The ethnofuturism of Kazakhstan’s clothing brand “Global Nomads” in the Fashion Design
Автор: Zhanguzhinova M.Y., Talgatbekova A.M., Ezieva M.M., Turumkozhayeva Zh.S.
Журнал: Вестник Алматинского технологического университета @vestnik-atu
Рубрика: Технология текстиля и одежды, дизайн
Статья в выпуске: 4 (146), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The relevance of the study on ethnofuturism in Kazakhstan's fashion design lies in the theoretical and methodological justification for integrating the identity of national cultural values with the sustainable development of the authenticity of the nomadic style. The research aims to analyze the formation of ethnofuturism trends in clothing design using the example of the Kazakhstan brand Global Nomads. The scientific significance of the study is in determining its contribution to the integration of cultural heritage into contemporary fashion and the creation of innovative and competitive products in the global market. The practical significance of the research allows for identifying the effectiveness of the brand in preserving and adapting traditional elements of nomadic culture and symbolism within the context of global fashion trends, as well as its influence on the perception of Kazakh national identity and the cultural heritage of Central Asia. The research methodology encompasses fields of art studies, cultural studies, history, ethnography, fashion, design, clothing technology, sustainable development, and sociology. Key positions and conclusions were established regarding the ethnofuturistic approach to the design of the Global Nomads clothing brand, innovations in interpreting national traditions, the social and cultural significance of clothing, its influence on global fashion, and the economic aspect. The results of the study involve an analysis of the brand's tools that allow for adapting historical and cultural codes to create relevant and commercially successful clothing; opening new horizons in understanding the process of modernization and preservation of cultural heritage through fashion, which aids in creating competitive advantages and strengthening market positions. The value of the conducted research includes the analysis of ethnofuturism trends, with recommendations for utilizing sustainable technologies, fostering cultural dialogue, and enhancing the brand's social responsibility.
Kazakhstan clothing brand, fashion design, global nomads, national cultural values, identity, ethnofuturism
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140308690
IDR: 140308690 | УДК: 687.12 | DOI: 10.48184/2304-568X-2024-4-192-201
Текст научной статьи The ethnofuturism of Kazakhstan’s clothing brand “Global Nomads” in the Fashion Design
The growing interest in the unique cultural aspects of Kazakhstan that shape fashion trends, commercial value in fashion design within the context of globalization, and educational and cultural significance justifies choosing this topic. The research problem is preserving the unique cultural identity of the Kazakh clothing brand Global Nomads amidst implementing innovations, adaptation, and social perception in a highly competitive global fashion landscape. The increased interest from domestic and foreign scholars in the fields of clothing and fashion design, cultural studies, cultural anthropology, branding, semantics, ethnography, and interdisciplinary studies in higher art and design education underscores the relevance of this topic. However, there has been no academic study focused on the formation of ethnofuturism in the context of the Kazakh clothing brand Global Nomads within scholarly research. The object of the study is the Kazakh fashion brand Global Nomads. The subject of the research is the cultural-anthropological approach to the formation of the Global Nomads style. The research tasks include: analyzing the concept of ethnofuturism in the context of fashion design for the Kazakh brand Global Nomads and its application in the modern fashion industry; exploring cultural and ethnic elements; analyzing design solutions; studying brand perception; assessing the impact on the fashion industry; and developing recommendations. The scientific novelty of the research lies in the analysis of traditional and modern approaches, the modernization of cultural heritage, the impact on cultural identity, and the influence on fashion trends. The research methods include theoretical and qualitative analyses, ethnographic and cultural-art studies, case studies, and trend analysis. The hypothesis of the research on ethnofuturism in the Kazakh clothing brand Global Nomads in fashion design posits that the integration of traditional cultural elements with modern design approaches can not only preserve the authenticity of Kazakh cultural identity but also enhance the brand's competitiveness in the global fashion market.
