Research of structural and mechanical properties of national restructured meat products
Автор: Uzakov Ya.M., Kaldarbekova M.A., Chernukha I.M.
Журнал: Вестник Алматинского технологического университета @vestnik-atu
Рубрика: Техника и технологии
Статья в выпуске: 4 (125), 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article presents the results of a study of the structural and mechanical properties, the dependence of the objective function and humidity of lamb and horse meat on the duration of the mechanical treatment. Changes in water activity and humidity of raw meat, depending on the duration of the mechanical treatment. It has been established that the use of multicomponent brine helps to increase water binding capacity (WBC) and improves the structural and mechanical properties of lamb and horse meat products. Studies have shown that increasing the WBC of meat occurs within 5 days of exposure, and the use of mechanical treatment helps to increase WBC in the first 24 hours.
Lamb, horsemeat, structural and mechanical properties, multicomponent brine, machining
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140249059
IDR: 140249059 | УДК: 637.525
Текст научной статьи Research of structural and mechanical properties of national restructured meat products
Meat and meat products are one of the most important components in human nutrition. This is mainly a source of high-quality protein and vitamins necessary for the proper development of the organism. Meat humidity varies from 41% to 78%. With pressure on the muscle tissue, moisture protrudes from it. The moisture content in a muscle, free from fat, ranges between 72 and 78%. With age, the water content in the muscle tissue of animals is reduced [1].
The quality of meat depends on the activity of water. To assess meat, the absolute value of humidity is not enough, since water is in different conditions in animal tissues. Water activity affects the stability of meat and meat products during storage, and is defined as the ratio of the pressure of water vapour over the product to the pressure of saturated steam of distilled water. One of the ways to reduce the activity of water in meat products (not dried) is to add technological additives to the recipe such as salt, sugar, vegetable dietary fiber, protein preparations, phosphate complexes and others, and it should be borne in mind that micromolecules will be most active food additives (for example: table salt, polyphosphates, etc.) than macromolecules (protein preparations, fats, etc.) [2].
Materials and methods of research
-
- hip leg of lamb of 1 category of fatness and zhaya;
-
- Goji berry extract;
-
- buckwheat flour;
-
- salt;
-
- sodium nitrite;
-
- phosphates;
-
- water.
Consider the analysis of physico-chemical and structural-mechanical characteristics on the example of a national restructured meat product from lamb and horse meat using a multicomponent brine.
To enrich the product with lamb and horse meat with nutritious ingredients during salting, we used Goji berry extract and buckwheat flour.
The meat was syringed in an amount of 5 to 20 mass. % and processed in the tender (brand -ЭТДУ, Model ТУЗ-KZ). The duration of the mechanical treatment and the content of the injection brine were optimized by changing the limit shear stress (LSS), plasticity (Pl) and humidity in raw meat.
The mathematical processing of the results is represented by a function in the form:
У = 0,024· Х4 – 0,3249· Х3 + 1,4457· Х2 – 2,7191· Х + 3,1167
Results and discussion
The results were optimized in four stages. Based on the obtained Trend equations, the maxima and minima of the functions by the method of finding the first derivative are revealed, correspond to the optimal values of LSS, plasticity and humidity (Y1, Y2, Y3) at a concentration of multicomponent brine (MCB) of 5 - 20%. For all cases, the maximum and minimum values of LSS, plasticity and humidity are within 18% of the content of multicomponent brine. (Fig. 1).
