 и OAW-42, средние значения трех экспериментов, вычисленные средние значения уровня раннего и позднего апоптоза и уровня некроза. Для всех экспериментов условия были одинаковы: время воздействия К26К – 24 часа, концентрация К26К – 10, 20, 30 и 40 мкМ, в качестве контроля использовались образцы клеток, инкубированные со средой без добавления пептидной последовательности ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К.
Таблица 1. Результаты исследования уровня апоптоза и некроза при воздействии на клетки культур НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42 пептидного ингибитора К26К в концентрациях 10, 20, 30 и 40 мкМ, время воздействия 24 часа. Результаты представлены в виде процентного соотношения окрашенных частиц
|
OVCAR-3 |
|||
|
Концентрация К26К, мкМ |
АннексинV-/Пропидий+, % |
АннексинV+ /Пропидий+, % |
АннексинV+/ Пропидий-, % |
|
0 |
3,2 |
1,2 |
2,6 |
|
10 |
7,5 |
4,7 |
1,5 |
|
20 |
12,3 |
5,3 |
3,8 |
|
30 |
14,3 |
5,5 |
5,7 |
|
40 |
18,6 |
6,1 |
5,3 |
|
OAW-42 |
|||
|
Концентрация К26К, мкМ |
АннексинV-/Пропидий+ |
АннексинV+ /Пропидий+ |
АннексинV+ /Пропидий- |
|
0 |
2,6 |
1,2 |
3,6 |
|
10 |
5,3 |
9,1 |
4,8 |
|
20 |
7,4 |
12,3 |
5,9 |
|
30 |
11,9 |
17,2 |
6,3 |
|
40 |
16,8 |
21,7 |
12,7 |
|
НТ-29 |
|||
|
Концентрация К26К, мкМ |
АннексинV-/Пропидий+ |
АннексинV+ /Пропидий+ |
АннексинV+ /Пропидий- |
|
0 |
4,6 |
1,3 |
2,4 |
|
10 |
6,3 |
9,5 |
12,7 |
|
20 |
7,8 |
12,8 |
18,6 |
|
30 |
7,4 |
17,9 |
25,4 |
|
40 |
11,6 |
22,6 |
43,2 |
Показано, что для исследуемых клеточных культур внесение пептидного ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы, последовательности К26К, вызывает индукцию апоптоза (положительные по окраске АннексинV клетки). Уровень апоптоза зависит от концентрации К26К, как и уровень клеток, погибших по пути некроза (клетки АннексинV-/Пропидий йодид+). Для противоопухолевой терапии предпочтителен вариант гибели опухолевых клеток по пути апоптоза, т.к. он не вызывает обширного воспаления и выхода в интерстициальное пространство продуктов клеточного распада и индукторов воспалительных реакций. Также наличие высокого уровня апоптоза косвенно свидетельствует о специфичности воздействия
К26К. На рисунке 2 представлено сравнение уровня апоптоза, индуцированного внесением в культуральную среду последовательности К26К; показано, что максимальный эффект наблюдается при воздействии на культуру клеток линии НТ-29.
Изменение уровня апоптоза при воздействии на клетки К26К
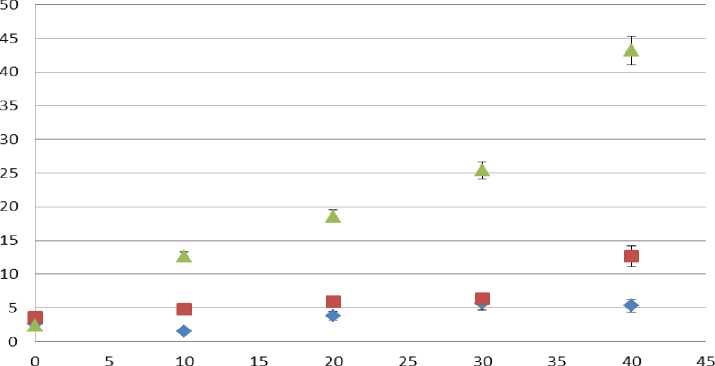
Концентрация К26К, мкМ
Рис. 2. Изменение уровня апоптоза в культурах клеток линий НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42 при воздействии последовательности К26К в концентрациях 10 – 40 мкМ, метод проточной цитофлуориметрии, окраска Annexin V-FITС (FL1) / PI (FL3).
