Milk systems of plant and animal origin: nutrient profile and significance for forming the physiological value of functional products
Автор: Ibragimova L.N., Yensebayeva G.B., Shvets S.V., Ibragimova R.Z., Akhramov N.A., Petrenko A.A., Ibragimov R.Z.
Журнал: Вестник Алматинского технологического университета @vestnik-atu
Рубрика: Технология пищевой и перерабатывающей промышленности
Статья в выпуске: 4 (150), 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article presents an analytical review of the literature on milk systems of animal and plant origin. Milk systems are considered as natural and biotechnological dispersed structures that combine proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and bioactive substances, providing high physiological and nutritional value. In the context of modern functional nutrition, they act as a universal technological platform for creating preventive and therapeutic health-promoting products. Particular attention is paid to hybrid systems that combine components of animal and plant origin, allowing for nutrient, antioxidant, and metabolically active compound synergy, which ensures an expanded range of physiological effects and increased bioavailability of key components. The aim of the work is to conduct an analytical review of the composition, structure, and functional properties of milk systems of animal and plant origin, as well as to determine directions for their integration into technologies of functional foods and nutraceuticals. The concept of the study is based on the principles of food system biodesign, implying the deliberate combination of natural matrices and biotechnological processes to achieve a targeted physiological effect. A systematic analysis method was applied to scientific publications, patent sources, and experimental data devoted to the chemical composition, fermentation, microencapsulation, and bioavailability of active components of milk systems. The results showed that animal milk is a source of easily digestible proteins and minerals, while plant analogues are rich in unsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants. Their combination ensures amino acid complementarity and enhances antioxidant potential. Fermentation and microencapsulation technologies are considered key tools for preserving probiotics and vitamins. This work contributes to the development of the concept of functional and sustainable nutrition, forming a scientific and practical basis for the creation of domestic functional beverages based on animal milk and milk derived from plant seeds of Kazakhstan.
Milk systems, functional products, fermentation, probiotics, microencapsulation, nutraceuticals
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140313227
IDR: 140313227 | УДК: 65.63.01 | DOI: 10.48184/2304-568X-2025-4-139-146
Текст научной статьи Milk systems of plant and animal origin: nutrient profile and significance for forming the physiological value of functional products
IRSTI 65.63.01
Milk systems represent natural and biotechnological dispersed structures composed of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, minerals, and biologically active components that possess high physiological value. In modern understanding, milk systems include both animal-derived milk and its plant-based analogues obtained from seeds, nuts, cereals, and legumes. Both types of systems share a common functional purpose — to provide the human body with essential nutrients, antioxidants, and compounds that support metabolic and immune balance [1, 2].
Table 1. presents the classification of plant-based and animal milk systems according to their origin.
Table 1. Classification of plant-based and animal milk systems by origin
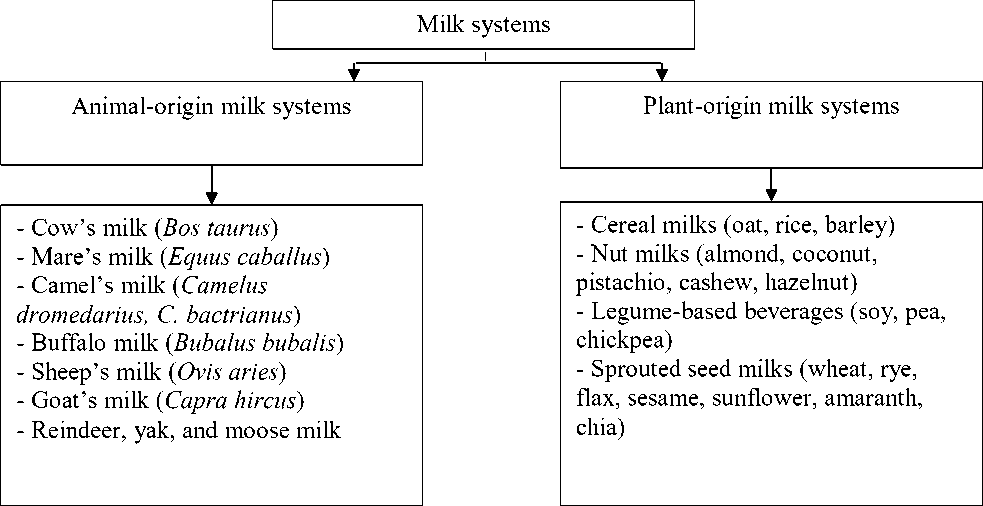
Milk systems of animal and plant origin differ in their nature, structure, and biochemical composition; however, they perform similar physiological functions, providing the human body with essential nutrients, vitamins, and bioactive compounds.
