Статьи журнала - Компьютерная оптика
Все статьи: 2553

One-shot learning with triplet loss for vegetation classification tasks
Статья научная
Triplet loss function is one of the options that can significantly improve the accuracy of the One-shot Learning tasks. Starting from 2015, many projects use Siamese networks and this kind of loss for face recognition and object classification. In our research, we focused on two tasks related to vegetation. The first one is plant disease detection on 25 classes of five crops (grape, cotton, wheat, cucumbers, and corn). This task is motivated because harvest losses due to diseases is a serious problem for both large farming structures and rural families. The second task is the identification of moss species (5 classes). Mosses are natural bioaccumulators of pollutants; therefore, they are used in environmental monitoring programs. The identification of moss species is an important step in the sample preprocessing. In both tasks, we used self-collected image databases. We tried several deep learning architectures and approaches. Our Siamese network architecture with a triplet loss function and MobileNetV2 as a base network showed the most impressive results in both above-mentioned tasks. The average accuracy for plant disease detection amounted to over 97.8 % and 97.6 % for moss species classification.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
This study considers the optoelectrical properties of thin films composed of linear carbon stabilized by gold nanoparticles. We explore the unique anisotropic behaviors exhibited by these films and their dependence on the degree of structural ordering. The fabrication process includes the use of colloidal systems, with a focus on the laser-induced fragmentation of gold nanoparticles within a carbon matrix. Our findings reveal that applying a potential difference significantly alters the absorption characteristics of the films, particularly enhancing absorption at frequencies associated with short linear chains, while also inducing a transparency effect in the visible range. The introduction of electrons into the carbon matrix is identified as a key factor influencing these optical properties, drawing parallels to existing literature on resonance pumping phenomena. Additionally, the results indicate a considerable modification of the Schottky barrier at the semiconductor-metal interface due to structural orientation. This research provides insight into the potential applications of these materials in optoelectronic devices and highlights the importance of structural characteristics in tailoring their properties.
Бесплатно
Optical elements based on silicon photonics
Статья научная
Silicon photonics is gaining substantial impulse because it permits optical devices to be realized inexpensively using standard semiconductor fabrication techniques and integrated with microelectronic chips. In this paper, we designed few optical elements such as optical power splitter, polarization beam splitter and Bragg grating based on silicon platform simulated using finite element method.
Бесплатно

Optical properties of lowest-energy carbon allotropes from first-principles calculations
Статья научная
We study optical properties of lowest-energy carbon allotropes in the infrared, visible and ultraviolet spectral ranges in the general gradient approximation of the density functional theory. In our calculations we use an all-electron approach as well as a pseudo-potential approximation. In the infrared range, complex dielectric functions, infrared and Raman spectra have been calculated using a CRYSTAL14 program. Electronic properties and energy-dependent dielectric functions in the visible and ultraviolet spectral ranges are calculated using a VASP program. We describe with good accuracy the experimentally known optical properties of a cubic diamond crystal. Using the obtained set of relevant calculation parameters, we predict the optical constants, dielectric functions and Raman spectra of the lowest-energy hypothetical carbon allotropes and lonsdaleite.
Бесплатно

Optical-digital system for real-time fingerprint identification
Статья научная
Performance of the optical-digital system for real-time fingerprint identification using a method of the optical construction of the direction field is reported.
Бесплатно

Optimal affine image normalization approach for optical character recognition
Статья
Optical character recognition (OCR) in images captured from arbitrary angles requires preliminary normalization, i.e. a geometric transformation resulting in an image as if it was captured at an angle suitable for OCR. In most cases, a surface containing characters can be considered flat, and a pinhole model can be adopted for a camera. Thus, in theory, the normalization should be projective. Usually, the camera optical axis is approximately perpendicular to the document surface, so the projective normalization can be replaced with an affine one without a significant loss of accuracy. An affine image transformation is performed significantly faster than a projective normalization, which is important for OCR on mobile devices. In this work, we propose a fast approach for image normalization. It utilizes an affine normalization instead of a projective one if there is no significant loss of accuracy. The approach is based on a proposed criterion for the normalization accuracy: root mean square (RMS) coordinate discrepancies over the region of interest (ROI). The problem of optimal affine normalization according to this criterion is considered. We have established that this unconstrained optimization is quadratic and can be reduced to a problem of fractional quadratic functions integration over the ROI. The latter was solved analytically in the case of OCR where the ROI consists of rectangles. The proposed approach is generalized for various cases when instead of the affine transform its special cases are used: scaling, translation, shearing, and their superposition, allowing the image normalization procedure to be further accelerated.
Бесплатно