Materials and research methods
In the context of studying the ethnofuturism of the Kazakh clothing brand Global Nomads in fashion design, this article employs theoretical and methodological materials related to the brand's concept and history, based on its values, aesthetic code, clothing assortment, color positioning, retail format, production, and social responsibility. The idea behind the Kazakh fashion brand Global Nomads is built around the brand's role model — “the traveling person,” who is open to the world, progressive, and actively explores new territories and knowledge. The target audience of the brand consists of young families focused on modern trends, conscious consumption, and concerned about the future of their children, and thus their homeland. The main values include quality, freedom, meaningfulness, and beauty, along with a sense of connection to global changes in human civilization, cultural heritage, sustainable development, and tolerance. The primary scientific materials for the brand's research were historical and cultural sources on the ethnography and traditional culture of Kazakhstan, which shape the aesthetic code. The brand's values are based on Kazakh national clothing and the attire of Central Asian nomads, ornamentation, traditional materials, and symbols. The aesthetic code of the brand is rooted in cultural heritage and artifacts that shape the national Kazakh identity in contemporary fashion design. The overview and analytical materials of the Global Nomads collection included design solutions, decorative elements used in collections related to ethnic symbolism, ornamentation, fabrics, and sewing techniques, reflecting national heritage within a futuristic approach. The research methods included qualitative approaches, such as:
-
• Content analysis of Global Nomads collections and their reinterpretation in modern fashion;
-
• Visual analysis of style, color, texture, and form in the brand's clothing design [1];
-
• Case studies examining brand promotion strategies through the lens of ethnofuturism;
-
• Ethnographic methods, including interviews and surveys of customers, designers, and marketers, as well as experts in fashion and cultural studies, to gather professional insights on the phenomenon of ethnofuturism in fashion [2,3,4];
-
• Sociological analysis of globalization and localization trends affecting the perception of Kazakh culture through fashion [5].
In connection with the study of the aforementioned scientific literature and the analysis of trends and issues in the fashion industry, a research question arises: How is clothing design formed in the context of ethnofuturism, using the example of the Kazakh brand "Global Nomads"?
Based on the established hypothesis of the research, it was assumed that the ethnofuturism of the Kazakh clothing brand "Global Nomads" in fashion design is possible through the integration of traditional cultural elements and modern design approaches. Preserving the authenticity of Kazakh cultural identity in the brand's clothing design stimulates the brand's competitiveness in the global fashion market. The thesis of the research states that the effective use of ethnofuturism will contribute to the positive perception of the brand, its sustainable development, and adaptation to contemporary fashion trends, as well as improving social responsibility and cultural dialogue.
The stages of the research include:
-
• Theoretical and methodological justification of ethnofuturism as the philosophy of the Global Nomads brand, the interpretation of traditional nomadic motifs in contemporary clothing, futuristic interpretations of clothing, cultural identity through fashion, eco-friendliness, and sustainability, and the social responsibility of the brand.
-
• The use of qualitative analysis methods based on the results of sociological surveys among key respondent groups (customers, target audience, business partners) allowed for the formulation of conclusions regarding the processes of forming ethnofuturism.
-
• Based on the results of the conducted research, conclusions were drawn that reflect the main positions of the study and the trends of ethnofuturism in the Kazakh clothing brand Global Nomads in fashion design, along with recommendations.
The literature relevant to this research includes recent articles from the last three years published in peer-reviewed journals in Kazakhstan (KOKSNVO) [1,3,4,6] and abroad (Scopus, WoS) [2,10-15], as well as fundamental works by scholars published in UNESCO publications [7,8] and applied research from the National Museum of China [9]. The bibliography encompasses articles and studies in the following fields: art studies [1,3,4,6], ethnography [2,8,9], pedagogy [3,4], history of costume [5], clothing and textile technology [6-9], design [6], fashion [10], virtual reality, digital technologies, and artificial intelligence [11,12], and creativity [13-15].
Results and discussion
Ethnofuturism of the Kazakh clothing brand Global Nomads in fashion design is a conceptual approach that combines the traditional Kazakh cultural code of nomadism with contemporary and futuristic fashion trends. This direction in fashion reflects the desire to preserve cultural identity by integrating it into global trends through innovative and modern solutions. The key aspects of ethnofuturism in Global Nomads fashion include:
Ethnofuturism, as the philosophy of the Global Nomads brand, engages with the idea of a future where national and cultural identities do not fade away in the process of globalization; instead, they become the foundation for creating new creative and aesthetic solutions. The sustainable development of cultural identity requires flexibility and adaptability while maintaining its essence [7]. By preserving the spirit of a nomadic lifestyle, the brand adapts to new challenges—whether economic, ecological, or cultural changes. The brand's designer, Maya Zhumanbekova, aims to reflect current realities in her collections while maintaining a global, cosmopolitan spirit.
