Дифракционная оптика, оптические технологии. Рубрика в журнале - Компьютерная оптика

Noise minimized high resolution digital holographic microscopy applied to surface topography
Статья научная
The topography of surface relief gratings was studied by digital holographic microscopy. The applicability of the method for quantitative measurements of surface microstructure at nanoscale was demonstrated. The method for wavefront reconstruction of surface relief from a digital hologram recorded in off-axis configuration was also applied. The main feature is noise filtration due to the presence of noise in the recorded intensity distribution and the use of all orders of the hologram. Reconstruction results proved a better effectiveness of our approach for topography studying of relief grating patterned on a ChG As2S3 - Se nanomultilayers in comparison with standard Fourier Transform and Atom Force Microscope methods.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
In this paper we investigate non-Markovian evolution of a two-level system (qubit) in a bosonic bath under influence of an external classical fluctuating environment. The interaction with the bath has the Lorentzian spectral density, and the fluctuating environment (stochastic field) is represented by a set of Ornstein-Uhlenbeck processes. Each of the subenvironments of the composite environment is able to induce non-Markovian dynamics of the two-level system. By means of the numerically exact method of hierarchical equations of motion, we study steady states of the two-level system, evolution of the reduced density matrix and the equilibrium emission spectra in dependence on the frequency cutoffs and the coupling strengths of the subenvironments. Additionally, we investigate the impact of the rotating wave approximation (RWA) for the interaction with the bath on accuracy of the results.
Бесплатно

Numerical approach to compound quantum repeater scheme with coherent states
Статья научная
A numerical model of a quantum repeater operating with Schrödinger cat states is constructed. The model describes the performance of such a system in the presence of decoherence effects, namely, noise in the quantum channel and the efficiency of the photon-number-resolving detector. In the framework of the numerical model, a theoretical analysis of the system functioning is carried out for the elementary link by calculating its performance characteristics. Namely, we calculate photodetector click probabilities and fidelity for various sets of decoherence parameters. These estimates are necessary in the context of further experimental research at the junction with other branches of quantum communications, so that to use the entanglement distribution when it comes to operating quantum teleportation and quantum key distribution protocols based on entanglement. The model will be developed further as a versatile drag-and-drop software simulating the full-fledged entanglement swapping protocol operation.
Бесплатно

Numerical simulation of 2D electrodynamic problems with unstructured triangular meshes
Статья научная
We present a generalization of standard leap-frog plus Yee mesh approach for Cauchy problem in electrodynamics simulations on unstructured triangulated mesh. The presented approach still inherits from finite-difference time-domain and do not use techniques developed in finite-volume time-domain approach. In the paper the whole flow from mesh creation to actual simulation is presented. The proposed computation flow is parallel ready and can be implemented for distributed systems (computation servers, graphical processing units, etc.). We studied the influence of non-regular triangulation on stability and dispersion properties of numerical solution.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
The response of fiber specklegram sensors (FSSs) is given as function of variations in the intensity distribution of the modal interference pattern or speckle pattern induced by external disturbances. In the present work, the behavior of a FSS sensing scheme under thermal perturbations is studied by means of computational simulations of the speckle patterns. These simulations are generated by applying the finite element method (FEM) to the modal interference in optical fibers as a function of the thermal disturbance and the length of the sensing zone. A correlation analysis is per-formed on the images generated in the simulations to evaluate the dependence between the changes in the speckle pattern grains and the intensity of the applied disturbance. The numerical simulation shows how the building characteristic of the length of sensing zone, combined with image processing, can be manipulated to control the metrological performance of the sensors.
Бесплатно

Numerically focused optical coherence microscopy with structured illumination aperture
Статья научная
In optical coherence microscopy (OCM) with a given numerical aperture ( NA ) of the objectives the transverse resolution can be increased by increasing the numerical aperture of illumination ( NAi ). However, this may also lead to attenuation of the signal with defocus preventing the effective numerically focused 3D imaging of the required sample volume. This paper presents an approach to structuring the illumination aperture, which allows combining the advantages of increased transverse resolution (peculiar to high NAi ) with small attenuation of the signal with defocus (peculiar to low NAi ) for high-resolution numerically focused 3D imaging in OCM.
Бесплатно