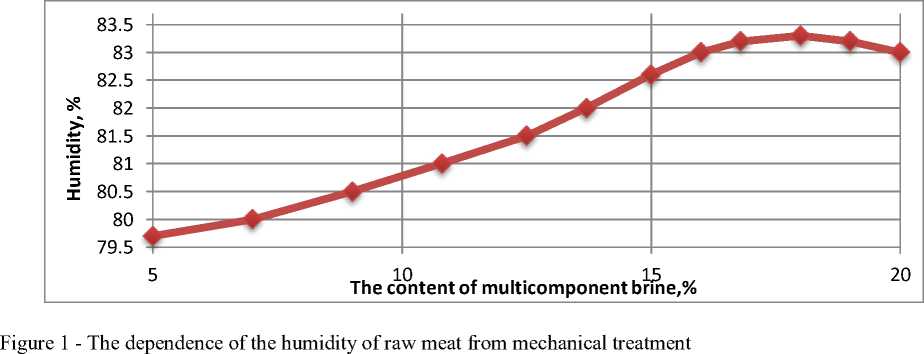
At the next stage, the dependence of Y1, Y2, Y3 on the duration of mechanical treatment was established for 1-6 hours. At the fourth stage, on the basis of the proposed objective function, the dependence k = f (τ) was constructed, where, τ is the duration of mechanical treatment. (Fig. 2)
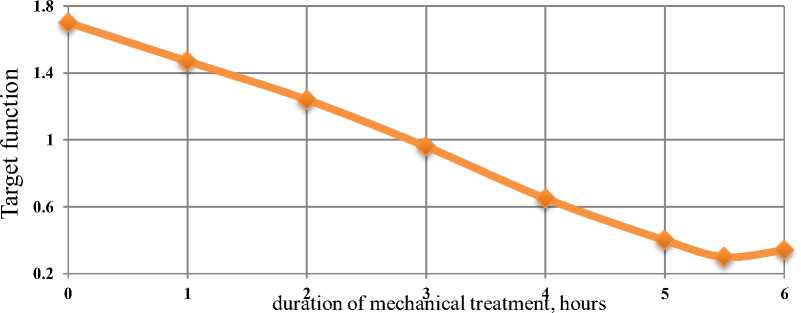
Figure 2 - Dependence of the objective function on the duration of mechanical treatment
An essential indicator of product quality is the tenderness of meat. The decrease in WBC of lamb and horse meat after mechanical treatment occurs as a result of a shift the pH of meat to acid, accelerating the development of rigidity of muscles. The degree of muscle contraction during post-mortem rigor mortis depends on the rate of decrease in pH, which in turn is a direct function of temperature. Changes in shear stress and plasticity, which are indicators of the consistency of meat, indicate their dependence on the duration of mechanical treatment
To control the optimal parameters for salting lamb and horsemeat MCB, were used water activity, heat of binding water and product humidity, which are most sensitive to various changes in technological factors in the production of national restructured meat products from lamb and horse meat.
The technology of restructured national meat products of lamb and horse meat using MCB based on the extract of Goji berry, buckwheat flour was developed. The amount of syringe brine is 5 - 20% by weight of the feedstock. As a control sample served raw meat from (horsemeat and lamb), salted with traditional brine.
Introduction to the composition of plant components - extract of Goji berry and buckwheat flour would ensure the production of national restructured meat products, with the specified structural and mechanical characteristics and shelf life of the finished products.
The injection of the proposed brine is characterized by a uniform saturation of the pieces of meat with a brine, minimal drainage of the brine after injection, and a uniform distribution of curing substances inside the pieces. The brine evenly fills the space between the fibers of the meat and carries the components to all areas inside the processed pieces. Thanks to this treatment, the meat becomes more elastic, juicy during heat treatment, has tendering properties, because the amount of brine held is up to 20 %.
Due to the action of salt, muscle tissue additionally swells, which helps to increase the yield of the finished product.
A change in the cellular structure promotes the introduction of curing substances, for example, dyes, meat quickly acquires the desired pink-red color. The composition of the composition for brine is shown in Figure 3.