Thus, the sustainable development of the Global Nomads brand's cultural identity involves not only preserving the key aspects of its philosophy but also the flexibility needed to adapt to contemporary changes. The brand actively maintains a balance between innovation and cultural authenticity, ensuring its competitiveness and demand in the global market. Adapting to changes in fashion is crucial and supports the brand's sustainable development. By following global trends, the brand interprets them through the lens of its unique identity, striking a balance between fashion trends and its cultural narrative. By implementing innovative technologies and design solutions, the brand remains true to nomadic values, making clothing comfortable and functional for the modern consumer.
Interpretation of traditional nomadic motifs in contemporary clothing. The brand incorporates elements of traditional Kazakh nomadic culture into its collections, such as ornaments, color palettes, textile techniques, forms, and silhouettes of national clothing. The innovation lies in adapting the cultural code of the nomads to meet modern aesthetic and functional needs. Ethnofuturism, in this context, demonstrates how ancient symbols and materials can coexist in harmony with futuristic trends—minimalism, technology, and sustainability.
The conceptual and artistic foundation of the Global Nomads brand is rooted in the aesthetic code of Kazakh and Central Asian nomads, whose semantics reflect worldview aspects—tribal history, cycles of birth, life, and death manifested in signs and symbols that serve as protective charms [1,3,4,6]. In the interpretation of the brand's lead designer, Maya Zhumanbekova, the aesthetic cultural code of Global Nomads is based on ten key symbols that describe the infinitely recurring processes of the universe and the life of any person. These symbols include two sacred nomadic symbols and a symbolic palette (flower, spiral, "shanyrak" — the roof of a house, circle, "tumar" — a protective amulet, "arkhar" — a sacred animal, diamond, tulip, square, "aruah" — the spirit of ancestors). The symbolism of the material heritage of nomads underpins the cultural values of the Kazakhs, which are intricately intertwined with their worldview orientations [1,3,4,6].

Figure 1. T-short from the collection of Global Nomads brand, designer Maya Zhumanbekova
The futuristic interpretations of clothing by the Global Nomads brand feature a modern and avant-garde aesthetic, embodying a sustainable development concept suited for today's lifestyle — digital nomads who constantly move around the world, working from various locations, traveling, and transitioning between countries. In the context of the case study method, the capsule collections of Global Nomads demonstrate an ergonomically organized design process that emphasizes eco- friendly materials and sustainability. The phenomenon of this case lies in the fact that the new format of clothing for modern nomads not only echoes traditional nomadic motifs but is created as modified versions of them. The brand's conceptual development includes market research and target audience analysis, collection concept develop-ment, material selection, sketch creation, collection design, sewing technology, and fabric treatment, along with innovative design approaches, production, testing, marketing, promotion, implementation, and sales [10-15]. As a result of the case study method, we can confirm the successful launch of the collection, increased brand recognition, and ongoing collaborations, which symbolize Kazakh identity within the context of globalization.
Cultural identity through fashion is reflected in the clothing from Global Nomads, which aims to convey and popularize Kazakh culture on an international level while preserving its uniqueness. The brand promotes the idea of "nomadic culture," evident in the use of lightweight, functional, and adaptive clothing elements that symbolize the mobility and freedom characteristic of the Kazakh nomadic lifestyle. The stylistic choices in forms, silhouettes, cuts, ornaments, and color palettes collectively embody the brand's vision of modern mobile digital nomads with a global perspective, while remaining rooted in their cultural identity [10-15].