Animal milk is a natural biological product intended for the nourishment of offspring, containing a balanced complex of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals, and vitamins. Cow’s milk is traditionally used as a primary source of calcium, phosphorus, and high-quality protein. Mare’s and camel’s milk are characterized by lower fat content and reduced β-lactoglobulin levels, making them more hypoallergenic and suitable for people with cow’s milk protein intolerance. Camel’s milk is rich in immunoglobulins and exhibits pronounced antidiabetic properties, while buffalo milk contains higher amounts of fat and minerals, which give it a rich flavor and high energy value.
Goat and sheep milk are easily digestible and contain short-chain fatty acids that have a beneficial effect on lipid metabolism. In northern and mountainous regions, reindeer, yak, and moose milk are traditionally consumed; they are high in fat and enriched with vitamins A and D. Animal-derived milk systems provide the human body with complete proteins and fats, support the musculoskeletal system, and possess high biological value [1–4].
Plant-based milk systems are aqueous emulsions obtained from plant raw materials such as seeds, cereals, nuts, and legumes. They serve as an important alternative to traditional milk and are used as sources of plant proteins, unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins, and antioxidants.
Cereal milks (oat, rice, barley) contain complex carbohydrates and β-glucans that help regulate cholesterol levels. Nut beverages (almond, coconut, pistachio, cashew, hazelnut) are rich in tocopherols and polyphenols, providing antioxidant effects. Legume-based drinks (soy, pea, chickpea) are valuable sources of plant protein and isoflavones.
A special category includes milk systems derived from sprouted seeds (wheat, rye, flax, sesame, sunflower, amaranth, chia), which become enriched with B vitamins, enzymes, and polyphenols during germination. These systems are characterized by high nutrient bioavailability and a mild taste, making them promising bases for functional beverages and health-oriented foods [5–9].
In general, both animal and plant milk systems serve as important platforms for the development of functional products aimed at preventing metabolic disorders, supporting the immune system, and maintaining the body’s energy balance.
The aim of this work is to conduct an analytical review of the composition, structure, and functional properties of milk systems of animal and plant origin, as well as to identify directions for their integration into the technologies of functional foods and nutraceuticals. The research concept is based on the principles of food system biodesign, which involve the deliberate combination of natural matrices and biotechnological processes to achieve targeted physiological effects.
Materials and methods
The study was conducted as an analytical review using domestic and international scientific publications, patent sources, and recent experimental research data focused on the composition, structure, and functional properties of milk systems of both animal and plant origin.
To systematize the information, databases such as Scopus, PubMed, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, MDPI, and open repositories of scientific journals were utilized. The analysis included articles published between 2010 and 2024, containing data on the chemical and nutrient composition of milk, as well as processes of fermentation, microencapsulation, and bioavailability of active components.
The methodological approach included:
-
• Systematic and comparative analysis of literature data on the composition and functional characteristics of milk systems;
-
• Structural and biochemical interpretation of protein and lipid fractions, considering their origin;
-
• Evaluation of technological approaches aimed at improving the stability and bioavailability of bioactive compounds (fermentation, microencapsulation, probiotic technologies).
