Лазерный diy-реогониометр для наблюдения эффекта Вайсенберга в сгущенных молокопродуктах как неньютоновских жидкостях
Автор: Градов Олег Валерьевич
Журнал: Молочнохозяйственный вестник @vestnik-molochnoe
Рубрика: Технические науки
Статья в выпуске: 2 (10), 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В этой статье описывается современный метод наблюдения эффекта Вайсенберга в сгущенном молоке или взбитых сливках с использованием простейшей лазерной оптической установки. Метод DIY, который будет описан здесь, включает минимальную номенклатуру недорогих или подержанных устройств и аксессуаров. Теперь мы опишем только общую методику реометрических измерений с этой установкой, так как любое изменение в указанном примере может быть обеспечено основным принципом конструкции установки.
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14998999
IDR: 14998999 | УДК: 637.142:532.135
Текст научной статьи Лазерный diy-реогониометр для наблюдения эффекта Вайсенберга в сгущенных молокопродуктах как неньютоновских жидкостях
Введение.
В последние десятилетия в молочно-хозяйственной и молочно-технической практике все большее значение придается не только химически-определяемым вкусовым качествам продукта, но и его консистенции, определяемой реологическими методами. Современная эра экспериментальной реологии молочных продуктов началась с книги «Dairy Rheology” [1], выпущенной издательством Wiley1 в 1992 году. Набиравшие вес компьютеризованные методы были внедрены, в основном, в более поздних монографиях по пищевой реологии [2-7]. Следует отметить, что в работах [5, 6] интенсивно внедрялся коллоидно-физический подход к проблеме, что, по-видимому, обусловливалось коллоидной физико-химической природой функционального органолептического восприятия консистенции [8, 9], поэтому автоматизированное исследование реологических характеристик коллоидных продуктов и субпродуктов в молочной и сыроваренной промышленности являет собой физиологически оправданную необходимость. Так, в монографии по “сырной науке” (“cheese science”) [10] за 2000 год в 13 части можно обнаружить утверждения о необходимости реологических измерений в сырной промышленности, а уже в 2003 году появляется специализированная монография по исследованию текстур и реологии сыров [11].
Особый интерес в реологическом аспекте представляет собой сгущенное молоко, что обусловлено его свойствами как неньютоновской жидкости, демонстрирующей известный для подобных сред эффект Вайсенберга (Weissenberg effect) [12]. Технологически данный эффект проявляется как закручивание вязкой сгущенно-молочной субстанции на стержень при вращении его в данной среде. Для исследования эффекта Вайсенберга используется достаточно элементарный, однако отчасти забытый во многих научных направлениях2 к настоящему времени прибор - реогониометр, специально разработанный К. Вайсенбергом [13, 14] и известный в литературе как реогониометр Вайсенберга [15-18]3. Реогониометр позволял измерять вращающий момент и осевое усилие, используемое при вычислениях нормальной составляющей напряжения как следствия упругости образца. Первый реометр - реогониометр системы фон Вайссенберга базировался на платформе токарного станка с электроприводом, допускавшим изменение скорости (отсюда появившееся впоследствии наименование «реометр контролируемой скорости», нередко встречаемое в отечественной литературе). Для исследования биологических сред, к которым относится и составляющие молочных производств, использовалась специализированная вариация реогониометра К. Вайсенберга, получившая название «био-реогониометр» (bio-rheogoniometer) [19]. Весьма весомый вклад в модернизацию реогониометра К. Вайсенберга для его использования при анализе биологических сред был сделан Кингом и Копли (King R.G., Copley A.L.) [20-24].
В дальнейшем конструкция реогониометра неоднократно подвергалась изменениям (после установления корреляции между результатами реогониометриче- ских измере ний и результатами использования других методов [25]). Была увели- 1 Это издательство до сих пор является одним из лидеров по изданию книг в данном направлении. Только на лето 2013 года планируется издание двух книг по пищевой реологии, в которой будут рассматриваться как частный случай и вышеуказанные вопросы: Castell-Perez E., Dokic L., Dokic P. Rheology Applications to Food Quality and Product Development, 300 p., Blackwell Pub Professional (Wiley), 2013 (in press); Senge B., Kaldasch J. Handbook of Food Rheology and Technology, 450 p., Wiley-VCH, 2013 (in press).
-
2 Но встречающийся до сих пор в энциклопедических словарях «Springer» разных лет издания - см., напр.: Encyclopedic Dictionary of Polymers - 2007, p. 839, p. 1063; Encyclopedic Dictionary of Polymers - 2011, p. 632.
-
3 Уже в первом номере журнала «Tribology» за 1968 год был опубликован новостной проспект: Weissenberg rheogoniometer. Tribology, Vol. 1, Issue 1, p. 5 (1968).
чена информативность его результатов за счет возможности измерения множества дополнительных параметров при различных режимах, что стало активно использоваться на практике [26-33]. Впоследствии появилась возможность проведения на подобных приборах динамических измерений [34-36] высокой прецизионности, причем этот тренд поддерживался трендом к автоматизации измерений на данных устройствах, обусловленной появлением портативных компактных ЭВМ, доступных для лабораторного использования. Если в начале 1970-х гг. калибровка реогони-ометра по ньютоновской жидкости [37] осуществлялась аппаратным способом, но без использования вычислительных средств, то уже к концу десятилетия [38] в практику реогониометрии были внедрены компьютерно-опосредованные процедуры калибровки и измерения. Примеры аппаратов Вейсенберга этих периодов соответственно приведены на рис. 1 а, б. К сожалению, роль СССР в развитии мировой реогониометрии неопределенно мала (см., напр.: [39, 40]) и характеризуется преобладанием теоретических статей, тогда как функционально-аналогичные отечественные приборы, разрабатывавшиеся в то время, были малодоступны и / или носили отличные наименования4 (см., напр.: [41]).
Рисунок 1а. Реогониометр Вайсенерга (Courtesey of Sangamo Controls Ltd.)
4 Впрочем, были и исключения - см., напр.: Патент СССР SU 505937 «Реогониометр» (дата подачи заявки 27.07.1973, дата публикации 05.03.1976). Заявитель: СКБ полимерного машиностроения (авторы Гончаренко В.В., Васильченко Л.А., Городинская С.А., Трохин Ю.И., Ещенко А.И.). Этот прибор выпускался серийно.
