Сравнение иммуногистохимического и ПЦР метода определения уровня экспрессии KI-67 в ткани рака молочной железы
Автор: Дергунова Ю.А., Кометова В.В., Боженко В.К., Варданян С.Г., Кулинич Т.М., Родионов В.В., Кудинова Е.А.
Журнал: Вестник Российского научного центра рентгенорадиологии Минздрава России @vestnik-rncrr
Рубрика: Молекулярная медицина
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.18, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Резюме Оценка статуса экспрессии Ki-67 имеет большое значение при дифференциальной диагностике фенотипов рака молочной железы (РМЖ). В настоящее время, многими авторами подчеркивается необходимость внедрения более точных критериев оценки этого идругих молекулярных маркеров, что обеспечит минимизацию ошибочных диагнозов. В представленной работе проведено сравнительное исследование определения уровня экспрессии Ki-67, оцененное методами иммуногистохимии и ПЦР в «реальном времени». Показано, что внедрение метода ПЦР в «реальном времени» в клиническую практику для определения величины пролиферативной активности ткани может обеспечить более высокую точность и может рассматриваться в качестве референсного или, по крайней мере, дополнительного метода.
Рак молочной железы, уровень экспрессии ki-67, пцр в "реальном времени", иммуногистохимия, молекулярные фенотипы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149132071
IDR: 149132071
Текст научной статьи Сравнение иммуногистохимического и ПЦР метода определения уровня экспрессии KI-67 в ткани рака молочной железы
Рак молочной железы (РМЖ) является наиболее распространенной формой рака у женщин, его доля в структуре всей онкологической заболеваемости в Европейском регионе составляет 28% (данные Европейского регионального бюро ВОЗ, 2018 г.) [1]. Опухоли МЖ, различные как с точки зрения гистологического типа, так и с точки зрения степени злокачественности, характеризуются различными биологическими и клиническими особенностями (в частности, общая выживаемость пациентов с тубулярным раком практически соответствует средней продолжительности жизни) [15]. Бесспорным остается факт, что наиболее значимыми факторами прогноза как общей, так и безрецидивной выживаемости больных РМЖ, остаются размер опухоли, наличие регионарных метастазов, возраст женщины. Совершенствование технологий маммологического скрининга и наличие парадигмы онкологической настороженности привели к ранней диагностике опухолей, когда чувствительности всех вышеописанных маркеров (клинических и радиологических данных) не хватает для индивидуализации тактики адьювантной терапии. Прогностические факторы определяют вероятность положительного исхода заболевания на момент хирургического лечения без учета характера адьювантной терапии. Такие факторы, как правило, характеризуют биологическую природу опухоли, пролиферативную активность, метастатический потенциал и др. [18]. Классическими клиническими независимыми факторами прогноза РМЖ являются возраст, наличие лимфогенных метастазов в аксиллярной области, размер опухоли, морфологические характеристики (гистологический тип, степень злокачественности, лимфоваскулярная инвазия, ИГХ экспрессия Ki-67 и др.) [11, 21]. Тем не менее, клиническая эффективность использования подобных классификаций является весьма условной, вследствие их низкой чувствительности и прецизионности при индивидуализации прогноза и тактики терапии у ряда больных РМЖ. Основной причиной этого является отсутствие стандартизованных подходов к формированию критериев классификаций и большая вариабельность патоморфологического диагноза вследствие субъективности подходов специалистов.
Ki-67 является маркером пролиферации, уровень экспрессии которого изменяется в зависимости от фазы клеточного цикла с пиком в фазе митоза и минимальными значениями в фазе G0 [6, 23]. Прогностическое значение иммуногистохимической экспрессии Ki-67 как маркера пролиферации изучено в большом количестве исследований; существуют доказательства его особого значения при прогнозе раннего РМЖ [23]. Также в работах последних лет появились доказательства роли уровня экспрессии Ki-67 в дифференциальной диагностике люминального А и люминального В подтипов РМЖ, а также, как предиктивного фактора эффективности адьювантной терапии в случае РМЖ с отрицательным прогнозом [4, 7].