Ecological sustainability is a vital element of nomadic culture. The use of natural materials and traditional production methods aligns with contemporary concepts of sustainable development for the brand. The brand's ecological responsibility involves ethical production with minimal waste, a respectful approach to regional communities, and the incorporation of artisanal traditions into manufacturing processes. The sustainable development of the values and philosophy of Global Nomads is reflected not only in their clothing but also in a cultural idea rooted in the concept of a nomadic lifestyle and international cultural exchange. The active integration of cultural elements from various Central Asian countries into their collections highlights the importance of intercultural dialogue [13-15]. This integration of local cultural features is achieved through immersion in the cultural traditions of different regions to create authentic collections. To maintain its cultural identity, the brand respects local Kazakh nomadic traditions in its design, fabric choices, patterns, and production methods.
The social responsibility and engagement of the brand Global Nomads contribute to sustainable development through various social and community projects, such as the Young Designers Competition and the international "Global Nomads Fashion Awards" (since 2021), Global Nomads Education (since 2021), the "Business with Meaning" project (2023), designing sportswear for the Kazakhstan team "Olimp Urban Culture" (2023), the "Umai Boost" program (2023), the Kod Nomada forum for modern nomads (2023), the Aruzhan Sain Foundation for helping children with autism (2024), the World Nomad Games in Astana (2024), collaboration with Dimash Kudaibergen for a concert in Astana (2024), creating promotional outfits for Dimash Kudaibergen for a concert in Istanbul (2024), the Eurasian Women’s Forum (2024), and collaboration with the Chinese automobile brand Tank in Kazakhstan (2024).
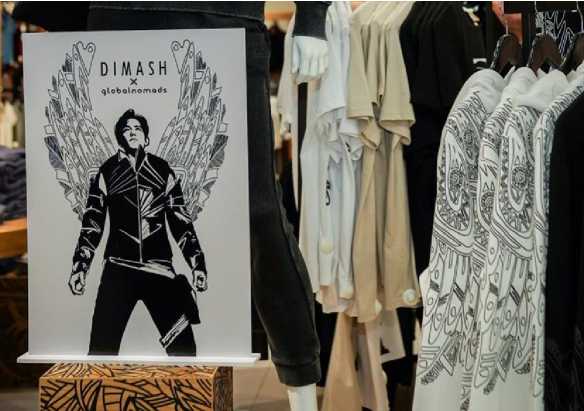

Figure 1. А collection of Global Nomads brand, the collaboration with Dimash Kudaibergen
Engagement with cultural societies, the Assembly of Peoples of Kazakhstan, and craft unions in Central Asia helps preserve local traditions and culture. The creation of programs aimed at developing projects to address socially vulnerable issues in society supports educational initiatives related to the preservation of cultural heritage. As a result of a sociological survey conducted among key respondent groups— consumers, the target audience, and business partners—globalization and localization trends in ethnofuturism that influence the perception of Kazakh culture through fashion were identified. The analysis of the survey revealed key directions and their percentage distribution, as illustrated in Diagram 1.
Trends of ethnofuturism

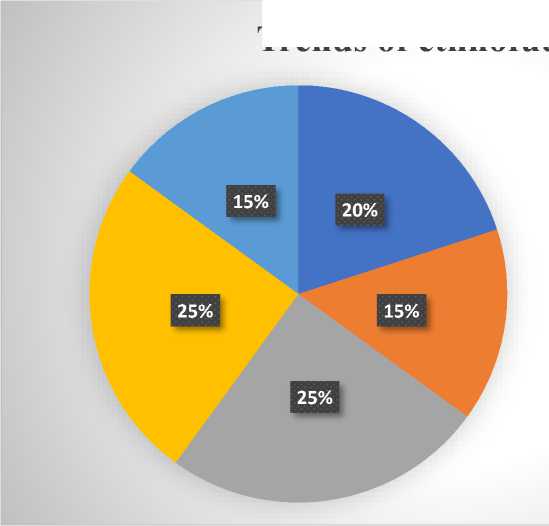
Diagram 1. Ethnofuturism trends of the Kazakhstani brand Global Nomads
-
■ Ethnofuturism as an Approach to Design
-
■ Innovations in the Interpretation of Traditions
-
■ Social and Cultural Significance
-
■ Influence on Global Fashion
■ Economic Aspect
Diagram 1 presents the percentage distribution of the results from a sociological survey among the main respondent groups (customers, target audience, business partners) who expressed their opinions on the ethnofuturism of the Kazakhstani brand Global Nomads. It reflects the following aspects:
-
- Ethnofuturism as an approach to design — 20%
-
- Innovations in the interpretation of traditions — 15%
-
- Social and cultural significance — 25%
-
- Influence on global fashion — 25%
-
- Economic aspect — 15%
Based on the research conducted, the diagram visualizes the key areas on which the brand focuses and their importance to the overall concept.