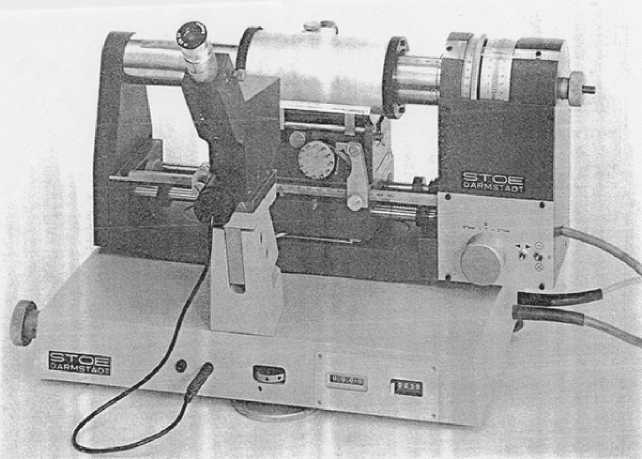
Рисунок 1б. Гониометр Вайсенберга (Courtesey of Stoe & CIE GMBH)
Следует немного остановиться на смысле гониометрической части названия прибора “реогониометр”. Речь в данном случае идет о гониометрии потока как прямом измерении распределения напряжений и деформаций в текучем материале в каждый момент времени и в любой точке пространства по полному телесному углу (именно поэтому производили измерения воздействия вторичных потоков на работу реогониометра [42] и анализировали эффект изменений поверхностного натяжения и углов контакта на результат измерений с использованием реогонио-метра [43]). C субъективной точки зрения, небезосновательны также гипотезы о влиянии на наименование К. Вейсенбергом своего прибора оптической аналогии с рентгеновской гониометрией, которой он как крупный кристаллограф, физико-химик и приборостроитель основательно занимался в довоенный период, причем ему же принадлежит честь разработки одного из передовых для своего времени рентгеновских гониометров [44].
Несмотря на оптическую аналогию, большинство реогониометров Вайсенберга и их аналогов [45, 46] имело электромеханический, а не оптический или оптоэлектронный тип регистрации информации. Однако впоследствии, апеллируя к конструкции Вайсенберга и цитируя его, W. Philippoff из Института Франклина (США) предложил оптический аналог метода, с помощью которого можно было корректно проводить стресс-анализ жидкостей [47, 48]. Почти одновременно с первой статьей данного автора по указанной тематике в том же журнале вышла еще одна его работа по инструментарию реологических измерений [49], а затем в тот же год еще одна его работа по измерениям в неньютоновской жидкости (неньютоновской вязкости) в Journal of Physical Chemistry [50]. Позднее было предложено совмещать измерения на реогониометрах Вайсенберга с поляризационной микроскопией [51], результатом чего стало появление первых опытных конструкций, в основу которых лег принцип измерения оптической анизотропии. В связи с этим необходимо отметить тот факт, что число Вайсенберга (критерий подобия, характеризующий вязкоупругое течение) по физическому смыслу указывает на степень анизотропии, порожденной деформацией и, вычисляясь как соотношение между временем релаксации и сдвиговой скоростью, имеет применимость к потокам с константной динамикой растяжения5 [52]. Поэтому возможно использование оптических методов, применимых в гидродинамике, индицирующих тренд (или векторное поле) потока, для регистрации информации в реогониометрах. Этот метод был применен уже в 1990-х гг. после появления средств лазерной велосиметрии (LDV + PIV - Laser Doppler Velocimetry + Particle Image Velocimetry), позволяющих трассировать направления потоков частиц [53]. В последнее время, пользуясь переходом от двумерной (2D) к трехмерной велосиметрии (3D-PTV - Three-Dimensional Particle tracking velocimetry) с использованием множественных (3-х или 4-х) камер с приборами с зарядовой связью в качестве регистраторов (что эквивалентно расположению объективной оптической схемы в таких методах конфокальной микроскопии как SPIM [54-56]), был осуществлен переход к кардинально новому - конфокальному методу реогониометрических и реометрических измерений6, разработанному на базе конфокальной лазерной сканирующей микроскопии.
Это дает возможность, используя оптические подходы, реализовывать конструкции реогониометрических приборов, не апеллируя к схеме-прототипу Вай-сенберга, так как на данный момент (начиная с 1990 года), права на реогониометр Вайсенберга принадлежат компании «Carri-Med”. Технологическая реализация подобных проектов не представляет затруднений, так как уже существуют методы вайсенберговского анализа, основанные на 3D-PIV [57] и стереоскопический метод PIV [58, 59], применимый для анализа потоков в неньютоновских жидкостях [60]. Так как, в общем случае, методы PIV используемые для реологических измерений и, в частности, измерений в неньютоновских жидкостях [61,62], достаточно универсальны и входят в направление Rheo-Particle Image Velocimetry (Rheo-PIV) [63], существует солидная физико-математическая и программная база для обработки данных подобных измерений. Кроме того, многие неспециализированные компьютерные способы отображения векторных полей, такие как визуализация векторных полей в методе компенсации движения (motion compensation) [64-66], используемом при преобразовании чересстрочной развертки в прогрессивную, деинтерлейсинге, могут быть использованы в ходе построения реологических картин анализируемого образца. Для этих целей можно использовать как специализированные средства MATLAB, так и общедоступные средства VirtualDub (например, фильтр Deshaker или же VirtualDub MSU Motion Estimation Filter разработки специалистов из Московского Государственного Университета), обладающие возможностью визуализации векторов движения.
Известно, что по ГОСТ 27709-88 “Консервы молочные сгущенные. Метод измерения вязкости” предписана морально-устаревшая вискозиметрическая методика определения η (Па·с), но приобретение современной реологической техники для многих отечественных лабораторий, увы, представляет собой финансово непосильную задачу. В ряде случаев, связанных с достаточно высокими требованиями к прецизионности измерений, этого не избежать, так как многие современные импортные реометры и реогониометры оснащены особыми подшипниками и системами компенсации, невоспроизводимыми в условиях отечественных мастерских, но для простейших демонстрационных случаев, связанных с иллюстрацией реологических и гидродинамических свойств сгущенно-молочных сред в образовательном процессе в специализированных ВУЗах и средних профессиональных учебных заведениях, возможно использовать упрощенную DIY-конструкцию, основные принципы построения которой и описываются в настоящей работе.
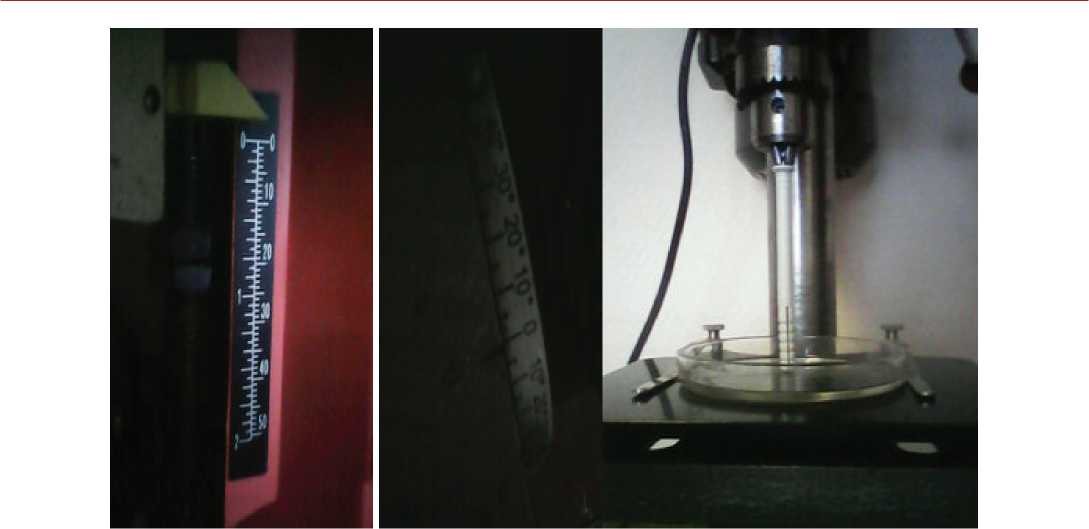

Рисунок 2. Шкалирование установки с использованием обычного предметного стола.