Согласно критериям St. Gallen 2011 г., уровень ИГХ экспрессии Ki-67 выше 14% характеризует люминальный подтип В РМЖ [7], однако многие авторы признают необоснованность выбора границы уровня экспрессии Ki-67 для стратификации биологического подтипа РМЖ [6] и прогноза эффективности адьювантной терапии у таких пациентов [12]. В исследованиях предложены различные пограничные значения для высокой и низкой пролиферативной активности, однако, наиболее распространенным является уровень 10 – 20 % для низко пролиферирующих клеток [6]. В исследовании Horimoto и соавт. (2014 г.) уровень ИГХ экспрессии Ki-67 выше 35% для Her2/neu-негативного люминального фенотипа В характеризует эффективность адьювантной химиотерапии и большую выживаемость больных [8]. Согласно рекомендациям Международного консенсуса (St.Gallen, 2013), в настоящее время, пороговое значение Ki-67 соответствует 20 % [3]. Иммуногистохимический метод (ИГХ) оценки уровня экспрессии эстрогенового рецептора (ER), прогестеронового рецептора (PR) и Ki-67 успешно и широко используется в клинической практике. Однако, в настоящее время, метод РТ-ПЦР (ПЦР в «реальном времени») активно внедряется в клинико- диагностическую практику и рассматривается рядом исследователей в качестве рефере́нтного метода оценки молекулярных маркеров. При оценке ER и PR методами ИГХ и РТ-ПЦР отмечается высокая сходимость результатов, но при сравнении двух методов РТ-ПЦР отображает более широкий динамический диапазон и более высокую чувствительность, чем ИГХ метод. В случае измерения Ki-67 отмечается, что корреляции между двумя методами не полные, и метод РТ-ПЦР превосходит ИГХ по точности и специфичности [17]. В исследовании Prihantono и соавт. показана возможность использования показателя экспрессии Ki-67, оцененного методами ИГХ и РТ-ПЦР, в качестве предиктового маркера ответа на неоадъювантную химиотерапию при местнораспространенном раке молочной железы [14]. В связи с вышеизложенным, нами было проведено исследование по оценке и сравнению значений уровня Ki-67 в парафинизированных образцах тканей РМЖ, полученных методами ИГХ и РТ-ПЦР.
Цель работы: сравнить ИГХ и ПЦР методы оценки молекулярного маркера Ki-67 для определения пролиферативной активности РМЖ.
Материалы и методы
Исследование проведено на парафинизированных образцах РМЖ, фиксированных в 10%-растворе забуференного формалина (FFPE – formalin fixed paraffin embedded). Послеоперационный материал получен от 199 пациенток, проходивших обследование и лечение в ФГБУ «РНЦРР» Минздрава России в период с 2005 по 2017 годы. Решение о включении в исследование принималось на основании морфологической верификации диагноза РМЖ и после получения добровольного информированного согласия пациентки. Распределение пациенток, включенных в исследование, по возрасту представлено в Таблице 1. Наибольшая возрастная группа от 50 до 60 лет включала 69 пациенток (34,7 %), средний возраст составил 61,6 лет.
Таблица 1. Распределение пациенток по возрасту
|
Возраст, лет/год |
Количество, n |
% |
|
20 ≤ x < 30 |
0 |
0,00 |
|
30 ≤ x < 40 |
4 |
2,01 |
|
40 ≤ x < 50 |
20 |
10,05 |
|
50 ≤ x < 60 |
69 |
34,67 |
|
60 ≤ x < 70 |
60 |
30,15 |
|
70 ≤ x < 80 |
39 |
19,60 |
|
80 ≤ x < 90 |
7 |
3,52 |
Включенные в исследование пациентки имели разные стадии заболевания и гистологически разные типы опухолей. Распределение пациенток по стадиям (в зависимости от клинических данных, в частности, размера опухолевого узла, наличия регионарных и отдаленных метастазов) представлено в Таблице 2 .