Data interpretation was carried out from the standpoint of the concept of functional and sustainable nutrition, which emphasizes the rational combination of animal and plant raw materials to create products with targeted physiological effects.
Results and discussion
The chemical and nutrient composition of milk is determined by its natural origin, the feeding base, and processing technology. Animal-derived milk systems are characterized by a balanced amino acid composition and high levels of calcium, phosphorus, and B vitamins, whereas plant-based milk systems generally contain lower amounts of protein but are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, dietary fiber, isoflavones, and antioxidants (Table 1) [1–4].
Proteins in animal milk (mainly casein and whey fractions — β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin) have high biological value and digestibility (up to 95%), while plant proteins are often limited in methionine and lysine content. However, due to fermentation and seed germination, the bioavailability of plant proteins significantly increases, and the profile of essential amino acids becomes more balanced [5].
Table 2. Comparative chemical composition of milk systems of animal and plant origin [1–9]
|
Indicator |
Animal milk systems (average value) |
Plant milk systems (average value) |
|
Protein, % |
2.8–3.8 |
0.5–2.0 (up to 3.0 after fermentation) |
|
Fat, % |
3.0–7.5 (depending on species) |
1.0–4.5 (mainly unsaturated fatty acids) |
|
Lactose, % |
4.5–5.0 |
absent |
|
Minerals (Ca, P, Mg), mg/100 ml |
Ca ≈ 120; P ≈ 95; Mg ≈ 10 |
Ca ≈ 25–60; P ≈ 40–80; Mg ≈ 30– 50 |
|
B-group Vitamins |
В 1 0.04; В 2 0.18; В 12 0.9 µg |
В 1 0.06–0.10; В 2 0.02–0.05 |
|
Antioxidants |
carotenoids, tocopherols, glutathione |
polyphenols, tocopherols, phytosterols |
|
Main fatty acids |
palmitic, stearic, oleic |
linoleic, α-linolenic, oleic |
|
рН |
6.5–6.8 |
6.7–7.2 |
|
Energy value, kcal/100 ml |
60–80 |
30–50 |
The composition and ratio of protein fractions vary among animal species. Mare’s and camel’s milk are characterized by low β-lactoglobulin content and a predominance of whey proteins similar in composition to human milk, ensuring high bioavailability and hypoallergenic properties. Buffalo and sheep milk contain increased amounts of casein and calcium, while goat’s milk is distinguished by its high content of short-chain fatty acids (capric and caprylic), which enhances lipid digestibility [10, 11].
The lipid fraction of animal milk is mainly represented by saturated fatty acids (C14:0–C18:0), whereas plant systems contain predominantly mono-and polyunsaturated fatty acids (oleic, linoleic, and α-linolenic), which exhibit hypocholesterolemic effects [7].
The fatty acid profile also plays an important role: the presence of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids determines the anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective properties of milk systems. Biologically active components — peptides, flavonoids, phytosterols, and tocopherols — enhance antioxidant activity, forming a complex physiological effect [12].
The mineral composition also differs: animal milk is rich in calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium, while plant-based beverages contain higher amounts of magnesium, potassium, and antioxidant elements (Fe, Mn).
Particular attention is given to biologically active compounds — vitamins (A, D, E, K, B1– B12) and natural antioxidants (polyphenols, tocopherols, carotenoids), which determine the physiological value of milk systems [6].
Despite compositional differences, plant and animal milk systems complement each other in terms of bioactive substances: animal-based systems provide easily digestible proteins and minerals, while plant-based systems supply antioxidants, unsaturated fatty acids, and dietary fibers. Their combined use forms the foundation for developing functional and preventive nutrition products [9].
