Статьи журнала - Сибирский аэрокосмический журнал
Все статьи: 3250

Determination of variables significance using estimations of the first-order partial derivative
Статья научная
In this paper we describe and investigate a method which allows us to detect the most informative features out of all data extracted from a certain data corpus. The significance of input features is estimated as an average absolute value of the first-order partial derivative. The method requires the values of the objective function at the certain assigned points. If there is no possibility to calculate these values (the object is not available for experiments), we use non-parametric kernel regression to approximate them. The algorithm is tested on different simulated objects and is used for investigation of the dependency between linguistic features of spoken utterances and speakers ' capabilities.
Бесплатно

Determining the source of transverse oscillations of an elastic rod
Статья научная
Solvability of an inverse problem for the equations of transverse oscillations of an elastic rod (determining the source of oscillations on the basis of the rod deflection at the final time) is proved.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
The main function of a thermal control system (TCS) is to maintain the temperature at nodal points of a spacecraft in given ranges due to redistribution of thermal energy and the discharge of excess thermal energy into space. TCS may have a different design and principle of operation. One of the most common options is TCS using a liquid circuit (LC) and pumping coolant circulation. In the development of promising design-layout schemes for instrument compartments of nonhermetic formation spacecraft, it becomes necessary to state and solve new problems associated with the creation of computational and mathematical models of intermediate convective heat transfer in a fluid circuit. For systems of integral equations of a LC thermal model with fairly complex topographic boundaries and connections, the justification and use of the defining (equivalent) thermal resistance seems to be a compromise of counting implementation of a system that simulates a TCS with integration along the length of the LC. In this paper, for the computational model of the liquid circuit of the thermal control system, including the system of equations of two-dimensional thermal balance of the characteristic surfaces of a nonhermetic formation spacecraft, a method of calculating the determining thermal resistances was proposed and implemented. This method includes the calculation of the complex heat transfer coefficient and the local heat transfer coefficient to the heat carrier flow. The approach considered in this paper allows us to obtain a numerical solution for the distribution of heat flows and temperatures of liquid circuits with complex topographic boundaries and connections with minimal loss of accuracy. The determination of the local heat transfer coefficient makes it possible to take into account the influence of changes in the temperature of the coolant flow on the overall picture of convective heat exchange.
Бесплатно

Developing the laboratory test bench of fuel three-point measurement
Статья научная
The development of digital technology allows continuous improvements in many areas. This paper reflects the development of a new fuel measurement method. To measure the fuel, the authors propose three fuel sensors and a computational element to simulate the position of the fuel level in space with further calculating the volume of fuel, to reduce errors due to the fuel meters operation. The main advantage of this system is the elimination of errors arising from the evolution of an aircraft, as well as its uneven movement. The paper demonstrates a phased development of a laboratory test bench to study the three-point method to measure fuel. In the course of the work, a vessel is assembled to simulate the fuel tank of the aircraft. The vessel is a glass container with submersible measuring sensors. Also, the research contains calculation of the bridge electrical circuit to compute a voltage value at each sensor. In the test, transformer fluid substitutes fuel, since it acted as a dielectric. The program code for the microcontroller is recorded. The proposed method has several advantages in comparison with traditional methods of measuring the fuel level; a mathematical model is presented, on the basis of which the level of fuel in the aircraft fuel tank is measured.
Бесплатно

Development and investigation of the effectiveness of the particle swarm optimization algorithm
Статья научная
This article deals with investigation of the effectiveness of the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [1] algorithm for solving constrained and unconstrained one- and multi-criteria optimization problems. Besides the investigations were conducted both the standard and the binary PSO. Also parallelized modifications of these algorithms were developed for multi-processor operations and two real-world problems were solved.
Бесплатно