Материалы и методы.
По аналогии с конструкцией К. фон Вайсенбрега, в которой использовался токарный станок, нами была построена демонстрационная установка на шасси сверлильного станка. В общем виде конструкция установки складывалась из десятка базовых единиц. В основу ротационной части был поставлен станок “Delmax Master BD-200”, подключавшийся через блок регуляции, обеспечивающий изменение параметров вращения ротора, к сети. На его предметном столе монтировался термостатирующий (нагревательный / охладительный, от -20 °С до +80 °С) стол “Stromversorgung Heiz- Und Kuhltish”, на вращающейся платформе которого располагалась чашка Петри или иной лабораторный сосуд со средой-аналитом. Для фиксации лазерного модуля, подключавшегося к стабилизированному блоку питания, использовалась шарнирная металлоконструкция, заимствованная из паяльной станции CT-84NPD с автоподачей припоя. Использование CT-84NPD cо сменными жалами оправдано тем, что, обладая блоком регуляции температуры, она позволяла локально введением жала как зонда в анализируемую среду термическим воздействием менять характер процессов и конвекцию в аналите, что было небезынтересно регистрировать в ходе демонстрационных опытов, проводившихся со студентами на исследовательском практикуме автора по схеме DIY. Исходно регистрация и контроль температурной регуляции в различных зонах среды проводилась с использованием самописца “Servotrace” (“Sefram”, Paris) типа PE, снятого с модернизированного спектрофотометра Gilford 241 F, однако затем были использованы компьютеризованные подходы к сбору данных через элементарный АЦП, что студентами было осуществлено с использованием рабочей станции SHNIDER VGA AT SYSTEM 40 c поддержкой OS/2. Осуществлялись также малоуспешные попытки контроля рН среды (по аналогии с требованиями ГОСТ 26781-85 “Молоко. Метод измерения рН”) с применением рН-метра - ионного анализатора IONALYSER model 701A и специальных электродов, но в силу динамической специфики эксперимента воспроизводимость и стабильность данных в этом случае была достаточно низка. Для целей регуляции и контроля угловых и линейных параметров использовались шкалы, юстировка по которым исходно производилась на базе не термостатирующего, а обычного микроскопического предметного стола (см. рис. 2).

Рисунок 2. Общий вид установки с описанием частей.
Вся установка, таким образом, была построена на базе морально устаревших деталей на основе списанных много лет назад приборов, но, тем не менее, была автоматизирована и работоспособна. Общий вид системы с подробным описанием каждого из элементов приведен на рис. 3. Особый вопрос – лазерная часть установки – будет рассмотрен ниже после описания альтернативного варианта компоновки. Дело в том, что во многих случаях необходимо анализировать среду не в планарных, а в вертикальных аналит-резервуарах. Это, в частности, необходимо при последующем рефлектометрическом измерении в тех же кюветах, в которых производились реологические измерения. На этот случай в список оборудования практикума была внедрена подвижная четырехкюветная система с подачей, способная работать как своего рода автосамплер в данной DIY-установке. Данная деталь была заимствована из демонтированного спектрофлуориметра “Hitachi 512” середины 70-х гг., где предназначалась для подачи газа, воды и т.д. в кюветное отделение. Результат ее монтажа на предметном столе станка приведен на рис. 3а, а внешний вид нижней части с патрубками подачи воды и газа – на рис. 3б. Можно видеть, что данная система обладает большим потенциалом применимости в мо-лочнохозяйственнных измерениях.
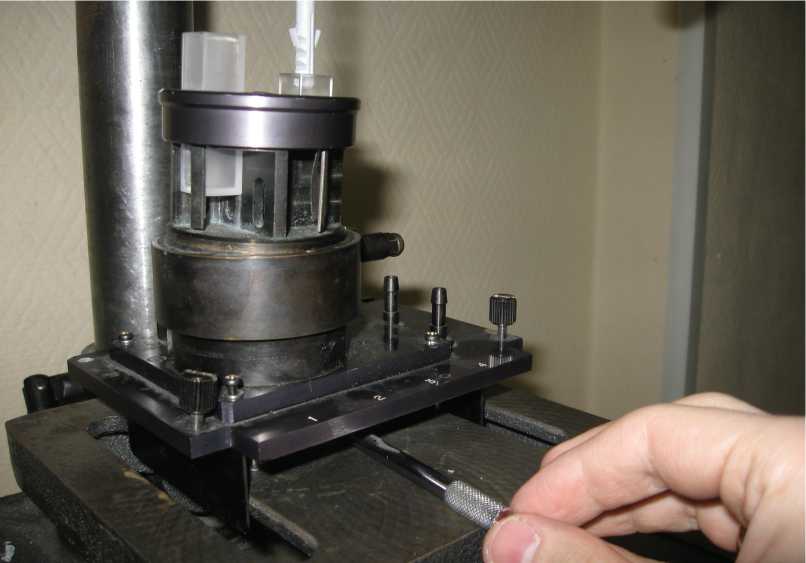

Рисунок 3а. Проточная кюветная система в составе реологической установки.
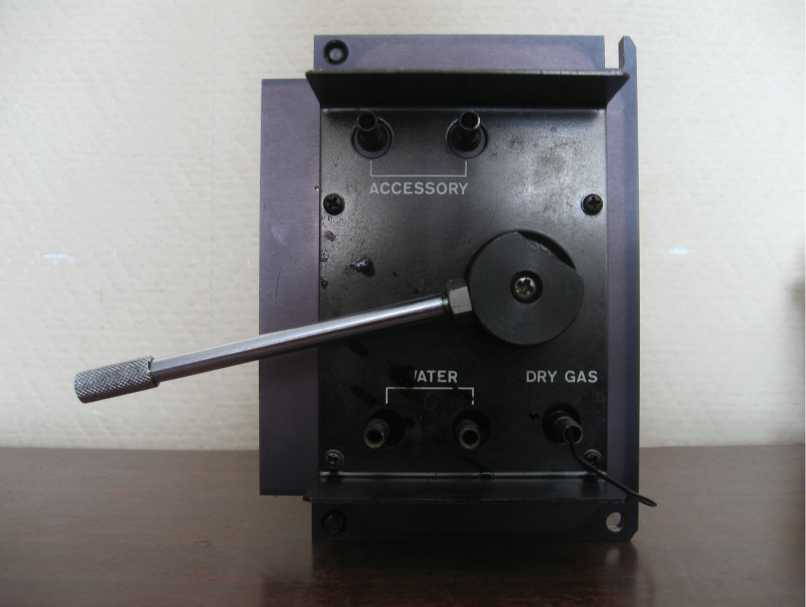

Рисунок 3б. Входные и выходные патрубки подачи газа, воды и пр. с нижней части кюветного отделения.