Таблица 2. Распределение пациенток по стадиям РМЖ
|
Стадия |
Количество пациенток, чел. |
Количество пациенток, % |
|
IA |
45 |
12,57 |
|
IIA |
68 |
18,99 |
|
IIB |
40 |
11,17 |
|
IIIB |
9 |
2,51 |
|
IIIA |
23 |
6,42 |
|
IIIC |
14 |
3,91 |
Наиболее часто диагностируемым гистологическим вариантом был инвазивный неспецифический рак (протоковый вариант), выявленный в 38,2 % случаев, на долю смешанного протоково-долькового варианта инвазивного неспецифического рака пришлось 26,6 % случаев, инвазивный дольковый рак был верифицирован в 23,1 % (ВОЗ, 2012 г.). Особые формы РМЖ были представлены редко и были объединены в общую группу (12,1 %). Степень злокачественности (G) определялась согласно критериям Ноттингемской классификации (система градирования инвазивного рака молочной железы Scarff-Bloom-Richardson в модификации Elston-Ellis). Распределение случаев РМЖ по степени злокачественности представлено в Таблице 3.
Таблица 3. Распределение опухолей по степени злокачественности (G)
|
Степень злокачественности, G |
Количество пациенток |
Процент, % |
|
1 |
14 |
3,91 |
|
2 |
117 |
32,68 |
|
3 |
68 |
18,99 |
Оценка уровня экспрессии Ki-67 методом ИГХ
Для всех включенных в исследование образцов были проведены иммуногистохимическое исследование (ИГХ) и постановка РТ-ПЦР для оценки уровня экспрессии Ki-67. ИГХ проводилось на фиксированных формалином парафинизированных срезах толщиной 4 мкм с использованием антител (Dako, Дания) к Ki-67 (клон MIB – 1, изотип IgG1 kappa, первичные моноклональные мышиные античеловеческие). Срезы подвергались предварительной депарафинизации и тепловой демаскировке антигена с использованием буферного раствора низким значением рН 0,6
для антител к Ki-67 в РТ-модуле. Процедура окрашивания производилась в автоматическом иммуногистостейнере (Thermoscientific, Великобритания). Эндогенная пероксидаза блокировалась путем контакта среза с 3% - раствором перекиси водорода в течение 5 мин. Далее происходила инкубация с первичным антителом в течение 20 мин с последующей 20 – минутной инкубацией с полимером. В качестве системы визуализации применялся 3,3 – диаминобензидин (DAB) в течение 10 минут, после чего ядра докрашивались гематоксилином. Далее срезы подвергались дегидратации в восходящей батарее спиртов и заключались в фиксирующую среду.
Подсчет Ki–67 осуществлялся визуальным и автоматическим (с помощью программы ImmunoRatio) методами в 10 полях зрения при увеличении микроскопа х 400. Индекс пролиферативной активности определялся как процент окрашенных клеточных ядер в опухолевой паренхиме. При наличии «горячих точек» (hot-points) их подсчёт обязательно включался в общий результат. Кроме этого, в протоколе указывался тип распределения делящихся клеток (диффузный или краевой).
Оценка уровня экспрессии Ki-67 методом РТ-ПЦР
Выделение РНК проводили на сорбирующих колонках с использованием набора RNeasyFFPEKit (QIAGEN, Германия, кат.№ 73504) по протоколу, рекомендованному производителем. Оценку качества экстрагированной тотальной РНК измеряли, используя микро-капиллярный электрофорез на чипе (Bioanalizer 2100, Agilent Technologies, Mississauga, Онтарио, Канада). Степень деградации/фрагментации РНК оценивали, определяя индекс целостности RIN (RNA integrity number) и соотношение площади целевого диапазона фрагментов к соотношению тотальной РНК. Значения RIN для всех образцов лежали в интервале 1,8 – 2,5. Концентрацию полученной РНК измеряли с помощью флюориметра Qubit 2,0 (Life Technologies).