Как видно из представленных результатов, зависимости уровней апоптоза и некроза для клеточных линий НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42 при воздействии на них последовательности К26К, имеют большие различия. Уровень апоптоза при воздействии лекарственного средства К26К на культуру НТ-29 достоверно возрастает по сравнению с контролем уже при концентрации К26К 10 мкМ, а при концентрации 40 мкМ достигает 43,2%. Для культур OVCAR-3 и OAW-42 наблюдается больший процент гибели клеток по пути некроза. Т.о., проведенное исследование видов клеточной гибели (апоптоз и некроз) при воздействии на клетки линий рака легкого человека методом проточной цитофлуориметрии с использованием двойной окраски Annexin V-FITС / PI показало, что пептидная последовательность ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы (К26К) обладает выраженным специфическим противоопухолевым действием в отношении культуры клеток аденокарциномы толстой кишки человека. Данный эффект характеризуется индукцией клеточной гибели преимущественно по пути апоптоза. Уровень индуцированного внесением в культуральную среду К26К апоптоза зависит от типа клеток и обусловлен, по-видимому, молекулярно-генетическими особенностями клеточной линии. Клетки линий рака яичника оказались менее чувствительны к воздействию пептидного ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К. Для динамического исследования влияния пептидного ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К на рост клеток культур клеточных линий НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42 использовали прибор RTCA iCELLIgence, фирмы ACEA Biosciences (США). Принцип метода основан на измерении импеданса приповерхностного слоя на дне культуральной лунки. Величина импеданса пропорциональна количеству клеток в лунке (или если точнее, площади, занимаемой клетками). Значения сопротивления, измеренные для электродов в индивидуальных лунках, зависят от геометрии электрода, концентрации ионов в лунке и от наличия клеток, фиксированных на электродах. При отсутствии клеток электрическое сопротивление в первую очередь определяется ионным составом среды на границе раствор/ электрод и в растворе. В присутствии клеток они присоединяются к сенсорной поверхности электрода и действуют как изолятор, что приводит к изменению локального ионного окружения на границе раствор/электрод и увеличению сопротивления. Таким образом, чем больше клеток располагается на электроде, тем сильнее меняется сопротивление этого электрода. Уникальность системы для клеточного анализа iCELLIgence в том, что она основана на микроэлектронных биосенсорах, которые позволяют динамически и в реальном времени анализировать клеточный ответ без использования дополнительных маркеров или меток. Таким образом, добавление ингибиторов роста или цитотоксических агентов к культуре растущих клеток приводит к угнетению роста и/или гибели клеток, что сопровождается снижением регистрируемого импеданса как абсолютного, так и по сравнению с контрольными лунками, в которых рост клеток продолжается. Измерение производится периодически в течение всего времени эксперимента, что позволяет регистрировать динамику роста в каждой лунке с заданной периодичностью. С применением метода клеточного анализа iCELLIgence было проведено исследование цитостатического воздействия последовательности фрагмента ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К на клетки культур клеточных линий НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42.
Для каждой клеточной линии была поставлена серия экспериментов по исследованию влияния К26К в диапазоне концентраций 10 – 40 мкМ. При проведении экспериментов клетки вносились на планшет в количестве 20 000 на лунку, инкубировались 3 часа для начального закрепления на дне планшета, а затем к культуральной среде добавлялось исследуемое вещество в различных концентрациях. На рисунке 3 представлены примеры графиков клеточного роста для культур НТ-29, OVCAR-3, OAW-42.