Conclusion
Thus, the study of the processes shaping ethnofuturism in the Kazakhstani clothing brand Global Nomads within fashion design has revealed the following key trends, reflecting the main points of the research:
-
1. The ethnofuturistic approach to the design of the Global Nomads clothing brand reshapes the visualization of traditional forms of nomadic Kazakh culture through the following key principles: the revival of ethnic traditions, the symbiosis of the traditional and technological, a critical view on the unification of cultures, the ecological aspect, cultural dialogue, avant-garde, and a cosmopolitan perspective. The focus on preserving, adapting, and reinterpreting nomadic Kazakh cultural traditions in a new context is synthesized with innovative design solutions and sustainable technologies. The Kazakhstani interpretation of ethnofuturism is open to intercultural dialogue, exchange, and adaptation of traditional values, reflecting the core principles of sustainable development and cultural dialogue of the Great Silk Road.
-
2. Innovations in the interpretation of national traditions by the brand Global Nomads reflect the potential for preserving the cultural code
-
3. The social and cultural significance of the clothing brand Global Nomads carries an important social mission related to the popularization of Kazakh culture and its international recognition, captivating the world with Kazakhstan and Central Asia. By exploring, preserving, and reviving the cultural codes of the Great Steppe civilization, the brand brings them to life through unique clothing designs imbued with deep ideas and meanings. The brand's role model is based on the concept of a "traveling person," someone open to the world, progressive, and actively exploring new territories and knowledge. By creating a bridge between tradition and the future, the brand helps strengthen national identity in the context of globalization through ethnofuturism. The brand’s active social and community life is open to collaboration in various fields: charity, sports, art, education, and more.
-
4. The influence of the brand Global Nomads on global fashion synthesizes with key life values: quality, freedom, meaning, and beauty, reflecting a connection to the global changes in human civilization. Positioning itself as a constructor of the image of the future, the identity of the neo-nomads emerges as free travelers navigating both terrestrial and digital spaces. By enhancing cultural diversity on the global fashion scene, the brand Global Nomads contributes to the development of the Kazakhstani fashion industry, successfully blending national motifs with global trends, and offering unique and in-demand products in international markets.
-
5. The economic aspect of the brand Global Nomads supports the development of Kazakhstan's creative industry. Collaboration with local projects, artisans, and craftsmen creates a foundation for the sustainable development of the local economy and the promotion of cultural products on a global scale.
of Kazakh nomads in the context of globalization and cultural dialogue. Ethnofuturism promotes the renewal of traditional forms through the use of new materials, technologies, and production methods. The brand's designers successfully reinterpret and adapt cultural elements into contemporary clothing while maintaining their authenticity. A profound understanding of cultural heritage through technology and sustainable practices shapes a relevant fashion trend—the commercialization of ethnic elements—in the following ways: the use of technology to preserve traditions, the digitization of ornaments, high-tech fabrics, global interpretations of local motifs, intercultural synthesis, designer collaborations, eco-fashion and sustainability, ethical production, quality models designed for long-term use, cultural immersion through interactive technologies, augmented reality (AR), QR codes and digital storytelling, modernization of traditional silhouettes, adaptation to contemporary needs and the conditions of digital nomads, and modular clothing designs.