Проведение обратной транскрипции (ОТ) и ПЦР осуществляли в два этапа. Реакцию ОТ проводили непосредственно после выделения РНК. Синтез кДНК выполняли в 40 мкл реакционной смеси при 40° C в течение 30 мин, с последующей инактивацией обратной транскриптазы при 95° C в течение 5 мин. Полученную кДНК хранили при -70° С до использования.
Для постановки реакций ОТ и ПЦР использовали ген-специфичные праймеры, наборы реагентов, протоколы и оборудование ЗАО «НПФ ДНК-Технология» (Россия). Относительную экспрессию мРНК генов определяли методом сравнения индикаторных циклов с использованием нормализации по генам «домашнего хозяйства» согласно методике, предложенной Vandesompel с соавторами[20]. В качестве контрольных генов были выбраны GUSB , HPRT и B2M , как наиболее стабильно экспрессируемые в различных тканях [10, 16, 19]. ПЦР в реальном времени выполняли в 384-луночном формате на амплификаторе DT-Prime5 «ДНК-Технология». Специфические праймеры, зонды и смеси для амплификации разработаны компанией «ДНК-Технология» с учетом особенности сильной фрагментации РНК в FFPE-образцах. Используемые праймеры и зонды специфически взаимодействуют с участками кДНК на стыке экзонов. Размер праймеров находился в диапазоне 100 п.н. Амплификацию осуществляли в режиме «реального времени» в объеме 12 мкл по протоколу, рекомендованному производителем. Уровень экспрессии генов с учётом нормировочного фактора рассчитывали согласно адаптированной/валидированной ранее методике [2].
Статистический анализ
Математическую обработку полученных данных осуществляли в программе Statistica 10,0 (USA). Данные были проверены на нормальное распределение. Параметрические тесты использованы в соответствующих случаях. Значения P < 0,05 считались статистически достоверными.
Результаты
При сравнительной оценке уровней экспрессии Ki-67 полученных двумя методами, были обнаружены достоверные корреляции (Таблица 4). В большинстве исследуемых образцов значения Ki-67, полученные методом ИГХ, соответствовали уровню экспрессии, определенному методом РТ-ПЦР (Рисунок 1), однако была выделена группа, в которой высокие значения экспрессии Ki-67 не согласуются со значениями, полученными ИГХ методом (зона выделения на Рисунке 1).
Таблица 4. Корреляция распределения значений уровня экспрессии Ki-67 определяемого методом ИГХ и ПЦР
|
МЕТОД |
Значение Ki-67, полученное ПЦР "в реальном времени" |
Значение lnKi-67, полученное ПЦР "в реальном времени" |
|
Значение Ki-67, полученное ИГХ |
0,523391 |
0,526618 |
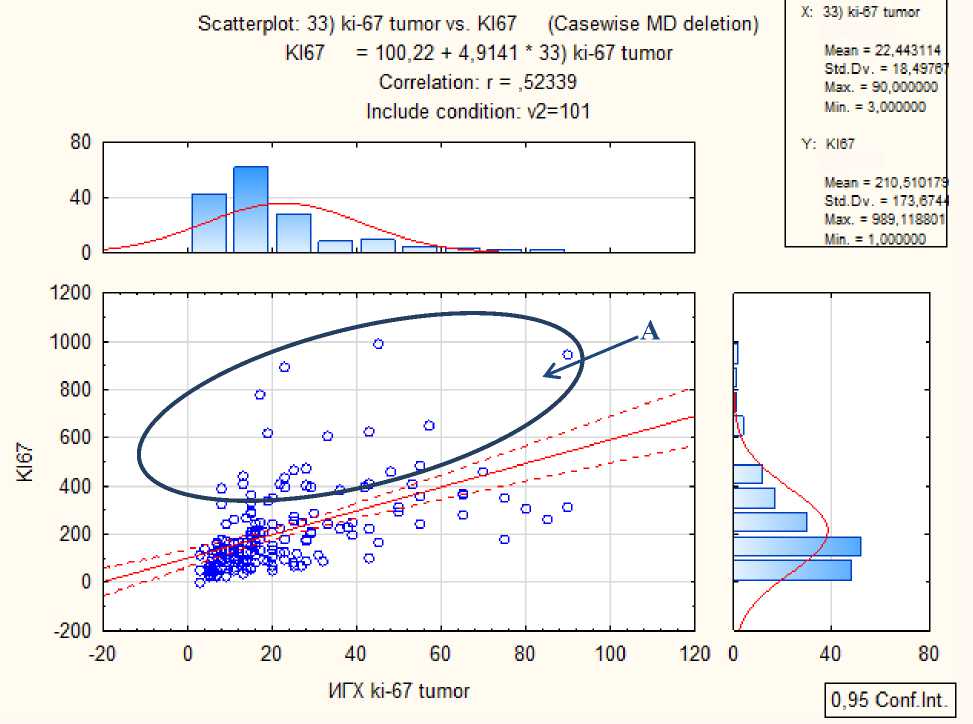
Рисунок 1. Корреляция и гистограммы распределения значений уровня экспрессии Ki-67, определяемого методом ИГХ и ПЦР. А – зона выделения, образцы с отличающимися значениями уровня экспрессии Ki-67 для двух методов.