Для дискретной ступенчатой визуализации уровня подъема неньютоновской среды - сгущенного молока по вращающемуся зонду были использованы дешевые одноразовые пластиковые дюбели. Так как дюбель, в элементарном случае, является телом вращения, не имеющим эксцентриситета и анизотропии, установка SPIM-подобной системы на базе двух-четырех объективов и лазерной системы была неактуальна, вследствие чего система регистрации была заменена на более простую однообъективную схему (без увеличения, не микроскопического типа) с регистрацией частично размонтированной цифровой камерой в режиме макросъемки, результаты которой подавались на ЭВМ и обрабатывались путем картирования изофот. В качестве элементарных источников лазерного пучка для съемки в ходе студенческого практикума можно рекомендовать лазерные указки, прижим кнопки в которых осуществляется микровинтом фиксатора шарнирной металлоконструкции от CT-84NPD, хотя в более простом случае можно использовать элементарный зажим штатива. Нами были использованы лазерные указки зеленого, синего, желтого и красного свечения с достаточно широким корпусом для зажима в означенном фиксаторе. Этот набор может быть доступен в любых средних специальных и высших технических учебных заведениях, так как его общая стоимость не превышает нескольких тысяч рублей (цена варьируется в зависимости от мощности). Любые неоднородности изофот реометрической регистрации интерпретировались с физико-химических позиций и тщательно идентифицировались.
а б
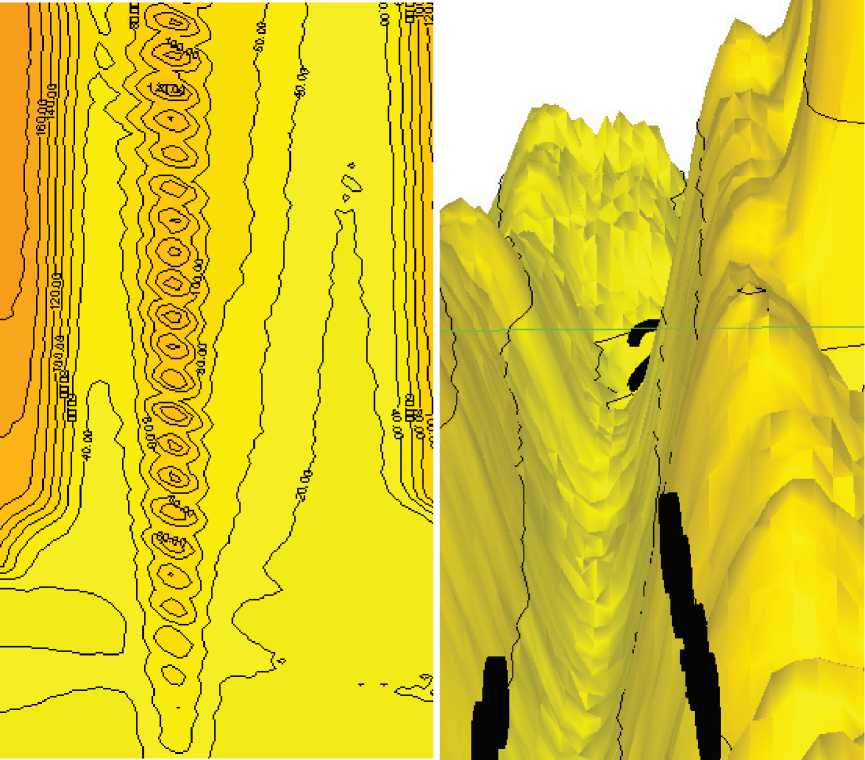
Рисунок 4. Наиболее сегментированный зонд с наилучшими результатами теста.
Результаты тестирования установки.
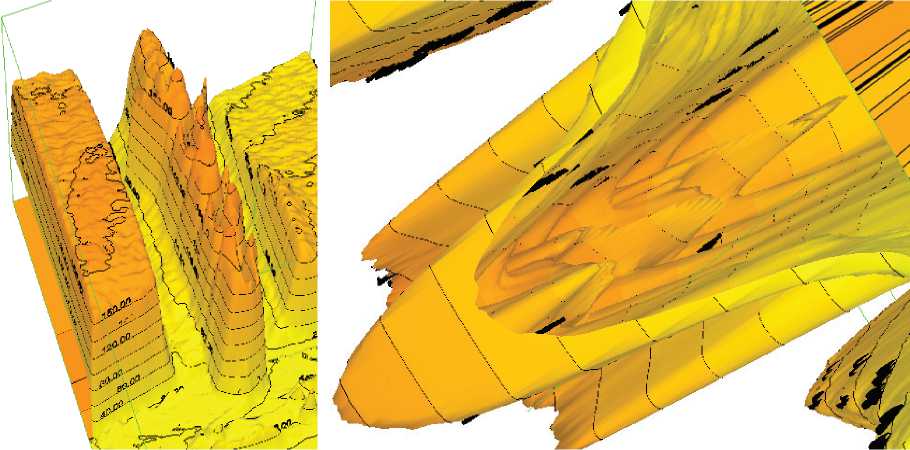
Ниже будут приведены некоторые результаты картирования изофот зондов-дюбелей в среде в ходе предварительного тестирования установки. По данным тестирования, более сегментированные дюбели более всего адаптированы для дискретной сегрегации среды в ходе наблюдений ее трека подъема. Так как использовались как отражающие зонды, так и зонды с высокой степенью поглощения, оптические параметры также были учтены в ходе тестирования. Наилучшие показатели были зарегистрированы при использовании зонда с отражающей металлической поверхностью и высокой регулярностью и частотой насечек. Результаты этих измерений приведены на рис. 4 а. Оптически-просвечиваемая зона трека вдоль зонда достаточно гетерогенна и не изоморфна поверхности зонда, что говорит о ее зависимости от параметров среды. Трехмерное оптическое картирование этой зоны дано на рис. 4 б. Зонды с меньшей сегментацией, оканчивающейся через относительно малое число сегментов, имеют худшие параметры, как это можно видеть из рис. 5.