water
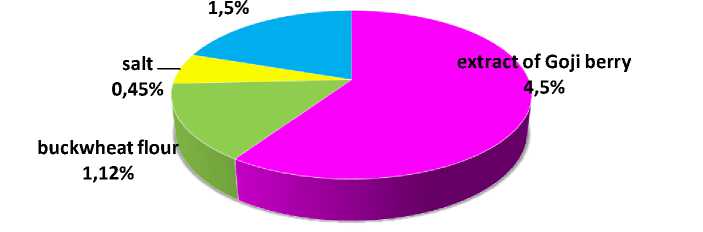
Figure 3 - Composition for multicomponent brine
With a meat moisture content of 73.6% and a duration of 6 hours of mechanical treatment, the water activity reaches 0.940. Further massage does not lead to a significant change in the magnitude of the activity of water. (Table 1)
Table 1 - Changes in water activity and humidity of salted meat raw materials depending on the duration of mechanical treatment
|
Duration of mechanical treatment, hours |
Water activity, Аw |
Humidity, W, % |
Heat water binding, ∆ r 103 J / kg |
|||
|
experience |
control |
experience |
control |
experience |
control |
|
|
0 |
0,988 |
0,965 |
87,3 |
75,4 |
0,5 |
0,5 |
|
1 |
0,976 |
0,960 |
82,7 |
73,8 |
0,9 |
0,7 |
|
2 |
0,968 |
0,956 |
78,1 |
72,6 |
1,6 |
1,3 |
|
3 |
0,960 |
0,951 |
76,0 |
72,1 |
1,9 |
1,4 |
|
4 |
0,954 |
0,947 |
74,9 |
71,8 |
2,3 |
1,9 |
|
5 |
0,947 |
0,943 |
74,2 |
71,1 |
2,5 |
2,0 |
|
6 |
0,940 |
0,938 |
73,6 |
70,4 |
2,6 |
2,3 |
As can be seen from table 2, with a duration of mechanical treatment of up to 6 hours, the humidity of lamb and horse meat with an MCB content of 20% reaches 85%.
Water in food products is a dispersion medium and determines their structure. The structural and mechanical properties of meat products are affected by both moisture content and the form of its connection with the product. Most products are subjected to mechanical, hygro- and hydrothermal processing and mass transfer processes in which of moisture content and change its state [3].
Table 2 - Dynamics of changes in LSS, plasticity and humidity of raw meat depending on the duration of mechanical treatment and the content of multicomponent brine
|
Duration of mechanical treatment, hours |
Сontent of MCB, % |
Dynamics of changes |
||
|
LSS, 10-5 |
Plasticity, 102 |
Humidity, % |
||
|
1 |
5 |
2,07 |
4,61 |
78,2 |
|
10 |
2,1 |
4,69 |
78,6 |
|
|
15 |
2,08 |
4,65 |
79,2 |
|
|
20 |
2,09 |
4,6 |
79,6 |
|
|
2 |
5 |
2,01 |
4,73 |
78,4 |
|
10 |
2,00 |
4,77 |
78,8 |
|
|
15 |
1,97 |
4,98 |
79,9 |
|
|
20 |
1,95 |
4,87 |
80,2 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
1,94 |
4,78 |
78,5 |
|
10 |
1,91 |
4,82 |
79,4 |
|
|
15 |
1,92 |
5,11 |
80,7 |
|
|
20 |
1,9 |
4,99 |
80,9 |
|
|
4 |
5 |
1,91 |
4,84 |
78,9 |
|
10 |
1,88 |
4,9 |
79,9 |
|
|
15 |
1,83 |
5,18 |
81,6 |
|
|
20 |
1,82 |
5,14 |
81,1 |
|
|
5 |
5 |
1,87 |
4,89 |
79,6 |
|
10 |
1,81 |
4,93 |
80,7 |
|
|
15 |
1,77 |
5,24 |
82,3 |
|
|
20 |
1,79 |
5,19 |
82,4 |
|
|
6 |
5 |
1,81 |
4,94 |
79,9 |
|
10 |
1,78 |
4,99 |
81,4 |
|
|
15 |
1,71 |
5,33 |
83,8 |
|
|
20 |
1,69 |
5,27 |
85,0 |
|
The structural and structural-mechanical properties of meat and meat products are closely related to their thermodynamic properties (humidity, water activity, energy and form of water bind) [4,5]. Establishing the dependence of the structural and structural-mechanical characteristics of food products on their thermodynamic characteristics makes it possible to identify forms of communication in the product. The dependence of the structure and structural-mechanical characteristics of lamb and horse meat products on the thermodynamic properties was studied.
The shear stress was taken as a structural-mechanical parameter, and the activity of water (aw) was taken as a thermodynamic parameter.