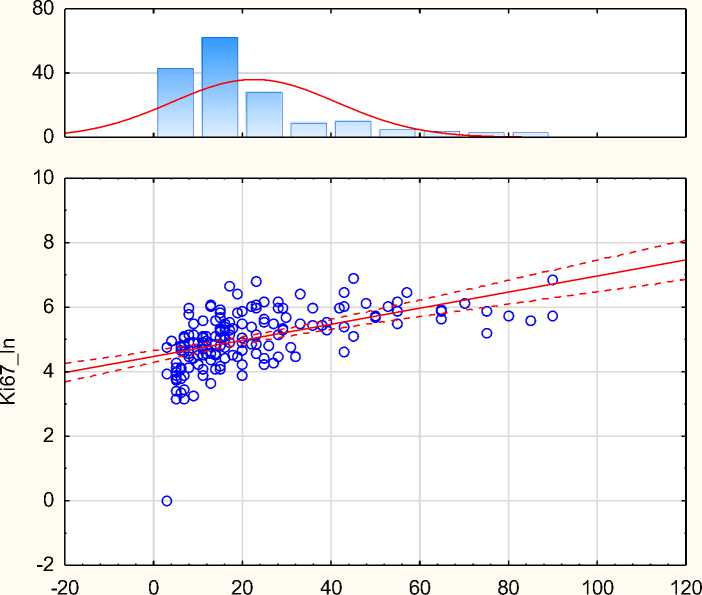
Для оценки нормальности распределения полученных зависимостей был рассчитан коэффициент корреляции относительно логарифмов значений экспрессии мРНК Ki-67 (Таблица 4, Рисунок 2). Показано, что коэффициенты корреляции для абсолютного и логарифмированного показателя практически не отличаются. Таким образом, было определено, что зависимость показателей методов ИГХ и РТ-ПЦР имеет «нормальный»
характер.
Ki67_ln = 4,4717 + ,02495 * 33) ki-67 tumor Correlation: r = ,52662
ИГХ ki-67 tumor
-
X: 33) ki-67 tumor
N = 167
Mean = 22,443114
Max. = 90,000000 Min. = 3,000000
-
Y: Ki67_ln
N = 167
Mean = 5,031750
Max. = 6,896814 Min. = 0,000000
0 40 80
Рисунок 2. Корреляция и гистограммы распределения значений уровня экспрессии Ki-67, определяемого методом ИГХ и логарифма уровня экспрессии, определяемого методом ПЦР.
При этом корреляционный анализ позволяет проанализировать линейную корреляцию между показателями и получить уравнение регрессии:
Ki-67РТ-ПЦР = 100,22 + 4,9141 * (ИГХ Ki-67tumor),
где ИГХ Ki-67tumor – значение, полученное методом ИГХ;
Ki-67 РТ-ПЦР – «предсказанное» значение, полученное методом РТ-ПЦР;
100,22 и 4,9141 – коэффициенты регрессии оценённой линии.