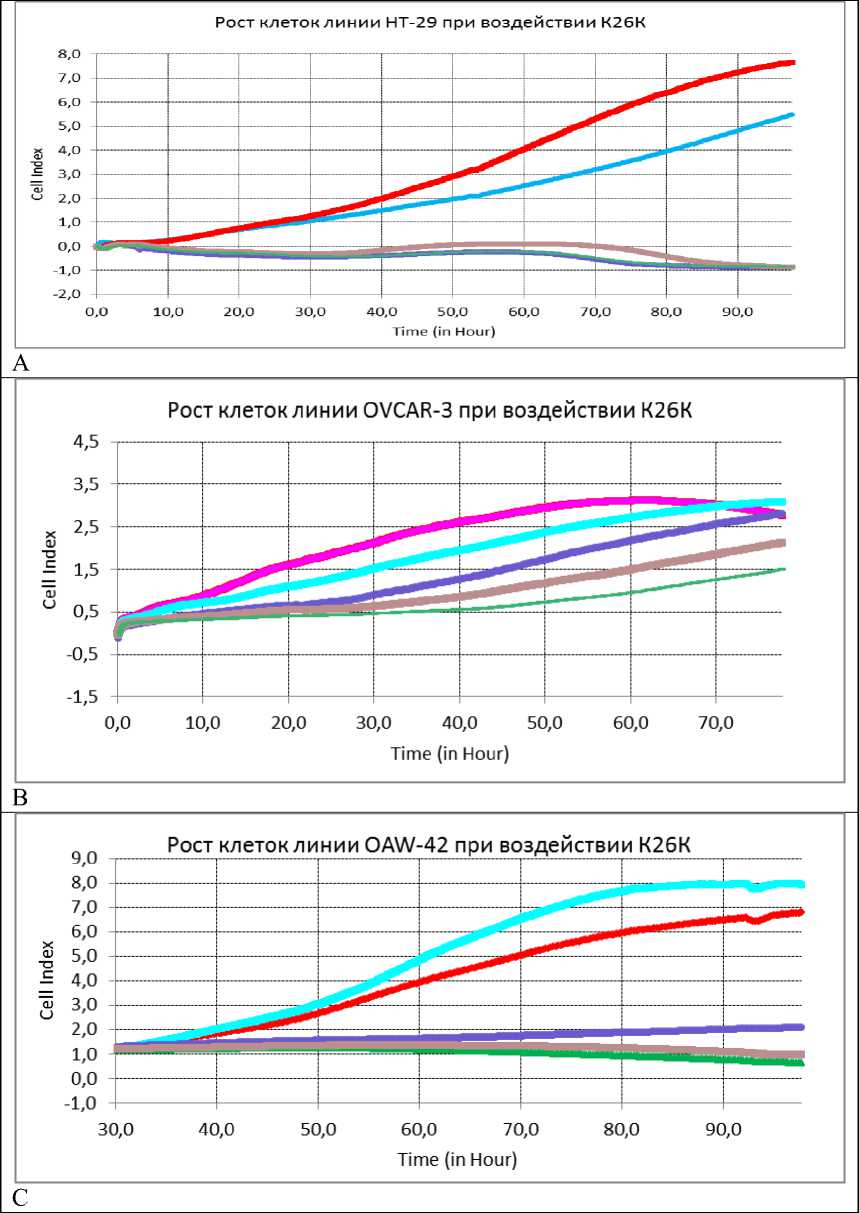
|
Цвет кривой |
Концентрация ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К |
|
Красная линия |
0 (контроль) |
|
Голубая линия |
10 мкМ |
|
Фиолетовая линия |
20 мкМ |
|
Коричневая линия |
30 мкМ |
|
Зеленая линия |
40 мкМ |
Рис. 3. Изменение показателя Cell index, отражающего пролиферативную активность клеток при воздействии лекарственного средства ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К в концентрациях 10 – 40 мкМ на культуры НТ-29 (А), OVCAR-3 (В), OAW-42 (С) методом клеточного анализа iCELLIgence.
При исследовании цитостатического эффекта лекарственного средства К26К в отношении клеток линии НТ-29, было показано, что при концентрации 10 мкМ наблюдается задержка пролиферации, клеточный индекс снижается в 1,5 раза. При концентрациях пептидного ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы более 20 мкМ наблюдается полная остановка клеточного деления (Рис. 3А), т.е. стойкий цитостатический эффект. В отношении культуры OVCAR-3 (аденокарцинома яичника), эффект задержки пролиферации также имеет концентрационную зависимость, однако эффект обратим, и через 70 часов инкубации наблюдается полное восстановление пролиферативной активности клеток с концентрацией К26К 10 и 20 мкМ (Рис. 3 В). Также, как и для культур клеток линии НТ-29, концентрации К26К более 20 мкМ вызывают полную и необратимую остановку клеточного роста клеток культуры OAW-42, однако при малых концентрациях (10 мкМ) наблюдалось незначительное усиление пролиферативной активности клеток линии OAW-42 (Рис. 3С).