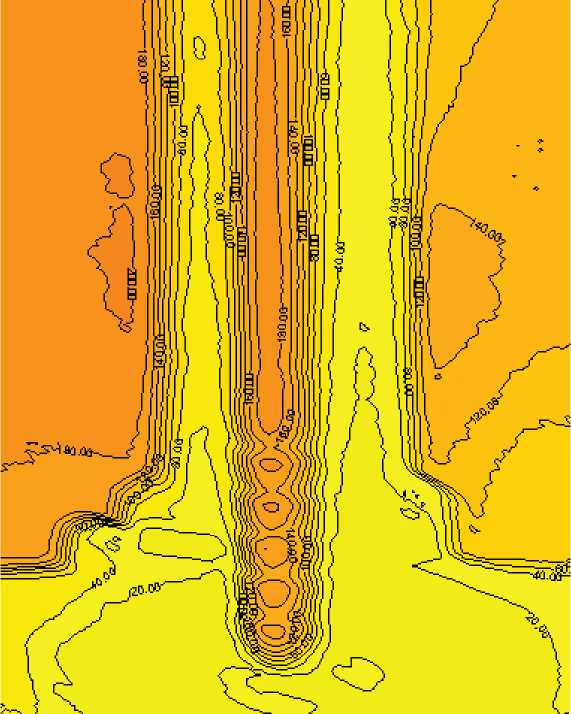
Рисунок 5. Результаты картирования изофот для менее сегметированного зонда.
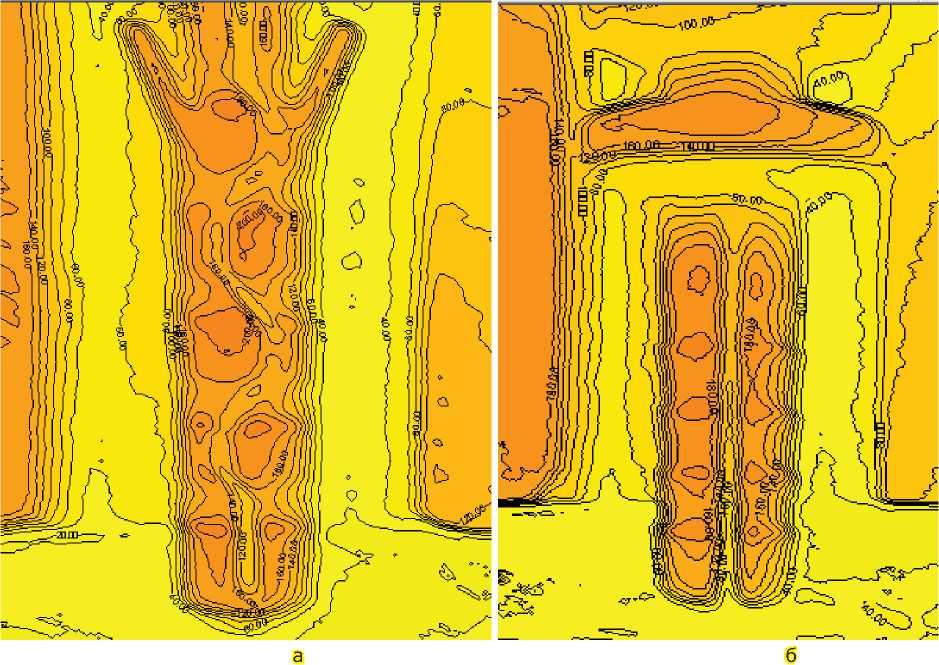
Небезынтересные эффекты наблюдаются на зондах-дюбелях с упругими оконечными фиксаторами, а также на модификациях с раздвоением. В первом случае при регистрации обтекания теряется прямая зависимость траектории потока от дискретных уровней зонда – извилистый паттерн не коррелирует с их формой, в отличие от того, как это видно было на предыдущих изображениях. Во втором случае (при наличии ограничителя типа «шляпки» и раздвоенного контура снизу) до определенных пределов каждый полуцилиндр дюбеля имеет свой автономный и не симметричный к другой половине паттерн. Пример первого случая приведен на рис. 6а, пример второго - на рис. 6б. Следует отметить, что в ряде случаев даже достаточно тонкое и высокоточное картирование по одиночному параметру не способ- но продемонстрировать механику и функциональные отличия профилей зондов. В таких случаях, как указывалось выше, логично прибегнуть к дифференциальному типу реологической визуализации – сравнивать карты поглощения и карты отражения, включая сравнение между зондами одинаковой формы, но с разными степенями поглощения или отражения. На рис. 6в приведен пример достаточно грубо-дискретного картирования со сплайн-интерполяцией зонда, диагностические изофоты которого приведены на рис. 6а. Распознать тонкую структуру паттерна по данному изображению фактически невозможно. Однако, инвертировав его (т.е. пойдя на выявление обратного параметра – поглощения), можно увидеть «изнутри» тонкую структуру этого пика, тем самым выявив на фоне пика зонда зоны потенциальной реологической напряженности или сорбции/фиксации аналита. Эта тонкая структура представлена на рис. 6г. Можно сделать очевидное заключение о большей информативности этого метода. Однако наиболее радикальным способом борьбы с собственными изофотами зонда и, как следствие, выявления исключительно реологии, а не оптических артефактов метода, является метод адсобрционного зонда-дюбеля, который позволяет визуализировать тонкую структуру в реологии анализируемой среды без учета изолиний зонда при обработке лапласианом.
в г
Рисунок 6. Экзотические формы вращающихся зондов и их трехмерная визуализация.
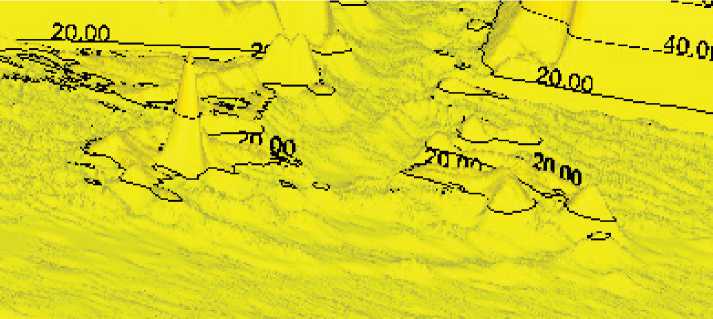
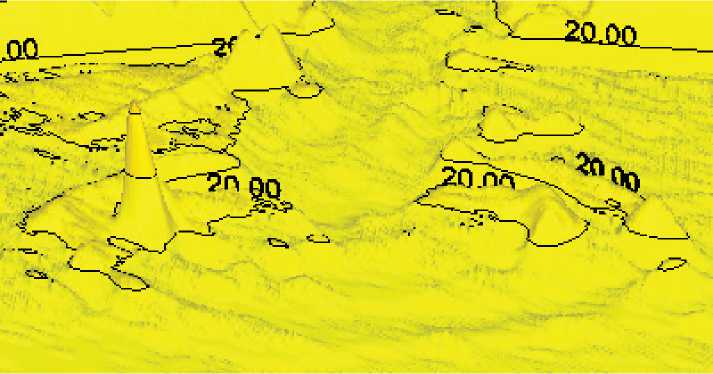
Для этого берется оптически-поглощающий черный дюбель или обычный дюбель со специально перекрашенной стойкой поглощающей краской поверхностью. Экстинция его может быть замерена и взята за условный ноль при обработке изображений, получаемых с камеры PIV-установки. Тогда только более светлые среды будут детектироваться на ней в виде положительных пиков с относительно высокой амплитудой. На рис. 7 приведены два примера одного и того же картируемого участка с обнуленным положением дюбеля-зонда, снятые с разным увеличением цифрового трансфокатора программы визуализации. Видно, что при различных увеличениях на диаграмме регистрируются явления разного масштаба, но самого стержня не видно, так как он по оптической плотности сопоставлен с уровнем “ватерлинии” юстировки (таким же путем можно регистрировать остаточные возмущения после удаления зонда из среды).