Полученное уравнение позволяет вычислить уровень экспрессии Ki-67, определенный методом ПЦР, в единицах (%) ИГХ метода, что имеет большое практическое значение в случаях, например, дифференциации Люминального А и В фенотипов, на основании соглашения Сент Гален, или любого другого регламентирующего соглашения, которое предлагает какой либо конкретный уровень, определяемый на основании Ki-67, регистрируемого методом ИГХ. Также уравнение регрессии позволяет оценить значения уровней экспрессии Ki-67, полученные РТ-ПЦР, необходимые для дифференциальной диагностики типов РМЖ. Например, если принять за дискриминирующий уровень величину 17 %, то уровень Ki-67, определяемый методом ПЦР будет равен:
Ki-67РТ-ПЦР = 100,22 + 4,9141 * 17=183,8;
где 17 – ИГХ Ki-67tumor (17%).
Полученные значения могут быть использованы в клинической практике, в случаях, например, регистрации ПЦР наборов для определения уровня Ki-67 и повышения объективизации данного параметра в конкретной опухоли.
Обсуждение
Результаты проведенного исследования доказывают возможность применения метода РТ-ПЦР при определении уровня Ki-67. Многими авторами в настоящее время подчеркивается необходимость поиска новых систем оценки рецепторного статуса и статуса Ki-67 при дифференциальной диагностике подтипов РМЖ [5, 13], вносятся предложения по изменению требований к проведению ИГХ метода оценки [9]. Большое значение точность определения уровня Ki-67 имеет для дифференциации Люминального А и В фенотипов, пациенты с такими фенотипами РМЖ составляют наиболее сложную категорию для выбора адьювантной терапии. Эксперты признают, что дифференциальная оценка люминального фенотипа А и HER2/neu -негативного люминального фенотипа В представляет большую проблему, с чем связано колебание пограничных значений в оценке экспрессии Ki-67 [7]. В работе Jiayi Wu и соавт. на большой выборке пациентов с диагнозом РМЖ показано, что применение метода РТ-ПЦР для дифференциальной диагностики молекулярных фенотипов обоснованно и позволяет получить более точные результаты по сравнению с ИГХ методом, хотя корреляции между двумя методами, несомненно, достоверные [22].
С другой стороны, обращает на себя внимание высокий разброс значений уровня экспрессии, регистрируемого методом ПЦР, для любого из фиксированных значений уровня экспрессии, регистрируемого методом ИГХ. Например, для значения 20 уровень экспрессии колеблется от практически нулевого до нескольких сотен относительных величин. Полученные зависимости могут еще раз подчеркнуть проблему определения (разграничения) Люминальных А и В молекулярных фенотипов, а также проблему выделения активно пролиферирующих опухолей только по одному показателю Ki-67 и необходимости использования нескольких молекулярно-генетических характеристик, отражающих пролиферацию опухолевых клеток. Проведенный нами анализ образцов РМЖ, попавших в ошибочную зону («зону выделения» на Рисунке 1) показал, что в большей степени они были отнесены к фенотипу «Люминальный А», что, возможно, являлось ошибочным. Уровень экспрессии Ki-67 данных образцов достаточно высокий, и полученные результаты, несомненно, требуют более глубокого анализа и повторного рассмотрения программ лечения данных пациентов.
Список литературы Сравнение иммуногистохимического и ПЦР метода определения уровня экспрессии KI-67 в ткани рака молочной железы
- Всемирная организация здравоохранения. Европейское региональное бюро. Вопросы и темы здравоохранения. Рак молочной железы. 2018. http://www.euro.who.int/ru/health-topics/noncommunicable- diseases/cancer/news/news/2012/2/early-detection-of-common-cancers/breast-cancer
- Кудинова Е.А. Молекулярно-генетические технологии в оптимизации диагностики и прогноза заболеваний молочной железы. Дис. доктора медицинских наук / Российский научный центр рентгенорадиологии. Москва. 2017.