Graphs of the dependence of the shear stress for boiled-smoked national meat products from lamb, as well as the activity of water on the humidity of meat products are given. The initial moisture content of meat products was 80-85%, А w = 0.97-0.98. From the graph (Fig. 1), at high humidity values, the dependence of the cut voltage of meat raw materials on humidity varies according to rectilinear law with a slight slope to the abscissa axis.
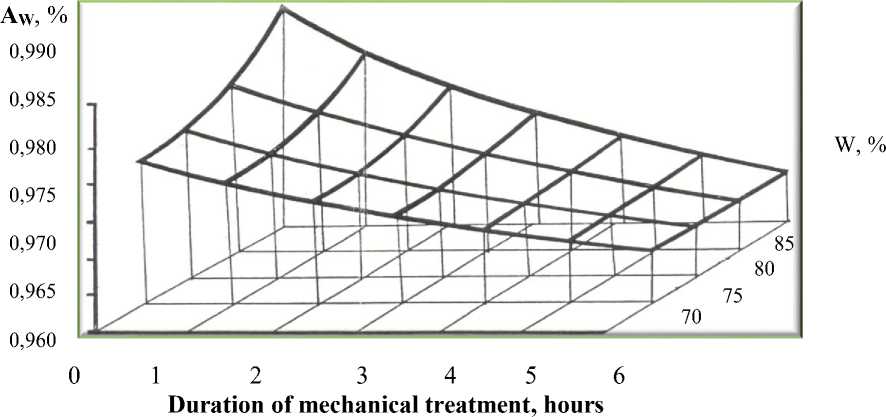
Figure 1- A graph of the dependence of the activity of water of salted meat raw materials on humidity and the duration of mechanical treatment
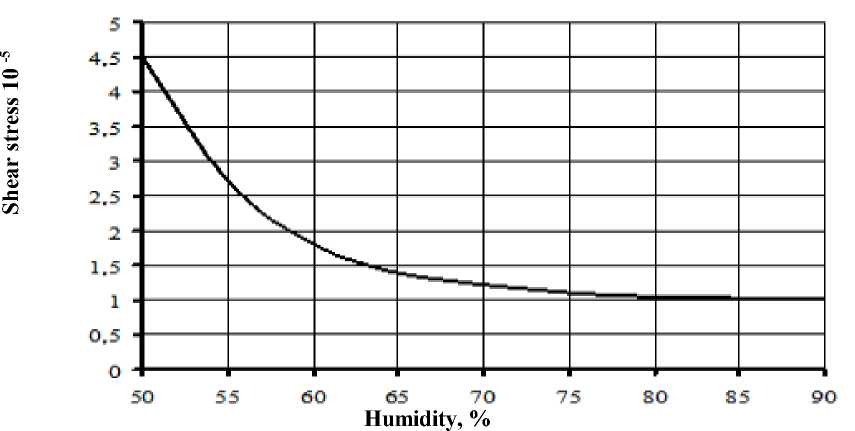
a) Graph of the dependence of the shear stress on the humidity of meat products from lamb and horse meat
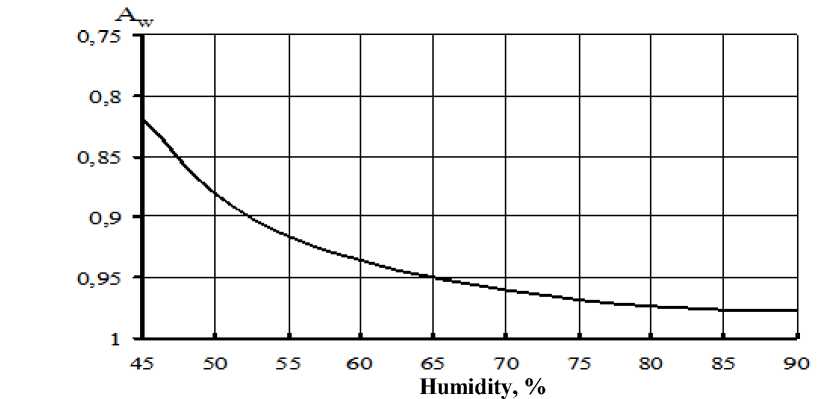
b) Graph of the dependence of the water activity on the humidity of meat products from lamb and horse meat Figure 2 - Graph of the dependence of the shear stress and water activity on the humidity of meat products from lamb and horse meat
Figure 2 shows a graph of the dependence of the shear stress and water activity on humidity of meat products from lamb and horse meat.