On chip optical neural networks based on mmi microring resonators for image classification
Статья научная
We propose a new on-chip optical neural network (OONN) based on multimode interference-microring resonators (MMI-RRs). The suggested structure eliminates the need for wavelength division multiplexers (WDM) to create an optical neuron on a single chip. New microring resonator structure based on 4×4 MMI coupler with a size of 24µm × 2900 µm is used for the basic elements of the computation matrix, as a result a higher bandwidth and free spectral range (FSR) can be achieved. The Si3N4 platform along with the graphene sheet is designed to modulate the signals and weights of the neural networks at a very high speed. The Si3N4 can provide wide range of operating wavelengths and can work directly with the wavelengths of color images. The structure's benefits include rapid computing speed, little loss, and the ability to handle both positive and negative values. The OONN has been applied to the MNIST dataset with a speed faster than 2.8 to 14x times compared with the conventional GPU methods.
Бесплатно
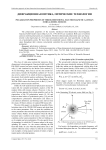
Polarization properties of three-dimensional electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model sources
Статья научная
The polarization properties of the recently introduced three-dimensional electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model sources [Opt. Lett. 42, 1792 (2017)] are examined. Both cases of uniform and non-uniform polarization are considered. The three-dimensional polarization states are characterized via the eigenvalues of a 3×3 source polarization matrix and, more specifically, via the indices of polarimetric purity. We show that the considered sources exhibit a variety of polarization states throughout their volumes conveniently controlled by several physically accessible source parameters.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
Nematic liquid crystal planar and smoothly-irregular waveguide structures were studied experimentally and by the computer modeling. Two types of optical smoothly-irregular waveguide structures promising for application in telecommunications and control systems are studied by numerical simulation: liquid crystal waveguides and thin film solid generalized waveguide Lune-burg lens. Study of the behavior of these waveguide structures where liquid crystal layer can be used to control the properties of the entire device, of course, promising, especially since such devices are also able to perform various sensory functions when changing some external parameters, accompanied by a change in a number of their properties. It can be of interest to researchers not only in the field of the integrated optics but also in some others areas: nano-photonics, optofluid-ics, telecommunications, and control systems. The dependences of the attenuation coefficient (optical losses) of waveguide modes and the effective sizes (correlation radii) of quasi-stationary irregularities of the liquid-crystal layers on the linear laser radiation polarization and on the presence of pulse-periodic electric field were experimentally observed...
Бесплатно

Статья научная
In this report we describe a fast 3-color method of the measurement of temperature distributions on a surface of a heated solid using a RGB color camera with a high frame rate (100 images per second). Statistical error the RGB method is not high, and do not exceed around 5.5 % which is surprising taking in to account the number of the measurements at each pixel. Comparison of the results of the temperature measurements on a tungsten plate heated by infra-red laser radiation and conducted with this technique and those obtained with the acousto-optical tunable filter technique demonstrate that error of the temperature measured by 3-color method is only two times as high as that of the tandem acousto-optic filter technique method.
Бесплатно

Retinal biometric identification using convolutional neural network
Статья научная
Authentication is needed to enhance and protect the system from vulnerabilities or weaknesses of the system. There are still many weaknesses in the use of traditional authentication methods such as PINs or passwords, such as being hacked. New methods such as system biometrics are used to deal with this problem. Biometric characteristics using retinal identification are unique and difficult to manipulate compared to other biometric characteristics such as iris or fingerprints because they are located behind the human eye thus they are difficult to reach by normal human vision. This study uses the characteristics of the retinal fundus image blood vessels that have been segmented for its features. The dataset used is sourced from the DRIVE dataset. The preprocessing stage is used to extract its features to produce an image of retinal blood vessel segmentation. The image resulting from the segmentation is carried out with a two-dimensional image transformation such as the process of rotation, enlargement, shifting, cutting, and reversing to increase the quantity of the sample of the retinal blood vessel segmentation image. The results of the image transformation resulted in 189 images divided with the details of the ratio of 80 % or 151 images as training data and 20 % or 38 images as validation data. The process of forming this research model uses the Convolutional Neural Network method. The model built during the training consists of 10 iterations and produces a model accuracy value of 98 %. The results of the model's accuracy value are used for the process of identifying individual retinas in the retinal biometric system.
Бесплатно