- Bustreo S., Osella-Abate S., Cassoni P., et al. Optimal Ki-67 cut-off for luminal breast cancer prognostic evaluation: a large case series study with a long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. V. 157. No. 2. P. 363-371.
- Cheang M.C., Chia S.K., Voduc D., et al. Ki-67 Index, HER2 Status, and Prognosis of Patients With Luminal B Breast Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009. V. 101. No. 10. P. 736- 750.
- Christgen M., von Ahsen S., Christgen H., et al.The region-of-interest size impacts on Ki- 67 quantification by computer-assisted image analysis in breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 2015. V. 46. No. 9. P. 1341-1349.
- Dowsett M., Nielsen T.O., A´Hern R., et al. Assessment of Ki-67 in Breast Cancer: Recommendations from the International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. V. 103. No. 22. P. 1656-1664.
- Goldhirsch A., Wood W.C., Coates A.S., et al. Stratefies for subtypes - dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011. V. 22. No. 8. P. 1736-1747.
- Horimoto Y., Arakawa A., Tanabe M., et al. Ki-67 expression and the effect of neo- adjuvant chemotherapy on luminal HER2-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014. V. 14: 550.
- Laurinavicius A., Plancoulaine B., Rasmusson A., et al. Bimodality of intratumor Ki-67 expression is an independent prognostic factor of overall survival in patients with invasive breast carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2016. V. 468. No. 4. P. 493-502.
- Lind G.E., Danielsen S.A., Ahlquist T., et al. Identification of an epigenetic biomarker panel with high sensitivity and specificity for colorectal cancer and adenomas. Mol Cancer. 2011. V. 10: 85.
- Ly A., Lester S.C., Dillon D. Prognostic factors for patients with breast cancer: traditional and new. Surg Pathol Clin. 2012. V. 5. No. 3. P. 775-785.
- Pérez-García J., Cortes J. Do we need biomarkers to predict the benefit of adding adjuvant taxanes for treatment of breast cancer? Breast Cancer Res. 2012. V. 14. No. 1: 104.
- Polley M.Y., Leung S.C., McShane L.M., et al. An international Ki-67 reproducibility study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013. V. 105. No. 24. P. 1897-1906.
- Prihantono P., Hatta M., Binekada C., et al. Ki-67 Expression by Immunohistochemistry and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction as Predictor of Clinical Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer. J Oncol. 2017. 2017: 6209849.
- Rakha E.A., Lee A.H., Evans A.J., et al. Tubular carcinoma of the breast: further evidence to support its excellent prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2010. V. 28. No. 1. P. 99-104.
- Sharan R.N., Vaiphei S.T., Nongrum S., et al. Consensus reference gene(s) for gene expression studies in human cancers: end of the tunnel visible? Cell Oncol. (Dordr.). 2015. V. 38. No. 6. P. 419-431.
- Sinn H.P., Schneeweiss A., Keller M., et al. Comparison of immunohistochemistry with PCR for assessment of ER, PR, and Ki-67 and prediction of pathological complete response in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2017. V. 17. No. 1. P. 124. Subramaniam D.S., Isaacs C. Utilizing Prognostic and Predictive Factors in Breast Cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2005. V. 6. No. 2. P. 147-159.
- Terrin L., Rampazzo E., Pucciarelli S., et al. Relationship between tumor and plasma levels of hTERT mRNA in patients with colorectal cancer: implications for monitoring of neoplastic disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. V. 14. No. 22. P. 7444-7451.
- Vandesompele J., De Preter K., Pattyn F., et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002. V. 3. No. 7. RESEARCH 0034.
- Weigel M.T., Dowsett M. Current and emerging biomarkers in breast cancer: prognosis and prediction. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010. V. 17. No. 4. P. 245-262.
- Wu J., Fang Y., Lin L., et al. Distribution patterns of 21-gene recurrence score in 980 Chinese estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017. V. 8. No. 24. P. 38706-38716.
- Yerushalmi R., Woods R., Ravdin P.M., et al. Ki-67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. 2010. V. 11. No. 2. P. 174-183.