Заключение
При исследовании противоопухолевого эффекта последовательности пептидного ингибитора Ras-ГТФазы – К26К в отношении культур рака толстой кишки человека (НТ-29), рака яичника (OAW-42 и OVCAR-3) было показано, что исследуемое лекарственное средство является потециальным противоопухолевым препаратом, воздействующим на клетки опухолей различной локализации. К26К обладает выраженной цитотоксической активностью, заключающейся в увеличении количества мертвых клеток и снижении количества живых клеток в культурах исследуемых линий. Исследуемое лекарственное средство индуцирует апоптоз в опухолевых клетках человека; данный эффект зависит от типа клеточной линии. Цитотоксический и проапоптотический эффекты имеют прямую концентрационную зависимость. Цитостатический ээфект лекарственного средства К26К, определяющейся в снижении пролиферативной активности клеток при внесении К26К в культуральную среду, также имеет концентрационную зависимость и различен для разного типа клеток. Было показано, что более сильная противоопухолевая активность наблюдается в отношении клеток аденокарциномы толстой кишки человека, и специфическая активность менее выражена в отношении клеток рака яичника.
Список литературы Изучение противоопухолевых свойств пептидной конструкции, включающей интернализуемую последовательность и ингибитор RAS-ГТ фазы, в отношении клеток линий рака толстой кишки (НТ29) и рака яичника (OAW-42, OVCAR-3)
- Marcus K., Mattos C. Direct Attack on RAS: Intramolecular Communication and Mutation-Specific Effects. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. V. 21. No. 8. P. 1810-1818. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2148.
- Marte B.M., Rodriguez-Viciana P., Wennström S., et al. R-Ras can activate the phosphoinositide 3-kinase but not the MAP kinase arm of the Ras effector pathways. Curr Biol. 1997. V. 7. No. 3. P. 197. DOI: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00028-5.
- Khwaja A., Rodriguez-Viciana P., Wennström S., et al. Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and protein kinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway. EMBO J. 1997. V. 16. No. 10. P. 2783-2793. DOI: 10.1093/emboj/16.10.2783.
- Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T. Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 2001. V. 81. No. 1. P. 153-208. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.1.153.
- Hu Q., Masuda T., Koike K., at al. Oxysterol binding protein-like 3 (OSBPL3) is a novel driver gene that promotes tumor growth in part through R-Ras/Akt signaling in gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2021. V. 11. No. 1. Article ID 19178. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-98485-9.
- Jung J., Cho K.J., Naji A.K., et al. HRAS-driven cancer cells are vulnerable to TRPML1 inhibition. EMBO Rep. 2019. V. 20. No. 4. Article ID e46685. DOI: 10.15252/embr.201846685.
- Cho K.J., Liang J.R., Crespo P., Aran V. Editorial: Ras and Other GTPases in Cancer: From Basic to Applied Research. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. V. 8. Article ID 804818. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.804818.
- Cortes J., Albitar M., Thomas D., et al. Efficacy of the farnesyl transferase inhibitor R115777 in chronic myeloid leukemia and other hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2003. V. 101. No. 5. P. 1692-1697. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2002-07-1973.
- Alsina M., Fonseca R., Wilson E.F., et al. Farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib is well tolerated, induces stabilization of disease, and inhibits farnesylation and oncogenic/tumor survival pathways in patients with advanced multiple myeloma. Blood. 2004. V. 103. No. 9. P. 3271-3277. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2003-08-2764.
- Rhett J.M., Khan I., O'Bryan J.P. Biology, pathology, and therapeutic targeting of RAS. Adv Cancer Res. 2020. V. 148. P. 69-146. DOI: 10.1016/bs.acr.2020.05.002.
- Ahmadian M.R., Stege P., Scheffzek K., Wittinghofer A. Confirmation of the arginine-finger hypothesis for the GAP-stimulated GTP-hydrolysis reaction of Ras. Nat Struct Biol. 1997. V. 4. No. 9. P. 686-689. DOI: 10.1038/nsb0997-686.
- Khrenova M.G., Bulavko E.S., Mulashkin F.D., Nemukhin A.V. Mechanism of Guanosine Triphosphate Hydrolysis by the Visual Proteins Arl3-RP2: Free Energy Reaction Profiles Computed with Ab Initio Type QM/MM Potentials. Molecules. 2021. V. 26. No.
- Article ID 3998. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26133998. 13. Colombo S., Peri F., Tisi R., et al. Design and characterization of a new class of inhibitors of ras activation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. V. 1030. P. 52-61. DOI: 10.1196/annals.1329.007.
- Ostrem J.M., Shokat K.M. Direct small-molecule inhibitors of KRAS: from structural insights to mechanism-based design. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. V. 15. No. 11. P. 771-785. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2016.139.
- Barnard D., Sun H., Baker L., Marshall M.S. In vitro inhibition of Ras-Raf association by short peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. V. 247. No. 1. P. 176-180. DOI: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8746.