The biological and physiological value of milk systems is determined by the degree of nutrient absorption, bioavailability, and the functional effects on the human body. Animal milk (cow, mare, camel, goat, buffalo) is traditionally considered a source of complete protein, calcium, and B vitamins, while plant-based milk systems (derived from sprouted seeds, nuts, legumes) are valuable sources of unsaturated fatty acids, polyphenols, and dietary fibers with systemic antioxidant and metabolic-regulatory effects [1, 13, 14].
Nutrient bioavailability in animal milk reaches 90–95% due to the optimal ratio of casein to whey proteins and the presence of phosphopeptides and trace elements that contribute to bone mineralization [15]. In plant-based milk systems, the digestibility of proteins and trace elements depends on the processing method. Fermentation and seed germination reduce antinutritional factors (phytic acid, protease inhibitors), thereby increasing the availability of iron, zinc, and amino acids [16].
Fermented forms of milk (ayran, shubat, kumis, yogurt) contain live cultures of Lactobacillus , Bifidobacterium , and Lacticaseibacillus , which help maintain normal gut microbiota and synthesize short-chain fatty acids (acetate, propionate, butyrate) that improve mucosal barrier function [17]. Fermented plant-based analogues can also possess probiotic potential: Lactobacillus plantarum and L. fermentum metabolize phenolic compounds of sprouted grains, producing bioactive metabolites with prebiotic effects [18].
Protein hydrolysates of mare’s and camel’s milk exhibit pronounced antioxidant and antiglycation properties due to the presence of peptides that inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and activate antioxidant enzymes [19]. Plant-based milk systems, owing to polyphenols and isoflavones, additionally reduce serum glucose and cholesterol levels, as confirmed by clinical studies on metabolic syndrome models [20].
The immunoregulatory effect of mare’s and camel’s milk is associated with the presence of lactoferrin, immunoglobulins, and antimicrobial peptides that enhance macrophage and NK-cell activity [21]. In plant-based milk systems, similar properties are provided by polyphenols, phytosterols, and tocopherols, which modulate cytokine expression (IL-6, TNF-α) and NF-κB– dependent inflammatory pathways [22].
Modern approaches to functional nutrition are based on the principle of amino acid complementarity: combining milk proteins (rich in leucine and methionine) with plant proteins (rich in lysine and arginine) allows for a complete amino acid profile and enhances the biological value of the product [23]. Such systems demonstrate synergistic effects, improving antioxidant activity, lipid metabolism, and resistance to oxidative stress [24].
Animal and plant milk systems represent complementary matrices that provide a wide range of physiological effects — from antioxidant and metabolic to immunomodulatory. Their rational combination forms the foundation for the development of functional foods aimed at preventing metabolic syndrome, dysbiosis, and chronic inflammatory processes.
Milk systems of animal and plant origin play a central role in functional food technology due to their high nutritional and biological value and their ability to serve as efficient carriers for probiotics, vitamins, peptides, and antioxidants [1, 6]. Current research focuses on the creation of hybrid systems that combine the advantages of animal proteins and plant biomolecules — amino acids, polyphenols, and unsaturated fatty acids — ensuring a synergistic physiological effect and product stability during storage [25].
Milk systems are widely used in the production of probiotic yogurts, beverages, porridges, and smoothies, where the protein-lipid matrix is combined with live cultures such as Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus thermophilus, and others [25]. The incorporation of plant extracts (including matcha tea, herbs, vitamins, and minerals) enriches the product with antioxidants and bioactive compounds, enhancing its preventive properties.
Combined fermented beverages based on milk and plant extracts demonstrate higher antioxidant activity and lipid oxidation stability compared to traditional dairy products [26, 27].
Protein concentrates and isolates derived from milk and plant raw materials (soy, oat, almond, hemp) are used in the formulation of nutraceutical complexes and sports nutrition products. The combination of animal and plant proteins provides a complete amino acid profile and contributes to more efficient muscle recovery after physical exertion [28]. In addition, the use of milk protein hydrolysates supplemented with antioxidants (EGCG, polyphenols) enables the creation of functional beverages with prolonged restorative and anti-inflammatory effects [29].