Optimal calibration of a prism-based videoendoscopic system for precise 3D measurements
Статья научная
Modern videoendoscopes are capable of performing precise three-dimensional (3D) measurements of hard-to-reach elements. An attachable prism-based stereo adapter allows one to register images from two different viewpoints using a single sensor and apply stereoscopic methods. The key condition for achieving high measurement accuracy is the optimal choice of a mathematical model for calibration and 3D reconstruction procedures. In this paper, the conventional pinhole camera models with polynomial distortion approximation were analyzed and compared to the ray tracing model based on the vector form of Snell’s law. We, first, conducted a series of experiments using an industrial videoendoscope and utilized the criteria based on the measurement error of a segment length to evaluate the mathematical models considered. The experimental results confirmed a theoretical conclusion that the ray tracing model outperforms the pinhole models in a wide range of working distances. The results may be useful for the development of new stereoscopic measurement tools and algorithms for remote visual inspection in industrial and medical applications.
Бесплатно

Orbital angular momentum of the spiral beams
Статья научная
At first sight, any rotation generates some angular momentum (it is true for a solid body). But these characteristics (rotation and orbital angular momentum) are rather different for optics and mechanics. In optics there are the situation when the rotation is important. On the other hand, there are the cases where the nonzero orbital angular momentum is necessary. The main goal of this article is to investigate a relationship between a rotation under propagation of spiral beam and its angular momentum. It can be done the following conclusion: there is no any relation between rotation under propagation of spiral beam and its OAM.
Бесплатно

P-CVD-SWIN: a parameterized neural network for image daltonization
Статья научная
Nowadays, about 8 % of men and 0.5 % of women worldwide suffer from color vision deficiency. People with color vision deficiency are mostly dichromats and closely related anomalous trichromats, and are subdivided into three types: protans, deutans, and tritans. Special image preprocessing methods referred to as daltonization techniques allow increasing the distinguishability of chromatic contrasts for people with dichromacy. State-of-the-art neural network architectures involve training separate models for each type of dichromacy, which makes such models cumbersome and inconvenient. In this paper, we propose for the first time a parameterized neural network architecture, which allows training the same neural network model for any type of dichromacy, being specified as a parameter. We named this model P-CVD-SWIN, supposing it a parametrized development of the recently suggested CVD-SWIN model. A generalization of the Vienot dichromacy simulation method was proposed for model training. Experiments have shown that the P-CVD-SWIN neural network parameterized by the type of dichromacy provides better preservation of chromatic naturalness during daltonization, compared to a combination of several CVD-SWIN models, each trained for its own type of dichromacy.
Бесплатно

Parallel implementation of a multi-view image segmentation algorithm using the Hough transform
Статья научная
We report on the parallel implementation of a multi-view image segmentation algorithm via segmenting the corresponding three-dimensional scene. The algorithm includes the reconstruction of a three-dimensional scene model in the form of a point cloud, and the segmentation of the resulting point cloud in three-dimensional space using the Hough space. The developed parallel algorithm was implemented on graphics processing units using CUDA technology. Experiments were performed to evaluate the speedup and efficiency of the proposed algorithm. The developed parallel program was tested on modelled scenes.
Бесплатно

Parallel implementation of the informative areas generation method in the spatial spectrum domain
Статья научная
This paper proposes a parallel implementation of the image informative segments extraction method. The images are segmented in the spatial spectrum domain. The median energy in each selected segment is viewed upon as an area. For purposes of time savings, a parallel implementation of the algorithm for calculating the areas is developed. The developed approach to the parallel algorithm implementation is tested on a high performance multicore computing system. The experiments have shown that the parallel implementation of the method allows us to obtain a three-fold speedup, which is a good result.
Бесплатно
Статья научная
The tracking-by-detection paradigm is widely used for people multi-object tracking tasks. Up to now, there exist many detectors and trackers, many evaluation benchmarks, which necessitates the use of relatively uniform estimation methods and metrics. It leads to necessity to choose better combined models of detectors and trackers. To solve this task, we developed a comprehensive performance evaluation methodology for estimation of people tracking accuracy and real-time by using different detectors and trackers. We conducted experiments by choosing the official pre-trained models of YOLOv5, YOLOv6, YOLOv7, YOLOv8 with representative BoTSORT, ByteTrack, DeepOCSORT, OCSORT, StrongSORT trackers under two benchmarks of MOT17 and MOT20. Detailed metrics in terms of error and speed such as higher order tracking accuracy and frames per second were analyzed for the combinations of detectors and trackers. It is concluded that the OCSORT+YOLOv6l model has the best comprehensive performance and the combination of OCSORT and YOLOv7 has the best average performance under MOT17 and MOT20.
Бесплатно

Phase reconstruction using a Zernike decomposition filter
Статья научная
Coherent wavefronts are analysed using a Zernike filter that decomposes the analyzed light field into a set of diffraction orders with amplitudes proportional to the circular Zernike polynomials. We also apply the algorithm to the calculation of the light field phase from measurements of the modules of decomposition coefficients. Operation of several filter are simulated.
Бесплатно