Development of SEM method for analysis of organ-containing objects using inverse opals
Статья научная
The purpose of this study is to test the possibility of using inorganic macroporous structures of inverse opal in sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy of biological objects. As an absorbent substrate we used silica inverse opals prepared by a sol-gel method to study the biological objects. The process of manufacturing the inverse opal involves a complex multi-stage technological process. First, we synthesized submicron spherical particles from polymethylmethacrylate by the method of emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization of methylmethacrylate in an aqueous medium in the presence of a diazoinitiator. This method can be used to obtain an ensemble of particles with high monodispersity, the average size of which can vary in the range from 100 to 500 nm. Then, by self-assembly technique, we deposited the beads of polymethylmethacrylate into ordered matrices (templates), mainly with a face-centered cubic lattice. The resulting mesoporous structures, called artificial opals or colloidal crystals, had lateral dimensions of about 10 × 10 × 2 mm. Then we heat-treated the opals to 120 °C to harden the template before being impregnated with the precursor. Further, we impregnated the opals with silica sol with a particle size distribution from 1 to 5 nm, obtained by hydrolysis of tetraethoxysilane in the presence of hydrochloric acid, and then, after curing and drying the impregnating composition in air at room temperature, we multi-stage fired them up to 550 °C at normal pressure in the air atmosphere to remove all organic components. As a result, the macroporous metamaterial (the so-called inverse opals) with an open system of pores up to 400 nm in size, occupying about 80 % of the volume, were obtained. We studied lactic acid bacteria of cucumber brine and human red blood cells with TM4000 Plus, SU3500 and S-5500 scanning electron microscopes. Auxiliary substance for the sample preparation was ionic liquid VetexQ EM (Interlab LLC). We showed that it is possible to use the inverse opal as an absorbent substrate for sample preparation and rapid analysis in scanning electron microscopy without pre-drying, chemical treatment, or temperature exposure. To improve imaging in the electron microscope, we used sputter coater to cover the inverse opal surface with a thin film of platinum. The use of ionic liquid in combination with the absorbent porous medium allows preserving an original shape of the biological structures. Using the human red blood cells and lactic acid bacteria, we showed that it is possible to carry out of the morphological analysis of the cells using various scanning electron microscopes. We found that on the basis of the inverse opal, there is a fundamental possibility of creating the absorbent substrate suitable for repeated use in the study of the biological objects. At the same time, trace remnants of previous samples remaining after annealing the plate do not introduce significant distortions when conducting new series of observations. In this study, we obtained high-quality electronic micrographs of the biological objects with high resolution and contrast. At the same time, due to the use of the inverse opals as the absorbent substrate, time and financial costs for research are reduced.
Бесплатно

Development of adaptive genetic algorithms for neural network models multicriteria design
Статья
In this paper modifications of single- and multi-objective genetic algorithms are described and testing results of these approaches are presented. The gist of the algorithms is the use of the self-adaptation idea leading to reducing of the expert significance for the algorithm setting and expanding of GAs’ application capabilities. On the basis of offered methods the program system realizing the technique for neural network models design was developed. The effectiveness of all algorithms was investigated on a set of test problems.
Бесплатно

Статья обзорная
Aluminum-based alloys are widely used in many branches of modern industry (aviation, mechanical engineer- ing, shipbuilding, instrument-making, energy and medicine, etc.). The promising method for further expanding the scope of these alloys is surface treatment based on the use of concentrated energy fluxes (laser beams, plasma flows, powerful ion beams, continuous and pulsed electron beams). The purpose of this paper is to establish the possibilities of integrated electron-ion-plasma modification of the structure and properties of the surface layer of technically pure aluminum A7. The surface alloy was formed in a single vacuum cycle using the “KOMPLEX” facility (ISE SB RAS) by spraying a titanium film with a thickness of 0.5 μm and the subsequent irradiation with an intense pulsed electron beam in the aluminum melting mode. After 20 “spraying/irradiation” cycles, nitriding (540 °C, 8 h) of the formed surface alloy was performed in a low-pressure gas discharge plasma using the plasma generator “PINK”. Surface alloy studies were carried out applying the modern materials science methods (scan- ning and transmission electron diffraction microscopy, X-ray phase analysis, determination of hardness and wear resistance). The choice of elements alloying the surface layer of aluminum was based on the analysis of binary state diagrams of Al-N, Al-Ti, Ti-N systems and the isotermal section of the ternary system Al-Ti-N. It has been shown that formation of an entire series of binary and ternary compounds, including MAX-phases of the composi- tion Ti2AlN and Ti4AlN3, is observed under equilibrium conditions in the Al-Ti-N system. The carried out research has allowed to state that an integrated method of electron-ion-plasma modification of technically pure A7 alumi- num by nitriding (540 °C, 8 h) of the surface alloy formed by pulsed melting in vacuum of the Al-Ti system (20 “spraying/irradiation” cycles with an electron beam with parameters 10 J/cm2; 50 μs; 10 pulses; the titanium film thickness in each cycle 0.5 μm) leads to formation of a multiphase multielement submicro-nanocrystalline surface layer up to 20 μm thick. It is shown that the mechanical (microhardness) and tribological (wear resistance and friction coefficient) properties of the formed surface layer exceed manifold the properties of the original commercially pure aluminum A7.
Бесплатно