а
б
Рисунок 7. Разные масштабы визуализации при нивелированном зонде.
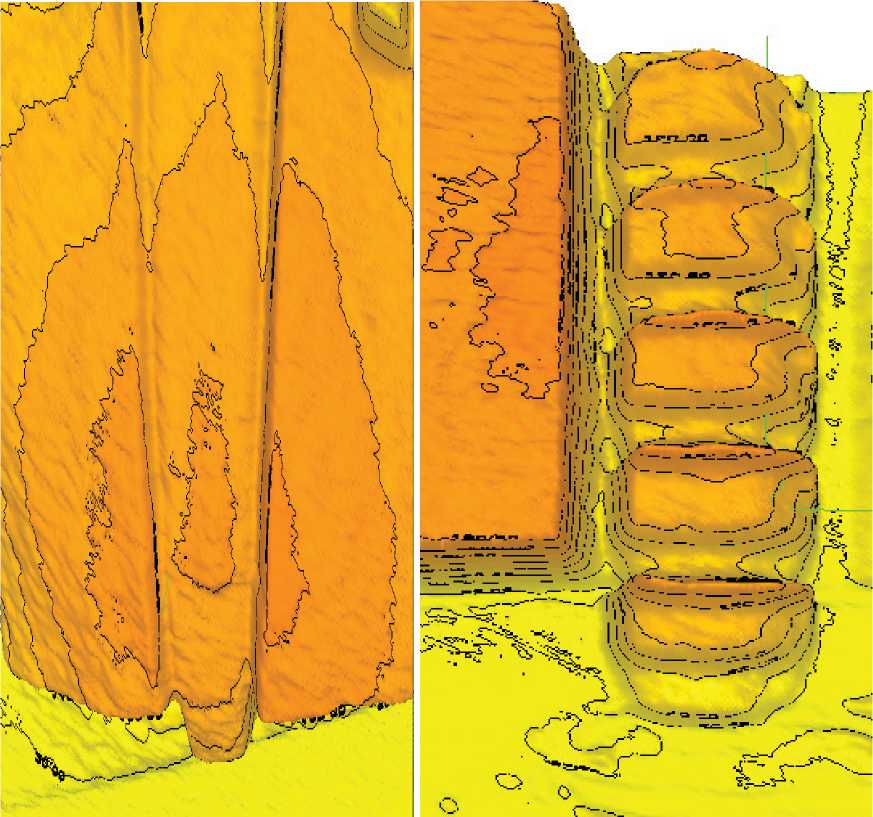
Наименьшей эффективностью демонстрации эффекта Вайсенберга при измерениях в сгущенно-молочной среде как неньютоновской жидкости показывает не-градуированный и несегментированный зонд с линейным угловым инкрементом. Его вид (функциональная 3D-репрезентация по изофотам) приведен на рис. 8а. Для сравнения на рис. 8б приведен аналогичный паттерн, реконструированный с сегментированного зонда. Очевидно, что по параметрам захвата среды второй (сегментированный) образец превосходит первый, хотя с точки зрения измерений, а не демонстрации, логично использовать обычный конический зонд. Обсчет любых результатов с формованных зондов значительно более сложен в силу их геометрической динамики, срабатывающей при увлечении неньютоновской жидкости. Однако, следует отметить, что в отличие от реометрических систем электромеханического типа, созданных по принципу разделения двигателей и измерительных преобразователей (separate motor and transducer, SMT), в методах оптической регистрации взаимодействием детектирующей и ротационной частей можно пренебречь, так как это не влияет на данные оптической обработки паттернов, получаемых как с дискретных, так и с линейных зондов. Более того, можно не использовать иных детекторов, кроме оптических, что удобно для малобюджетных лабораторий ССУЗов и ВТУЗов.
а б
Рисунок 8. Сравнение псевдотрехмерных репрезентаций линейного и сегментированного зондов.
Обсуждение.
Дискретный зонд работает подобно винту Архимеда (см. реконструкцию на рис. 9), вследствие чего сам управляет параметрами потока. Учитывая возможность варьирования скоростей блоком управления ротора станка, можно добиться эффекта Вайсенберга и не в неньютоноских жидкостях, а в обычном молоке, пользуясь подобными построениями [67]. Многие эффекты, наблюдавшиеся при применении дискретных и спирально-бороздчатых зондов, могут быть объяснены и симулированы с помощью известных подходов [68, 69]. Кроме того, возможно влияние зондов сложных форм как миксеров исходного молочного сырья на его консистенцию и коагуляционные эффекты, изменяющие характер потоков в процессе перемешивания [70] (хотя из животноводческого сырья и продуктов не только молочные продукты способны демонстрировать эффект Вайсенберга [71]). При попытках интерпретации и моделирования эффектов, регистрируемых в подобных экспериментах, логично, опираясь на практику последних лет, отраженную в монографиях, использовать группы Ли [72], методы компьютерной жидкостной динамики (CFD) и соответствующие программные пакеты (Autodesk Simulation CFD и др.) [73], численное моделирование [74].
Рисунок 9. Сегментированный метамерный зонд-дюбель как винт Архимеда.
Заключение.
Таким образом, предложенный DIY подход к разработке функциональных аналогов реогониометра фон Вайсенберга оправдывает себя. При минимальных вложениях средств и времени можно создать прибор с высокой степенью наглядности демонстрирующий на практических занятиях или студенческих практикумах эффект Вайсенберга и ряд других реологических феноменов. Получаемые формы визуализации достаточно наглядны, чтобы быть дидактически доступными даже для средних специальных учебных заведений, но, в то же время, достаточно эстетичны, что хорошо с мнемонической стороны преподавания. Автор не претендует на разработку нового метода, так как, как указывается им в обзорной части, существуют полные аналоги описанных конструктивных единиц и тектологических принципов их взаиморасположения в установке. Единственное что двигало в разработке настоящей тематики – это гуманистическое чувство по отношению к необеспеченным, как правило, современными измерительными приборами учебным лабораториям и желание внедрения конструктивного подхода студенчества к созданию установок на лабораторных практикумах, вырабатывавшееся ими в ходе педагогического эксперимента, в том числе – с использованием настоящей установки.
Автор специально не останавливался на реогониометрах типа Ламмимана и Робертса (как модернизированном реогониометре Вайсенберга), Адамса - Лоджа и альтернативном замещающем реогониометре Морозова, известных в РФ, поскольку информация о таких приборах хорошо известна в практике отечественной при- кладной реологии7. Измерения угловых характеристик по изображениям и, через них, - реологических параметров среды имеют значительную точность и для указанных целей не уступают указанным приборам.