Point cloud registration based on global compatibility feature
Статья научная
In this paper, we present a point cloud registration method that utilizes a global point cloud compatibility feature. We introduce an evaluation technique called global compatibility, which helps distinguish between correct and incorrect feature point pairs by calculating the corresponding compatibility weights. To begin, we employ a spectral matching technique to select reliable seed points, allowing us to construct a consistent point set in the vicinity of these seed points. We then design a consistent filter to eliminate outliers from the obtained set. Our approach includes proposing optimal weight matching based on the characteristics of each compatible point set, alongside spectral matching for decomposing the constructed multiple compatible point sets. We assign smaller weights for points affected by larger noise, which aids in generating the corresponding rigid transformation. Ultimately, we select the best transformation as the final result. Notably, our method does not require retrieving all features from the entire point set, and it effectively removes discrete points, thereby constructing a more efficient and robust consistent point set. Experimental results demonstrate that our method performs very well on both indoor and outdoor datasets, as well as on datasets with low overlap.
Бесплатно
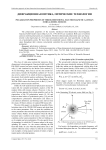
Polarization properties of three-dimensional electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model sources
Статья научная
The polarization properties of the recently introduced three-dimensional electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model sources [Opt. Lett. 42, 1792 (2017)] are examined. Both cases of uniform and non-uniform polarization are considered. The three-dimensional polarization states are characterized via the eigenvalues of a 3×3 source polarization matrix and, more specifically, via the indices of polarimetric purity. We show that the considered sources exhibit a variety of polarization states throughout their volumes conveniently controlled by several physically accessible source parameters.
Бесплатно

Preliminary results in investigation of diffractive high-efficiency objectives
Статья научная
It has been shown that high-efficiency diffractive objectives are an alternative to their refractive counterparts for applications requiring high precision transformation of monochromatic light (for example in interferometers). A 80 mm diameter prototype (N.A. - 0.158; design wavelength 632.8 nm) has been fabricated by direct laser writing on photoresist. It was manufactured on a polar coordinate laser writing system CLWS-300 that is able to write high precision DOEs up to a diameter of 300 mm. The blazed diffractive structures were written directly into a photoresist layer that was spinned on a high-precision substrate. The fabricated objective has a rms wavefront error of less than л/20 in single pass. The residual errors are predictable using manufacturing data that is recorded during the writing process for each element. This permits to provide each element with calibration data. Measurements of the fabricated DOEs show excellent agreement between the predicted and measured wavefront quality.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
Nematic liquid crystal planar and smoothly-irregular waveguide structures were studied experimentally and by the computer modeling. Two types of optical smoothly-irregular waveguide structures promising for application in telecommunications and control systems are studied by numerical simulation: liquid crystal waveguides and thin film solid generalized waveguide Lune-burg lens. Study of the behavior of these waveguide structures where liquid crystal layer can be used to control the properties of the entire device, of course, promising, especially since such devices are also able to perform various sensory functions when changing some external parameters, accompanied by a change in a number of their properties. It can be of interest to researchers not only in the field of the integrated optics but also in some others areas: nano-photonics, optofluid-ics, telecommunications, and control systems. The dependences of the attenuation coefficient (optical losses) of waveguide modes and the effective sizes (correlation radii) of quasi-stationary irregularities of the liquid-crystal layers on the linear laser radiation polarization and on the presence of pulse-periodic electric field were experimentally observed...
Бесплатно

Статья научная
We present a general-purpose, training-free framework for dimensionality reduction and clustering based on per–sample pseudo–Boolean polynomials (PBP). The method constructs compact, interpreTab. features without model fitting and is evaluated under a standardized protocol that compares PBP to PCA, t-SNE, and UMAP using identical inputs and metrics: clustering alignment (V-measure, Adjusted Rand Index), cluster geometry (Silhouette coefficient, Calinski–Harabasz index, Davies–Bouldin index), and supervised probes (linear separability and boundary complexity (1–NN error)). Across 11 diverse datasets spanning tabular, signal, and ecological domains, PBP leads on linear separability in 5/11 datasets and achieves lower boundary complexity in 2/11 datasets, while remaining competitive on clustering metrics. We report best-performing aggregation and sorting configurations per dataset and provide guidance on when PBP should be preferred for interpreTab. analysis and reproducible evaluation.
Бесплатно

Quality inspection of fertilizer granules using computer vision – a review
Статья научная
This research explores the fusion of computer vision and agricultural quality control. It investigates the efficacy of computer vision algorithms, particularly in image classification and object detection, for non-destructive assessment. These algorithms offer objective, rapid, and error-resistant analysis compared to human inspection. The study provides an extensive overview of using computer vision to evaluate grain and fertilizer granule quality, highlighting granule size’s significance. It assesses prevailing object detection methods, outlining their advantages and drawbacks. The paper identifies the prevailing trend of framing quality inspection as an image classification challenge and suggests future research directions. These involve exploring object detection, image segmentation, or hybrid models to enhance fertilizer granule quality assessment.
Бесплатно