Development of interface module emulator architecture for spacecraft life support systems
Статья научная
The article gives an analysis of special characteristics of ground-based experimental evaluation of on-board radioelectronic equipment, taking the control unit of up-to date spacecraft on-board control complex as the test objective. The focus is the problem of providing testing procedures of the specific software employed in design and manufacture process. A solution of the problem is worked out on the basis of performance of a hardware-software complex which emulates interface modules for the computing module of control unit. According to the general operation algorithm of the control unit, the developed complex is regarded as a multi-user system. The main functional requirements for hardware-software emulator, regarded as the corresponding queuing system, are also defined. The results of the experiments with the computer module operation prompted the requirements for the emulator response time from the point of view of its operation stability in real strict-time mode. In order to ensure the required efficiency of operation, the emulated functions of the interface modules are classified according to the severity level of their execution determinacy. The results of experimental evaluation оf the service channel hardware design variants when applying multi-functional reconfigurable input-output digital devices allowed to develop a hardware-software emulator structural circuit based on operation parallelism of programmable integrated logic circuits and flexibility of software reconfiguration. The realization of emulated functions of selected classes within the available architecture was carried out using the corresponding hardware blocks and software module. The presented analysis of the emulator response limits was performed with the application of National Instruments technologies. The results of the developed hardwaresoftware emulator evaluation and practical application, as well as other possible ways of applying the proposed approach for tests of spacecraft on-board radio-electronic equipment and space system components were also analyzed.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
The control system of a launch vehicle (LV) at the initial phase of flight at altitudes between 0 and 300 meters is the object of investigation in the article. At this phase the flame of the LV jet engine is the cause of a negative impact on facilities of the launch complex. This effect can be reduced by displacing the jet flame in a certain radial direction with increased resistance of the facilities using a specially developed vehicle motion control program. The purpose of the article is to develop an algorithm for the controller of the LV motion control system on the considered “displacement phase” of the trajectory that provides an implementation of such a program. To solve the problem, we developed the modified version of the Letov’s method of analytical construction of regula- tors (ACOR). The peculiarity of the modified statement of the problem solved in the work is that the controlled output vector of the system depends explicitly not only on the LV state vector, but also on the control variable. The quality of control is evaluated using a quadratic terminal-integral optimality criterion. This kind of criterion allows to trace with the specified accuracy the preliminary calculated program for supporting the required position of the trace of the LV jet flame on the launching plane, and also to ensure the vertical position and the zero angular velocity of the vehicle at the end of the displacement phase. To solve the problem of constructing the algorithm, a special linearized model of the LV motion has been developed. The results of simulating the controlled motion of a launch vehicle with the use of the algorithm confirm the operability and demonstrate efficiency of the developed optimal regulator of the LV control system at the displacement phase under consideration. Calculation results show that angular position of the LV at the end of the displacement phase is close to vertical, the angle of the engine nozzle deflection is within the permissible limits and the deviation of the current position of the jet flame track from the program value does not exceed 0.5 meters.
Бесплатно

Development of mechanical test procedure for the fuel bellows tanks
Статья научная
The mechanical qualification and acceptance test requirements are considered for the fuel bellows tanks. Some procedural mistakes taking place during these tests are described.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
The article provides a brief description of the flight scheme of a prospective automatic spacecraft intended for the study of Mars and its satellites by remote and contact methods. At the near-Martian expedition site, it is planned to first bring the vehicle into orbit of the artificial satellite Deimos, and then landing on Phobos with the subsequent delivery of its soil to Earth. The main ballistic characteristics of the spacecraft flight conditions at all stages of the flight at launch after 2025 are given. The time frames for the five starting periods are considered - in 2026, 2028, 2030, 2033 and 2035. The launch of the spacecraft on the flight path to Mars is performed by a heavy class launcher. The article describes the design of the vehicle, propulsion systems of its modules and flight scheme at all stages - from launch from the Earth to landing on Phobos, and returning back to Earth. The article describes the propulsion systems of the main spacecraft units proposed for the mission implementation - the propulsion module, the flight landing platform and the return vehicle. The designs of these units are provided in the work. Flight schemes have been developed in accordance with their characteristics, which allows conducting remote study of Deimos, making a soft landing on the surface of Phobos, and then delivering samples of its soil to Earth. The project should be developed on the basis of the spacecraft launch from the Vostochny launch site by the Angara-A5 launch vehicle and the KVTK upper stage. An alternative variant of the construction of a spacecraft involves the use of a vehicle of a lighter class - perspective Soyuz-5 launch vehicle and Fregat-SBU upper stage. In this case, the engine module is excluded, and the flight and landing module is replaced by a heavier version with larger tanks. Both proposed options for constructing a spacecraft make it possible to implement the developed trajectory, while ensuring full-time operation of the target equipment and conducting a set of experiments during a given period of active spacecraft existence.
Бесплатно