Thus, the conducted research has achieved its goal of analyzing the formation of ethnofuturism trends in clothing design through the example of the Kazakhstani brand Global Nomads. The study revealed that the preservation of cultural heritage and integration with contemporary fashion trends are possible through the actualization of national identity and competitiveness in the fashion world. The prospects and opportunities for implementing and applying the findings include entering international markets thanks to the unique combination of traditional and modern elements. Sustainable development through the use of traditional motifs from Kazakh nomads in clothing for creating ecofriendly and ethical products supports Kazakh cultural identity and promotes it to a broader audience. The development of innovative clothing collections fosters social responsibility and a positive brand image by supporting local crafts and cultural initiatives. Building a dialogue between cultures contributes to the promotion of Kazakh culture on the international stage and its influence on global fashion.
Список литературы The ethnofuturism of Kazakhstan’s clothing brand “Global Nomads” in the Fashion Design
- Кудабаыева А.К., Жумабаева А.Е. Этникалық стильде материалға принт түсіру арқылы әйелдер топтамасының жобалау протсесін әзірлеу. АТУ Хабаршысы, №4, (2023):13-18.
- Mühlemann, C., Nikolaos Vryzidis (ed): The Hidden Life of Textiles in the Medieval and Early Modern Mediterranean. Contexts and Cross-Cultural Encounters in the Islamic, Latinate and Eastern Christian Worlds. Medieval and Post-Medieval Mediterranean Archaeology Series, III. Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, (2021): 579-581.
- Жангужинова М., Ербол А., Ашинов Р.Б., Талгатбекова А.Ж., Абекова А.Ж. Архетипы символов номадов (на примере казахского костюма). Педагогика и психология. №4 (53), (2022): 273-283
- Жангужинова М., Ербол А., Жуманазарова А.Е., Рысымбетов Е.К., Есеналиева Д.Б. Аксиологическии анализ символизма в казахском костюме. Педагогика и психология. №3 (52), (2022): 273-283
- Demir, G., Ilhan Korkmaz, R., Nosch, M.-L. Ottoman clothing regulations and the Kemalist clothing legislation in the early 20th century. Artex journal 1 (2022): 49- 66.
- Zhanguzhinova M.Ye., Iskakova A.O., Kumargaliyeva N., Kaupuzs A. Image design for Kazakhstan children’s sports uniform. The Journal of Almaty Technological University. no 2, (2024):135-143.
- Zhao, F. and Nosch, M.-L. (eds.) Textiles and Dress cultures along the Silk Roads. Thematic Collection of the Cultural Exchanges along the Silk Roads. UNESCO publications. (2022):401.
- Nosch, M.-L., Zhao, F., Frankopan, P. The World-Wide Web. In Nosch, M.-L., Zhao (eds.) Textiles and Dress cultures along the Silk Roads. UNESCO publications. (2022):362-401.
- Andersson Strand, E., Mannering, U. and Shamir, O. Sheep wool across Eurasia. In Textile and clothing along the Silk Roads. Feng Zhao and Marie- Louise Nosch (eds). Unesco, China National Silk Museum. Hangzhou. (2022):31-34
- Boughlala, A., & Smelik, A. Tracing the History of Digital Fashion. Clothing and Textiles Research Journal, (2024).
- Portia Wang, Mark R. Miller, Eugy Han, Cyan DeVeaux, Jeremy N. Bailenson, Understanding virtual design behaviors: A large-scale analysis of the design process in Virtual Reality, Design Studies, no 90, (2024):101237.
- Kang, J. Y. M., & Choi, D. Artificial intelligence-powered digital solutions in the fashion industry: a mixed-methods study on AI-based customer services. International Journal of Fashion Design, Technology and Education, 17(2), (2023):162–176.
- Suhaimi, S. N., Walters, A., & Ward, J. Design thinking mindset: a user-centered approach toward innovation in the Welsh creative industries. International Journal of Design Creativity and Innovation, no 12(4), (2024): 238–257.
- de Wet, A. J. C., & Smal, D. Innovative, environmentally sustainable fashion design: a blended learning teaching framework that supports positive emotions and creativity during a design process. International Journal of Fashion Design, Technology and Education, no 17(2), (2023):133–143.
- Dahunsi, B., Woelfle, H., Gagliardi, N., & Dunne, L. E. Review and synthesis of expert perspectives on user attribute and profile definitions for fashion recommendation. International Journal of Fashion Design, Technology and Education, no 17(2), (2023):202–213.