Список литературы Лазерный diy-реогониометр для наблюдения эффекта Вайсенберга в сгущенных молокопродуктах как неньютоновских жидкостях
- Prentice J.H. Dairy Rheology: A Concise Guide, 165 p., Wiley-Interscience, 1992.
- Steffe J.F. Rheological methods in food process engineering, 418 p., Freeman Press, East Lansing, Michigan, 1996.
- Aguilera J.M., Stanley D.W. Microstructural Principles of Food Processing Engineering, 432 p., AN Aspen Pub., Gaithersburg, Maryland, 1999.
- Boume M. Food Texture and Viscosity, Second Edition: Concept and Measurement. p., Academic Press, San Diego -San Francisco -New York -Boston -London -Sidney -Tokyo, 2002.
- Brummer R. Rheology Essentials of Cosmetic and Food Emulsions, 198 p., Springer, Berlin Heidelberg; 2006.
- Rao M.A. Rheology of Fluid and Semisolid Foods: Principles and Applications, 498 p., Springer, New York, 2007.
- Figura L., Teixeira A.A. Food Physics: Physical Properties -Measurement and Applications, 566 p., Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2010.
- Pomeranz Y. Functional Properties of Food Components, 582 p., Academic Press, San Diego -New York -Boston -London -Sydney -Tokyo -Toronto, 1991.
- Chen J., Engelen L. Food Oral Processing: Fundamentals of Eating and Sensory Perception, 408 p., Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester -Oxford -Ames, 2012.
- Fox P.F., McSweeney P.L.H., Cogan T.M., Guinee T.P. Fundamentals of Cheese Science, 608 p., AN Aspen Pub., Gaithersburg, 2000.
- Gunasekaran S., Mehmet Ak M. Cheese Rheology and Texture, 512 p., CRC Press; Boca Raton, 2003.
- Reiner M., Scott Blair G.W., Hawley H.B. The Weissenberg effect in sweetened condensed milk. Journal of the Society of Chemical Industry, Vol. 68, Issue 11, pp. 327-328 (1949).
- Weissenberg K. Specification of rheological phenomena by means of a rheogoniometer. Proc. Int. Congr. Rheol. II, North Holland Publisherm p. 114-118 (1948).
- Weissenberg K. The Testing of Materials by means of the Rheogoniometer, 19 p., Sangamo Controls Ltd., Bognor Regis., Sussex 1963.
- Meißner J. Neue Meßmöglichkeiten mit einem zur Untersuchung von Kunststoff-Schmelzen geeigneten modifizierten Weissenberg-Rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 14, issue 3, pp. 201-218 (1975).
- Krozer S., Schurz J. Rheologische Messungen an Polyisobutylenlösungen im Weissenberg-Rheogoniometer. Progress in Colloid & Polymer Science, Vol. 58, pp. 90-101 (1975)
- Bogie K., Harris J. An experimental analysis of the Weissenberg rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 5, Issue 3, pp. 212-215 (1966).
- van Rijn C.F.H. Short communications to the article “An experimental analysis of the Weissenberg rheogoniometer” by K. Bogie and J. Harris in Rheol. Acta 5, 212 (1966). Rheologica Acta, Vol. 6, issue 3, pp. 295-296 (1967)
- Shorthouse B.O., Hutchinson M.T. Investigation into the visco-elasicity of cell-free plasma using the bio-rheogoniometer. Bib. Anat., Vol. 9, pp. 232-239 (1967)
- King R.G., Copley A.L. Modifications to the Weissenberg rheogoniometer fo r hemorheological and other biorheological studies. Biorheology, Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 1-4 (1970).
- King R.G., Copley A.L. Some Modifications of the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer for Adaptation to Hemorheological Studies. In: Theoretical and Clinical Hemorheology, 1971, pp 386-387.
- King R.G., Copley A.L. An accessory to the Weissenberg rheogoniometer for the measurement of viscoelasticity of surface layers of protein solutions. Biorheology, Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 541-543 (1973).
- King R.G., Copley A.L. Some new accessories to the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer: an exhibit. Biorheology, Vol. 12, No. 6, 355-360 (1975).
- King R.G., Chien S., Usami S., Copley A.L. Biorheological methods employing the Weissenberg rheogoniometer. Biorheology Supplement -the official journal of the International Society of Biorheology, No. 1, 1984, pp. 23-34.
- Philippoff W., Stratton R.A. Correlation of the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer with Other Methods. Trans. Soc. Rheol., Vol. 10, Issue 2, pp. 467-487 (1966)
- Batchelor J., Berry J.P., Horsfall F. The measurement of melt stress relaxation in the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 8, Issue 2, pp. 221-225 (1969).
- Meissner J. Modifications of the weissenberg rheogoniometer for measurement of transient rheological properties of molten polyethylene under shear. Comparison with tensile data. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Vol. 16, Issue 11, pp. 2877-2899 (1972).
- Brindley G., Broadbent J. M. The measurements of normal stress differences in a cone-and-plate rheogoniometer using flush-mounted pressure transducers. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 12, Issue 1, pp. 48-52 (1973).
- Higman R.W. A new torque and normal thrust measuring system for the Weissenberg rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 12, Issue 4, pp. 533-539 (1973).
- Hutton J. F. On using the Weissenberg rheogoniometer to measure normal stresses in lubricating greases as examples of materials which have a yield stress. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 14, Issue 11, pp. 979-992 (1975).
- Ellenberger J, Klijn PJ, Tels M, Vleggaar J. Construction and performance of a cone-and-plate rheogoniometer with air bearings. Journ. Phys E., Vol. 9, No. 9, pp. 763-765 (1976).
- Acharya A., Maaskant P. The measurement of the material parameters of viscoelastic fluids using a rotating sphere and a rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 17, Issue 4, pp. 377-382 (1978).
- Klijn P.-J., Ellenberger J., Fortuin J.M.H. Shear stress and normal stress measurements of aqueous polymer solutions in a cone-and-plate rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 18, Issue 3, pp. 360-368 (1979).
- MacSporran W.C., Spiers R.P. The dynamic performance of the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer. I. Small amplitude oscillatory shearing. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 21, Issue 2, pp. 193-200 (1982).
- MacSporran W.C., Spiers R.P. The dynamic performance of the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer. II. Large amplitude oscillatory shearing -Fundamental responce. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 21, Issue 2, pp. 184-192 (1982)
- MacSporran W.C., Spiers R.P. The dynamic performance of the Weissenberg rheogoniometer III. Large amplitude oscillatory shearing -harmonic analysis. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 23, Issue 1, pp. 90-97 (1984).
- Davis S.S. Calibration of the rheogoniometer with Newtonian fluids. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 11, Issue 2, pp. 199-202 (1972).
- Enthoven N.L.M., Jalink H.L. Calibration of and measurements on a rheogoniometer by means of a small computer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 17, Issue 2, pp. 188-192 (1978).
- Alekseenko A.I. Variation of the frequency and amplitude of periodic deformation in a Weissenberg rheogoniometer. Polymer Mechanics, Vol. 6, issue 5, pp. 816-818 (1970).