Key challenges in developing functional milk-based products include maintaining protein and lipid stability during heat treatment, ensuring compatibility with probiotics, and preserving the activity of added bioactive substances [30]. Factors such as pH, temperature, and fermentation duration significantly affect probiotic viability and protein matrix structure. At pH 6.0–6.5 and temperatures ≤45 °C, maximum viability of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum cells is maintained [31].
To enhance stability and prolong the activity of biomolecules, technologies of microencapsulation of peptides, vitamins, and antioxidants are applied using protein (caseinate, whey isolate) and polysaccharide (alginate, pectin, chitosan) carriers
-
[32] . Such systems protect active substances from degradation during pasteurization and oxygen exposure and allow controlled release in the gastrointestinal tract [33].
The preservation of bioactive substances largely depends on packaging technology. The most effective are aseptic filling and the use of multilayer barrier materials protecting against light and oxygen [34]. The use of mild fermentation and pasteurization conditions (≤70 °C) minimizes the loss of catechins, vitamins B and C, tocopherols, and flavonoids, which is especially important for the development of combined beverages based on milk and plant extracts [35].
Milk systems serve as a universal technological platform for creating next-generation functional products — from probiotic yogurts and protein blends to fermented beverages with high antioxidant and metabolic activity. The combination of animal and plant raw materials provides not only an optimal nutrient profile but also a synergistic physiological effect aimed at strengthening health and preventing chronic diseases.
Modern trends in functional nutrition are directed toward the development of milk and plant– milk systems with targeted physiological effects — adaptogenic, neuroprotective, antioxidant, and probiotic [36–38]. The advancement of such products is based on in-depth research into the biochemical mechanisms of action of biomolecules — peptides, polyphenols, unsaturated fatty acids, and amino acids — as well as their interactions in combined applications.
Priority directions include:
-
• Development of milk and plant–milk products with adaptogenic and neuroprotective properties. The combination of L-theanine and matcha tea catechins with bioactive peptides from mare’s and camel’s milk shows potential for regulating cognitive function, stress response, and neuroinflammation [39]. Such systems may be used in the prevention of cognitive disorders and as part of specialized nutrition for mental and physical performance.
-
• Formulation of combined probiotic beverages with plant extracts. The use of symbiotic combinations (Lactobacillus plantarum, Bifidobacterium breve, matcha extract, Melissa officinalis, Rhodiola rosea, Schisandra chinensis) supports gut microbiota and enhances stress resistance. These products exhibit antioxidant, antiinflammatory, and metabolic effects, making them promising for metabolic syndrome prevention [40].
-
• Nutraceutical formulas for metabolic regulation. Scientific studies confirm that combining
milk peptides (especially casein hydrolysates) with plant polyphenols enhances the activity of AMPK and Nrf2 signaling pathways, contributing to the reduction of hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and oxidative stress [41]. The implementation of such complexes in dry blends and beverages offers potential for preventing metabolic disorders.
Conclusions
For Kazakhstan, special importance lies in the use of domestic resources — mare’s, camel’s, and cow’s milk, as well as plant materials (willowherb, cistanche, rosehip, barberry, sea buckthorn, licorice). These ingredients possess high biological value and can serve as the foundation for developing regional functional products with export potential [42].
The introduction of local technologies for fermentation, microencapsulation, and standardization of bioactive compounds will enable the creation of a product line that meets international quality and safety standards (ISO 22000, Codex Alimentarius, EFSA).
The future development of functional milk systems is closely linked to the concepts of sustainable and personalized nutrition. Hybrid products of animal and plant origin provide an optimal balance between environmental sustainability, nutrient density, and individual physiological needs.
The integration of artificial intelligence and nutrigenomics technologies into formulation development will allow the creation of personalized dietary recommendations based on genetic, metabolic, and microbiome profiles, opening new horizons for precision functional nutrition [43].