Development of three-point aviation fuel quantity gauge
Статья научная
In response to the well-developed digital technologies, modern methods can be worked out for the spheres where radical changes seemed hardly possible. This paper describes the development of a new method of fuel quantity meas- urement that has not been applied before. To measure the level of fuel in the fuel tank of an aircraft, it is proposed to use three fuel level gauges and a special electronic calculation unit; they model the fuel level surface inside the given volume, and then the actual amount of fuel can also be calculated. This can considerably reduce the evaluation errors allowed with the application of the existing fuel quantity gauges. The main advantage of the system offered is the elimi- nation of the errors arising with the aircraft evolutions and irregular motions. The article gives the analysis of the fuel level assessment methods used in the aviation sphere at present, the types of fuel quantity gauges used in aviation, and the specific conditions of measuring the fuel level in the aircraft fuel tanks. The proposed method has a number of advantages, in comparison with the traditional ways of measuring the fuel level; a basic mathematical model of the aircraft tank fuel level calculation has also been worked out.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
The paper describes materials based on solid solutions GdxMn1-xS and GdxMn1--xSe, which in the future can be used in aerospace industry as sensors, detectors, and information writer-readers. In solid solutions GdxMn1-xA (A = S, Se) (x ≤ 0.2), capacitance and tangent of the dielectric loss angle were meas- ured at the frequency of 10 kHz without a magnetic field and in the magnetic field of 8 kOe in the temperature range 100-500 К. The growth of the dielectric permittivity and the maximum of dielectric losses in the low-temperature region were observed. The displacement of the temperature of the maximum of the imaginary part of the permittivity in the direction of high temperatures is found with increasing concentration. For two compositions, a magnetocapacitance effect was observed. The magnetocapacitance effect δεН = (ε(Н,T)-ε(0,Т))/ε(0,Т)) was determined as a result of inves- tigation of the complex dielectric permittivity. The synthesis of new chalcogenide compounds in the cationic substitution of manganese by gadolinium in the MnS and MnSe systems will make it possible to clarify the effect of the anion system, as a result of studying its magnetoresis- tive properties with concentration in the gadolinium ion flux region along the x ≤ 0.2 lattice. Dielectric losses are described in the Debye model with the freezing of dipole moments and in the model of orbital- charge ordering.
Бесплатно

Differential evolution in the decision tree learning algorithm
Статья научная
Decision trees (DT) belong to the most effective classification methods. The main advantage of decision trees is a simple and user-friendly interpretation of the results obtained. But despite its well-known advantages the method has some disadvantages as well. One of them is that DT training on high-dimensional data is very time-consuming. The paper considers the way to reduce the DT learning process duration without losses of classification accuracy. There are different algorithms of DT training; the main of them being ID3 and CART algorithms. The paper proposes a modification of DT learning algorithms by means of the information criterion optimization for some selected attribute. The use of this modification allows avoiding optimization by means of enumeration search over the entire data set. The Separation Measure method is used to select the attribute. The method selects the attribute whose class-based averages are most distant from each other. Optimization of the selected attribute is carried out using the method of differential evolution, which is one of the evolutionary modeling methods designed to solve problems of multidimensional optimization. Self-configuring at the population level based on the probabilities of using mutation operator's variants was applied for differential evolution. The classification problems were solved to compare standard DT learning algorithms with the modified ones. Algorithm efficiency refers to the percentage of correctly classified test sample objects. Statistical analysis based on Student's t-test was carried out to compare the efficiency of the algorithms. The analysis showed that the use of the proposed modification of the DT learning algorithm makes it possible to significantly speed up the training process without losses in the classification effectiveness.
Бесплатно