- Leonov A.I., Lipkina E.H., Paskhin E.D., Prokunin A.N. Theoretical and experimental investigation of shearing in elastic polymer liquids. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 15, Issue 7-8, pp. 411-426 (1976).
- Isaev A.I., Konstantinov A.A., Kulapov A.K., Rogov B.A., Bystrov A.B., Shakhrai A.A. VR-72 vibrorheometer for determining the viscoelastic properties of polymers. Polymer Mechanics, Vol. 12, Issue 3, pp. 502-506 (1976).
- King M.J., Waters N.D. The effect of secondary flows in the use of a rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 9, Issue 2, pp. 164-170 (1970)
- Hutton J.F. Effect of changes of surface tension and contact angle on normal force measurement with the Weissenberg rheogoniometer. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 11, Issue 1, pp. 70-72 (1972)
- Weissenberg K. Ein neues Röntgengoniometer. Zeitschrift für Physik, Vol. 23, Issue 1, pp. 229-238 (1924).
- Ward A.F.H., Lord P. A new self-recording rheogoniometer. Journal of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 34, No. 9, pp. 363-366 (1957).
- Adams N., Jackson R. A trifilar-suspension rheogoniometer. Journal of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 44, Issue 6, pp. 461-464 (1967).
- Philippoff W. Stress-optical analysis of fluids. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 1, Issue 4-6, pp. 371-375 (1961).
- Philippoff W. Stress-Optical Analysis of Fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 51, No. 7, pp. 883-884 (1959).
- Gaskins F.H., Philippoff W. Instrumentation for Rheological Investigation of Viscoelastic Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 51, Issue 7, pp. 871-873 (1959).
- Philippoff W., Gaskins F.H. The Experimental Check of Theories of the Viscosities of Solutions. Journ. Phys. Chem., 1959, Vol. 63, Issue 6, pp. 985-989 (1959).
- Horn R.G. Addition of a polarizing microscope to the Weissenberg Rheogoniometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum., Vol. 50, No. 5, p. 659 (1979).
- Phan-Thien N. Understanding Viscoelasticity: An Introduction to Rheology.p., Springer, Heidelberg -New York -Dordrecht -London, 2013.
- Dudgeon D.J., Wedgewood L.E. Laser Doppler measurements of flow in a cone-and-plate rheometer and the effect of cone misalignment. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 36, Issue 1, pp. 28-37 (1997)
- Engelbrecht C.J., Stelzer E.H. Resolution enhancement in a light-sheet-based microscope (SPIM). Opt. Lett., Vol. 31, Issue 10, pp. 1477-1479 (2006).
- Huisken J., Stainier D.Y.R. Selective plane illumination microscopy techniques in developmental biology. Development, Vol. 136, Issue 12, pp. 1963-1975 (2009).
- Wohland T., Shi X., Sankaran J., Stelzer E.H.K. Single Plane Illumination Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (SPIM-FCS) probes inhomogeneous three-dimensional environments. Optics Express, Vol. 18, Issue 10, pp. 10627-10641 (2010)
- Tatum J.A., Finnis M.V., Lawson N.J., Harrison G.M. 3D particle image velocimetry of the flow field around a sphere sedimenting near a wall: Part 1. Effects of Weissenberg number. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 141, Issues 2-3, pp. 99-115 (2007).
- Prasad A.K., Adrian R.J. Stereoscopic particle image velocimetry applied to liquid flows. Experiments in Fluids, Vol. 15, Issue 1, pp. 49-60 (1993)
- Prasad A.K. Stereoscopic particle image velocimetry. Experiments in Fluids, Vol. 29, Issue 2, pp. 103-116 (2000).
- Lawson N.J., Tatum J.A., Finnis M.V., Harrison G.M. Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry: Application to a non-Newtonian Flow Field Generated by a Sedimenting Sphere. Paper 21 6. Proc. 12th International Symposium «Application of Laser Techniques for Fluid Mechanics», Lisbon, Portugal, 12-15.07.2004 (http://ltces.dem.ist.utl.pt/LXLASER/lxlaser2004/pdf/paper_21_6. pdf)
- Muller S.J. Velocity measurements in complex flows of non-Newtonian fluids. Kor.-Aus. Rheology Journal, Vol. 14, No. 3, pp. 93-105 (2002).
- Smith M.I., Bertola V. Particle velocimetry inside Newtonian and non-Newtonian droplets impacting a hydrophobic surface. Experiments in Fluids, Vol. 50, Issue 5, pp. 1385-1391 (2011).
- Perez-Gonzalez J., Marin-Santibanez B.M., Rodriguez-Gonzalez F., Gonzalez-Santos J.G. Rheo-Particle Image Velocimetry for the Analysis of the Flow of Polymer Melts. pp. 203-228. In: «The Particle Image Velocimetry -Characteristics, Limits and Possible Applications» (Ed. by G. Cavazzini), 386 p., InTech, Rijeka -New York -Shanghai, 2012.
- Konrad J., Dubois E. Bayesian Estimation of Motion Vector Fields. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Vol.14, No. 9, pp. 910-927 (1992).
- Karczewicz M., Nieweglowski J., Haavisto P. Video coding using motion compensation with polynomial motion vector fields. Signal Processing: Image Communication. Vol. 10, No. 1-3, pp. 63-91 (1997).
- Flierl M., Girod B. Video Coding with Superimposed Motion-Compensated Signals: Applications to H.264 and Beyond. 174 p. Boston, Dordrecht, London: Kluwer Acad. Publisher, 2004.
- Bobrovsky B.Z., Shlien D.J., Brosh A., Kleinstein G. Weissenberg effect in Newtonian liquids. Physics of Fluids, Vol. 22, Issue 4, p. 781 (1979).
- Tanner R.I. Helical flow of elastico-viscous liquids. Rheologica Acta, Vol. 13, Issue 1, pp. 21-26 (1963).
- Bertrand F., Tanguy P.A., de la Fuente E.B., Carreau P. Numerical modeling of the mixing flow of second-order fluids with helical ribbon impellers. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. Vol. 180, Issues 3-4, pp. 267-280 (1999).
- Janes D.E., Thomas H.W. Weissenberg Effect as an End-point in Coagulation Studies. Nature, Vol. 216, pp. 197-198 (1967)
- Muller H.G. Weissenberg Effect in the Thick White of the Hen’s Egg. Nature, Vol. 189, pp. 213-214 (1961)
- Hamad M., Ibrahim F., Mansour M. Lie-group analysis of Newtonian/non-Newtonian fluids flow: Similarity Solutions of Partial Differential Equations Govern Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluids Flow Via Lie-Group. 260 p., Lambert Academic Publishing, Saarbrücken, 2012.
- Ogugbue C.C.E. Non-Newtonian power-law fluid flow in eccentric annuli: CFD simulation and experimental study. 180 p., UMI, Ann Arbor, 2011.
- Abbas Z. Flows of some non-Newtonian fluids on moving surfaces: Numerical and series solutions. 204 p., VDM Verlag, Saarbrücken, 2010.