Sensor with enhanced performance based on photonic crystal with a defect layer
Статья научная
We propose an improved structure of an optical biosensor based on a photonic crystal with a defect layer, which can detect the concentration of organic contaminants in water by defect mode shift. We investigated 4 types of defective photonic crystals with different arrangements of layers inside the perfect photonic crystals and their impact on the performance of the sensor. The sensitivity and amplitude of defect mode were examined as a function of defect layer thickness. Also, the peculiarities of edge modes in the presence of defect layer were investigated. Finally, we obtained a characteristic equation to determine the wavelengths of defect modes for an arbitrary 1D photonic crystal with an isotropic defect inside.
Бесплатно

Simulation of the evolution of laser beams in impurity carbon nanotubes using the Madelung approach
Статья научная
The relevance of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic waves with various materials exhibiting nonlinear properties is increasing every year. In this work, we studied the dynamics of laser beams propagating in a medium of single-walled carbon nanotubes with impurities, placed in a dielectric. By multilevel impurity, we mean an impurity whose energy levels are separated from the conduction band and valence band in carbon nanotubes and lie inside the band gap of the dielectric medium. The novelty of this work lies in the development of a model for the evolution of electromagnetic radiation in the infrared range is constructed using the Madelung transform for the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, the numerical implementation of which is carried out using the smoothed-particle hydrodynamics. The influence of impurity parameters on the laser beam propagation in a given medium, namely, the energy of electron transitions from impurity levels to the first and second sublattices of nanotubes, is analyzed.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
One of important tasks of the day is increasing the efficiency and decreasing the cost of the silicon solar cells. There is method of introducing of metal nanoparticles into solar cells to improve its absorption and reduce transmission as well as reflection coefficients. When metal nanoparticles are introduced into silicon solar cell, nanoplasmonic effect will occur. Nanoplasmonic effect lead to modification of light spectrum and generation of extra hot electrons. Nanoplasmonic effect strongly depends on size of nanoparticles. Therefore, in this paper, effect of gold nanoparticles size on properties of silicon solar cell has been studied by using simulation. Gold nanoparticles with sizes of 4 nm, 6 nm, 9 nm, 11 nm and 21 nm have been input into emitter region of silicon solar cell in order to use both of nanoplasmonic-electric and nanoplasmonic-optic effects for enhancing efficiency of silicon solar cell. Open circuit voltage didn’t change when size of nanoparticles has been changed from 4 nm to 11 nm. It dropped by 0.017 V when size of nanoparticles was 21 nm. Short circuit current has been maximum 6.7 mA/cm2 at nanoparticle size of 11 nm and minimum 3.1 mA/cm2 at nanoparticle size of 21 nm. It has been found from obtained results that gold nanoparticle with size of 11 nm affected significantly on properties of silicon solar cell. Besides, thickness of silicon solar cell can be decreased without dropping of efficiency by introducing gold nanoparticles. Because, main part of photons is absorbed near to metal nanoparticles inputted region.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
In the study we derive a solution of the inverse diffraction problem aimed at retrieving the dielectric permittivity of a phase object by using the changes in the intensity and phase shift of coherent laser radiation probing the object. The theoretical considerations involve the results of solving the scalar Helmholtz wave equation in the first Rytov approximation. For an axisymmetric phase object probed with a plane wave, both with and without radiation absorption, computationally efficient equations are obtained, which reveal the relationship between the object dielectric permittivity and the Fourier spectra of the diffracted wave characteristics described in terms of the wave intensity and phase shift in free space. The equations provide reliable data when solving the inverse diffraction problem, since they take into account diffraction effects accompanying the wave passage through the object and enhancing in free space. Fundamental properties of the equations obtained are discussed together with their broad applications. The findings can open new perspectives in the diagnostics of various objects in different wavelength ranges.
Бесплатно