- Keeton A.B., Salter E.A., Piazza G.A. The RAS-Effector Interaction as a Drug Target. Cancer Res. 2017. V. 77. No. 2. P. 221-226. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0938.
- Smith M.J., Neel B.G., Ikura M. NMR-based functional profiling of RASopathies and oncogenic RAS mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. V. 110. No. 12. P. 4574-4579. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1218173110.
- Fang Z., Marshall C.B., Yin J.C., et al. Biochemical Classification of Disease-associated Mutants of RAS-like Protein Expressed in Many Tissues (RIT1). J Biol Chem. 2016. V. 291. No. 30. P. 15641-15652. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.714196.
- Spiegel J., Cromm P.M., Zimmermann G., et al. Small-molecule modulation of Ras signaling. Nat Chem Biol. 2014. V. 10. No. 8. P. 613-622. DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1560.
- Lim S.M., Westover K.D., Ficarro S.B., et al. Therapeutic targeting of oncogenic K-Ras by a covalent catalytic site inhibitor. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. V. 53. No. 1. P. 199-204. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201307387.
- Ostrem J.M., Peters U., Sos M.L., et al. K-Ras(G12C) inhibitors allosterically control GTP affinity and effector interactions. Nature. 2013. V. 503. No. 7477. P. 548-551. DOI: 10.1038/nature12796.
- Yoshikawa Y., Takano O., Kato I., et al. Ras inhibitors display an anti-metastatic effect by downregulation of lysyl oxidase through inhibition of the Ras-PI3K-Akt-HIF-1α pathway. Cancer Lett. 2017. V. 410. P. 82-91. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.017.
- Liu L., Yan J., Cao Y., et al. Proliferation, migration and invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells are suppressed by berbamine via the PI3K/Akt/MDM2/p53 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Oncol Lett. 2021. V. 21. No. 1. Article ID 70. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12331.
- Buhrman G., O'Connor C., Zerbe B., et al. Analysis of binding site hot spots on the surface of Ras GTPase. J Mol Biol. 2011. V. 413. No. 4. P. 773-789. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.09.011.
- Qiu Y., Wang Y., Chai Z., et al. Targeting RAS phosphorylation in cancer therapy: Mechanisms and modulators. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. V. 11. No. 11. P. 3433-3446. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.014.
- Abraham S.J., Nolet R.P., Calvert R.J., et al. The hypervariable region of K-Ras4B is responsible for its specific interactions with calmodulin. Biochemistry. 2009. V. 48. No. 32. P. 7575-7583. DOI: 10.1021/bi900769j.
- Lu S., Banerjee A., Jang H., et al. GTP Binding and Oncogenic Mutations May Attenuate Hypervariable Region (HVR)-Catalytic Domain Interactions in Small GTPase K-Ras4B, Exposing the Effector Binding Site. J Biol Chem. 2015. V. 290. No. 48. P. 28887-28900. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.664755.
- Nussinov R., Tsai C.J., Mattos C. 'Pathway drug cocktail': targeting Ras signaling based on structural pathways. Trends Mol Med. 2013.V. 19. No. 11. P. 695-704. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.07.009.
- Upadhyaya P., Qian Z., Selner N.G., et al. Inhibition of Ras signaling by blocking Ras-effector interactions with cyclic peptides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015. V. 54. No. 26. P. 7602-7606. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201502763.
- Li C., Zhao N., An L., et al. Apoptosis-inducing activity of synthetic hydrocarbon-stapled peptides in H358 cancer cells expressing KRASG12C. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. V. 11. No. 9. P. 2670-2684. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.06.013.
- Li F.Y., Zhang Z.F., Voss S., et al. Inhibition of K-Ras4B-plasma membrane association with a membrane microdomain-targeting peptide. Chem Sci. 2019. V. 11. No. 3. P. 826-832. DOI: 10.1039/c9sc04726c.
- Stiltner J., McCandless K., Zahid M. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Applications in Tumor Diagnosis and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics. 2021. V. 13. No. 6. Article ID 890. DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060890.
- Yoo D.Y., Barros S.A., Brown G.C., et al. Macropinocytosis as a Key Determinant of Peptidomimetic Uptake in Cancer Cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. V. 142. No. 34. P. 14461-14471. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c02109.
- Dissanayake S., Denny W.A., Gamage S., Sarojini V. Recent developments in anticancer drug delivery using cell penetrating and tumor targeting peptides. J Control Release. 2017. V. 250. P. 62-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.02.006.