Distributed self-configuring evolutionary algorithms for artificial neural networks design
Статья
In this paper we describe the method of automatic neural network design based on the modified evolutionary algorithms. The main features of the modification proposed are self-configuration and the usage of distributed computing. Implemented algorithms have been tested on the set of classification tasks. The comparison of the genetic algorithm and the genetic programming algorithm’s efficiencies is presented.
Бесплатно
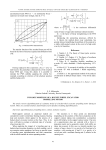
Dynamic modeling of a bucket-wheel excavator propelling motor
Статья научная
The article reviews algorithmization of a dynamic model of a bucket-wheel excavator propelling motor during its motion. There are essential schemes and formulas used in dynamic modeling algorithmization.
Бесплатно

Economic methods of spectrum/orbit management for satellite networks
Статья научная
Satellite systems continue to play an important role in developing of telecommunication and broadcasting services market by offering an effective technical solution for the transmission and dissemination of various types of information to mobile and fixed subscriber receivers. This trend is raising demand for the spectrum-orbit resource (SOR) which provides the operation of any radio-electronic system and this leads to a shortage of this valuable resource. The inter- national administrative management system, based on technical and normative principles and procedures set in the Radio Regulations, which successfully coped with its tasks of SOR distribution under conditions when several satellite nations have an insignificant number of satellites in the geostationary orbit, under conditions of current loading, shows its inefficiency. The procedure of obtaining authorization to use the resource involves considerable expenditure of time and material resources raising transaction costs on development of satellite projects and increasing financial risks, which makes investment in satellite projects less attractive. In this regard there is a question of the necessity of stimu- lating rational use of SOR methods introduction. We are considering the possibility of introducing economic methods into the international SOR management system as an additional tool to encourage the rational use of the resource. An analysis of the existing approaches of contempo- rary economic theory has identified some basic options for applying economic methods to the SOR management system. For the planned frequency bands, distributed for satellite services, the introduction of national assignments rent system is offered. For unplanned frequency bands, the introduction of payments for the SOR use is being considered. On the basis of electromagnetic compatibility of satellite communication systems assessment analysis, the methods to deter- mine payments for SOR based on assessments of a satellite system aggressivity in terms of creating interference and of its sensitivity to interference from other systems are offered.
Бесплатно

Efficiency of the organization staff work: synthesis of organizational behaviour
Статья научная
There have been described several types of workers behaviour and their influence on the productivity in organization. There is presented a number of issues which make it possible to determine the type of staff behavior and possible ways to control this behavior.
Бесплатно

Efficient method of calculating layered conical shells with Lagrange multigrid elements use
Статья научная
The increased requirements for strength calculations of space-rocket and aviation technology designs cause the need for the development and improvement of approximate solutions for elasticity theory tasks with small error algo- rithms. The article considers the numerical method of calculating elastic layered conical shells (LCS) of various thickness under static loading which are widely used in space-rocket technology. The suggested method uses three-dimensional curvilinear Lagrange multigrid finite elements (MGFE). A system of nested grids is used for MGFE constructing. The fine grid is generated by the basic partition that takes into account MGFE heterogeneous structure. The basic partition dimensionality is reduced with the help of large grids which leads to the system of linear algebraic equations of the small dimension finite elements method. Three-dimensional elasticity theory equations use allows to apply MGFE for calculating LCS of any thickness. Displacements in MGFE are approximated by Lagrange polynomials which, in con- trast to power polynomials, gives the opportunity to design big size three-dimensional thin shell elements. Lagrange polynomials nodes coincide in shell thickness with the nodes of MGFE large grids which lie on the shared borders of multi-module layers. The efficiency of the presented method is that the suggested MGFE generate small dimension discrete models that require 103-107 times less electronic computing machine (ECM) memory than basic models. The suggested law of dis- crete models grinding generates uniform and fast convergence of numerical solutions which allows to make solutions with the specified (small) error. Examples of LCS calculating (whole ones as well as with holes) under axisymmetric and local loading are given. Comparative analysis of solutions obtained with the help of MGFE, single-grid finite elements and the program com- plex ANSYS has been conducted.
Бесплатно