Study on the Mainardi beam through the fractional Fourier transforms system
Статья научная
In this paper, we introduced the Mainardi beam and indicated its attributes under the Fractional Fourier transform for power variations of Fractional Fourier transform. The results represent that the behavior of the Mainardi beam is similar to that of the Airy beam. The obtained formula is a very powerful tool to describe propagation of a Mainardi beam through the FFT and the FrFT sys-tems. An analytical expression of the Mainardi beam passing through an Fractional Fourier trans-form system presented. The influences of the Fractional Fourier transform, rational order of the Mittag-Leffler function (Fourier transform of the Mainardi function) on the normalized intensity distribution and characteristics of the Mainardi beam in the Fractional Fourier transform system examined. Power of the Fractional Fourier transform (p) and rational order of the Mittag-Leffler function (q) control characteristics of the Mainardi beam such as effective beam size, number, width, height, and orientation of the beam spot.
Бесплатно

Статья научная
In this paper, we continue the study of the quantum cryptographic GG02 protocol, performed using the approach based on the subcarrier waves. We modify the scheme via heterodyne detection and perform security analysis for the full trusted hardware noise model in the presence of collective attacks with finite-key effects. It is shown that the system can potentially distribute the key even if the level of losses in the channel is above 9 dB. This result is consistent with the general technical level and comply with modern standards of practical CV-QKD systems. Finally, the system under consideration fully meets the criterion of composability.
Бесплатно

Testing edible oil authenticity by using smartphone based spectrometer
Статья научная
In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in the classification of edible vegetable oils, examining authenticity and in detecting possible adulteration of high quality, expensive extra virgin olive oils with low-cost edible oils. Classical methods such as gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, Fourier transform infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance, mass spectrometry, and Raman spectroscopy have been widely applied to examine the authenticity of edible oils. Despite of their high sensitivity and accuracy, these methods are significantly expensive for daily life testing, especially in resource-poor regions. Furthermore, they are time-consuming as samples have to be analyzed in dedicated laboratories. In this paper, we propose a compact, low-cost, portable smartphone-based spectrometer for testing edible oil authenticity. Using simple laboratory optical components and a smartphone, we developed a compact spectrometer which can function in the wavelength range of 400-700 nm with the spectrum/pixel resolution of 0.334 nm / pixel...
Бесплатно

Статья научная
We concern the problem of laser beam diffraction by a phase object with and without radiation absorption. In terms of a plane optical wave passing through the object, we solve the scalar Helmholtz wave equation in the first Rytov approximation and discuss the consequences of the equation obtained in such an approximation. By taking into account the wave diffraction spreading, numerous features of the phase object visualization in the field of coherent laser radiation are predicted. We reveal the fundamental relationships between the Fourier spectra of the object dielectric permittivity and diffracted wave characteristics described in terms of the wave intensity and phase shift in free space. The findings are of a general nature and can be useful in optical imaging of various objects.
Бесплатно

The mathematical model of quantum dots pair orientation under laser radiation field
Статья научная
One approach for the formation of structures with complex geometries at the nanoscale is the step-by-step assembly. In this case, it is necessary to be able to estimate the time required to establish orientational equilibrium for a preformed pair of particles. This process is statistical in nature and depends on the mechanism of interaction of the ensemble with the external field. The orientation of particles in an alternating field is associated with certain relaxation times, which depend on the viscosity and temperature of the medium, as well as on the geometric structure of the samples. This paper proposes an mathematical model of the process of establishing the distribution of nanoparticles pairs orientations taking into account the friction force, thermal motion, and the orienting laser field. A statistical orientation distribution was obtained for CdTe particles in the field of moderate laser radiation, and the average time for establishing orientational equilibrium was estimated.
Бесплатно