During this period, humidity in macro- and mesopores does not affect the shear stress. With a decrease in the humidity of cooked smoked lamb products below 60 % and A w = 0.9, the shear stress begins to increase according to a curved law. This curved section continues to moisture content of 45-50% and A w = 0.80-0.85. After that, the value of the shear stress increases according to a straightforward law, but with a greater slope to the abscissa axis than at the beginning, that is, when meat products have high humidity.
The nature of the change in water activity from the moisture content of lamb and horse meat products mainly corresponds to the nature of the change in shear stress.
Straight portion at the shear stress and water activity graph characterizes contents of macro- and mesocapillary humidity. Over a given humidity interval, the shear stress depends only on the structure of the meat.
The curved section on the graph of the cutoff voltage and water activity makes it possible to judge that this section characterizes the state of humidity in the micropores of meat products.
With a decrease in the humidity of meat products below 45% and Aw = 0.8-0.9, microcapillary humidity is removed, while the mobility of water molecules gradually decreases, which leads to a hardening of the structure of meat products. With a further decrease in humidity, the shear stress value increases sharply. This section corresponds to humidity at which intermolecular-structural humidity remains in the products, which has a significant effect on the magnitude of the voltage. With a gradual decrease in this humidity, the product shrinks due to the convergence of macromolecules, and their mobility is limited. During this period, the dependence of water activity on humidity also has a straight section. A decrease in humidity leads to a sharp decrease in the activity of water and, accordingly, an increase in the binding energy of water.
Thus, based on the data obtained, the dependence of the shear stress on the humidity content of lamb and horse meat products characterizes their structural and mechanical properties depending on the forms of water binding.
Conclusions
The experiments showed that the use of multicomponent brine and mechanical treatment improves WBC and improves the structural and mechanical properties of national restructured lamb and horse meat products. An increase in WBC of meat takes place within 5 days of exposure, and the use of mechanical treatment increases WBC in the first 24 hours. With further exposure, the values of WBC practically do not change (69,0-69,3%).
The use of MCB favorably affects the strength properties of meat products. Using mechanical treatment improves plasticity by 8– 9%. The study of shear stress confirms the pattern of change in the plasticity of meat.
Also, the use of multicomponent brine favorably affects the strength properties of national restructured meat products. The injection of the proposed brine is characterized by a uniform saturation of the pieces of meat with a brine, minimal drainage of the brine after injection, and a uniform distribution of curing substances inside the pieces. The brine evenly fills the space between the fibers of the meat and carries the components to all areas inside the processed pieces. According mechnical treatment, the meat becomes more elastic, juicy during heat treatment, has tendering properties.
Список литературы Research of structural and mechanical properties of national restructured meat products
- Kaim G. Meat Processing Technology-St. Petersburg: Profession, 2012. - 448 p.
- Mashanova N.S. Biotechnological aspects of the use of collagen-containing raw materials in the production of meat products. - Almaty: Editorial and publishing Department of ATU, 2010.- 217 p.
- Rogov I.A., Zabashta A.G., Kazyulin G.P. Technology of meat and meat products. Book 1. General technology of meat. - M.: KolosS, 2009. - 565 p.
- Koroleva M.K., Smurygin V.Yu., Smurygina N.V. Meat products and gastronomy of different countries. Recipes and recommendations - St. Petersburg: Publishing House Profession, 2016. - 208 p.
- Mikolaychik I.N., Morozova L.A., Iltyakov A.V., Pryanishnikov V.V. Technological basics of meat processing. - Kurgan: publishing house of the Kurgan State Agricultural Academy, 2016.- 336 p.


